微信聊天机器人,不使用iChat,可以群聊
目录
1. 微信聊天界面截图
2. 图片文字识别
3. 获取最新消息
3.1 独聊
3.2 群聊
4. 机器人聊天系统
5. 成果展示
6. 全部代码
本文参考大神【喵王叭】的文章:python实现微信、QQ聊天自动回复【纯物理】_喵王叭的博客-CSDN博客_python自动回复纯物理方式实现微信和QQ等任意聊天软件的自动回复功能,实验性质,自己搭着玩https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40815218/article/details/124689147?spm=1001.2101.3001.6650.15&utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-2~default~BlogCommendFromBaidu~Rate-15-124689147-blog-105598293.pc_relevant_antiscanv3&depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-2~default~BlogCommendFromBaidu~Rate-15-124689147-blog-105598293.pc_relevant_antiscanv3&utm_relevant_index=21
由于ichat网页登录微信的方式,被腾讯禁止。其他的替代品也无法使用。本人小程序一枚,没钱使用大佬付费的软件,所以只能另辟蹊径。
先说原理:简单来说就是四个字:文字识别。微信聊天界面截图,对截图进行文字识别,判断是对方发送的最新消息,调用机器人系统,将机器人返回的消息,复制,粘贴到聊天内容框,enter点击发送。
具体步骤如下:
我捡几个重要的步骤来讲解:
1. 微信聊天界面截图
截图软件,使用的是 PIL包的 ImageGrab 方法。首先确定聊天界面的两个分辨率点位,对两个点位组成的界面进行截图。
from PIL import ImageGrab, Image
# (x1, y1), (x2, y2) 用于控制对屏幕聊天截图的范围
# 需要自己调整 两个点位的分辨率坐标
(x1, y1), (x2, y2) = (400,80) , (3840/2-300,2160-490)
box = (x1, y1, x2, y2)
pic = ImageGrab.grab(box)代码里面的坐标,是根据自己的电脑调整的。3840,2160是我电脑的分辨率。可以通过
ImageGrab.grab().size获取电脑的分辨率,然后调整微信聊天页面的大小(比如占用左半边的屏幕),随之调整坐标的值,得到完整的聊天界面截图。
下图是我的微信聊天截图:
2. 图片文字识别
大神用的是tesserocr包的文字识别,但是这个包的文字识别准确率不高,而且无法定位是自己发送还是对方发送的最新消息【其实我也没有测过】。因此我们用 科大讯飞的免费的图片识别API(也测试过百度免费的图片识别API,同样只能识别文字,无法判断谁发送的消息)。
有关科大讯飞免费图片识别API的申请方式,请参考官网:
通用文字识别-文字识别-讯飞开放平台
API使用文档(python)请参考官网:
通用文字识别 API 文档 | 讯飞开放平台文档中心
将讯飞提供的python demo代码进行封装def,如下:
from datetime import datetime
from wsgiref.handlers import format_date_time
from time import mktime
import hashlib
import base64
import hmac
from urllib.parse import urlencode
import json
import requests
'''
1、通用文字识别,图像数据base64编码后大小不得超过10M
2、appid、apiSecret、apiKey请到讯飞开放平台控制台获取并填写到此demo中
3、支持中英文,支持手写和印刷文字。
4、在倾斜文字上效果有提升,同时支持部分生僻字的识别
'''
## 自己去官网申请获取
APPId = "" # 控制台获取
APISecret = "" # 控制台获取
APIKey = "" # 控制台获取
def OCR_XF(filepath):
with open(filepath, "rb") as f:
imageBytes = f.read()
class AssembleHeaderException(Exception):
def __init__(self, msg):
self.message = msg
class Url:
def __init__(self, host, path, schema):
self.host = host
self.path = path
self.schema = schema
pass
# calculate sha256 and encode to base64
def sha256base64(data):
sha256 = hashlib.sha256()
sha256.update(data)
digest = base64.b64encode(sha256.digest()).decode(encoding='utf-8')
return digest
def parse_url(requset_url):
stidx = requset_url.index("://")
host = requset_url[stidx + 3:]
schema = requset_url[:stidx + 3]
edidx = host.index("/")
if edidx <= 0:
raise AssembleHeaderException("invalid request url:" + requset_url)
path = host[edidx:]
host = host[:edidx]
u = Url(host, path, schema)
return u
# build websocket auth request url
def assemble_ws_auth_url(requset_url, method="POST", api_key="", api_secret=""):
u = parse_url(requset_url)
host = u.host
path = u.path
now = datetime.now()
date = format_date_time(mktime(now.timetuple()))
# print(date)
# date = "Thu, 12 Dec 2019 01:57:27 GMT"
signature_origin = "host: {}\ndate: {}\n{} {} HTTP/1.1".format(host, date, method, path)
# print(signature_origin)
signature_sha = hmac.new(api_secret.encode('utf-8'), signature_origin.encode('utf-8'),
digestmod=hashlib.sha256).digest()
signature_sha = base64.b64encode(signature_sha).decode(encoding='utf-8')
authorization_origin = "api_key=\"%s\", algorithm=\"%s\", headers=\"%s\", signature=\"%s\"" % (
api_key, "hmac-sha256", "host date request-line", signature_sha)
authorization = base64.b64encode(authorization_origin.encode('utf-8')).decode(encoding='utf-8')
# print(authorization_origin)
values = {
"host": host,
"date": date,
"authorization": authorization
}
return requset_url + "?" + urlencode(values)
url = 'https://api.xf-yun.com/v1/private/sf8e6aca1'
body = {
"header": {
"app_id": APPId,
"status": 3
},
"parameter": {
"sf8e6aca1": {
"category": "ch_en_public_cloud",
"result": {
"encoding": "utf8",
"compress": "raw",
"format": "json"
}
}
},
"payload": {
"sf8e6aca1_data_1": {
"encoding": "jpg",
"image": str(base64.b64encode(imageBytes), 'UTF-8'),
"status": 3
}
}
}
request_url = assemble_ws_auth_url(url, "POST", APIKey, APISecret)
headers = {'content-type': "application/json", 'host': 'api.xf-yun.com', 'app_id': APPId}
# print(request_url)
response = requests.post(request_url, data=json.dumps(body), headers=headers)
# print(response)
# print(response.content)
# print("resp=>" + response.content.decode())
tempResult = json.loads(response.content.decode())
# print(tempResult)
finalResult = base64.b64decode(tempResult['payload']['result']['text']).decode()
finalResult = finalResult.replace(" ", "").replace("\n", "").replace("\t", "").strip()
# print("text字段Base64解码后=>" + finalResult)
finalResult_js = json.loads(finalResult)
return finalResult_js
为什么要用科大讯飞的API,因为讯飞的图片识别,可以给出文字新的详细坐标(x,y),通过坐标分辨出是对方发出的信息,还是我们自己发出的信息
Location_Friend_Spt = 200 ## 判断谁发出的坐标 x 的值
Friendlt = [] ## 对方发出信息集合
Melt = [] ## 我方发出信息集合
def ChatInfo(finalResult_js):
Friendlt = []
Melt = []
for word in finalResult_js['pages'][0]['lines']:
if 'words' in word.keys():
if word['coord'][0]['x'] < Location_Friend_Spt:
print('Fri->', word['words'][0]['content'])
Friendlt.append(word['words'][0]['content'])
else:
print(' ', word['words'][0]['content'], '<-Me')
Melt.append(word['words'][0]['content'])
## 返回朋友的所有消息
return Friendlt结果如下:
3. 获取最新消息
3.1 独聊
跟一个朋友聊天时:将上述 ChatInfo 返回的内容,放入如下函数:
def OneChat(Frilt):
## 返回对方最新的消息
return {'':Frilt[-1]}3.2 群聊
如果是群聊时,需要预先设置群里每个人的名称,必须和群聊中显示的保持一直
GroupName = ['高艳子', '吴倩', '飞飞', '李苏娟']
def GroupChat(Frilt,GroupName):
## 获取群聊里面每个人最新消息
def FriName(x):
if x in GroupName:
return x
else:
return pd.NA
df = pd.DataFrame({"Dialogue": Frilt})
df['FriName'] = df['Dialogue'].apply(FriName)
df['FriName'] = df['FriName'].fillna(method='ffill')
df['row_num'] = df.index.to_list()
df = df[df['FriName'].notnull()]
df = df.sort_values(['FriName','row_num'],ascending=[True,False]).drop_duplicates(['FriName'])
## 返回对方最新的消息
dialogue = df['Dialogue'].tolist()
FriName = df['FriName'].tolist()
## 将每个人最新消息,存储在json里面
dial_info_json = {}
for index, value in enumerate(dialogue):
dial_info_json[FriName[index]] = value
return dial_info_json群聊函数返回的内容是每个人的最新消息。如下图:
4. 机器人聊天系统
本文采用的是 青云客 免费的机器人聊天系统。
import requests
import json
## 调用青云客的API,免费的API
def qingyunke(msg:str):
data = requests.get("http://api.qingyunke.com/api.php?key=free&appid=0&msg=" + msg).content
data = json.loads(data)
data = data['content'].replace("{br}","\n")
return data如果资金雄厚的,可以购买付费的聊天机器人。目前最经典的机器人系统是 图灵机器人,之前是免费的,现在也收钱了。
也可以自己搭建聊天机器人。我参考大神 基于医疗知识图谱的问答系统 搭建了一套医疗机器人,有兴趣的同学,可以私信我。
## 在本地创建的医疗机器人
## 有兴趣的可以参考 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/379202949 文章内容,将 local.py 改成api形式即可。
def medical_robot(msg:str):
url = "http://localhost:60063/service/api/medical_robot"
data = {"question": msg }
print('data', data)
headers = {'Content-Type': 'application/json;charset=utf8'}
response = requests.post(url, data=json.dumps(data), headers=headers)
# print('response', response)
if response.status_code == 200:
response = json.loads(response.text)
# print(response, '========')
return response["data"]
else:
return "您的问题我无法理解,我还需要学习"
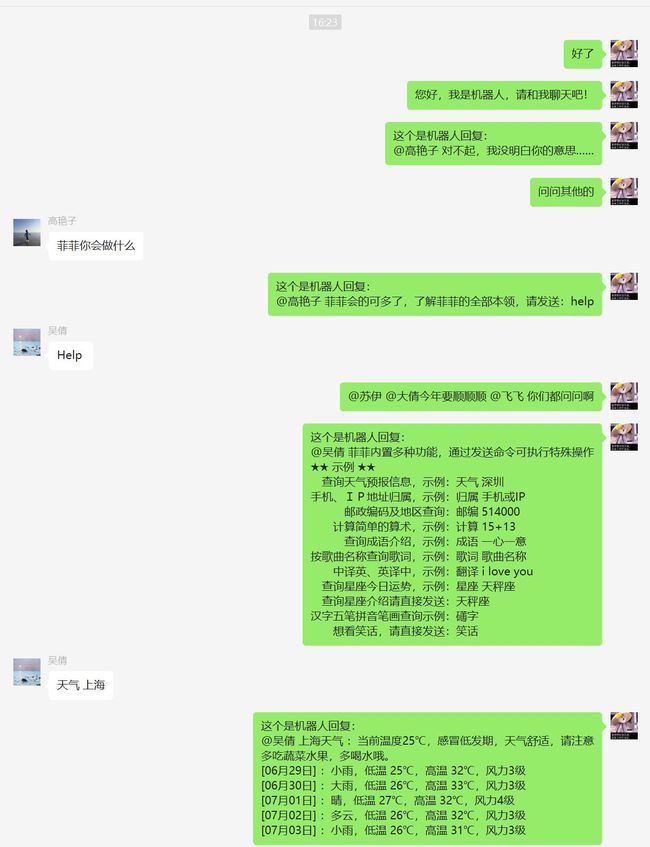
5. 成果展示
群聊,闲聊机器人
6. 全部代码
微信聊天机器人(github源码)![]() https://github.com/chengzhen123/WeChatRobot
https://github.com/chengzhen123/WeChatRobot