非极大值抑制(NMS)-python实现
算法原理
最近在做图像识别工作,发现常常会遇到在某一点出框出多个特征图,影响图像处理的工作,因此有必要去研究nms算法。
在进行图像识别成功时,我们得到的数据是包含一组坐标点和他的得分值。算法原理:
- 根据得分值进行一个降序排序
- 选取得分值最大的入栈,用该得分值计算与其他数据的iou值,如果得到的iou值大于指定的阈值,那么说明该框与选定的相似,可以舍去。如果得到的iou值小于阈值,那么说明该框与选定的不相似。
- 把计算得到的iou小于指定阈值的数据加入新的集合中,然后再依次执行上述操作。栈内的元素即是不相干的数据。
iou原理以及计算
iou是值用来度量目标检测中预测框与真实框的重叠程度。iou也即是交并比,计算的公式如下:

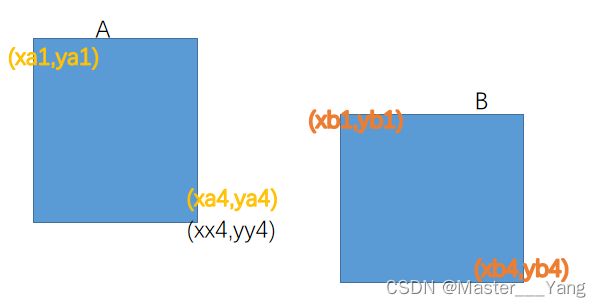
通常还有其他方法进行计算,比如用公共区域面积除得分值最高的区域面积等。下面采用交并比的方法。以长方形矩阵为例,A,B有两种情况,一种A和B有部分交集,其情况如下:
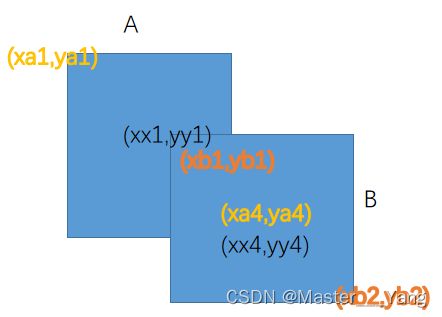
对于A和B没有交集:
对于上述情况中,可以求得公共区域的坐标为:
xx1 = max(xa1,xb1) yy1=max(ya1,yb1) xx4=min(xa4,ya4) yy4 = min(ya4,yb4)
接着求公共区域的宽和高,对于A和B是否有交集用最大值函数即可。
w, h = np.maximum(np.array([0]), xx2 - xx1), np.maximum(np.array([0]), yy2 - yy1)
iou代码如下:
def iou(box, boxes, isMin=False):
box_area = (box[3] - box[1]) * (box[4] - box[2])
boxes_area = (boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]) * (boxes[:, 4] - boxes[:, 2])
# 求交集
xx1 = np.maximum(box[1], boxes[:, 1])
yy1 = np.maximum(box[2], boxes[:, 2])
xx2 = np.minimum(box[3], boxes[:, 3])
yy2 = np.minimum(box[4], boxes[:, 4])
w, h = np.maximum(np.array([0]), xx2 - xx1), np.maximum(np.array([0]), yy2 - yy1)
ovr_area = w * h
if isMin:
return ovr_area / np.min(box_area, boxes_area)
else:
return ovr_area / (box_area + boxes_area - ovr_area)
nms代码
nms的具体原理在上述中,主要采用的是一个压栈的思想。具体的代码如下:
def nms(boxes, threshold=0.3, isMin=False):
new_boxes = boxes[boxes[:, 0].argsort()[::-1]] # 根据置信度进行从大到小排序
keep_boxes = []
while len(new_boxes) > 0:
_box = new_boxes[0]
keep_boxes.append(_box)
if len(new_boxes) > 1:
_boxes = new_boxes[1:]
iou_value = iou(_box, _boxes, isMin)
new_boxes = _boxes[np.where(iou_value < threshold)]
else:
break
return np.stack(keep_boxes)
测试代码如下:
import numpy as np
def iou(box, boxes, isMin=False):
box_area = (box[3] - box[1]) * (box[4] - box[2])
boxes_area = (boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]) * (boxes[:, 4] - boxes[:, 2])
# 求交集
xx1 = np.maximum(box[1], boxes[:, 1])
yy1 = np.maximum(box[2], boxes[:, 2])
xx2 = np.minimum(box[3], boxes[:, 3])
yy2 = np.minimum(box[4], boxes[:, 4])
w, h = np.maximum(np.array([0]), xx2 - xx1), np.maximum(np.array([0]), yy2 - yy1)
ovr_area = w * h
if isMin:
return ovr_area / np.min(box_area, boxes_area)
else:
return ovr_area / (box_area + boxes_area - ovr_area)
def nms(boxes, threshold=0.3, isMin=False):
new_boxes = boxes[boxes[:, 0].argsort()[::-1]] # 根据置信度进行从大到小排序
keep_boxes = []
while len(new_boxes) > 0:
_box = new_boxes[0]
keep_boxes.append(_box)
if len(new_boxes) > 1:
_boxes = new_boxes[1:]
iou_value = iou(_box, _boxes, isMin)
new_boxes = _boxes[np.where(iou_value < threshold)]
else:
break
return np.stack(keep_boxes)
if __name__ == '__main__':
boxes = np.array([[0.89, 3, 3, 5, 5], [0.37, 0, 0, 4, 4], [0.15, 1, 1, 5, 5], [0.36, 99, 99, 110, 110]])
print(nms(boxes))
输出结果:
[[ 0.89 3. 3. 5. 5. ]
[ 0.37 0. 0. 4. 4. ]
[ 0.36 99. 99. 110. 110. ]]
算法输出思路:
首先把【3,3,5,5】首先入栈,计算与其他的数据的iou结果如下:
[0.05263158 0. 0.25 ]
因为得到的iou均小于0.3。因此可以认为这三个数据与【3,3,5,5】无关。
接着把得分值最大的【0,0,4,4】入栈。再次计算与其他数据的iou:
[0. 0.39130435]
可以得到第二个数据大于阈值,因此只保留第一个数据。而此时数组中仅剩一个数据,因此把【99,99,110,110】入栈。算法执行结束。
参考文献:
https://pyimagesearch.com/2014/11/17/non-maximum-suppression-object-detection-python/