Spring之Joinpoint类详解
说明
Joinpoint是AOP的连接点。一个连接点代表一个被代理的方法。我们从源码角度看连接点有哪些属性和功能。
源码
/*
* Copyright 2002-2016 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.aopalliance.intercept;
import java.lang.reflect.AccessibleObject;
/**
* This interface represents a generic runtime joinpoint (in the AOP
* terminology).
*这个接口就是AOP中的连接点。
* A runtime joinpoint is an event that occurs on a static
* joinpoint (i.e. a location in a the program). For instance, an
* invocation is the runtime joinpoint on a method (static joinpoint).
* The static part of a given joinpoint can be generically retrieved
* using the {@link #getStaticPart()} method.
*静态连接点就是被代理的方法本身,可以通过getStaticPart方法调用。动态连接点就是对
*静态方法之外的增强方法
*
In the context of an interception framework, a runtime joinpoint
* is then the reification of an access to an accessible object (a
* method, a constructor, a field), i.e. the static part of the
* joinpoint. It is passed to the interceptors that are installed on
* the static joinpoint.
*动态连接点从静态连接点的拦截器上获取静态部分,并进行相应的加强,从而形成动态连接点
* @author Rod Johnson
* @see Interceptor
*/
public interface Joinpoint {
/**
* Proceed to the next interceptor in the chain.
* 转到链的下一个拦截器上。详细请看子类的实现
* The implementation and the semantics of this method depends
* on the actual joinpoint type (see the children interfaces).
* @return see the children interfaces' proceed definition
* @throws Throwable if the joinpoint throws an exception
*/
Object proceed() throws Throwable;
/**
* Return the object that holds the current joinpoint's static part.
* 返回持有当前连接点静态部分的对象,例如,调用的目标对象
* For instance, the target object for an invocation.
* @return the object (can be null if the accessible object is static)
*/
Object getThis();
/**
* Return the static part of this joinpoint.
* The static part is an accessible object on which a chain of
* interceptors are installed.
* 返回连接点的静态部分。静态部分是一个拥有连接器链的对象。意思就是这个静态方法都要被谁拦截,可以通过getStaticPart返回。
*/
AccessibleObject getStaticPart();
}
从上面源码来看,我们可以知道,Joinpoint分为动态和静态,且有一个拦截器链作用于Joinpoint。那么具体静态和动态是什么,拦截器链又是什么,我们看其子类实现。
ReflectiveMethodInvocation类源码
Spring提供的Joinpoint实现类只有ReflectiveMethodInvocation类。当然这个类实现了Joinpoint的扩展来,要比Jointpoint功能强大,我们来看这个类源码。
/*
* Copyright 2002-2019 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.aop.framework;
import java.lang.reflect.AccessibleObject;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;
import org.springframework.aop.ProxyMethodInvocation;
import org.springframework.aop.support.AopUtils;
import org.springframework.core.BridgeMethodResolver;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
/**
* Spring's implementation of the AOP Alliance
* {@link org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation} interface,
* implementing the extended
* {@link org.springframework.aop.ProxyMethodInvocation} interface.
*
* Invokes the target object using reflection. Subclasses can override the
* {@link #invokeJoinpoint()} method to change this behavior, so this is also
* a useful base class for more specialized MethodInvocation implementations.
*
*
It is possible to clone an invocation, to invoke {@link #proceed()}
* repeatedly (once per clone), using the {@link #invocableClone()} method.
* It is also possible to attach custom attributes to the invocation,
* using the {@link #setUserAttribute} / {@link #getUserAttribute} methods.
*
*
NOTE: This class is considered internal and should not be
* directly accessed. The sole reason for it being public is compatibility
* with existing framework integrations (e.g. Pitchfork). For any other
* purposes, use the {@link ProxyMethodInvocation} interface instead.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Adrian Colyer
* @see #invokeJoinpoint
* @see #proceed
* @see #invocableClone
* @see #setUserAttribute
* @see #getUserAttribute
*/
public class ReflectiveMethodInvocation implements ProxyMethodInvocation, Cloneable {
protected final Object proxy;
@Nullable
protected final Object target;
protected final Method method;
protected Object[] arguments;
@Nullable
private final Class<?> targetClass;
/**
* Lazily initialized map of user-specific attributes for this invocation.
*/
@Nullable
private Map<String, Object> userAttributes;
/**
* List of MethodInterceptor and InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher
* that need dynamic checks.
*/
protected final List<?> interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers;
/**
* Index from 0 of the current interceptor we're invoking.
* -1 until we invoke: then the current interceptor.
*/
private int currentInterceptorIndex = -1;
/**
* Construct a new ReflectiveMethodInvocation with the given arguments.
* @param proxy the proxy object that the invocation was made on
* @param target the target object to invoke
* @param method the method to invoke
* @param arguments the arguments to invoke the method with
* @param targetClass the target class, for MethodMatcher invocations
* @param interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers interceptors that should be applied,
* along with any InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatchers that need evaluation at runtime.
* MethodMatchers included in this struct must already have been found to have matched
* as far as was possibly statically. Passing an array might be about 10% faster,
* but would complicate the code. And it would work only for static pointcuts.
*/
protected ReflectiveMethodInvocation(
Object proxy, @Nullable Object target, Method method, @Nullable Object[] arguments,
@Nullable Class<?> targetClass, List<Object> interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers) {
this.proxy = proxy;
this.target = target;
this.targetClass = targetClass;
this.method = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
this.arguments = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, arguments);
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers = interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers;
}
@Override
public final Object getProxy() {
return this.proxy;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public final Object getThis() {
return this.target;
}
@Override
public final AccessibleObject getStaticPart() {
return this.method;
}
/**
* Return the method invoked on the proxied interface.
* May or may not correspond with a method invoked on an underlying
* implementation of that interface.
*/
@Override
public final Method getMethod() {
return this.method;
}
@Override
public final Object[] getArguments() {
return this.arguments;
}
@Override
public void setArguments(Object... arguments) {
this.arguments = arguments;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
Class<?> targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass());
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
/**
* Invoke the joinpoint using reflection.
* Subclasses can override this to use custom invocation.
* @return the return value of the joinpoint
* @throws Throwable if invoking the joinpoint resulted in an exception
*/
@Nullable
protected Object invokeJoinpoint() throws Throwable {
return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.target, this.method, this.arguments);
}
/**
* This implementation returns a shallow copy of this invocation object,
* including an independent copy of the original arguments array.
* We want a shallow copy in this case: We want to use the same interceptor
* chain and other object references, but we want an independent value for the
* current interceptor index.
* @see java.lang.Object#clone()
*/
@Override
public MethodInvocation invocableClone() {
Object[] cloneArguments = this.arguments;
if (this.arguments.length > 0) {
// Build an independent copy of the arguments array.
cloneArguments = new Object[this.arguments.length];
System.arraycopy(this.arguments, 0, cloneArguments, 0, this.arguments.length);
}
return invocableClone(cloneArguments);
}
/**
* This implementation returns a shallow copy of this invocation object,
* using the given arguments array for the clone.
* We want a shallow copy in this case: We want to use the same interceptor
* chain and other object references, but we want an independent value for the
* current interceptor index.
* @see java.lang.Object#clone()
*/
@Override
public MethodInvocation invocableClone(Object... arguments) {
// Force initialization of the user attributes Map,
// for having a shared Map reference in the clone.
if (this.userAttributes == null) {
this.userAttributes = new HashMap<>();
}
// Create the MethodInvocation clone.
try {
ReflectiveMethodInvocation clone = (ReflectiveMethodInvocation) clone();
clone.arguments = arguments;
return clone;
}
catch (CloneNotSupportedException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Should be able to clone object of type [" + getClass() + "]: " + ex);
}
}
@Override
public void setUserAttribute(String key, @Nullable Object value) {
if (value != null) {
if (this.userAttributes == null) {
this.userAttributes = new HashMap<>();
}
this.userAttributes.put(key, value);
}
else {
if (this.userAttributes != null) {
this.userAttributes.remove(key);
}
}
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object getUserAttribute(String key) {
return (this.userAttributes != null ? this.userAttributes.get(key) : null);
}
/**
* Return user attributes associated with this invocation.
* This method provides an invocation-bound alternative to a ThreadLocal.
* This map is initialized lazily and is not used in the AOP framework itself.
* @return any user attributes associated with this invocation
* (never {@code null})
*/
public Map<String, Object> getUserAttributes() {
if (this.userAttributes == null) {
this.userAttributes = new HashMap<>();
}
return this.userAttributes;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// Don't do toString on target, it may be proxied.
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("ReflectiveMethodInvocation: ");
sb.append(this.method).append("; ");
if (this.target == null) {
sb.append("target is null");
}
else {
sb.append("target is of class [").append(this.target.getClass().getName()).append(']');
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
我们看其几个重要的属性:
protected final Object proxy; //代理对象
@Nullable
protected final Object target; //目标对象
protected final Method method; //调用的方法
protected Object[] arguments; //调用方法的参数
@Nullable
private final Class<?> targetClass; //目标类的class对象
//需要动态核对的MethodInterceptor和InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher列表
protected final List<?> interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers;
private int currentInterceptorIndex = -1; //拦截器脚本
我们分析其核心方法,proceed()方法代码:
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
Class<?> targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass());
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
首先,分析这段:
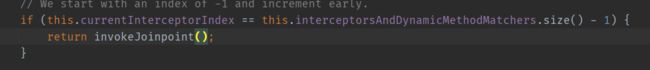
当拦截器的角标达到和interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers列表的最后一个元素时,执行invokeJoinpoint()方法。
我们首先要搞清楚,interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers的作用是什么。上面提到,interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers里存放的是MethodInterceptor和InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher对象。要清楚interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers的作用,必须知道MethodInterceptor和InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher对象是干什么的。
我们看MethodInterceptor的源码:
public interface MethodInterceptor extends Interceptor {
/**
* Implement this method to perform extra treatments before and
* after the invocation. Polite implementations would certainly
* like to invoke {@link Joinpoint#proceed()}.
* @param invocation the method invocation joinpoint
* @return the result of the call to {@link Joinpoint#proceed()};
* might be intercepted by the interceptor
* @throws Throwable if the interceptors or the target object
* throws an exception
*/
Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable;
}
该接口只有一个invoke方法,该方法的参数MethodInvocation接口就是Joinpoint接口的一个扩展接口。在Joinpoint的proceed方法中调用此方法,通过MethodInvocation对象可以获取到目标类的原方法,然后还能进行一些其他的操作。所以,invoke方法就是原方法的增强,也就是代理方法的实现。
我们看InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher对象的源码:
class InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher {
final MethodInterceptor interceptor;
final MethodMatcher methodMatcher;
public InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher(MethodInterceptor interceptor, MethodMatcher methodMatcher) {
this.interceptor = interceptor;
this.methodMatcher = methodMatcher;
}
}
由源码可知,InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher对象将MethodInterceptor 和MethodMatcher 整合到了一起。MethodMatcher 类我们在之前讲过,具体请查阅《Spring AOP之PointCut详解》。
综上所述,Joinpoint的interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers属性里存的是MethodInterceptor对象和MethodMatcher对象。通过MethodMatcher对象判断调用方法是否需要代理,如果需要代理,则放入MethodIntecptor对象。所以,interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers属性里存的是需要被代理加强的方法。
我们继续看proceed方法,搞清楚interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers属性后,当过滤器的角标到interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers集合的最后一位时,会执行invokeJoinpoint()方法。我们看这个方法源码:
protected Object invokeJoinpoint() throws Throwable {
return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.target, this.method, this.arguments);
}
可以看到,该方法是利用反射调用目标方法执行了。即一个方法如果没有被增强,interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers集合就没有值,角标就是-1。这时就直接执行目标方法,不做任何处理。如此看来,只要一个类的某个方法被加强了,那么这个类所有方法都会执行proceed()方法,然后通过MethodMatcher方法,判断是否要进行加强。
我们继续往下看proceed()方法的源码:

如果interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers有值,则说明要进行拦截操作了。如果获取的元素是InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher对象,则进入if分支,否则,进入else分支。我们先看if分支的逻辑。
if分支的核心代码为:

这里我们一定要有一个概念,连接点针对的是方法,所以,这里用MethodMatcher比较该连接点的方法是否匹配,如果匹配,则调用MethodIntecptor的invoke方法,进行增强。如果不匹配,则说明该InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher里的MethodMatcher不是该连接点方法的,则递归调用proceed方法,比较interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers属性中的下一个对象。
(问题:interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers属性中存的是这个类相关的MethodMatcher还是所有类的MethodMatcher?需要验证)
下面我们看else分支,即interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers属性里取出的元素不是InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher对象。

可以看到其直接强转成了MethodInterceptor对象,调用了invoke方法。
(问题:interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers属性里为什么会存两种类型的对象呢? )
至此,proceed()方法解析完毕。我们来总结一下。
首先要明确的一点就是一个连接点代表着一个对象里的一个方法。一个对象里的多个方法,就是多个连接点。每个连接点对象中,都存着一个拦截器链,proceed方法就是遍历拦截器链,如果和连接点所代表的方法一致,则执行MethodInterceptor的invoke方法,进行方法的代理,如果拦截器和代理方法不匹配,则进入下一个拦截器。直到都不匹配,则执行原始方法。
下面,我们结合实际应用,来梳理一下上面的源码流程。我们先定义一个切面:
@Aspect
@Component
public class SendMessageAspect{
public SendMessageAspect(){
System.out.println("测试入口");
}
@Autowired
ICimKeywordService keywordService;
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.farsunset.cim.component.handler.SendMessageHandler.process(..))")
// @Pointcut("execution(public * com.farsunset.cim.config.CIMConfig.process(..))")
public void execute() {
}
@Around("execute()")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint)throws Throwable {
SendMessageHandler sendMessageHandler = SpringUtils.getBean("sendMessageHandler");
sendMessageHandler.toString();
// 获取目标方法的名称
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
// 获取方法传入参数
Object[] params = joinPoint.getArgs();
SentBody body=(SentBody)params[1];
String content=body.get("content");
String format=body.get("format");
if("text".equals(format)&& StringUtils.isNotEmpty(content)){
//将关键字替换成*
List<CimKeyword> keywords= keywordService.selectCimKeywordList(null);
if(keywords!=null&&keywords.size()>0){
for (CimKeyword keyword:
keywords) {
if(content.contains(keyword.getKeyword())){
content=content.replaceAll(keyword.getKeyword(),"**");
}
}
body.put("content",content);
params[1]=body;
}
}
// 执行源方法
joinPoint.proceed(params);
}
@Before("execute()")
public void before()throws Throwable {
System.out.println("执行了");
// 获取目标方法的名称
}
}
这里我们定义了两个加强,Around和Before。实际开发中不会同时定义这两个。这里我们只是用于研究测试用。
我们从Spring容器中先获得SendMessageAspect对象,可以看到,其是一个代理对象:

然后我们调用该对象的toString方法,可以看到,代码会进入proceed方法。这也说明,代理对象的所有方法,都会形成一个连接点对象。如下:
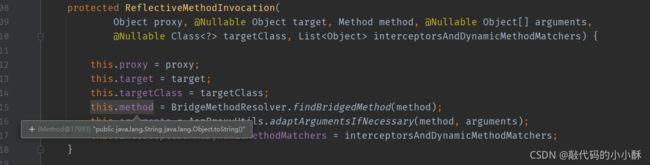
可以看到,此时的连接点中的method属性,就是toString()。然后执行proceed方法,因为并没有对toString方法进行加强,所以最终执行的是目标对象的toString方法。
我们再看连接点的interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers属性,看其拦截器都是什么:

可以看到,拦截器中就一个默认的ExposeInvocationInterceptor拦截器。这个拦截器我们单独讲解,所有的代理对象第一个拦截器都是这个默认拦截器。所以,toString方法没有任何其他拦截器,不进行加强。
我们再看调用SendMessageHandler对象的process方法,连接点对象的内部情况:

该连接点是要加强的方法,我们看其拦截器有哪些:
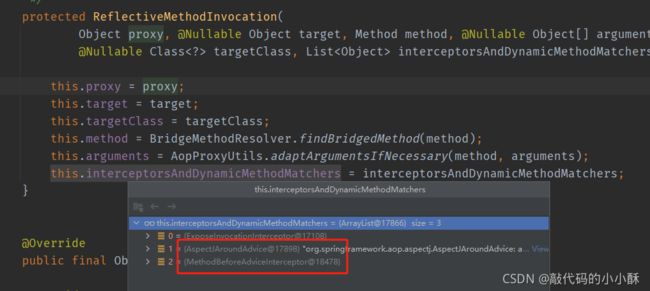
可以看到,除了第一个默认的拦截器,process连接点的拦截器还有AspectJAroundAdvice拦截器和MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor。这两个对象都是MethodInterceptor的子类。当调用proceed方法的时候,会执行这两个类的invoke方法。这两个类的invoke方法就分别对应着@Around和@Before所对应的方法。
由此可知,我们定义的加强方法,最终会封装成相应的MethodInterceptor对象,在连接点的proceed中被调用。而在连接点的拦截器中,已经封装好了连接点所代理方法MethodInterceptor。连接点直接用拦截器进行方法的调用即可。
总结
综上所述,连接点是Spring AOP中的最小单元。连接点里存放了代理对象的目标类,目标方法,方法拦截器。进行代理的时候,调用拦截器MethodInterceptor的加强方法,执行代理方法。