MapReduce API 基本概念
在正式分析新旧 API 之前, 先要介绍几个基本概念。 这些概念贯穿于所有 API 之中,因此, 有必要单独讲解。
1.序列化
序列化是指将结构化对象转为字节流以便于通过网络进行传输或写入持久存储的过程。反序列化指的是将字节流转为结构化对象的过程。 在 Hadoop MapReduce 中, 序列化的主
要作用有两个: 永久存储和进程间通信。为了能够读取或者存储 Java 对象, MapReduce 编程模型要求用户输入和输出数据中的 key 和 value 必须是可序列化的。 在 Hadoop MapReduce 中 , 使一个 Java 对象可序列化的方法是让其对应的类实现 Writable 接口 。 但对于 key 而言,由于它是数据排序的关键字, 因此还需要提供比较两个 key 对象的方法。 为此,key对应类需实现WritableComparable 接口 , 它的类如图: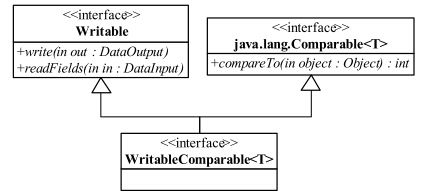
在package org.apache.hadoop.io 中的WritableComparable.java文件中定义:
public interface WritableComparable<T> extends Writable, Comparable<T> { }
再来看看Writable接口的定义:
public interface Writable { /** * Serialize the fields of this object to <code>out</code>. * * @param out <code>DataOuput</code> to serialize this object into. * @throws IOException */ void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException; /** * Deserialize the fields of this object from <code>in</code>. * * <p>For efficiency, implementations should attempt to re-use storage in the * existing object where possible.</p> * * @param in <code>DataInput</code> to deseriablize this object from. * @throws IOException */ void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException; }
可以很明显的看出,write(DataOutput out)方法的作用是将指定对象的域序列化为out相同的类型;readFields(DataInput in)方法的作用是将in对象中的域反序列化,考虑效率因素,实现接口的时候应该使用已经存在的对象存储。
DataInput接口定义源代码如下:
public interface DataInput { void readFully(byte b[]) throws IOException; void readFully(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException; int skipBytes(int n) throws IOException; boolean readBoolean() throws IOException; byte readByte() throws IOException; int readUnsignedByte() throws IOException; short readShort() throws IOException; int readUnsignedShort() throws IOException; char readChar() throws IOException; int readInt() throws IOException; long readLong() throws IOException; float readFloat() throws IOException; double readDouble() throws IOException; String readLine() throws IOException; String readUTF() throws IOException; }
每个方法的含义差不多,具体可参见java jdk源码
DataOutput接口定义源代码如下:
public interface DataOutput { void write(int b) throws IOException; void write(byte b[]) throws IOException; void write(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException; void writeBoolean(boolean v) throws IOException; void writeByte(int v) throws IOException; void writeShort(int v) throws IOException; void writeChar(int v) throws IOException; void writeInt(int v) throws IOException; void writeLong(long v) throws IOException; void writeFloat(float v) throws IOException; void writeDouble(double v) throws IOException; void writeBytes(String s) throws IOException; void writeChars(String s) throws IOException; void writeUTF(String s) throws IOException; }
WritableComparable可以用来比较,通常通过Comparator . 在hadoop的Map-Reduce框架中任何被用作key的类型都要实现这个接口。
看一个例子:
public class MyWritableComparable implements WritableComparable { // Some data private int counter; private long timestamp; public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { out.writeInt(counter); out.writeLong(timestamp); } public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { counter = in.readInt(); timestamp = in.readLong(); } public int compareTo(MyWritableComparable w) { int thisValue = this.value; int thatValue = ((IntWritable)o).value; return (thisValue < thatValue ? -1 : (thisValue==thatValue ? 0 : 1)); } }
2.Reporter 参数
Reporter 是 MapReduce 提供给应用程序的工具。 如图所示,应用程序可使用Reporter 中的方法报告完成进度(progress)、设定状态消息(setStatus 以及更新计数器( incrCounter)。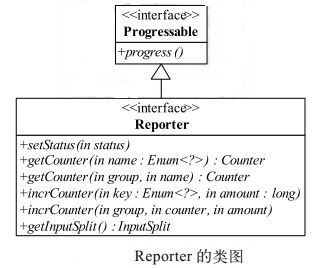
Reporter 是一个基础参数。 MapReduce 对外提供的大部分组件, 包括 InputFormat、Mapper 和 Reducer 等,均在其主要方法中添加了该参数。
3.回调机制
回调机制是一种常见的设计模式。它将工作流内的某个功能按照约定的接口暴露给外部使用者, 为外部使用者提供数据,或要求外部使用者提供数据。
Hadoop MapReduce 对外提供的 5 个组件( InputFormat、 Mapper、 Partitioner、 Reducer 和 OutputFormat) 实际上全部属于回调接口 。 当用户按照约定实现这几个接口后, MapReduce运行时环境会自 动调用它们。如图所示,MapReduce 给用户暴露了接口 Mapper, 当用户按照自己的应用程序逻辑实现自己的 MyMapper 后,Hadoop MapReduce 运行时环境会将输入数据解析成 key/value 对, 并调用 map() 函数迭代处理。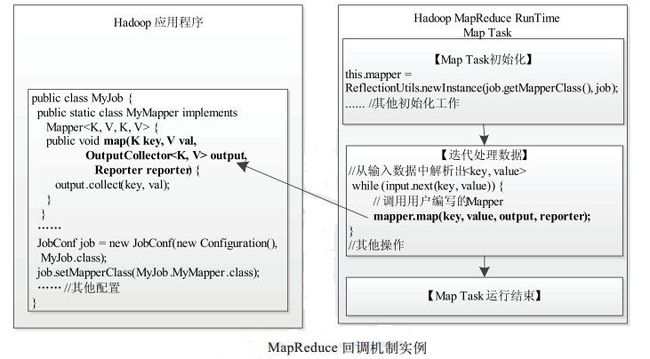
参考资料
《Hadoop技术内幕 深入理解MapReduce架构设计与实现原理》