SpringCloud Alibaba系列——17Seata AT模式源码分析
学习目标
- Seata AT模式源码流程
第1章 AT模式流程
1.1 思维流程推导
上文中已经讲了AT模式的大体原理,在源码中,通过README也能看出来AT模式的使用,那本文将从底层源码层面去分析AT模式的原理,在分析原理之前咱们先来看三幅图,理解一下他的工作思路和模式:
先看看思维推导图
1.2 初始化流程推导
1.3 执行流程推导
第2章 源码分析
2.1 SeataAutoConfiguration
对于seata源码的研究主要看seata如何拦截业务SQL生成undo_log数据,如何在一阶段完成后提交全局事务,如何在一阶段业务失败后通过undo_log回滚事务,进行事务补偿。
seata也是与spring整合使用的,结合SpringBoot,seata也是做了一些自动配置
seata的自动配置类命名非常的直接,就叫做:SeataAutoConfiguration,我们打开这个类
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "io.seata.spring.boot.autoconfigure.properties")
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = StarterConstants.SEATA_PREFIX, name = "enabled", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties({SeataProperties.class})
public class SeataAutoConfiguration {
}首先,@ComponentScan扫描了一下properties包,加载了一大堆类似SeataProperties的Bean对象。
@ConditionalOnProperty将配置类生效条件设置为seata.enabled=true,默认值是true,所以可以开关分布式事务功能(在client端的file.conf里面可以配置)。
@Configuration表明,SeataAutoConfiguration被定义为了spring的配置类。
@EnableConfigurationProperties将配置包转成了一个SeataProperties的Bean对象来使用。
接下来阅读SeataAutoConfiguration的内部代码
@Bean
@DependsOn({BEAN_NAME_SPRING_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_PROVIDER, BEAN_NAME_FAILURE_HANDLER})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(GlobalTransactionScanner.class)
public GlobalTransactionScanner globalTransactionScanner(SeataProperties seataProperties, FailureHandler failureHandler) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Automatically configure Seata");
}
return new GlobalTransactionScanner(seataProperties.getApplicationId(), seataProperties.getTxServiceGroup(), failureHandler);
}自动配置的核心点落在了下面的一个Bean,GlobalTransactionScanner。
我们看到构造这个Bean非常的简单,构造方法只需要一个applicationId和txServiceGroup。
applicationId: 就是spring.application.name=你定义的当前应用的名字,例如:userService
txServiceGroup: 就是以applicationId 加上 -seata-service-group命名的,例如:userService-seata-service-group。如果版本较低的话,那时候可能还不叫seata而是fescar,因此默认命名就是以fescar为后缀。
new了一个GlobalTransactionScanner对象,SeataAutoConfiguration这个自动配置类的作用就结束了。SeataAutoConfiguration只是做了一个启动引导的作用。
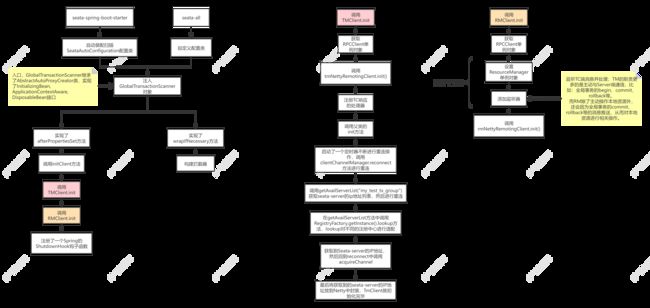
2.2 GlobalTransactionScanner
既然核心点落在GlobalTransactionScanner这个类,我们继续关注它。看这个名字其实就可以猜测到一点它的作用,扫描@GlobalTransactional这个注解,并对代理方法进行拦截增强事务的功能。
要了解这个类,不得不先阅读一下它的UML图
可以看到,GlobalTransactionScanner主要有4个点值得关注:
1)ApplicationContextAware表示可以拿到spring容器
2)InitializingBean接口,表达了初始化的时候会进行一些操作
3)AbstractAutoProxyCreator表示它会对spring容器中的Bean进行切面增强,也就是我们上面的拦截事务增强的猜测。
4)Disposable接口,表达了spring容器销毁的时候会进行一些操作
这里我们稍微关注一下这4个的执行顺序:
ApplicationContextAware -> InitializingBean -> AbstractAutoProxyCreator -> DisposableBean
2.3 InitializingBean
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
if (disableGlobalTransaction) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Global transaction is disabled.");
}
return;
}
initClient();
}初始化Seata的Client端的东西,Client端主要包括TransactionManager和ResourceManager。或许是为了简化吧,并没有把initClient这件事从GlobalTransactionScanner里面独立出来一个类。
跟进initClient方法
private void initClient() {
//init TM
TMClient.init(applicationId, txServiceGroup);
//init RM
RMClient.init(applicationId, txServiceGroup);
registerSpringShutdownHook();
}initClient逻辑并不复杂,单纯调用TMClient.init初始化TransactionManager的RPC客户端,RMClient.init初始化ResourceManager的RPC客户端。seata的RPC采用netty来实现,seata封装简化了一下使用。并注册了一个Spring的ShutdownHook钩子函数
2.3.1 TMClient初始化
@Override
public void init() {
timerExecutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
clientChannelManager.reconnect(getTransactionServiceGroup());
}
}, SCHEDULE_DELAY_MILLS, SCHEDULE_INTERVAL_MILLS, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (NettyClientConfig.isEnableClientBatchSendRequest()) {
mergeSendExecutorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(MAX_MERGE_SEND_THREAD,
MAX_MERGE_SEND_THREAD,
KEEP_ALIVE_TIME, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(),
new NamedThreadFactory(getThreadPrefix(), MAX_MERGE_SEND_THREAD));
mergeSendExecutorService.submit(new MergedSendRunnable());
}
super.init();
clientBootstrap.start();
}启动了一个定时器不断进行重连操作,调用clientChannelManager.reconnect方法进行重连
void reconnect(String transactionServiceGroup) {
List availList = null;
try {
availList = getAvailServerList(transactionServiceGroup);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("Failed to get available servers: {}", e.getMessage(), e);
return;
}
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(availList)) {
String serviceGroup = RegistryFactory.getInstance()
.getServiceGroup(transactionServiceGroup);
LOGGER.error("no available service '{}' found, please make sure registry config correct", serviceGroup);
return;
}
for (String serverAddress : availList) {
try {
acquireChannel(serverAddress);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("{} can not connect to {} cause:{}",FrameworkErrorCode.NetConnect.getErrCode(), serverAddress, e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
} 根据transactionServiceGroup获取seata-server的ip地址列表,然后进行重连
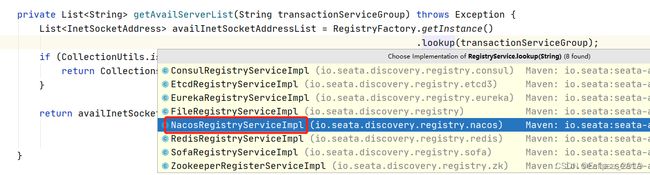
private List getAvailServerList(String transactionServiceGroup) throws Exception {
List availInetSocketAddressList = RegistryFactory.getInstance()
.lookup(transactionServiceGroup);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(availInetSocketAddressList)) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
return availInetSocketAddressList.stream()
.map(NetUtil::toStringAddress)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
} RegistryFactory.getInstance().lookup(transactionServiceGroup);是对不同注册中心做了适配的,默认看下Nacos形式的实现
先根据事务分组找到分组所属的server集群名称,这里是default,然后根据集群名称找到server对应ip端口地址
@Override
public List lookup(String key) throws Exception {
//default
String clusterName = getServiceGroup(key);
if (clusterName == null) {
return null;
}
if (!LISTENER_SERVICE_MAP.containsKey(clusterName)) {
synchronized (LOCK_OBJ) {
if (!LISTENER_SERVICE_MAP.containsKey(clusterName)) {
List clusters = new ArrayList<>();
clusters.add(clusterName);
List firstAllInstances = getNamingInstance().getAllInstances(getServiceName(), getServiceGroup(), clusters);
if (null != firstAllInstances) {
List newAddressList = firstAllInstances.stream()
.filter(instance -> instance.isEnabled() && instance.isHealthy())
.map(instance -> new InetSocketAddress(instance.getIp(), instance.getPort()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
CLUSTER_ADDRESS_MAP.put(clusterName, newAddressList);
}
subscribe(clusterName, event -> {
List instances = ((NamingEvent) event).getInstances();
if (null == instances && null != CLUSTER_ADDRESS_MAP.get(clusterName)) {
CLUSTER_ADDRESS_MAP.remove(clusterName);
} else if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(instances)) {
List newAddressList = instances.stream()
.filter(instance -> instance.isEnabled() && instance.isHealthy())
.map(instance -> new InetSocketAddress(instance.getIp(), instance.getPort()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
CLUSTER_ADDRESS_MAP.put(clusterName, newAddressList);
}
});
}
}
}
return CLUSTER_ADDRESS_MAP.get(clusterName);
} Seata-server的IP地址已获取到,然后调用acquireChannel
Channel acquireChannel(String serverAddress) {
Channel channelToServer = channels.get(serverAddress);
if (channelToServer != null) {
channelToServer = getExistAliveChannel(channelToServer, serverAddress);
if (channelToServer != null) {
return channelToServer;
}
}
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("will connect to " + serverAddress);
}
channelLocks.putIfAbsent(serverAddress, new Object());
synchronized (channelLocks.get(serverAddress)) {
return doConnect(serverAddress);
}
}最后将获取到的seata-server的IP地址放到Netty中封装,TmClient就初始化完毕
TmClient初始化总结:
-
启动定时器,尝试进行一次重连seata-server
-
重连时,先从nacos(或则其他配置)中根据分组名称(service_group)找到集群名称(cluster_name)
-
再根据集群名称找到集群ip端口列表
-
从ip列表中选择一个用netty进行连接
2.3.2 RMClient初始化
public static void init(String applicationId, String transactionServiceGroup) {
// 获取单例对象
RmRpcClient rmRpcClient = RmRpcClient.getInstance(applicationId, transactionServiceGroup);
// 设置ResourceManager的单例对象
rmRpcClient.setResourceManager(DefaultResourceManager.get());
// 添加监听器,监听Server端的消息推送
rmRpcClient.setClientMessageListener(new RmMessageListener(DefaultRMHandler.get()));
// 初始化RPC
rmRpcClient.init();
}和TMClient想比,RMClient多出了一个监听Server端消息并处理的机制。也就是说TM的职责更多的是主动与Server端通信,比如:全局事务的begin、commit、rollback等。
而RM除了主动操作本地资源外,还会因为全局事务的commit、rollback等的消息推送,从而对本地资源进行相关操作。
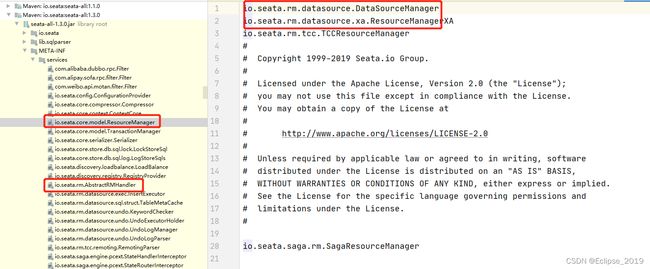
设置资源管理器resourceManager,设置消息回调监听器用于接收TC在二阶段发出的提交或者回滚请求,Seata中对ResourceManager,AbstractRMHandler做了SPI适配,以ResouceManager为例:
public class DefaultResourceManager implements ResourceManager {
protected void initResourceManagers() {
//init all resource managers
List allResourceManagers = EnhancedServiceLoader.loadAll(ResourceManager.class);
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(allResourceManagers)) {
for (ResourceManager rm : allResourceManagers) {
resourceManagers.put(rm.getBranchType(), rm);
}
}
}
} 可以看到初始化DefaultResouceManager时会使用ClassLoader去加载对应Jar下的实现,而默认AT模式使用的实现是数据库,也就是rm-datasource包下的实现,找实现类路径需要定位到/resources/META-INF/扩展接口全路径去找,就会找到对应的实现类
ResourceManager对应实现类全路径 io.seata.rm.datasource.DataSourceManager,该类中指定了了提交和回滚的方法,DefaultRMHandler对应实现类全路径io.seata.rm.RMHandlerAT,是个接收server消息并做对应提交或者回滚操作的回调处理类。
RMClinet的init()方法与TMClient基本一致
2.3.3 总结
-
Spring启动时,初始化了2个客户端TmClient、RmClient
-
TmClient与seata-server通过Netty建立连接并发送消息
-
RmClient与seata-server通过Netty建立连接,负责接收二阶段提交、回滚消息并在回调器(RmHandler)中做处理
2.4 AbstractAutoProxyCreator
GlobalTransactionScanner初始化完了TM和RM以后,我们再关注一下AbstractAutoProxyCreator,自动代理。
自动代理,它代理啥东西呢?或者说它给spring中的Bean增强了什么功能?
GlobalTransactionScanner主要扩展了AbstractAutoProxyCreator的wrapIfNecessary
代理增强的前置判断处理,表示是否该Bean需要增强,如果增强的话创建代理类
2.4.1 wrapIfNecessary
@Override
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (disableGlobalTransaction) {
return bean;
}
try {
synchronized (PROXYED_SET) {
// 相同Bean排重
if (PROXYED_SET.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
interceptor = null;
// 判断是否开启TCC模式
if (TCCBeanParserUtils.isTccAutoProxy(bean, beanName, applicationContext)) {
// TCC实现的拦截器
interceptor = new TccActionInterceptor(TCCBeanParserUtils.getRemotingDesc(beanName));
} else {
Class serviceInterface = SpringProxyUtils.findTargetClass(bean);
Class[] interfacesIfJdk = SpringProxyUtils.findInterfaces(bean);
// 判断是否存在@GlobalTransactional或者@GlobalLock注解
if (!existsAnnotation(new Class[]{serviceInterface})
&& !existsAnnotation(interfacesIfJdk)) {
return bean;
}
if (interceptor == null) {
// 非TCC的拦截器
if (globalTransactionalInterceptor == null) {
globalTransactionalInterceptor = new GlobalTransactionalInterceptor(failureHandlerHook);
ConfigurationCache.addConfigListener(
ConfigurationKeys.DISABLE_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION,
(ConfigurationChangeListener)globalTransactionalInterceptor);
}
interceptor = globalTransactionalInterceptor;
}
}
// 判断当前Bean是否已经是spring的代理类了
if (!AopUtils.isAopProxy(bean)) {
// 如果还不是,那么走一轮spring的代理过程即可
bean = super.wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
} else {
// 如果是一个spring的代理类,那么反射获取代理类中已经存在的拦截器集合,然后添加到该集合当中
AdvisedSupport advised = SpringProxyUtils.getAdvisedSupport(bean);
Advisor[] advisor = buildAdvisors(beanName, getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(null, null, null));
for (Advisor avr : advisor) {
advised.addAdvisor(0, avr);
}
}
PROXYED_SET.add(beanName);
return bean;
}
} catch (Exception exx) {}
}wrapIfNecessary方法较长我们分步骤看看
1)isTccAutoProxy判断是否开启tcc模式,开启的话选择了TccActionInterceptor拦截器,非tcc模式选择GlobalTransactionalInterceptor拦截器,默认不开启
2)existAnnotation判断当前Bean是否有类或者接口的方法存在@GlobalTransactional或者@GlobalLock注解,如果没有则直接返回
3)isAopProxy方法是判断当前的Bean是否已经是spring的代理类了,无论是JDK动态代理还是Cglib类代理。如果是普通的Bean,走原有的生成代理逻辑即可,如果已经是代理类,那么要通过反射获取代理对象内的拦截器集合也叫做Advisor,直接添加到该集合当中。
wrapIfNecessary的方法并不复杂,但是如果对代理不是很熟悉或许对细节点会有些困惑。
2.4.1.1 AT一阶段开启全局事务
在需要进行全局事务管理的接口上,会加@GlobalTransactional注解,这个注解会又一个对应的拦截器进行拦截GlobalTransactionalInterceptor,invoke就是拦截方法
@Override
public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
Class targetClass =
methodInvocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(methodInvocation.getThis()) : null;
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(methodInvocation.getMethod(), targetClass);
if (specificMethod != null && !specificMethod.getDeclaringClass().equals(Object.class)) {
final Method method = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
//获取方法上的全局事务注解
final GlobalTransactional globalTransactionalAnnotation =
getAnnotation(method, targetClass, GlobalTransactional.class);
//获取方法上的全局锁注解
final GlobalLock globalLockAnnotation = getAnnotation(method, targetClass, GlobalLock.class);
boolean localDisable = disable || (degradeCheck && degradeNum >= degradeCheckAllowTimes);
if (!localDisable) {
//如果方法上有全局事务注解,调用handleGlobalTransaction开启全局事务
if (globalTransactionalAnnotation != null) {
return handleGlobalTransaction(methodInvocation, globalTransactionalAnnotation);
//如果方法上有全局锁注解,调用handleGlobalLock开启全局锁
} else if (globalLockAnnotation != null) {
return handleGlobalLock(methodInvocation);
}
}
}
//如果啥都没有,按普通方法执行,提升性能
return methodInvocation.proceed();
}在handleGlobalTransaction方法中调用了transactionalTemplate.execute方法
// 2. 开启全局事务beginTransaction
beginTransaction(txInfo, tx);
Object rs = null;
try {
// 执行业务方法business.execute()
rs = business.execute();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 3.出现异常执行completeTransactionAfterThrowing回滚
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, tx, ex);
throw ex;
}
// 4. 没有异常提交事务commitTransaction
commitTransaction(tx);开启全局事务最终调用io.seata.tm.api.DefaultGlobalTransaction#begin(int, java.lang.String)方法
@Override
public void begin(int timeout, String name) throws TransactionException {
//此处的角色判断有关键的作用
//表明当前是全局事务的发起者(Launcher)还是参与者(Participant)
//如果在分布式事务的下游系统方法中也加上GlobalTransactional注解
//那么它的角色就是Participant,即会忽略后面的begin就退出了
//而判断是发起者(Launcher)还是参与者(Participant)是根据当前上下文是否已存在XID来判断
//没有XID的就是Launcher,已经存在XID的就是Participant
if (role != GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher) {
assertXIDNotNull();
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Ignore Begin(): just involved in global transaction [{}]", xid);
}
return;
}
assertXIDNull();
if (RootContext.getXID() != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
xid = transactionManager.begin(null, null, name, timeout);
status = GlobalStatus.Begin;
RootContext.bind(xid);
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Begin new global transaction [{}]", xid);
}
}请求seata-server获取全局事务XID
@Override
public String begin(String applicationId, String transactionServiceGroup, String name, int timeout)
throws TransactionException {
GlobalBeginRequest request = new GlobalBeginRequest();
request.setTransactionName(name);
request.setTimeout(timeout);
//跟进
GlobalBeginResponse response = (GlobalBeginResponse) syncCall(request);
if (response.getResultCode() == ResultCode.Failed) {
throw new TmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.BeginFailed, response.getMsg());
}
return response.getXid();
}private AbstractTransactionResponse syncCall(AbstractTransactionRequest request) throws TransactionException {
try {
//TMClient封装的Netty对象
return (AbstractTransactionResponse) TmNettyRemotingClient.getInstance().sendSyncRequest(request);
} catch (TimeoutException toe) {
throw new TmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.IO, "RPC timeout", toe);
}
}将XID绑定在RootContext中,由此可以看出全局事务是由TM发起的,TM发起全局事务请求给seata-server服务,seata-server服务接受到请求后处理(以下是seata服务代码):
@Override
protected void doGlobalBegin(GlobalBeginRequest request, GlobalBeginResponse response, RpcContext rpcContext)
throws TransactionException {
//进入begin
response.setXid(core.begin(rpcContext.getApplicationId(), rpcContext.getTransactionServiceGroup(),
request.getTransactionName(), request.getTimeout()));
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Begin new global transaction applicationId: {},transactionServiceGroup: {}, transactionName: {},timeout:{},xid:{}",
rpcContext.getApplicationId(), rpcContext.getTransactionServiceGroup(), request.getTransactionName(), request.getTimeout(), response.getXid());
}
}io.seata.server.coordinator.DefaultCoordinator#doGlobalBegin方法接受客户端开启全局事务的请求,调用io.seata.server.coordinator.DefaultCore#begin开启全局事务
@Override
public String begin(String applicationId, String transactionServiceGroup, String name, int timeout)
throws TransactionException {
GlobalSession session = GlobalSession.createGlobalSession(applicationId, transactionServiceGroup, name,
timeout);
MDC.put(RootContext.MDC_KEY_XID, session.getXid());
session.addSessionLifecycleListener(SessionHolder.getRootSessionManager());
//开启会话
session.begin();
// transaction start event
eventBus.post(new GlobalTransactionEvent(session.getTransactionId(), GlobalTransactionEvent.ROLE_TC,
session.getTransactionName(), applicationId, transactionServiceGroup, session.getBeginTime(), null, session.getStatus()));
return session.getXid();
}通过当前会话开启
@Override
public void begin() throws TransactionException {
this.status = GlobalStatus.Begin;
this.beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.active = true;
for (SessionLifecycleListener lifecycleListener : lifecycleListeners) {
lifecycleListener.onBegin(this);
}
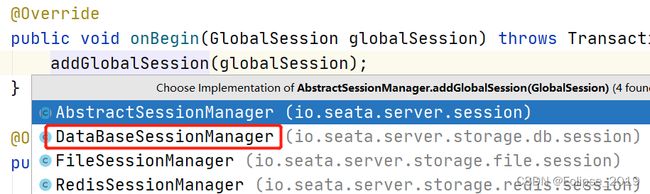
}调用io.seata.server.session.AbstractSessionManager#onBegin方法,又调用io.seata.server.storage.db.session.DataBaseSessionManager#addGlobalSession方法
@Override
public void addGlobalSession(GlobalSession session) throws TransactionException {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(taskName)) {
//进入
boolean ret = transactionStoreManager.writeSession(LogOperation.GLOBAL_ADD, session);
if (!ret) {
throw new StoreException("addGlobalSession failed.");
}
} else {
boolean ret = transactionStoreManager.writeSession(LogOperation.GLOBAL_UPDATE, session);
if (!ret) {
throw new StoreException("addGlobalSession failed.");
}
}
}这里往数据库里写入数据
@Override
public boolean writeSession(LogOperation logOperation, SessionStorable session) {
if (LogOperation.GLOBAL_ADD.equals(logOperation)) {
return logStore.insertGlobalTransactionDO(SessionConverter.convertGlobalTransactionDO(session));
} else if (LogOperation.GLOBAL_UPDATE.equals(logOperation)) {
return logStore.updateGlobalTransactionDO(SessionConverter.convertGlobalTransactionDO(session));
} else if (LogOperation.GLOBAL_REMOVE.equals(logOperation)) {
return logStore.deleteGlobalTransactionDO(SessionConverter.convertGlobalTransactionDO(session));
} else if (LogOperation.BRANCH_ADD.equals(logOperation)) {
return logStore.insertBranchTransactionDO(SessionConverter.convertBranchTransactionDO(session));
} else if (LogOperation.BRANCH_UPDATE.equals(logOperation)) {
return logStore.updateBranchTransactionDO(SessionConverter.convertBranchTransactionDO(session));
} else if (LogOperation.BRANCH_REMOVE.equals(logOperation)) {
return logStore.deleteBranchTransactionDO(SessionConverter.convertBranchTransactionDO(session));
} else {
throw new StoreException("Unknown LogOperation:" + logOperation.name());
}
}这里向seata库global_tab插入数据,到此全局事务已开启
2.4.1.2 AT一阶段执行业务SQL
全局事务已开启,下面需要执行业务SQL,生成undo_log数据,全局事务拦截成功后最终还是执行了业务方法的,但是由于Seata对数据源做了代理,所以sql解析与undo_log入库操作是在数据源代理中执行的,代理就是Seata对DataSource,Connection,Statement做的代理封装类
/**
* 构造datasource代理对象,替换原来的的datasource
*/
@Primary
@Bean("dataSource")
public DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy(DataSource druidDataSource){
return new DataSourceProxy(druidDataSource);
}项目中使用的数据源均用seata的DataSourceProxy代替
最终对Sql进行解析操作,发生在StatementProxy类中
@Override
public boolean execute(String sql) throws SQLException {
this.targetSQL = sql;
return ExecuteTemplate.execute(this, (statement, args) -> statement.execute((String) args[0]), sql);
}public static T execute(List sqlRecognizers,
StatementProxy statementProxy,
StatementCallback statementCallback,
Object... args) throws SQLException {
if (!RootContext.requireGlobalLock() && !StringUtils.equals(BranchType.AT.name(), RootContext.getBranchType())) {
//不是全局事务的直接执行,提升性能
return statementCallback.execute(statementProxy.getTargetStatement(), args);
}
String dbType = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().getDbType();
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(sqlRecognizers)) {
sqlRecognizers = SQLVisitorFactory.get(
statementProxy.getTargetSQL(),
dbType);
}
Executor executor;
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(sqlRecognizers)) {
executor = new PlainExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback);
} else {
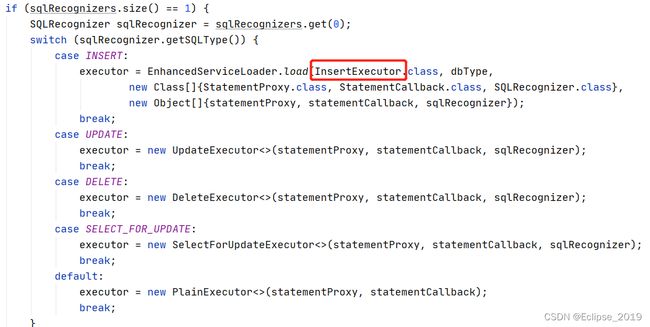
if (sqlRecognizers.size() == 1) {
SQLRecognizer sqlRecognizer = sqlRecognizers.get(0);
//不同SQL类型,不同处理
switch (sqlRecognizer.getSQLType()) {
case INSERT:
executor = EnhancedServiceLoader.load(InsertExecutor.class, dbType,
new Class[]{StatementProxy.class, StatementCallback.class, SQLRecognizer.class},
new Object[]{statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer});
break;
case UPDATE:
executor = new UpdateExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
break;
case DELETE:
executor = new DeleteExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
break;
case SELECT_FOR_UPDATE:
executor = new SelectForUpdateExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
break;
default:
executor = new PlainExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback);
break;
}
} else {
executor = new MultiExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizers);
}
}
T rs;
try {
//执行SQL
rs = executor.execute(args);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
if (!(ex instanceof SQLException)) {
// Turn other exception into SQLException
ex = new SQLException(ex);
}
throw (SQLException) ex;
}
return rs;
} -
先判断是否开启了全局事务,如果没有,不走代理,不解析sql,提升性能
-
调用SQLVisitorFactory对目标sql进行解析
-
针对特定类型sql操作(INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE,SELECT_FOR_UPDATE)等进行特殊解析
-
执行sql并返回结果
不同类型的SQL处理方法不一样,这里以insert为例
insert使用的是InsertExecutor.execute方法,但其实最终还是使用io.seata.rm.datasource.exec.BaseTransactionalExecutor#execute方法
@Override
public T execute(Object... args) throws Throwable {
if (RootContext.inGlobalTransaction()) {
String xid = RootContext.getXID();
statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().bind(xid);
}
statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().setGlobalLockRequire(RootContext.requireGlobalLock());
return doExecute(args);
}将上下文中的xid绑定到了statementProxy中,并调用了doExecute方法,看下AbstractDMLBaseExecutor中的doExecute方法
@Override
public T doExecute(Object... args) throws Throwable {
AbstractConnectionProxy connectionProxy = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy();
if (connectionProxy.getAutoCommit()) {
return executeAutoCommitTrue(args);
} else {
return executeAutoCommitFalse(args);
}
}方法中调用了executeAutoCommitTrue/executeAutoCommitFalse
protected T executeAutoCommitTrue(Object[] args) throws Throwable {
ConnectionProxy connectionProxy = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy();
try {
connectionProxy.setAutoCommit(false);
return new LockRetryPolicy(connectionProxy).execute(() -> {
T result = executeAutoCommitFalse(args);
connectionProxy.commit();
return result;
});
} catch (Exception e) {
// when exception occur in finally,this exception will lost, so just print it here
LOGGER.error("execute executeAutoCommitTrue error:{}", e.getMessage(), e);
if (!LockRetryPolicy.isLockRetryPolicyBranchRollbackOnConflict()) {
connectionProxy.getTargetConnection().rollback();
}
throw e;
} finally {
connectionProxy.getContext().reset();
connectionProxy.setAutoCommit(true);
}
}但仔细发现,最终都是调用executeAutoCommitFalse方法
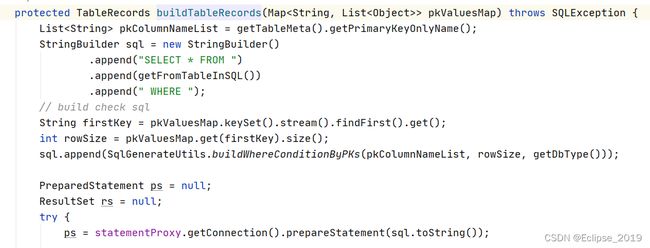
protected T executeAutoCommitFalse(Object[] args) throws Exception {
//跟入getTableMeta方法
if (!JdbcConstants.MYSQL.equalsIgnoreCase(getDbType()) && getTableMeta().getPrimaryKeyOnlyName().size() > 1)
{
throw new NotSupportYetException("multi pk only support mysql!");
}
//获取beforeImage
TableRecords beforeImage = beforeImage();
//执行业务sql
T result = statementCallback.execute(statementProxy.getTargetStatement(), args);
//获取afterImage
TableRecords afterImage = afterImage(beforeImage);
//保存image
prepareUndoLog(beforeImage, afterImage);
return result;
}获取beforeImage
//tableMeta里面包含表名、列、索引等数据
protected TableMeta getTableMeta(String tableName) {
if (tableMeta != null) {
return tableMeta;
}
ConnectionProxy connectionProxy = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy();
tableMeta = TableMetaCacheFactory.getTableMetaCache(connectionProxy.getDbType())
.getTableMeta(connectionProxy.getTargetConnection(), tableName, connectionProxy.getDataSourceProxy().getResourceId());
return tableMeta;
}执行业务sql还是使用com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidPooledPreparedStatement#execute方法执行
获取afterImage
在提交事务时,插入undo_log日志
protected T executeAutoCommitTrue(Object[] args) throws Throwable {
ConnectionProxy connectionProxy = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy();
try {
connectionProxy.setAutoCommit(false);
return new LockRetryPolicy(connectionProxy).execute(() -> {
T result = executeAutoCommitFalse(args);
//跟入
connectionProxy.commit();
return result;
});
} catch (Exception e) {
// when exception occur in finally,this exception will lost, so just print it here
LOGGER.error("execute executeAutoCommitTrue error:{}", e.getMessage(), e);
if (!LockRetryPolicy.isLockRetryPolicyBranchRollbackOnConflict()) {
connectionProxy.getTargetConnection().rollback();
}
throw e;
} finally {
connectionProxy.getContext().reset();
connectionProxy.setAutoCommit(true);
}
}public void commit() throws SQLException {
try {
LOCK_RETRY_POLICY.execute(() -> {
//跟入
doCommit();
return null;
});
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new SQLException(e);
}
}private void doCommit() throws SQLException {
if (context.inGlobalTransaction()) {
//跟入
processGlobalTransactionCommit();
} else if (context.isGlobalLockRequire()) {
processLocalCommitWithGlobalLocks();
} else {
targetConnection.commit();
}
}private void processGlobalTransactionCommit() throws SQLException {
try {
//向seata-server注册分支信息
register();
} catch (TransactionException e) {
recognizeLockKeyConflictException(e, context.buildLockKeys());
}
try {
//提交事务之前,插入undo_log,跟入flushUndoLogs
UndoLogManagerFactory.getUndoLogManager(this.getDbType()).flushUndoLogs(this);
targetConnection.commit();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
LOGGER.error("process connectionProxy commit error: {}", ex.getMessage(), ex);
report(false);
throw new SQLException(ex);
}
if (IS_REPORT_SUCCESS_ENABLE) {
report(true);
}
context.reset();
}public void flushUndoLogs(ConnectionProxy cp) throws SQLException {
ConnectionContext connectionContext = cp.getContext();
if (!connectionContext.hasUndoLog()) {
return;
}
String xid = connectionContext.getXid();
long branchId = connectionContext.getBranchId();
BranchUndoLog branchUndoLog = new BranchUndoLog();
branchUndoLog.setXid(xid);
branchUndoLog.setBranchId(branchId);
branchUndoLog.setSqlUndoLogs(connectionContext.getUndoItems());
UndoLogParser parser = UndoLogParserFactory.getInstance();
byte[] undoLogContent = parser.encode(branchUndoLog);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Flushing UNDO LOG: {}", new String(undoLogContent, Constants.DEFAULT_CHARSET));
}
//该方法插入undo_log
insertUndoLogWithNormal(xid, branchId, buildContext(parser.getName()), undoLogContent,
cp.getTargetConnection());
}在该方法中注册分支事务
提交事务,向seata-server注册分支信息,seata-server接收到请求(seata源码)
io.seata.server.coordinator.DefaultCoordinator#doBranchRegister方法
public Long branchRegister(BranchType branchType, String resourceId, String clientId, String xid,
String applicationData, String lockKeys) throws TransactionException {
GlobalSession globalSession = assertGlobalSessionNotNull(xid, false);
return SessionHolder.lockAndExecute(globalSession, () -> {
globalSessionStatusCheck(globalSession);
globalSession.addSessionLifecycleListener(SessionHolder.getRootSessionManager());
BranchSession branchSession = SessionHelper.newBranchByGlobal(globalSession, branchType, resourceId,
applicationData, lockKeys, clientId);
MDC.put(RootContext.MDC_KEY_BRANCH_ID, String.valueOf(branchSession.getBranchId()));
branchSessionLock(globalSession, branchSession);
try {
//进行注册
globalSession.addBranch(branchSession);
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
branchSessionUnlock(branchSession);
throw new BranchTransactionException(FailedToAddBranch, String
.format("Failed to store branch xid = %s branchId = %s", globalSession.getXid(),
branchSession.getBranchId()), ex);
}
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Register branch successfully, xid = {}, branchId = {}, resourceId = {} ,lockKeys = {}",
globalSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId(), resourceId, lockKeys);
}
return branchSession.getBranchId();
});
}@Override
public void addBranch(BranchSession branchSession) throws TransactionException {
for (SessionLifecycleListener lifecycleListener : lifecycleListeners) {
//跟入onAddBranch,选择AbstractSessionManager
lifecycleListener.onAddBranch(this, branchSession);
}
branchSession.setStatus(BranchStatus.Registered);
add(branchSession);
}io.seata.server.storage.db.session.DataBaseSessionManager#addBranchSession方法
@Override
public void onAddBranch(GlobalSession globalSession, BranchSession branchSession) throws TransactionException {
//跟入,选择DataBaseSessionManager
addBranchSession(globalSession, branchSession);
}@Override
public void addBranchSession(GlobalSession globalSession, BranchSession session) throws TransactionException {
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(taskName)) {
return;
}
//跟入
boolean ret = transactionStoreManager.writeSession(LogOperation.BRANCH_ADD, session);
if (!ret) {
throw new StoreException("addBranchSession failed.");
}
}@Override
public boolean writeSession(LogOperation logOperation, SessionStorable session) {
if (LogOperation.GLOBAL_ADD.equals(logOperation)) {
return logStore.insertGlobalTransactionDO(SessionConverter.convertGlobalTransactionDO(session));
} else if (LogOperation.GLOBAL_UPDATE.equals(logOperation)) {
return logStore.updateGlobalTransactionDO(SessionConverter.convertGlobalTransactionDO(session));
} else if (LogOperation.GLOBAL_REMOVE.equals(logOperation)) {
return logStore.deleteGlobalTransactionDO(SessionConverter.convertGlobalTransactionDO(session));
} else if (LogOperation.BRANCH_ADD.equals(logOperation)) {
return logStore.insertBranchTransactionDO(SessionConverter.convertBranchTransactionDO(session));
} else if (LogOperation.BRANCH_UPDATE.equals(logOperation)) {
return logStore.updateBranchTransactionDO(SessionConverter.convertBranchTransactionDO(session));
} else if (LogOperation.BRANCH_REMOVE.equals(logOperation)) {
return logStore.deleteBranchTransactionDO(SessionConverter.convertBranchTransactionDO(session));
} else {
throw new StoreException("Unknown LogOperation:" + logOperation.name());
}
}@Override
public boolean insertBranchTransactionDO(BranchTransactionDO branchTransactionDO) {
String sql = LogStoreSqlsFactory.getLogStoreSqls(dbType).getInsertBranchTransactionSQL(branchTable);
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
int index = 1;
conn = logStoreDataSource.getConnection();
conn.setAutoCommit(true);
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(index++, branchTransactionDO.getXid());
ps.setLong(index++, branchTransactionDO.getTransactionId());
ps.setLong(index++, branchTransactionDO.getBranchId());
ps.setString(index++, branchTransactionDO.getResourceGroupId());
ps.setString(index++, branchTransactionDO.getResourceId());
ps.setString(index++, branchTransactionDO.getBranchType());
ps.setInt(index++, branchTransactionDO.getStatus());
ps.setString(index++, branchTransactionDO.getClientId());
ps.setString(index++, branchTransactionDO.getApplicationData());
return ps.executeUpdate() > 0;
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new StoreException(e);
} finally {
IOUtil.close(ps, conn);
}
}Seata-server添加分支信息完成,到这里,一阶段结束,业务数据,undo_log,分支信息都已经写入数据库
2.4.1.3 AT二阶段提交
回到handleGlobalTransaction方法中,调用了transactionalTemplate.execute方法
// 2. 开启全局事务beginTransaction
beginTransaction(txInfo, tx);
Object rs = null;
try {
// 执行业务方法business.execute()
rs = business.execute();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
//上面是一阶段
//下面是二阶段
// 3.出现异常执行completeTransactionAfterThrowing回滚
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, tx, ex);
throw ex;
}
// 4. 没有异常提交事务commitTransaction
commitTransaction(tx);二阶段提交
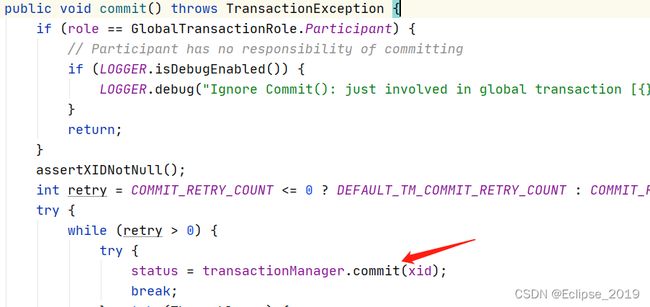
commitTransaction(tx);跟进
private void commitTransaction(GlobalTransaction tx) throws TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException {
try {
triggerBeforeCommit();
//跟入
tx.commit();
triggerAfterCommit();
} catch (TransactionException txe) {
// 4.1 Failed to commit
throw new TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException(tx, txe,
TransactionalExecutor.Code.CommitFailure);
}
}@Override
public GlobalStatus commit(String xid) throws TransactionException {
GlobalCommitRequest globalCommit = new GlobalCommitRequest();
globalCommit.setXid(xid);
//跟入syncCall
GlobalCommitResponse response = (GlobalCommitResponse) syncCall(globalCommit);
return response.getGlobalStatus();
}private AbstractTransactionResponse syncCall(AbstractTransactionRequest request) throws TransactionException {
try {
return (AbstractTransactionResponse) TmNettyRemotingClient.getInstance().sendSyncRequest(request);
} catch (TimeoutException toe) {
throw new TmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.IO, "RPC timeout", toe);
}
}最终通过TM请求seata-server,Seata-server接收到全局提交请求(seata源码)
DefaultCoordinator中
@Override
protected void doGlobalCommit(GlobalCommitRequest request, GlobalCommitResponse response, RpcContext rpcContext)
throws TransactionException {
MDC.put(RootContext.MDC_KEY_XID, request.getXid());
//跟入commit
response.setGlobalStatus(core.commit(request.getXid()));
}Seata-server接收到客户端全局提交请求后,先回调客户端,删除undo_log,seata在删除分支及全局事务
之前说过RMClient在初始化时,设置资源管理器resourceManager,设置消息回调监听器用于接收TC在二阶段发出的提交或者回滚请求
Seata-server删除分支数据及全局事务数据
@Override
public void removeBranch(BranchSession branchSession) throws TransactionException {
// do not unlock if global status in (Committing, CommitRetrying, AsyncCommitting),
// because it's already unlocked in 'DefaultCore.commit()'
if (status != Committing && status != CommitRetrying && status != AsyncCommitting) {
if (!branchSession.unlock()) {
throw new TransactionException("Unlock branch lock failed, xid = " + this.xid + ", branchId = " + branchSession.getBranchId());
}
}
for (SessionLifecycleListener lifecycleListener : lifecycleListeners) {
//跟入
lifecycleListener.onRemoveBranch(this, branchSession);
}
remove(branchSession);
}private void writeSession(LogOperation logOperation, SessionStorable sessionStorable) throws TransactionException {
if (!transactionStoreManager.writeSession(logOperation, sessionStorable)) {
if (LogOperation.GLOBAL_ADD.equals(logOperation)) {
throw new GlobalTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.FailedWriteSession,
"Fail to store global session");
} else if (LogOperation.GLOBAL_UPDATE.equals(logOperation)) {
throw new GlobalTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.FailedWriteSession,
"Fail to update global session");
} else if (LogOperation.GLOBAL_REMOVE.equals(logOperation)) {
throw new GlobalTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.FailedWriteSession,
"Fail to remove global session");
} else if (LogOperation.BRANCH_ADD.equals(logOperation)) {
throw new BranchTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.FailedWriteSession,
"Fail to store branch session");
} else if (LogOperation.BRANCH_UPDATE.equals(logOperation)) {
throw new BranchTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.FailedWriteSession,
"Fail to update branch session");
} else if (LogOperation.BRANCH_REMOVE.equals(logOperation)) {
throw new BranchTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.FailedWriteSession,
"Fail to remove branch session");
} else {
throw new BranchTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.FailedWriteSession,
"Unknown LogOperation:" + logOperation.name());
}
}
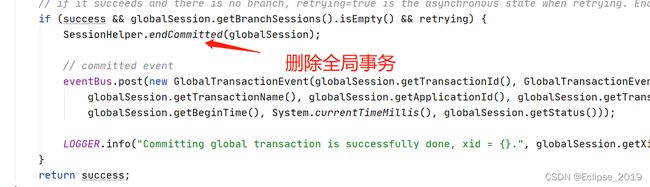
}public static void endCommitted(GlobalSession globalSession) throws TransactionException {
globalSession.changeStatus(GlobalStatus.Committed);
//删除全局事务
globalSession.end();
}客户端删除undo_log数据
在接收提交里面
protected void doBranchCommit(BranchCommitRequest request, BranchCommitResponse response)
throws TransactionException {
String xid = request.getXid();
long branchId = request.getBranchId();
String resourceId = request.getResourceId();
String applicationData = request.getApplicationData();
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Branch committing: " + xid + " " + branchId + " " + resourceId + " " + applicationData);
}
//跟入
BranchStatus status = getResourceManager().branchCommit(request.getBranchType(), xid, branchId, resourceId,
applicationData);
response.setXid(xid);
response.setBranchId(branchId);
response.setBranchStatus(status);
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Branch commit result: " + status);
}
}getResourceManager获取的就是RMClient初始化时设置的资源管理器DataSourceManager
public BranchStatus branchCommit(BranchType branchType, String xid, long branchId, String resourceId,
String applicationData) throws TransactionException {
return asyncWorker.branchCommit(branchType, xid, branchId, resourceId, applicationData);
}@Override
public BranchStatus branchCommit(BranchType branchType, String xid, long branchId, String resourceId,
String applicationData) throws TransactionException {
if (!ASYNC_COMMIT_BUFFER.offer(new Phase2Context(branchType, xid, branchId, resourceId, applicationData))) {
LOGGER.warn("Async commit buffer is FULL. Rejected branch [{}/{}] will be handled by housekeeping later.", branchId, xid);
}
return BranchStatus.PhaseTwo_Committed;
}这边只是往一个ASYNC_COMMIT_BUFFER缓冲List中新增了一个二阶段提交的context,但真正提交在AsyncWorker的init()方法
public synchronized void init() {
LOGGER.info("Async Commit Buffer Limit: {}", ASYNC_COMMIT_BUFFER_LIMIT);
ScheduledExecutorService timerExecutor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1, new NamedThreadFactory("AsyncWorker", 1, true));
timerExecutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
try {
//跟入
doBranchCommits();
} catch (Throwable e) {
LOGGER.info("Failed at async committing ... {}", e.getMessage());
}
}, 10, 1000 * 1, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}删除Undo_log
二阶段回滚
二阶段回滚seata-server端代码与二阶段提交类似,这里省略
protected void doGlobalRollback(GlobalRollbackRequest request, GlobalRollbackResponse response,
RpcContext rpcContext) throws TransactionException {
MDC.put(RootContext.MDC_KEY_XID, request.getXid());
//全局回滚sea他接收请求
response.setGlobalStatus(core.rollback(request.getXid()));
}主要看回滚客户端如何进行事务补偿
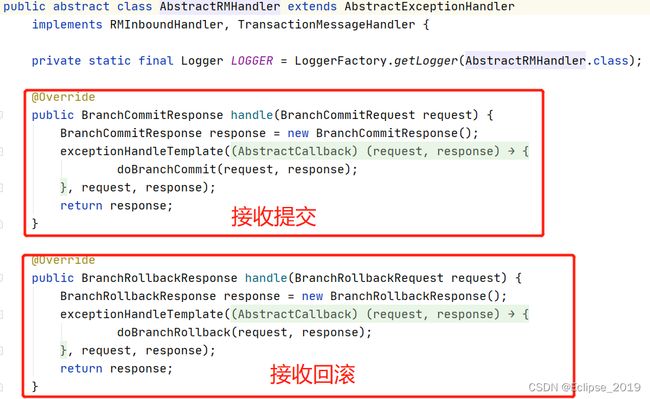
@Override
public BranchRollbackResponse handle(BranchRollbackRequest request) {
BranchRollbackResponse response = new BranchRollbackResponse();
exceptionHandleTemplate(new AbstractCallback() {
@Override
public void execute(BranchRollbackRequest request, BranchRollbackResponse response)
throws TransactionException {
//跟入
doBranchRollback(request, response);
}
}, request, response);
return response;
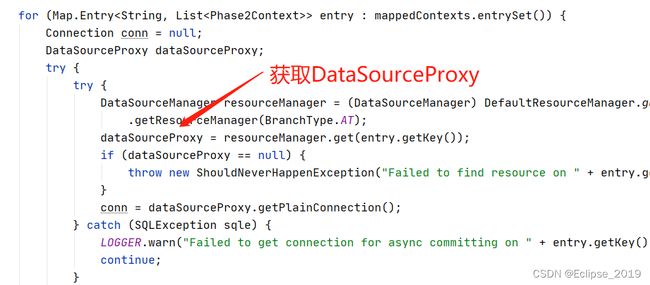
} public BranchStatus branchRollback(BranchType branchType, String xid, long branchId, String resourceId,
String applicationData) throws TransactionException {
DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy = get(resourceId);
if (dataSourceProxy == null) {
throw new ShouldNeverHappenException();
}
try {
UndoLogManagerFactory.getUndoLogManager(dataSourceProxy.getDbType()).undo(dataSourceProxy, xid, branchId);
} catch (TransactionException te) {
StackTraceLogger.info(LOGGER, te,
"branchRollback failed. branchType:[{}], xid:[{}], branchId:[{}], resourceId:[{}], applicationData:[{}]. reason:[{}]",
new Object[]{branchType, xid, branchId, resourceId, applicationData, te.getMessage()});
if (te.getCode() == TransactionExceptionCode.BranchRollbackFailed_Unretriable) {
return BranchStatus.PhaseTwo_RollbackFailed_Unretryable;
} else {
return BranchStatus.PhaseTwo_RollbackFailed_Retryable;
}
}
return BranchStatus.PhaseTwo_Rollbacked;
}最终回滚方法调用的是UndoLogManager.undo(dataSourceProxy, xid, branchId);
判断undolog是否存在,存在则删除对应undolog,并一起提交,到此seata的AT模式源码解析完毕。