原型聚类(二)学习向量量化(LVQ)和python实现
学习向量量化(Learning Vector Quantization,LVQ)和k-means类似,也属于原型聚类的一种算法,不同的是,LVQ处理的是有标签的样本集,学习过程利用样本的标签进行辅助聚类,个人感觉这个算法更像是一个分类算法。。。
若存在一个样本集 D = { ( x 1 , y 1 ) , ( x 2 , y 2 ) , . . . , ( x m , y m ) } D=\begin{Bmatrix} (x_{1},y_{1}),(x_{2},y_{2}),...,(x_{m},y_{m}) \end{Bmatrix} D={(x1,y1),(x2,y2),...,(xm,ym)},LVQ希望通过这些样本和标签,学习一组原型向量 { p 1 , p 2 , . . . , p q } \begin{Bmatrix} p_{1},p_{2},...,p_{q} \end{Bmatrix} {p1,p2,...,pq},其中q为样本中的类别总数,算法的思想大概是在初始化原型向量后,根据样本自带的标签让对应的原型向量像该样本靠拢,最终趋于稳定,返回得到的原型向量。

(图片来自《机器学习》周志华
python3.6实现
# -*- coding: gbk -*-
import numpy as np
import copy
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons
from sklearn.datasets.samples_generator import make_blobs
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class LVQ():
def __init__(self, max_iter=10000, eta=0.1, e=0.01):
self.max_iter = max_iter
self.eta = eta
self.e = e
def dist(self, x1, x2):
return np.linalg.norm(x1 - x2)
def get_mu(self, X, Y):
k = len(set(Y))
index = np.random.choice(X.shape[0], 1, replace=False)
mus = []
mus.append(X[index])
mus_label = []
mus_label.append(Y[index])
for _ in range(k - 1):
max_dist_index = 0
max_distance = 0
for j in range(X.shape[0]):
min_dist_with_mu = 999999
for mu in mus:
dist_with_mu = self.dist(mu, X[j])
if min_dist_with_mu > dist_with_mu:
min_dist_with_mu = dist_with_mu
if max_distance < min_dist_with_mu:
max_distance = min_dist_with_mu
max_dist_index = j
mus.append(X[max_dist_index])
mus_label.append(Y[max_dist_index])
mus_array = np.array([])
for i in range(k):
if i == 0:
mus_array = mus[i]
else:
mus[i] = mus[i].reshape(mus[0].shape)
mus_array = np.append(mus_array, mus[i], axis=0)
mus_label_array = np.array(mus_label)
return mus_array, mus_label_array
def get_mu_index(self, x):
min_dist_with_mu = 999999
index = -1
for i in range(self.mus_array.shape[0]):
dist_with_mu = self.dist(self.mus_array[i], x)
if min_dist_with_mu > dist_with_mu:
min_dist_with_mu = dist_with_mu
index = i
return index
def fit(self, X, Y):
self.mus_array, self.mus_label_array = self.get_mu(X, Y)
iter = 0
while(iter < self.max_iter):
old_mus_array = copy.deepcopy(self.mus_array)
index = np.random.choice(Y.shape[0], 1, replace=False)
mu_index = self.get_mu_index(X[index])
if self.mus_label_array[mu_index] == Y[index]:
self.mus_array[mu_index] = self.mus_array[mu_index] + \
self.eta * (X[index] - self.mus_array[mu_index])
else:
self.mus_array[mu_index] = self.mus_array[mu_index] - \
self.eta * (X[index] - self.mus_array[mu_index])
diff = 0
for i in range(self.mus_array.shape[0]):
diff += np.linalg.norm(self.mus_array[i] - old_mus_array[i])
if diff < self.e:
print('迭代{}次退出'.format(iter))
return
iter += 1
print("迭代超过{}次,退出迭代".format(self.max_iter))
if __name__ == '__main__':
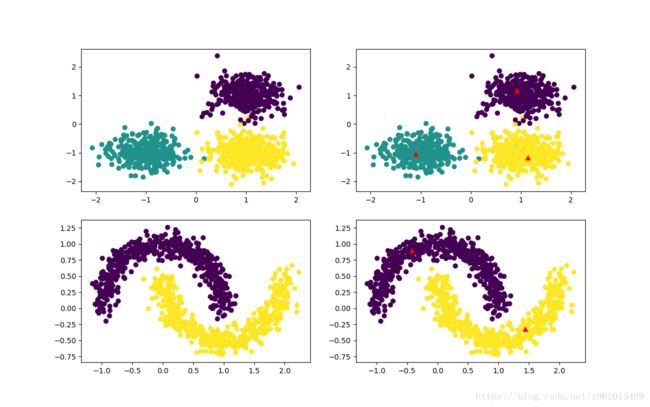
fig = plt.figure(1)
plt.subplot(221)
center = [[1, 1], [-1, -1], [1, -1]]
cluster_std = 0.35
X1, Y1 = make_blobs(n_samples=1000, centers=center,
n_features=2, cluster_std=cluster_std, random_state=1)
plt.scatter(X1[:, 0], X1[:, 1], marker='o', c=Y1)
plt.subplot(222)
lvq1 = LVQ()
lvq1.fit(X1, Y1)
mus = lvq1.mus_array
plt.scatter(X1[:, 0], X1[:, 1], marker='o', c=Y1)
plt.scatter(mus[:, 0], mus[:, 1], marker='^', c='r')
plt.subplot(223)
X2, Y2 = make_moons(n_samples=1000, noise=0.1)
plt.scatter(X2[:, 0], X2[:, 1], marker='o', c=Y2)
plt.subplot(224)
lvq2 = LVQ()
lvq2.fit(X2, Y2)
mus = lvq2.mus_array
plt.scatter(X2[:, 0], X2[:, 1], marker='o', c=Y2)
plt.scatter(mus[:, 0], mus[:, 1], marker='^', c='r')
plt.show()
图中左侧为原始生成的数据,右边红色三角为LVQ聚类获得的原型向量
参考
《机器学习》周志华