【刷题】剑指Offer篇
本文中的部分图片摘自相关题解榜主,如有侵权,请联系删除。
特别感谢k神在剑指Offer刷题路上提供的清晰图解、和堪称完美的思路与方法
小文目录:
- T3:数组中重复的数字
- T3-2:不修改数组找出重复的数字
- T4:二维数组中的查找
- T5:替换空格
- T6:从尾到头打印链表
- T7:重建二叉树
- ?? T8:二叉树的下一个节点
- T9: 用两个栈实现队列
- T10 - |:斐波那契数列
- T10 - ||:青蛙跳台
- T10 - |||:矩形覆盖
- T11 :旋转数组的最小数字(有、无重复)
- T12:矩阵中的路径
- T13 :机器人的运动范围
- T14-| :剪绳子
- T14-|| :剪绳子
- T15: 二进制中1的个数
- T16:数值的整数次方(考虑负次、0)
- T17:打印从1到最大的n位数(考虑大数溢出)
- T18 -| :删除链表的节点
- T18 -||:删除链表的重复节点
- ?T19 :正则表达式的匹配
- T20 :表示数值的字符串
- T21 :调整数组顺序使奇数放在偶数前面
- T22 :链表中倒数k个节点
- T24 :反转链表
- T25 :合并两个排序的链表
- T26 :树的子结构
- T27 :二叉树的镜像
- T28 :对称的二叉树
- T29 :顺时针打印矩阵
- T30 :栈最小元素
- T31 :栈的压入、弹出序列
- T32 | :从上到下打印二叉树
- T32 ||:从上到下打印二叉树(每层打印一行)
- T32 |||:从上到下打印二叉树(“之”字打印)
- T33:二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
- T34: 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
- T35:复杂链表的复制
- T36:二叉搜索树与双向循环链表
- T37:二叉树序列化与反序列化
- ?T38 :字符串的排列
- T39 :数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
- T40 :最小的k个数
- T41 :数据流中的中位数
- T42 :连续子数组的最大和
- T43 :1~n整数中1出现的次数
- T44 :数字序列中某一位的数字
- T45 :把数组排成最小的数
- T46 :把数字翻译成字符串
- T47 :礼物的最大值
- T48 :最长不含重复字符的子字符串
- T49 :丑数
- T50 :第一个只出现一次的字符
- T51 : 数组中的逆序对
- T52 :两个链表的第一个公共节点
- T53 - I. 在排序数组中查找数字 I
- T53 - I I . 0~n-1中缺失的数字
- T54 : 二叉搜索树的第k大节点
- T55 : 二叉树的深度
- T55 -||:平衡二叉树
- T56 -I: 数组中数字出现的次数
- T56-|| :数组中数字出现的次数 II
- T57:和为s的两个数字
- T57-||:和为s的连续正数序列
- T58-|| :左旋转字符串
- T59-|:滑动窗口的最大值
- T59-|| : 队列的最大值
- T60 :n个骰子的点数
- T61: 扑克牌中的顺子
- T62:圆圈中最后剩下的数字(约瑟夫环)
- T63 :股票的最大利润
- T64:求1+2+…+n
- T65:不用加减乘除做加法
- T66: 构建乘积数组
- T67:把字符串转换成整数
- T68-| :二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
- T68-||:二叉树的最近公共祖先
LeetCode刷题 码 码 不停蹄
T3:数组中重复的数字
- 题目:


把数放到该放的位置去
- 代码:
class Solution {
public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) {
int len = nums.length;
if(len == 0){return -1;}
for(int i =0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(nums[i]<0 || nums[i]>=len){
return -1;
}
while(nums[i] != i){
if(nums[i] == nums[nums[i]]){return nums[i];}
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[temp];
nums[temp] = temp;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
T3-2:不修改数组找出重复的数字
对于一个整数范围L~ R,如果在这个范围内的整数的数量超过R-L+1,那么此范围内的整数中必然有整数会出现多次【重复】。因此选定范围1-n/2,并记录输入数组中在此范围内的元素的数量,若数量大于n/2,则在此整数范围内必然有整数在数组中出现了多次,否则在范围(n/2)+1~n内必然有整数在数组中出现多次。对确定出现重复整数的范围再进行前面的划分和【计数】操作,直到找到重复的数字。
代码:
class Solution {
//l和r只是表示数的范围,并不是数组的指针和下标,每次用于统计在这个范围内的数量
public int duplicateInArray(int[] nums) {
int l = 1;//数字范围是1~n
int r = nums.length-1;
while(l<r){
int count = 0;
int mid = l + r >> 1;
for(int num : nums){//统计在左半边[1,l]数的个数
if(num<=mid && num>=l) count++;
}
if(count>mid-l+1) r=mid;//左半边重复
else l = mid+1;//右半边重复
}
return r;
}
}
T4:二维数组中的查找
- 题目:

T5:替换空格
- 题目:

T6:从尾到头打印链表
- 题目:

-牛客上返回ArrayList:用栈的先进后出思想
T7:重建二叉树
- 题目:

class Solution {
public HashMap<Integer,Integer> IndexMap;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
int len = preorder.length;
IndexMap = new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
IndexMap.put(inorder[i],i);
}
return mybuildTree(preorder,inorder,0,len-1,0,len-1);
}
public TreeNode mybuildTree(int[] preorder,int[] inorder,int preorder_left,int preorder_right,int inorder_left,int inorder_right){//前序左边界、右边界、中序左边界、右边界
if(preorder_left>preorder_right){
return null;//出界,表示此树已经遍历完
}
int pre_root_index = preorder_left;//当前 前序根节点位置,即第一个节点
int in_root_index = IndexMap.get(preorder[pre_root_index]);//根据上面找到的根节点查找其在当前中序中的位置
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[pre_root_index]);//定义当前根节点
int len_in_left = in_root_index-inorder_left; //在中序中找到当前左子树的结点个数
// 递归地构造左子树,并连接到根节点
// 先序遍历中「从 左边界+1 开始的 size_left_subtree」个元素就对应了中序遍历中「从 左边界 开始到 根节点定位-1」的元素
root.left = mybuildTree(preorder,inorder,preorder_left+1,preorder_left+len_in_left,inorder_left,in_root_index-1);
// 递归地构造右子树,并连接到根节点
// 先序遍历中「从 左边界+1+左子树节点数目 开始到 右边界」的元素就对应了中序遍历中「从 根节点定位+1 到 右边界」的元素
root.right = mybuildTree(preorder,inorder,preorder_left+len_in_left+1,preorder_right,in_root_index+1,inorder_right);
return root;
}
}
?? T8:二叉树的下一个节点
- 题目:

这里的pNode.next 指的是指向父节点的指针,而不是下一个节点

T9: 用两个栈实现队列
- 题目:

- 代码:
class CQueue {
private Stack<Integer> stackPush;//加入只从stackPush栈加入
private Stack<Integer> stackPop;//删除只从stackPop栈弹出
public CQueue() {
stackPush = new Stack<>();
stackPop = new Stack<>();
}
public void appendTail(int value) {
stackPush.push(value);
pushTopop();//只有pop栈为空才执行
}
public int deleteHead() {
if(stackPop.isEmpty() && stackPush.isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
pushTopop();
return stackPop.pop();
}
public void pushTopop(){
if(stackPop.isEmpty()){//只有pop栈为空才执行
while(!stackPush.isEmpty()){//要倒就全倒过去
stackPop.push(stackPush.pop());
}
}
}
}
T10 - |:斐波那契数列
- 题目:

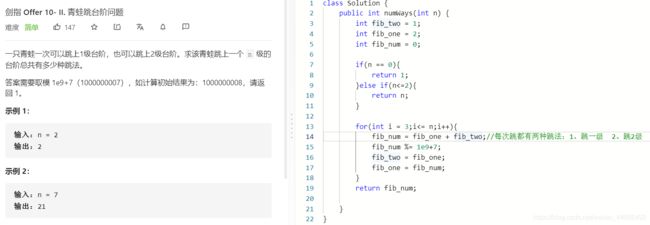
T10 - ||:青蛙跳台
- 题目:

T10 - |||:矩形覆盖
- 题目:

- 代码:
public class Solution {
public int rectCover(int n) {
int fib_two = 1;
int fib_one = 2;
int fib_N = 0;
if(n<=2){
return n;
}
for(int i = 3;i<=n;i++){
fib_N = fib_one+fib_two;
fib_two = fib_one;
fib_one = fib_N;
}
return fib_N;
}
}
T11 :旋转数组的最小数字(有、无重复)
- 题目:

- 思路:




- 代码
此代码为数组含有重复数字,若没有重复数字,则直接去掉最后的else即可
class Solution {
public int findMin(int[] arr) {
int start = 0;
int end = arr.length-1;
if(arr == null || arr.length == 0) return -1;
if(arr.length == 1) return arr[0];
while(start < end){
int mid = start + (end-start)/2;
if(arr[mid] > arr[end]){
//大于arr[end]说明arr[mid]必定不是最小值 ,因为arr[end]左边的值更小,所以mid+1
start = mid +1;
}else if(arr[mid] < arr[end]){
end = mid;//小于arr[end]说明 arr[mid]可能是最小值 ,所以mid不减1
}else{//arr[end] = arr[mid]
end--;//若arr[mid]在最小值右边,则end左移即可
//若arr[mid]在最小值左边,end左移即可
}
}
return arr[start];
}
}
T12:矩阵中的路径
- 题目:
class Solution {
public boolean exist(char[][] arr, String word) {
char[] words = word.toCharArray();
if(arr == null || arr.length == 0){
return false;
}
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<arr[0].length;j++){
if(hasPath(arr,words,i, j, 0)) return true;//从words第0个元素开始
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean hasPath(char[][] arr, char[] words, int i, int j, int word_k){
if(i>=arr.length || i<0 ||j<0 ||j>=arr[0].length || arr[i][j]!=words[word_k]) {
return false;
//1)行或列越界2)当前矩阵元素与目标字符不同3)当前元素已访问过,其中(3)可合并至(2),因为访问过即为'\0',必!=words[word_k]
}
if(word_k == words.length-1) return true;//到达字符串末尾,说明都找到了
arr[i][j] = '\0';
//朝当前元素的 上、下、左、右 四个方向开启下层递归
boolean res = hasPath(arr,words,i+1,j,word_k+1) || hasPath(arr,words,i-1,j,word_k+1)
|| hasPath(arr,words,i,j+1,word_k+1) || hasPath(arr,words,i,j-1,word_k+1);
arr[i][j] = words[word_k]; //当一直搜索至字符串最后一个元素后,开始回溯返回,依次把置空的元素恢复
return res;//返回布尔量 res ,代表是否搜索到目标字符串
}
}
T13 :机器人的运动范围
- 题目:

- 思路:


- 代码:
class Solution {
int m,n,k;
boolean[][] isVisted;
public int movingCount(int m, int n, int k) {
this.m = m; this.n = n; this.k = k;
isVisted = new boolean[m][n];
int count = isGoTo(0,0,0,0);//从(0,0)位置开始搜索
return count;
}
public int isGoTo(int i,int j,int sum_i,int sum_j){
if(i>=m || j>=n ||sum_i+sum_j>k || isVisted[i][j] == true){
return 0;
}
isVisted[i][j] = true;
return 1 + isGoTo(i+1,j,sum(i+1),sum_j) + isGoTo(i,j+1,sum_i,sum(j+1));
//因为从(0,0)开始,走的方向只有向下和向上
//返回 当前格子 + 下搜索的个数 + 右搜索的个数
}
public int sum(int x){
int s =0;
while(x!=0){
s += x%10;
x = x/10;
}
return s;
}
}
T14-| :剪绳子


T14-|| :剪绳子
- 题目:
只是比| 多了大数溢出,但是方法完全不同了,两道题没有什么关系

- 代码:
class Solution {
//有价值的因子只有2和3,因为4 = 2+2=2*2分不分都一样了,而5以后的数都需要进一步做分解才更优。而且同样的n,分出3比分出2更优(比如3*3大于2*2*2),所以尽可能分出更多的3就是解法,当分出若干3后,n≤4时,此时n若为2,为3,为4,直接乘就都是最优解了
//所有绳子的长度相等时,乘积最大 2、最优绳长为3,先按3分段,即n=3*a+b,则b可能=0,1,2.
//b=0则直接返回3^a取余; b=1,将一个1+3换成2+2,即返回(3^(a-1)*4)取余; b=2,则返回(3^a*2)取余
public int cuttingRope(int n) {
if(n<2) return 0;
if(n == 2) return 1;
if(n == 3) return 2;
long res = 1;
while(n>4){//n=4 :分为2*2,即res*2*2 = res*4 = res*n对应b=1的情况
res *= 3;
res %= 1000000007;
n -= 3;
}//出来循环有三种情况,分别是n=2、3、4,分别对应b=2、b=0、b=1的情况
return (int)(res * n % 1000000007);
}
}
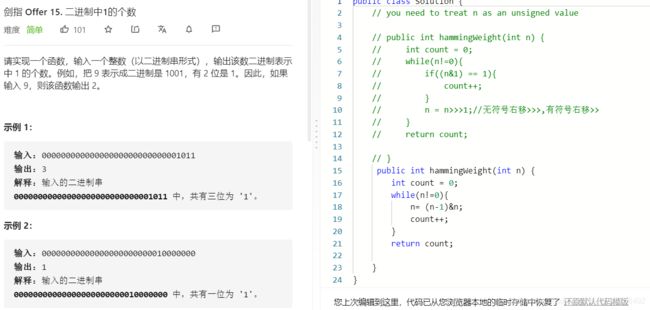
T15: 二进制中1的个数

T16:数值的整数次方(考虑负次、0)
- 题目:


T17:打印从1到最大的n位数(考虑大数溢出)
- 题目:

- 思路(主要考虑大数溢出问题):
用递归回溯解决:0到9,从0开始向下深度搜索,然后回溯到下一个;如n=4,0000>0001>0002…>0009>0010>0011…>9999

- 代码
class Solution {
// 不考虑大数
// public int[] printNumbers(int n) {
// int end = (int)Math.pow(10,n)-1;
// int[] res = new int[end];
// for(int i=0;i
// res[i] = i+1;
// }
// return res;
// }
private List<Integer> list;//list用来存每一次的数
public int[] printNumbers(int n) {
list = new ArrayList();
dfs(n,0,new StringBuilder());//从0开始递归
int[] res = new int[list.size()];
for(int i=0;i<res.length;i++){
res[i] = list.get(i);//res 将list变为数组,因为题目要求输出数组
}
return res;
}
public void dfs(int n,int n_index,StringBuilder num){//n_index 用来计数当前到达的位数
if( n_index == n ){//递归结束条件
//当到达指定位数,结束当前,开始回溯。如:到达000000001后回溯到000000010;到达000018889后,回溯到000019000
while(num.length() != 0 && num.charAt(0) == '0'){//num 用来存放当前的这个数,即只有一个
num.deleteCharAt(0);//字符串将左边多余的0删除;num.length() != 0:保证至少留下最后一个0
}
// 将字符串形式的'数',转化为整数
if(num.length() != 0){
list.add(Integer.valueOf(num.toString()));//list 存放每一个数,累积存
}
return;
}
for(int j=0;j<=9;j++){
num.append(j);
dfs(n,n_index+1,num);//向下深度一遍,n_index计数+1
if(num.length() != 0){
num.deleteCharAt(num.length()-1);
//回溯时,把上一次的最后一个数删除,否则会加入下一次中
//否则输入 1,正确结果是[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9],
//不删的话是[1,12,123,1234,12345,123456,1234567,12345678,123456789]
}
}
}
}
T18 -| :删除链表的节点
- 题目:
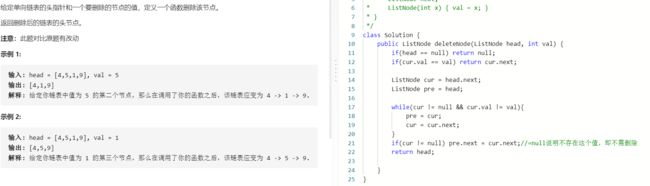
T18 -||:删除链表的重复节点
- 题目:

?T19 :正则表达式的匹配
- 题目:
- 代码:
class Solution {
public boolean isMatch(String s, String p) {
int slen = s.length();
int plen = p.length();
boolean[][] dp = new boolean[slen+1][plen+1];
for(int i=0;i<=slen;i++){//[0,slen]
for(int j =0;j<=plen;j++){//[0,plen]
//分成1、空正则和 2、非空正则两种
if(j==0){//1、空正则
dp[i][j] = i==0 ;//只有i=0且j=0 才匹配,其他都为false
}else{// 2、非空正则
//非空正则分为两种情况 2.1、当前正则串字符是非* 和 2.2、是*
if(p.charAt(j-1) != '*' ){ // 2.1、非*
if(i>0 && (s.charAt(i-1) == p.charAt(j-1) || p.charAt(j-1) == '.')){
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1];
}
}else{// 2.2、*
//碰到 * 了,分为看和不看两种情况
if(j>=2){//不看,即当前s字符不等于p*字符前的那个字符,直接砍掉p的*和*前字符
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j-2];
}
//看,即当前s的字符等于p*字符前的那个字符
if(i>=1 && j>=2 &&
(s.charAt(i-1) == p.charAt(j-2) || p.charAt(j-2) == '.')){
dp[i][j] |= dp[i-1][j];//注意或非:考虑到上面的情况,或上不看的结果
}
}
}
}
}
return dp[slen][plen];
}
}
T20 :表示数值的字符串
- 题目:

class Solution {
public boolean isNumber(String s) {
boolean hasNum= false,hasDot= false,hasE= false,hasSign = false;
int index=0;
int n = s.length();
while(index<n && s.charAt(index) == ' ') index++;
while(index<n){
while(index<n && s.charAt(index)>='0' && s.charAt(index)<='9'){
index++;
hasNum = true;
}
if(index == n) break;
char c = s.charAt(index);
if(c == 'e' || c =='E' ){
if(hasE || !hasNum) return false;
hasE = true;
hasNum = false;hasDot = false;hasSign = false;
//开始遍历e后的新数字,其他状态都清空。
//如:0e,hasNum不清空的话,会输出true。 但 0e ×
}else if(c == '+' || c == '-'){
if(hasNum || hasSign || hasDot) return false;
hasSign = true;
}else if(c == '.'){
if(hasDot || hasE) return false;//.前没数字也可以。如:.1 √
hasDot = true;
}else if(c == ' '){
break;//如果字符之间有空格 则跳出本次循环,使得最终的index不能和n相等
}else{//表示是其他非法字符
return false;
}
index++;
}
while(index<n && s.charAt(index) == ' '){
index++;
}
return hasNum && index == n;
}
}
T21 :调整数组顺序使奇数放在偶数前面
- 题目:

- 思路:

T22 :链表中倒数k个节点
- 题目:
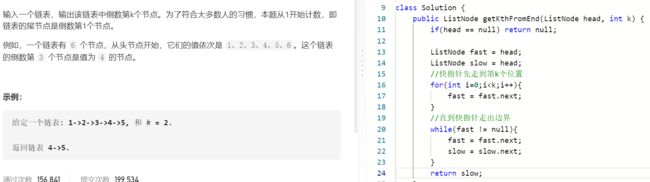
- 思路:
双指针法(避免计算链表长度):
1、慢指针指向头节点,快指针走到第k个节点,此时两节点差k个距离
2、快慢指针同时走,当快指针走出边界,慢指针刚好走到倒数第k个。因为他俩一直相差k个距离

-添加边界:k大于链表长度
T24 :反转链表
- 题目:

- 思路:

T25 :合并两个排序的链表
- 题目:

- 思路:

T26 :树的子结构
- 题目:

- 思路:


T27 :二叉树的镜像
- 题目:
- 思路:
1、递归:从树的“右下子树”开始,交换左右节点,然后依次向上再向左循环进行
class Solution {//递归
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return null;
TreeNode tmp = root.left;
root.left = mirrorTree(root.right);
root.right = mirrorTree(tmp);
return root;
}
}
2、辅助栈:先交换左子树的左右节点,然后再交换右子树的左右节点

class Solution {//辅助栈
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return null;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.add(root);//先加入根节点
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
//当前节点出栈(理论上是上一轮中后入栈的右节点,但上一轮又交换了左右节点,所以出栈的是上一轮左节点
if(node.left != null) stack.add(node.left);//先加入左节点
if(node.right != null) stack.add(node.right);//次加入右节点
TreeNode tmp = node.left;//交换两节点
node.left = node.right;
node.right = tmp;
}
return root;
}
}
T28 :对称的二叉树
- 题目:
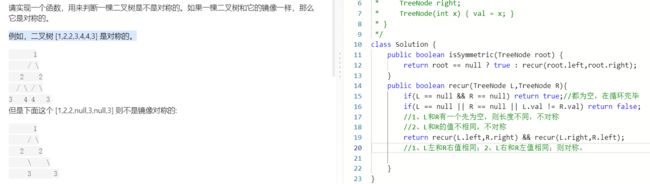
- 思路:

T29 :顺时针打印矩阵
-
题目:
同LeetCodeT54:螺旋矩阵
-
方法
1)、把矩阵按照一圈一圈处理,先顺时针输出最外圈。初始化最外圈左上角和右下角元素坐标。
2)、向内缩减一圈(左上和右下元素坐标向内移动),再次顺时针遍历
3)、直到最后只剩下一列或者一行,则输出该列或者行 -
代码:
class Solution {
public int[] spiralOrder(int[][] arr) {
if(arr.length == 0) return new int[0];
int Lr = 0;
int Lc = 0;
int Rr = arr.length-1;
int Rc = arr[0].length-1;
int[] res = new int[(Rr+1)*(Rc+1)];
int i = 0;
//顺时针遍历一圈
while(Lr<=Rr && Lc<=Rc){
int cur_r = Lr;
int cur_c = Lc;
if(Lr == Rr){//如果只剩下一行
res[i++] = arr[Lr][Lc++];
}else if(Lc == Rc){//如果只剩下一列
res[i++] = arr[Lr++][Lc];
}else{
while(cur_c<Rc){//先从左往右
res[i++] = arr[cur_r][cur_c++];
}
while(cur_r<Rr){//再从上至下
res[i++] = arr[cur_r++][cur_c];
}
while(cur_c>Lc){//再从右向左
res[i++] = arr[cur_r][cur_c--];
}
while(cur_r>Lr){//再从下至上
res[i++] = arr[cur_r--][cur_c];
}
//整体向内移动一圈
Lr++;
Lc++;
Rr--;
Rc--;
}
}
return res;
}
}
T30 :栈最小元素
-
题目:
同LeetCodeT155:最小栈:定义栈的数据结构,请在该类型中实现一个能够得到栈的最小元素的 min 函数在该栈中,调用 min、push 及 pop 的时间复杂度都是 O(1)。
方法
创建两个栈,一个存数据,一个存数据的最小值。
- stackData存储数据,stackMin存储stackData的最小值,且stackMin栈顶永远存储当前stackData栈的最小值
- stackData每压入一个数newNum,stackMin也压入一个数x,x要不等于newNum,要不就是上次压入的值
- 如果stackMin为空,就直接压入newNum;否则比较newNum与当前stackMin栈顶的大小
- 如果newNum小于当前栈顶,x=newNum,否则(说明newNum比上次压入的数还大)继续压入上一次压入的数(即当前栈顶);
- stackData每弹出一个数,同时弹出stackMin的栈顶
class MinStack {
private Stack<Integer> stackData;
private Stack<Integer> stackMin;
/** initialize your data structure here. */
public MinStack() {
this.stackData = new Stack();
this.stackMin = new Stack();
}
public void push(int x) {
stackData.push(x);
if(stackMin.isEmpty() || x< stackMin.peek()){
stackMin.push(x);
}else{
stackMin.push(stackMin.peek());// 如果输入的数大于当前辅助栈顶,则辅助栈压入上一次压入的最小值(栈顶)
}
}
public void pop() {
if(!stackData.isEmpty()){
stackData.pop();
stackMin.pop();
// 因为数据栈和辅助栈同时入栈、出栈,故长度保持一致,你空它也空
}
}
public int top() {
return stackData.peek();
}
public int min() {
return stackMin.peek();
}
}
T31 :栈的压入、弹出序列
- 题目:

- 思路:
用一个辅助栈stack 来模拟栈的压入和弹出过程,如果正确的话这个辅助栈最终会为空


-
如图,在辅助栈先按照给的压栈顺序压入数字1、2、3、4,当压入的数字4和给定的弹出第一个数字4相同时,说明该弹出了,于是从辅助栈中弹出这个相同的数4,然后指向弹出顺序的i后移,指向5,接着按照压入栈顺序压入5,发现和i指向的数相同,说明该弹出来,于是从辅助栈弹出5,i后移,此时stack栈顶是3,和i指向相同,弹出3,i后移指向2,stack此时 栈顶是2,一样则弹出2…弹出1,stack为空,模拟成功
-
代码:
class Solution {
public boolean validateStackSequences(int[] pushed, int[] popped) {
int n = pushed.length;
int m = popped.length;
if(m != n) return false;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack();
int j =0;
for(int i =0;i<n;i++){
stack.push(pushed[i]);//先压入第一个数
while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() == popped[j]){
//辅助栈栈顶数 == 指向的弹出数,说明该模拟弹出了
stack.pop();
j++;//指向弹出顺序栈的索引后移
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
T32 | :从上到下打印二叉树
- 题目:

- 思路:(广度优先遍历 ——>队列)
根据【队列】的【先入先出】:队列加入根节点8;然后弹出8,依次加入8的左右子节点6、10,queue={6,10};队列弹出6,然后加入6的左右子节点5、7,queue={10,5,7};弹出队列的10,加入10的左右节点9、11,queue={5,7,9,11};弹出5、7、9、11,queue={},结束;

- 代码:
class Solution {//BFS--->队列
public int[] levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return new int[0];
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(){{add(root);}};
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
while(!queue.isEmpty()){//队列空跳出循环
TreeNode node = queue.poll();//弹出当前数
res.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null) {//加入当前数的左节点
queue.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){//加入当前数的右节点
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
int[] res_arr = new int[res.size()];
for(int i=0;i<res_arr.length;i++){
res_arr[i] = res.get(i);
}
return res_arr;
}
}
T32 ||:从上到下打印二叉树(每层打印一行)
- 题目:

T32 |||:从上到下打印二叉树(“之”字打印)
- 题目:

- 思路:

T33:二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
- 题目:
- 思路分析
要求:如图,给定的数组若为二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列,则需同时满足 ①后续遍历 + ②二叉搜索树 的条件

- 递归法:找到数组中的左子树、右子树、根节点,判断它们是否满足要求(即其后序遍历是否满足二叉搜索树的定义);然后对这三项分别递归进行判断;如果递归后都满足,则是;否则不是;

- 代码:
class Solution {
public boolean verifyPostorder(int[] postorder) {
return recur(postorder,0,postorder.length-1);
}
public boolean recur(int[] arr, int i , int j){
if(i>=j){
return true;
}
int temp = i;
while(arr[temp]<arr[j]){// 找左子树
temp++;
}
int m = temp;// m表示当前右子树的第一个节点
while(arr[temp]>arr[j]){//找右子树
temp++;
}
return temp == j && recur(arr, i, m-1) && recur(arr,m,j-1);
}
}
T34: 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
- 题目:

- 思路:先序遍历+路径记录


- 代码:
class Solution {
private LinkedList<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<>();//记录符合要求的路径集合
private LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();//记录当前的路径
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int tar) {
recur(root,tar);
return res;
}
public void recur(TreeNode root ,int tar){
if(root == null) return;//回溯条件
path.add(root.val);
tar -= root.val;
if(tar == 0 && root.left == null && root.right == null){
//如果tar=0,且到达叶节点,才说明符合要求
res.add(new LinkedList(path));
// res.add(path)是将path对象加入了res后续path改变时,res中的path对象也变了
}
recur(root.left,tar);
recur(root.right,tar);
path.removeLast();//回溯时,删除当前节点值
}
}
T35:复杂链表的复制
- 题目:
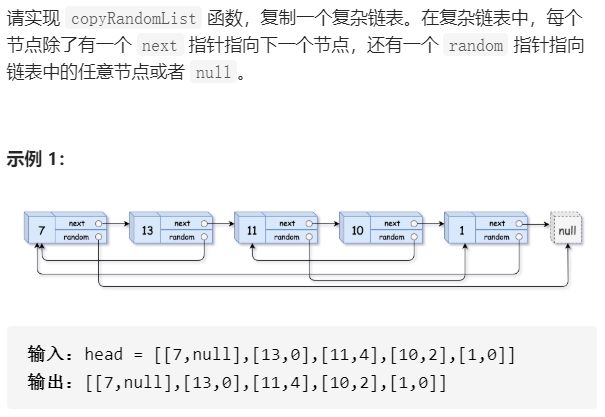
-
和普通链表区别: 普通链表一般只有next指针,此链表多了一个指向随机的指针random;因此不能像一般的一个节点一个节点的复制指、next,因为random指向的数在复制时可能还没定义,比如第二个node的random指向第7个node,此时第7个node还未被定义
-
过程:
1、构建一新链表,用哈希表的dic存原表和新链表对应键值关系,哈希表存的是每一个节点,即包括每个节点的next和random指向
2、构建新链表的引用指向

-
代码:
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
Node cur = head;
if(head == null) return null;
// 复制各节点,并建立 “原节点 -> 新节点” 的 Map 映射
HashMap<Node,Node> dis = new HashMap();
while(cur != null){
dis.put(cur,new Node(cur.val));
cur = cur.next;
}
//构建新节点的 next 和 random 指向
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
//将原链表每个节点的next、random指向,添加到哈希表中对应的这个节点上
dis.get(cur).next = dis.get(cur.next);
dis.get(cur).random = dis.get(cur.random);
cur = cur.next;
}
//返回新链表的头节点
return dis.get(head);
}
}
T36:二叉搜索树与双向循环链表
-
题目:
输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的循环双向链表。要求不能创建任何新的节点,只能调整树中节点指针的指向。 -
思路:
实则为每一个节点重新分配.left、.right指向,实现循环链表的表示



- 代码:
class Solution {
Node pre;
Node head;
public Node treeToDoublyList(Node root) {
if(root == null) return null;
dfs(root);
//建立首尾指向,pre此时指向链表最后一个元素
head.left = pre;
pre.right = head;
return head;
}
public void dfs(Node cur){
if(cur == null) return;//递归中止条件
//开始中序遍历
dfs(cur.left);
if(pre!=null){
pre.right = cur;
}else head = cur;
//pre = null,说明此时cur是链表第一个节点,因为 空.right ×
cur.left = pre;
pre = cur;//pre后移
dfs(cur.right);
}
}
T37:二叉树序列化与反序列化
同LeetCodeT297
- 题目:

- 思路:
序列化:队列层序遍历BFS
反序列化:队列层序遍历BFS

- 代码:
public class Codec {
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {//层序遍历+队列
if(root == null) return "[]";
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder("[");
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(){{add(root);}};
while(!queue.isEmpty()){//以队列的形式进行层序遍历
TreeNode node = queue.poll();//当前节点出队列,下面准备加入该节点的左右节点
if(node != null){
res.append(node.val + ",");
queue.add(node.left);
queue.add(node.right);
}else res.append("null,");//如果为空则用null表示
}
res.deleteCharAt(res.length()-1);//删除最后一个“,”
res.append("]");
return res.toString();
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
if(data.equals("[]")) return null;
String[] vals = data.substring(1,data.length()-1).split(",");//去掉首尾[],以,分割
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(vals[0]));
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(){{add(root);}};
int i = 1;//从vals第2个数开始,因为第一个数肯定是根节点,上面已经加到queue
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();//当前节点出队列,下面准备加入该节点的左右节点
if(!vals[i].equals("null")){
node.left= new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(vals[i]));//加入当前node左节点
queue.add(node.left);
}
i++;//i后移
if(!vals[i].equals("null")){
node.right= new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(vals[i]));//加入当前node右节点
queue.add(node.right);
}
i++;
}
return root;//返回root
}
}
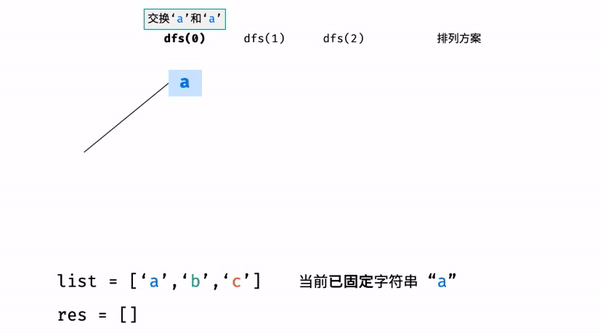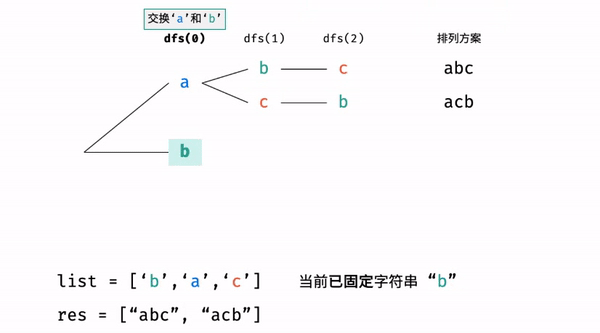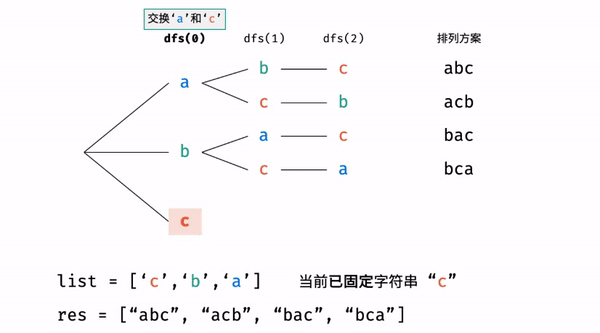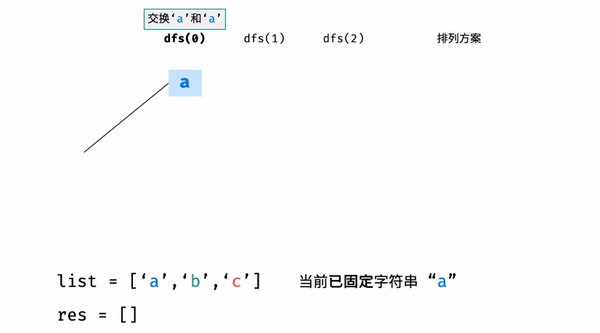
?T38 :字符串的排列
- 题目:
- 思路:



为什么要还原交换?
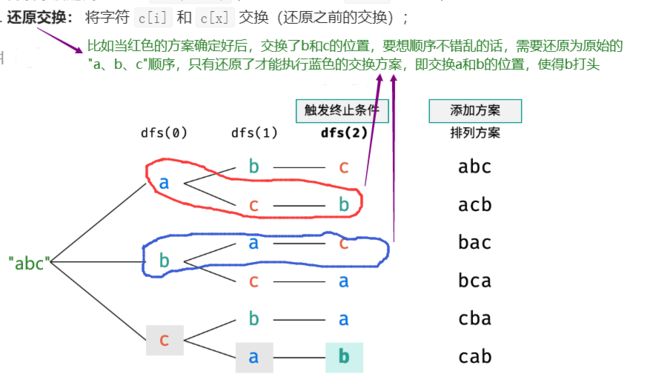
- 举例:
- 代码:
class Solution {
List<String> res = new LinkedList<>();
char[] c;
public String[] permutation(String s) {
c = s.toCharArray();
dfs(0);
return res.toArray(new String[res.size()]);
}
void dfs(int x){
HashSet<Character> set = new HashSet<>();
if(x == (c.length-1)){//一种排列方案已排好
res.add(String.valueOf(c));//res 添加这种方案
}
for(int i=x;i<c.length;i++){//交换当前为x 和x之后的每一位
if(set.contains(c[i])) continue;//包含,说明当前字符在该位置之前排过,则剪枝
set.add(c[i]);//不包含,则排,加入set
swap(i,x);//交换,将c[i]固定在第x位,
dfs(x+1);//开启固定第x+1 位字符
swap(x,i);//恢复交换
//返回时交换回来,这样保证到达第1层的时候,一直都是abc。
//这里捋顺一下,开始一直都是abc,那么第一位置总共就3个交换
//分别是a与a交换,这个就相当于 x = 0, i = 0;
// a与b交换 x = 0, i = 1;
// a与c交换 x = 0, i = 2;
//就相当于上图中一开始的三条路径
//第一个元素(eg. a)固定后,每个引出两条路径,
// b与b交换 x = 1, i = 1;
// b与c交换 x = 1, i = 2;
//所以,结合上图,在每条路径上标注上i的值,就会非常容易好理解了
}
}
void swap(int i,int j){
char tmp = c[i];
c[i] = c[j];
c[j] = tmp;
}
}
T39 :数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
-
题目:
数组中有一个数字出现的次数超过数组长度的一半,请找出这个数字。 -
思路1:数组排序法
数组排序法:将数组 nums 排序,数组中点的元素 一定为众数
//1、数组排序法:排序后的数组的中点必定是“众数”,因为排序后,要想超过一半的数,则这个数的起点肯定落在0~中点的位置,且长度>=一半,则这个数覆盖的长度必定会跨过中点
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
return nums[nums.length/2];
}
- 思路2:摩尔投票法
摩尔投票法: 核心理念为 票数正负抵消 (主要是推论2)。

 如图,i=0,从1开始,假设众数x=nums[i]=1,然后vote=1,i后移=1;2!=1,vote=-1,count=0,结束当前区间,i后移=2;假设众数是x=nums[i]=3,vote=1,i后移=3,2!=3,vote=-1,count=0,结束当前区间,i后移=4;假设当前众数是x=nums[i]=2,vote=1,i后移=5,2=2,vote=1,count=2,i后移=6,5!=2,vote = -1,count = 1;i后移=7,4!=2,vote = -1,count = 0,结束当前区间,i后移=8;假设众数是x=nums[i]=2,vote=1,后面没数了,count=1,找到了是2;
如图,i=0,从1开始,假设众数x=nums[i]=1,然后vote=1,i后移=1;2!=1,vote=-1,count=0,结束当前区间,i后移=2;假设众数是x=nums[i]=3,vote=1,i后移=3,2!=3,vote=-1,count=0,结束当前区间,i后移=4;假设当前众数是x=nums[i]=2,vote=1,i后移=5,2=2,vote=1,count=2,i后移=6,5!=2,vote = -1,count = 1;i后移=7,4!=2,vote = -1,count = 0,结束当前区间,i后移=8;假设众数是x=nums[i]=2,vote=1,后面没数了,count=1,找到了是2;
//推论:若数组的前a个数字票数和=0 ,则数组剩余 (n-a)个数字的票数和一定仍>0即后(n−a)个数字的众数仍是x
//遍历数组每一个数,假设当前这个数是众数,然后计票数+1,后面遇到和他相等的数,票数+1,遇到不等的数-1,直到票数=0,则当区间可去掉,因为后面区间的众数仍为x,则从下一个数开始循环上述操作。
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
int count = 0;//票数总和
int vote = 0;//投票数:+1、-1
int res = 0;//假设众数
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(count == 0 ) res =nums[i];//如果遇到票数和=0,从后面区间重新循环计数
vote = res == nums[i]? +1 : -1;//相等则投+1,否则-1
count += vote;
}
return res;
}
}
T40 :最小的k个数
同LeetCodeT215: 数组中的第K个最大元素
-
题目:
输入整数数组 arr ,找出其中最小的 k 个数。例如,输入4、5、1、6、2、7、3、8这8个数字,则最小的4个数字是1、2、3、4。 -
思路:大根堆(父节点的值大于或等于左、右子节点的值)
用一个大根堆实时维护数组的前 k 小值。首先将前 k个数插入大根堆中,随后从第 k+1 个数开始,如果当前遍历到的数比大根堆的堆顶的数要小,就把堆顶的数弹出,再插入当前遍历到的数。最后将大根堆里的数存入数组返回即可。 -
代码:
class Solution {
//1、排序法去前k
// public int[] getLeastNumbers(int[] arr, int k) {
// Arrays.sort(arr);
// int[] res = new int[k];
// for(int i=0;i
// res[i] = arr[i];
// }
// return res;
// }
//2、大根堆法:利用java中现成的PriorityQueue
// 保持堆的大小为K,然后遍历数组中的数字,遍历的时候做如下判断:
// 1).若目前堆的大小小于K,将当前数字放入堆中。
// 2).否则判断当前数字与大根堆堆顶元素的大小关系,如果当前数字比大根堆堆顶大,这个数直接跳过;
// 反之如果当前数字比大根堆堆顶小,先poll掉堆顶,再将该数字放入堆中。
public int[] getLeastNumbers(int[] arr, int k) {
if(k == 0 || arr.length == 0) return new int[0];
// 默认是小根堆,实现大根堆需要重写一下比较器。
Queue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((v1, v2) -> v2 - v1);
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(queue.size()<k){
queue.offer(arr[i]);
}else if(queue.peek()>arr[i]){//找小于 大根堆 堆顶的
queue.poll();//弹出堆顶(即大根堆最大值
queue.offer(arr[i]);//把这个数按照大根堆规则放入其中
}
}
//返回堆中元素
int[] res = new int[queue.size()];
for(int j=0;j<res.length;j++){
res[j] = queue.poll();
}
return res;
}
}
- LeetCodeT215: 数组中的第K个最大元素
在未排序的数组中找到第 k 个最大的元素。请注意,你需要找的是数组排序后的第 k 个最大的元素,而不是第 k 个不同的元素
class Solution {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
if(k == 0 || nums.length == 0) return -1;
Queue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
//用java现成的PriorityQueue,即小根堆,不用重写比较器
for(int i =0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(queue.size()<k){
queue.offer(nums[i]);
}else if(queue.peek()<nums[i]){//找比堆顶小的
queue.poll();
queue.offer(nums[i]);
}
}
return queue.poll();//返回小根堆堆顶
}
}
T41 :数据流中的中位数
- 题目:

- 思路:双堆法(大根堆+小根堆)
小根堆A存放大的数,堆顶a1为A最小的;
大根堆B存放小的数,堆顶b1为B最大的;
即用两堆实现排序功能,所以两个堆的堆顶数即是中位数位置
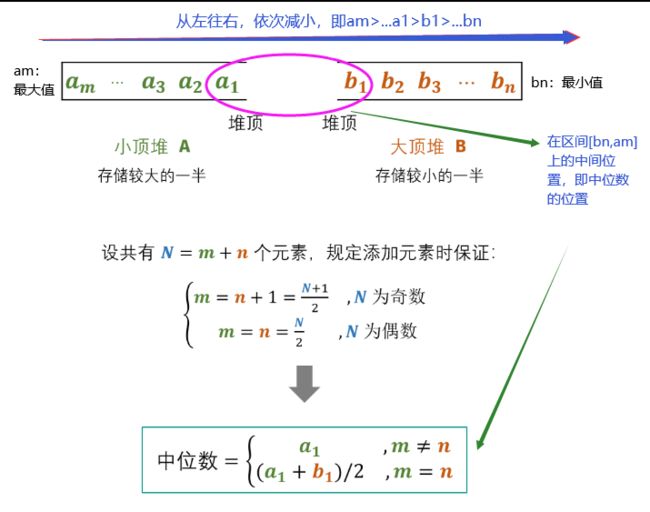

- 代码:
class MedianFinder {
//小根堆存放大的数,堆顶为最小的;大根堆存放小的数,堆顶为最大的;所以两个堆的堆顶数即是中位数位置
Queue<Integer> A;//小根堆,A.size() = m ; N=奇数时,m=n+1,即m>n; N=偶数,m=n
Queue<Integer> B;//大根堆, B.size() = n
/** initialize your data structure here. */
public MedianFinder() {
this.A = new PriorityQueue<>();//PriorityQueue默认小根堆
this.B = new PriorityQueue<>((x,y) -> (y-x));//修改比较器,成为大根堆
}
// 【维持堆数据平衡】,并保证小根堆A的最小值大于或等于大根堆B的最大值
// 即那边的数少,新元素加到那一边;
// 1、N=奇数,m>n, 即A的数多,应该放在B里;
// 放B中时,为了保证A的最小值>=B的最大值,先把数放在A,选出最小值的即A顶,再把A顶放到B
// 2、N=偶数,m=n, 即A和B的数一样多,默认放在A里;
// 放A中时,为了保证A的最小值>=B的最大值,先把数放在B,选出最大值的即B顶,再把B顶放到A
public void addNum(int num) {
if(A.size() != B.size()){//N=奇数,B少,放B
A.add(num);
B.add(A.poll());
}else {//N=偶数,一样多,放A
B.add(num);
A.add(B.poll());
}
}
public double findMedian() {//两个堆顶即是中位数所在的位置,即堆顶的数是整个范围的中间数
return A.size() == B.size() ? (A.peek()+B.peek())/2.0 : A.peek();
//注意:这里是2.0 不能是2,否则数会出错
}
}
T42 :连续子数组的最大和
- 题目:

- 思路:动态规划(从一个数开始蔓延到整个数组)

图解:

- 代码:
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int res = nums[0];
for(int i=1;i<nums.length;i++){
//此时可把nums[i]看作是状态方程dp[],此题为了节省空间,直接在原数组修改
nums[i] += Math.max(nums[i-1],0);
//dp[i] = nums[i] + max(dp[i-1],0);dp[i-1]>0,则加上,否则+0,相当于不加
res = Math.max(res,nums[i]);
}
return res;
}
}
T43 :1~n整数中1出现的次数
-
题目:
输入一个整数 n ,求1~n这n个整数的十进制表示中1出现的次数。例如,输入12,1~12这些整数中包含1 的数字有1、10、11和12,1一共出现了5次。 -
思路:递归
将一个数拆成不同的部分,然后递归再把每一部分拆成不同的部分…
函数f(n):表示1~n这n个整数中1出现的次数。
将n拆分为两部分,最高一位的数字high和其他位的数字last,分别判断情况后将结果相加。 其中最高位是1时比较特殊,需要考虑2部分:
1、最高位包含“1”的个数;
2、除去最高位,其他位含“1”的个数 -
举例:
-
1、最高位是1的情况:

- 2、最高位 >1 的情况:

- 代码:
class Solution {
public int countDigitOne(int n) {
return getnum(n);
}
public int getnum(int n){
if(n<=0) return 0;
String s = String.valueOf(n);
int high = s.charAt(0) - '0';
int pow = (int)Math.pow(10,s.length()-1);//这里需要从double强转为int
int last = n - high*pow;
//其实就是最高位是1时需要考虑2部分:1、最高位包含“1”的个数;2、除去最高位,其他位含“1”的个数
if(high == 1){//最高位是1的情况
return getnum(pow-1) + last + 1 + getnum(last);// [1~999] + 【1000~1234】 + [234]
}else{// 最高位不是1的情况
return pow + high*getnum(pow-1) + getnum(last);
// [1~999] + 【1000~1999】 + [2000~2999] + [3000~3567] + [567]
}
}
}
T44 :数字序列中某一位的数字
如图,按照不同的位数可以分为不同的区间

- 过程:
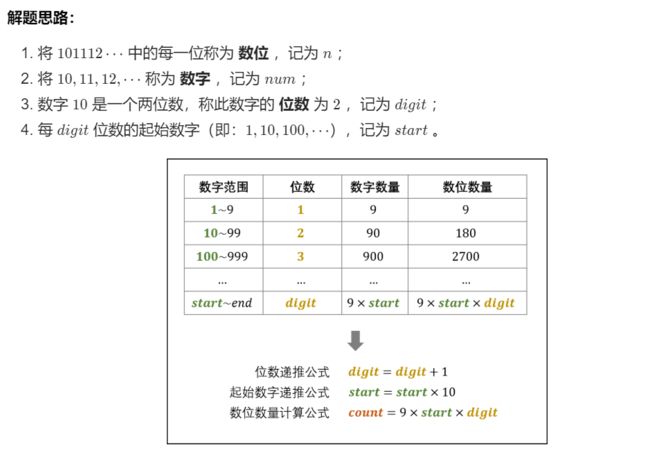

-
第一步:求所在区间的起始数以及位数;
循环执行 nn 减去 一位数、两位数、… 的数位数量 count ,直至 n≤count 时跳出。由于 n 已经减去了一位数、两位数、…、(digit-1) 位数的 数位数量 count,因而此时的 n 是从起始数字 start 开始计数的。 -
第二步:确定所求数位所在的数字
所求数位 在从数字 start 开始的第 [(n - 1) / digit] 个 数字 中( start 为第 0 个数字) -
第三步:确定所求数位在 num的哪一数位
所求数位为数字 num 的第 (n - 1) % digit 位( 数字的首个数位为第 0 位) -
代码:
class Solution {
public int findNthDigit(int n) {
int digit = 1;//当前区间的位数,1、2、3、4......
long start = 1;//当前区间的起始数,0、10、100、1000......
long count = 9;//当前区间的数共占的位数,9、180、2700、36000......count=9*digit*start
//第一步:求所在区间的起始数以及位数
while(n>count){//当n<=count 跳出循环
n -= count;
digit += 1;
start *= 10;
count = 9*digit*start;
}
//第二步:找到区间上的那个数
long num = start + (n-1)/digit;
//第三步:找到这个数的第几位
int i = (n-1)%digit;
return Long.toString(num).charAt(i)-'0';
}
}
T45 :把数组排成最小的数
参考LeetCode179:最大数
- 题目:

class Solution {
public String largestNumber(int[] nums) {
int n =nums.length;
String[] arr = new String[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
arr[i] = String.valueOf(nums[i]);
}
//对数组arr按照拼接后的大小进行降序排列
//通过比较(a+b)和(b+a)的大小,就可以判断出a,b两个字符串谁应该在前面
//eg,[3,30,34]排序后变为[34,3,30];[233,23333]排序后变为[23333,233]
Arrays.sort(arr,(a,b)->{
return (b+a).compareTo(a+b);
});
//如果排序后的第一个元素是0,那后面的元素肯定小于或等于0,则可直接返回0
//但要注意equals和==的区别,前者判断值是否相等,后者判断引用地址是否相等
if(arr[0].equals("0")) return "0";
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
res.append(arr[i]);
}
return res.toString();
}
}
T46 :把数字翻译成字符串
类似LeetCodeT91:解码方法
- 题目:

- 思路:动态规划图解

- 过程

- 举例:
1、实则比较当前的两位数Xi-1Xi是否构成字母(10~25)
2、根据是否构成分为两种情况,选择对应的情况来计算dp[i]。
3、通过字符串切片 s[i - 2:i]获取数字组合 10 x_{i-1} + x_i
4、由于 dp[i]只与 dp[i - 1] 有关,因此可使用两个变量 a, b 分别记录 dp[i], dp[i - 1],两变量交替前进即可。此方法可省去 dp列表使用的 O(N) 的额外空间

- 代码:
class Solution {
public int translateNum(int num) {
String s = String.valueOf(num);
int[] dp = new int[s.length()+1];//dp[]∈[0,num.length],多了一个dp[0]
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = 1;
for(int i=2;i<dp.length;i++){//i从第2个开始
String tmp = s.substring(i-2,i);//[i-2,i)
if(tmp.compareTo("10") >= 0 && tmp.compareTo("25")<=0){
dp[i] = dp[i-1] + dp[i-2];
}else{
dp[i] = dp[i-1];
}
}
return dp[s.length()];//返回最后一个数
}
}
- 优化代码:节省dp[]空间
class Solution {
public int translateNum(int num) {
String s = String.valueOf(num);
int a = 1, b = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= s.length(); i++) {
String tmp = s.substring(i - 2, i);
int c = tmp.compareTo("10") >= 0 && tmp.compareTo("25") <= 0 ? a + b : a;
b = a;
a = c;
}
return a;
}
}
- LeetCodeT91:解码方法
上题中是0-25代表字母,本题是1~26代表字母,且两位数不能以0开头,说明本题中就不能包含“0”,不管是1位数还是2位数;故每次需要判断是否包含0;上题用的if else ;本题是两个if ,因此在dp[i-1]的表示上略有差别

T47 :礼物的最大值
-
题目:
在一个 m*n 的棋盘的每一格都放有一个礼物,每个礼物都有一定的价值(价值大于 0)。你可以从棋盘的左上角开始拿格子里的礼物,并每次向右或者向下移动一格、直到到达棋盘的右下角。给定一个棋盘及其上面的礼物的价值,请计算你最多能拿到多少价值的礼物? -
思路:动态规划



- 代码:
class Solution {
public int maxValue(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(i==0 && j==0) continue;
if(i == 0){//在第一行的情况
grid[i][j] += grid[i][j-1];
}else if(j == 0){//在第一列的情况
grid[i][j] += grid[i-1][j];
}else{//不在第一行也不在第一列
grid[i][j] += Math.max(grid[i][j-1],grid[i-1][j]);
}
}
}
return grid[m-1][n-1];
}
}
- 优化:
当 gridgrid 矩阵很大时, i = 0i=0 或 j = 0j=0 的情况仅占极少数,相当循环每轮都冗余了一次判断。因此,可先初始化矩阵第一行和第一列,再开始遍历递推。
public int maxValue(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
for(int i = 1;i<m;i++){ grid[i][0] += grid[i-1][0];}
for(int j = 1;j<n;j++){ grid[0][j] += grid[0][j-1];}
for(int i=1;i<m;i++){
for(int j=1;j<n;j++){
grid[i][j] += Math.max(grid[i-1][j],grid[i][j-1]);
}
}
return grid[m-1][n-1];
}
T48 :最长不含重复字符的子字符串
同LeetCodeT3
- 题目:

- 思路:动态规划+哈希表


- 哈希表:计算重复字符的索引 i
哈希表: 遍历字符串 s 时,使用哈希表(dic)统计各字符【最后一次】出现的索引位置 - 代码:
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
HashMap<Character,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int res = 0;
int tmp = 0;
int n = s.length();
for(int i = 0; i<n;i++){
//查看在当前字符之前与当前字符重复的字符所在的索引
int index = map.getOrDefault(s.charAt(i),-1);//获取指定key对应的value,没有的话默认为-1
map.put(s.charAt(i),i);
//map每次会更新,即使相同的key,这次的value会覆盖上次的value(index),即实现最近的index
tmp = i-index > tmp ? tmp+1 : i-index; // dp[i] = i-index > dp[i-1] ? dp[i-1]+1 : i-index
//d = i-index:当前字符和其最近重复字符的距离
//如果第i个字符之前没有出现过,index=-1,i-index>tmp,直接在上次的子串加入当前字符,即长度是dp[i] = dp[i-1]+1
//2.1、如果 d>dp[i-1],说明该重复字符位于上次出现在dp[i-1]对应的最长字符串之前,
// 因此不影响本次,直接在上次的子串加入当前字符,即长度是dp[i-1]+1
//2.2、如果 d<=dp[i-1],说明该重复字符位于上次出现在dp[i-1]对应的最长字符串中,
// 所以本次只能从该重复字符位置开始计算到当前字符,即长度是i-index
res = Math.max(res,tmp);
}
return res;
}
}
T49 :丑数
同LeetCodeT264
- 题目:

- 思路:三指针(动态规划)

T50 :第一个只出现一次的字符
- 题目:
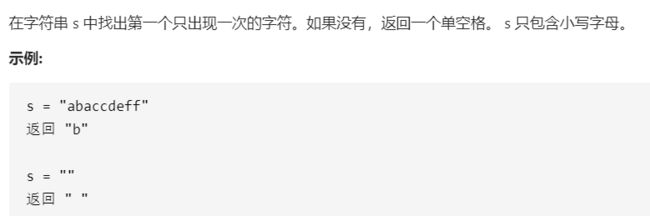
- 思路:使用哈希表存储字符和出现的次数
对字符串进行两次遍历。
第一次遍历,使用哈希映射统计出字符串中每个字符出现的次数。
第二次遍历,只要遍历到了一个只出现一次的字符,就返回该字符,否则在遍历结束后返回空格。 - 代码:
用到HashMap中的getOrDefault(key,v )函数:获取指定key的value,不存在则返回 v
class Solution {
public char firstUniqChar(String s) {
HashMap<Character,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
map.put(s.charAt(i),map.getOrDefault(s.charAt(i),0)+1);//map的键存字符,值存这个字符出现的次数
}
for(int j =0;j<s.length();j++){
if(map.get(s.charAt(j)) == 1) return s.charAt(j);
//字符串从前往后遍历,当在map中该字符的次数是1是,说明只出现1此,同时也是第一个出现的
}
return ' ';
}
}
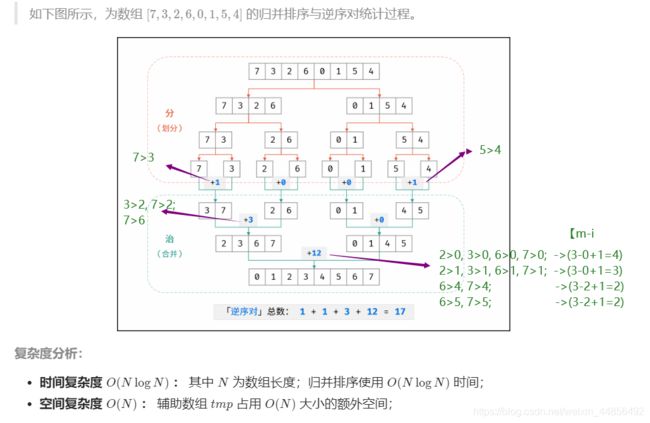
T51 : 数组中的逆序对
![]()
- 举例:
- 代码:
class Solution {
int count;
public int reversePairs(int[] nums) {
this.count = 0;
merge(nums,0,nums.length-1);
return count;
}
public void merge(int[] nums,int left, int right){
int mid = left + ((right-left)>>2);
if(left>=right) return ;
else{
merge(nums,left,mid);
merge(nums,mid+1,right);
mergeSort(nums,left,mid,right);
}
}
public int mergeSort(int[] nums, int left, int mid, int right){
int[] tmp = new int[right-left+1];
int index =0;
int i = left;
int j = mid+1;
while(i<=mid && j<=right){
if(nums[i] <= nums[j]){
tmp[index++] = nums[i++];
}else{//只有左边大于右边的才是逆序对,才统计个数
count += (mid-i+1);//加括号
tmp[index++] = nums[j++];
}
}
while(i<=mid){//当右边数组已经遍历完,把左边剩余的数移入数组
tmp[index++] = nums[i++];
}
while(j<=right){//当左边数组已经遍历完,把右边剩余的数移入数组
tmp[index++] = nums[j++];
}
//把新数组的数覆盖nums数组,
//其实就是把当前的nums进行排序,供下一次和其他的数组归并和计数count
for(int k =0;k<tmp.length;k++){
nums[k+left] = tmp[k];
}
return count;
}
}
T52 :两个链表的第一个公共节点
- 题目:
输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null. 在返回结果后,两个链表仍须保持原有的结构。可假定整个链表结构中没有循环。程序尽量满足 O(n) 时间复杂度,且仅用 O(1) 内存

- 思路:双指针
两个链表长度分别为L1+C、L2+C, C为公共部分的长度: node1走了L1+C步后,回到node2的起点走L2步;node2走了L2+C步后,回到node1起点走L1步。当两者都走到L1+L2+C,即相遇之时

- 代码:
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode node1 = headA;
ListNode node2 = headB;
while(node1 != node2){
node1 = node1!= null ? node1.next : headB;//这里判断node1!= null 而不是 node1.next != null
node2 = node2!= null ? node2.next : headA;
//假如两个链表没有公共节点,就把NULL当作它们的公共节点,所以两个判断是X!=NULL而不是X.next!=NULL
}
return node1;
}
}
T53 - I. 在排序数组中查找数字 I
- 题目:

- 思路:二分法查找
因为数组有序,所以考虑用二分法查找右边界;如下图所示,由于数组 nums 中元素都为整数,因此可以分别二分查找 【target】 和 【target - 1】的 右边界,将两结果相减并返回即可。
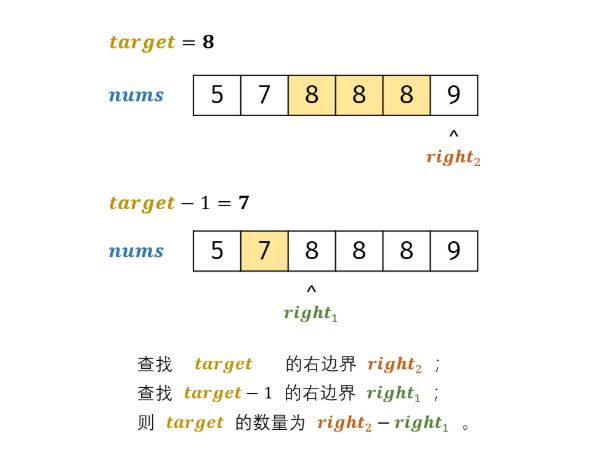 将二分查找右边界 right的代码 封装至函数 helper();本质上看, helper() 函数旨在查找数字 tar在数组 nums中的 插入点 ,且若数组中存在值相同的元素,则插入到这些元素的右边。
将二分查找右边界 right的代码 封装至函数 helper();本质上看, helper() 函数旨在查找数字 tar在数组 nums中的 插入点 ,且若数组中存在值相同的元素,则插入到这些元素的右边。
- 代码:
class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
return helper(nums,target) - helper(nums,target-1);
}
public int helper(int[] nums, int target){
int i =0 ; int j = nums.length-1;
while(i<=j){//i,j是定位右边界的区间,即在[i,j]内找右边界,当i>j时,找到右边界了
int mid = (i+j)/2;
if(nums[mid] <= target){
//这里是<=,包含不存在target的情况;当nums[mid] <= target,说明右边界还在nums[mid]的右边
i = mid+1;
}else j = mid-1;//当nums[mid] > target,说明右边界在nums[mid]的左边
//就是不存在target,最后返回target-1后面的元素,其实就是target-1的右边界,两者做差=0
}
return i;//右边界找到了,i
}
}
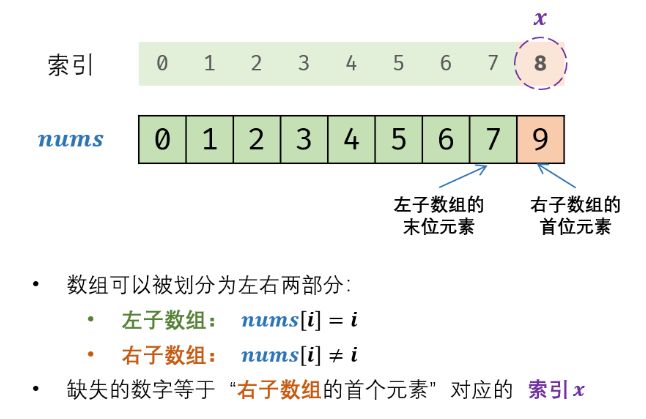
T53 - I I . 0~n-1中缺失的数字
- 题目:

- 思路:二分法查找
因为数组有序,故想到二分法;按照题意,如果没有缺失数的话,每个数和其索引值相同;用二分法查找定位到不相等的那个数,返回它的索引,即使缺失的数
T54 : 二叉搜索树的第k大节点
- 题目:

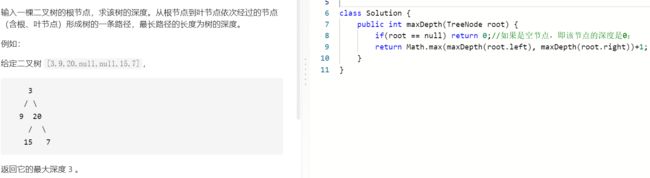
T55 : 二叉树的深度


- 举例:

T55 -||:平衡二叉树
- 题目:

- 思路:后序遍历+剪枝

T56 -I: 数组中数字出现的次数
- 题目:

- 思路:位运算、异或
1、问题简化:整型数组 nums 里除【 一个】 数字之外,其他数字都出现了两次

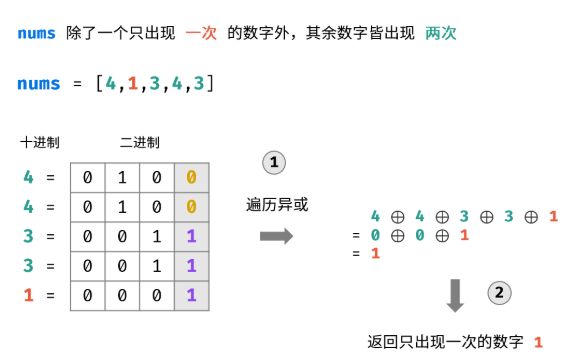
2、本题:nums 里除【 两个】 数字之外,其他数字都出现了两次
- 方法:假设这两个数字是x和y,于是把nums分成两个子数组,一个子数组包含x,一个包含y,然后分别对这两个子数组按照上述方式异或,即可分别得到x、y,然后返回x,y.
例如:nums=[a,a,b,b,c,c,x,e,e,y,y] ----->nums1=[a,a,b,b,x]; nums2= [c,c,e,e,y];
遍历异或nums1 得到a⊕a⊕b⊕b⊕x=x; 遍历异或nums2 得到c⊕c⊕e⊕e⊕y=y - 重点步骤 1:怎样对数组nums进行分组?
因为x和y不相同,即在它们的二进制表示中,至少有一个二进制位是不相同的,即这个二进制位上必定一个是0,另一个是1,本题中只要找到任意一个m位即可。假设这一位是m,m ∈{0,1},然后根据这一位把数组nums分成两份,即二进制m位是0的分为一组,m是1的分为一组 - 重点步骤 2:怎样求得x、y在二进制表示中不相等的二进制位m?——>循环与
让(x⊕y)后从右往左的每一位依次都和1进行“与”操作,如果x和y不相同,即x和y在二进制中对应位的数不同,一个是1,一个是0,异或⊕以后这个不相同的位肯定是1,然后1再和1 “与&”得1;反之如果这一位上x和y相同,异或后是0,再与“1”后是0;从右往左,依次和1与,即0001、0010、0100、1000,循环与,直到找到不同的位m。 - 整体流程:


- 举例:

- 代码:
class Solution {
public int[] singleNumbers(int[] nums) {
int m =1;//不相等的二进制位,从右边第一位开始,即0001
int x =0;//x 存在于nums1 子数组
int y= 0;//y 存在于nums2 子数组
int n=0;//记录整个数组一起异或后的结果,即x⊕y的结果
//1、遍历异或得到n=x⊕y
for(int num : nums){
n ^= num;//^:java中的异或运算符,依次⊕数组的每一个数,最终得到x⊕y
}
//2、循环左移,计算m
while((n & m) == 0 ){
m<<=1;//m循环左移,即0001、0010、0100、1000.。。最终找到x和y第一个(从要往左)不相等二进制位
}
//3、分组,每组分别异或
for(int num:nums){
if((num & m)== 0) x^=num;//把数组中每个数中的m二进制位是0的分为一组nums1;然后对nums1异或得到x
//这里在for循环遍历时执行异或:x^=num,相当于对nums1的每个数轮流异或,下面的nums2同理
else y^=num;//把数组中每个数中的m二进制位是1的分为一组nums2;然后对nums2异或得到y
}
return new int[]{x,y};
}
}
T56-|| :数组中数字出现的次数 II

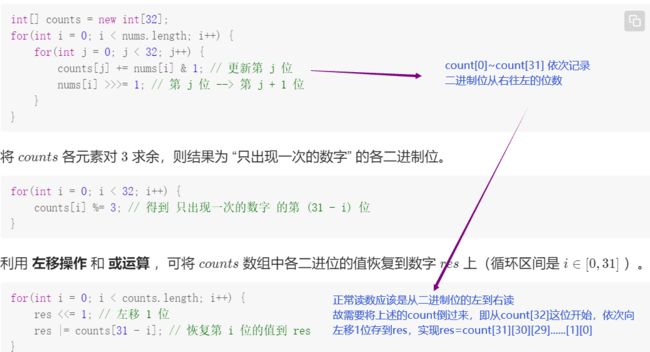 其中左移和或运算作用:将count[0]~[32] 倒过来
其中左移和或运算作用:将count[0]~[32] 倒过来
eg:count= 10100011 –>res=00000001->00000011->00000110->00001100->00011000->00110001->01100010-> 11000101
- 代码:
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int[] count = new int[32];//初始化count数组,存每个数的32个二进制位上的1的个数
//1、计算数组中所有数在每一个二进制位上1的计数
for(int num : nums){
for(int i =0;i<count.length;i++){
count[i] += (num & 1);
//count先对第一个数num的每一位进行 与“1”,然后对第二个数num每一位进行 与“1”,
//并和上一次的count结果相加,最终实现每一位的1的统计
num >>>= 1;//num 右移,结合上述num & 1操作,实现num的每一位与1与操作;
//num从右边第一位开始右移,直到左边第一位到达最右边,count[0]~[32]依次记录num从右往左的二进制位
}
}
//2、每个二进制位对m求余,m为题中每个数重复的次数
int res=0; int m =3;
for(int j=0;j<count.length;j++){
res<<=1;
res |= count[31-j]%m;
//|:或运算;eg count=10100011-->res=00000001->00000011->00000110->00001100->00011000->00110001->01100010->11000101
//每个二进制位对m求余,count[0]~[32]记录num从右往左的二进制位,需要倒回来
}
return res;
}
}
T57:和为s的两个数字
T57-||:和为s的连续正数序列
- 题目:

- 思路:滑动窗口(双指针)

- 举例:
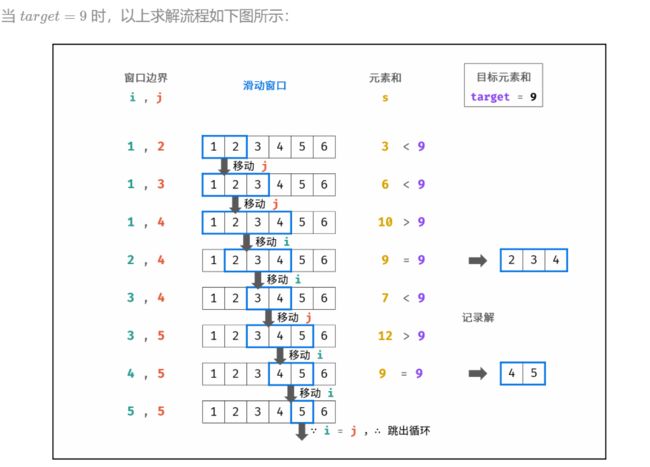
- 代码:
class Solution {
public int[][] findContinuousSequence(int target) {
int i =1;//初始化左边界的数是1
int j =2;//初始化右边界的数是2
int s = 3;//初始化区间[i,j]的和是1+2=3
List<int[]> res = new ArrayList<>();
while(i<j){//当i=j时退出循环;∵连续区间和=target,∴区间元素最多到target/2,即j<=target/2,i和j一直往右走,一直在增大,直到i=j=target/2时,就退出
if(s == target){
int[] ans = new int[j-i+1];//若区间数和=target,则返回这个区间的数组
for(int k = i;k<=j;k++){//k∈[i,j]
ans[k-i] = k;//∵k从i开始,∴k-i表示当前第几个的索引;
//∵是正整数序列,且i从1开始,∴当前索引位置的数 == 索引值
}
res.add(ans);
}
if(s<target){//如果
j++;//先扩大
s +=j;//再调整区间和
}else{//res>=target;
//>时,说明区间和大了,需要减小,即从左边开始去掉一位小的数;
//=时,添加当前区间之后,需要左边界右移一位,即遍历后面的情况; 故>和=都需要左边界右移
s -=i;//先去掉左边的数
i++;//指针右移
}
}
return res.toArray(new int[0][]);//list转为array
}
}
T58-|| :左旋转字符串
- 题目:

- 思路:
参考LeetCode189:旋转数组

- 代码
class Solution {
public String reverseLeftWords(String s, int n) {
if(s == null) return null;
int len = s.length();
if(n%len == 0) return s;
char[] words = s.toCharArray();
reverse(words,0,len-1);//先全反转
reverse(words,0,len-1-n);// 前边反转
reverse(words,len-n,len-1);//后边反转
return new String(words);
}
public void reverse(char[] arr ,int start, int end){
while(start<end){
char temp = arr[end];
arr[end--] = arr[start];
arr[start++] = temp;
}
}
}
- 其他解法


T59-|:滑动窗口的最大值
- 题目:

- 思路:单调队列
用deque的头部存储当前窗口的最大值,在窗口移动时,窗口左边会移除一位,右边会添加一位;假设窗口区间为 [i, j],当窗口向前移动一格,则区间变为 [i+1,j+1],即添加了 nums[j + 1]],删除了 nums[i]。
如何保证queue的头部一直保存当前窗口的最大值?有下面2个规则:
重点步骤1:每轮窗口滑动移除了元素 nums[i - 1]时,需将 deque内的对应元素一起删除。
重点步骤2:每轮窗口滑动添加了元素 nums[j + 1]时,需将 deque内所有 < nums[j + 1] 的元素删除。
i∈[1−k,n−k] ,j∈[0,n−1]

class Solution {
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] res = new int[n-k+1];//依次存储每个窗口的最大值
Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList<>();//头部存储当前窗口最大值
if(n == 0 || k==0){
return new int[0];
}
for(int j =0,i=1-k;j<n;i++,j++){//i∈[1−k,n−k] ,j∈[0,n−1]
if(i>0 && deque.peekFirst() == nums[i-1]) deque.removeFirst();
//形成窗口后,当窗口左边移除的数=deque头部
while(!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peekLast()<nums[j]) deque.removeLast();
//删除queue中<窗口右边添加的数
deque.addLast(nums[j]); //此时的j是移动后的,即j+1
if(i>=0) res[i] = deque.peekFirst();
//记录窗口最大值,当形成窗口时,j=0时直接执行这一步,即res[0]作为初始化的deque头部
}
return res;
}
}
T59-|| : 队列的最大值
- 题目:

- 思路:双端队列
最直观的想法是 维护一个最大值变量 ,在元素入队时更新此变量即可;但当最大值出队后,并无法确定下一个 次最大值 ,因此不可行。于是引入双端队列queue:构建一个递减列表来保存队列所有递减的元素 ,递减链表随着入队和出队操作实时更新,这样队列最大元素就始终对应递减列表的首元素。

- 过程:

- 举例:
感谢博主腐烂的橘子的完美动态图
1、辅助队列deque出队时从左端出;入队时,队中小于入队元素的从右端出;
2、辅助队列 deque 队首元素就是队列的最大值。
- 代码:
class MaxQueue {
Queue<Integer> queue;//单队列,模拟给定的队列
Deque<Integer> deque;//双队列,头部存储当前队列最大值
public MaxQueue() {
queue = new LinkedList<>();
deque = new LinkedList<>();
}
public int max_value() {
return deque.isEmpty()? -1 : deque.peekFirst();
}
public void push_back(int value) {
queue.offer(value);//入队queue
while(!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peekLast()<value) deque.pollLast();//deque朝【右】弹出
deque.offerLast(value);//deque 入队value
}
public int pop_front() {
if(queue.isEmpty()) return -1;
if(queue.peek().equals(deque.peekFirst())) deque.pollFirst();//这里用equals(),不能用 ==
//若queue弹出的数和deque首部数相同,则朝【左】弹出deque首部数
return queue.poll();
}
}
/**
* Your MaxQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MaxQueue obj = new MaxQueue();
* int param_1 = obj.max_value();
* obj.push_back(value);
* int param_3 = obj.pop_front();
*/
T60 :n个骰子的点数
- 题目:

- 原理:
给定 n 个骰子,有:
1、每个骰子摇到 1 至 6 的概率相等,都为1/6;
2、将每个骰子的点数看作独立情况,共有 6n种「点数组合。
3、n 个骰子「点数和」的范围为 [n, 6n],数量为 6n - n + 1 ==5n+1 种。(点数和最小情况,即n个骰子都是1,和为1n,最大情况是都是6,和为6n)

-
思路:动态规划
1、设输入 n个骰子的解(即概率列表)为 f(n) ,其中「点数和」 x 的概率为 f(n,x) 。
2、由于新增骰子的点数只可能为 1 至 6 ,因此概率f(n−1,x) 仅与 f(n,x+1) , f(n, x + 2), … , f(n,x+6) 相关。因而,遍历 f(n−1) 中各点数和的概率,并将其相加至f(n) 中所有相关项,即可完成f(n−1) 至 f(n) 的递推。
3、将 f(i) 记为动态规划列表形式 dp[i]; -
代码:
class Solution {
public double[] dicesProbability(int n) {
double[] dp = new double[6];//初始化dp
Arrays.fill(dp,1.0/6.0);//dp=[1/6,1/6,1/6,1/6,1/6,1/6],即只有一个骰子时的各点数和概率
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){//假设骰子总数是i时
double[] tmp = new double[5*i+1];
//当前所有点数和对应的概率;i个骰子的点数和区间[i*1,i*6],共6i-i+1=5i+1个
for(int j=0;j<dp.length;j++){//当前i个骰子时,dp.length为上一次(i-1)的dp[]长度
//拿i-1个骰子的点数之和数组的第j个值,它所影响的是i个骰子时的temp[j+k]的值
for(int k=0;k<6;k++){
tmp[j+k] += dp[j] *1.0/6.0;
//这里记得是加上dp数组值与1/6的乘积,1/6是第i个骰子投出某个值的概率
}
}
dp = tmp;//i个骰子的点数之和全都算出来后,要将tmp数组移交给dp数组,
//dp数组代表i个骰子时的可能出现的点数之和的概率;用于计算i+1个骰子时的点数之和的概率
}
return dp;
}
}
T61: 扑克牌中的顺子
- 题目:

- 思路:集合 Set + 遍历

- 代码:
class Solution {
public boolean isStraight(int[] nums) {
Set<Integer> repeat = new HashSet<>();
int max = 0, min = 14;
for(int num : nums) {
if(num == 0) continue; // 跳过大小王
max = Math.max(max, num); // 最大牌
min = Math.min(min, num); // 最小牌
if(repeat.contains(num)) return false; // 若有重复,提前返回 false
repeat.add(num); // 添加此牌至 Set
}
return max - min < 5; // 最大牌 - 最小牌 < 5 则可构成顺子
}
}
- 方法二:排序 + 遍历
1、先对数组执行排序。
2、判别重复: 排序数组中的相同元素位置相邻,因此可通过遍历数组,判断 nums[i] = nums[i + 1] 是否成立来判重。
3、获取最大 / 最小的牌: 排序后,数组末位元素 nums[4]为最大牌;元素 nums[joker]为最小牌,其中 jokerj为大小王的数量。
class Solution {
public boolean isStraight(int[] nums) {
int joker = 0;
Arrays.sort(nums); // 数组排序
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
if(nums[i] == 0) joker++; // 统计大小王数量
else if(nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) return false; // 若有重复,提前返回 false
}
return nums[4] - nums[joker] < 5; // 最大牌 - 最小牌 < 5 则可构成顺子
}
}
T62:圆圈中最后剩下的数字(约瑟夫环)
- 题目:

- 思路:
最后只剩下一个元素,假设这个最后存活的元素为 num, 这个元素最终的的下标一定是0 (因为最后只剩这一个元素),所以如果我们可以推出上一轮次中这个num的下标,然后根据上一轮num的下标推断出上上一轮num的下标,直到推断出元素个数为n的那一轮num的下标,那我们就可以根据这个下标获取到最终的元素了。推断过程如下:
1、首先最后一轮中num的下标一定是0, 这个是已知的。
2、那上一轮是有两个元素,此轮中 num 的下标为 (0 + m)%n = (0+3)%2 = 1; 说明这一轮删除之前num的下标为1;
3、再上一轮有3个元素,此轮中 num 的下标为 (1+3)%3 = 1;说明这一轮某元素被删除之前num的下标为1;
4、再上一轮有4个元素,此轮中 num 的下标为 (1+3)%4 = 0;说明这一轮某元素被删除之前num的下标为0;
5、再上一轮有5个元素,此轮中 num 的下标为 (0+3)%5 = 3;说明这一轮某元素被删除之前num的下标为3;
…
因为我们要删除的序列为0 ~ n-1(【原始】数组的每个数和其索引值相同), 所以最终求得下标其实就是求得了最终的结果。比如当n 为5的时候,num的【初始】下标为3,所以num就是3,也就是说从0-n-1的序列中, 经过n-1轮的淘汰,3这个元素最终存活下来了,也是最终的结果。
总结一下推导公式:(此轮中num下标 + m) % 上轮元素个数 = 上轮num的下标

- 代码:
class Solution {
public int lastRemaining(int n, int m) {
int ans = 0;//最后一轮中只剩一个数,也就是只有一个索引,即0
for(int i = 2;i<=n;i++){
//倒数第二轮中有2个数,因此i从2开始,直到i=n,回到原始数组,即还没开始删除
ans = (ans + m) % i;//用这一轮的索引反推上一轮的索引
}
return ans;
}
}
T63 :股票的最大利润
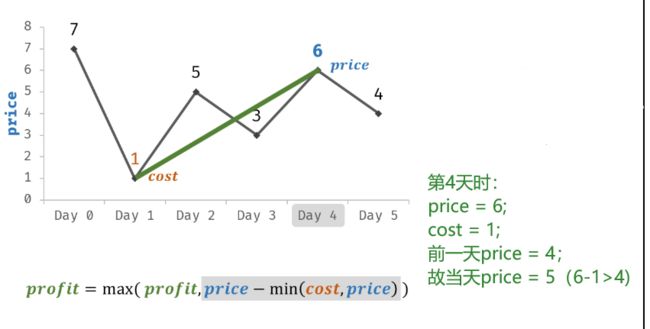
- 代码:
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int cost = Integer.MAX_VALUE;//记录有史以来最低的价格
int profit = 0;//初始化利润为0
for(int price : prices){
cost = Math.min(price,cost);//比较当前价格和历史的最低价格
profit = Math.max(profit,price-cost);//比较前一日的最大利润,和当日可获得的最大利润
}
return profit;
}
}
T64:求1+2+…+n
class Solution {
public int sumNums(int n) {
boolean flag = n>1 && (n += sumNums(n-1))>0;
//只有n>1,才会执行后面的递归;否则flag=false,return n;
return n;
}
}
T65:不用加减乘除做加法
-
题目:
写一个函数,求两个整数之和,要求在函数体内不得使用 “+”、“-”、“*”、“/” 四则运算符号。 -
循环终止条件:进位c=0;
本题原理是利用位运算计算两个数,如求5+7,先通过位运算转换为10+2(进位+无进位和),再转换为4+8(进位+无进位和),再转换为0+12(进位+无进位和),此时仅为c=0,直接输出无进位和,即12;

- 代码:
class Solution {
public int add(int a, int b) {
//存储进位
while(b != 0){// 当进位为 0 时跳出
int c = (a&b)<<1;//存储进位,这里记得加括号,不然先执行左移
a = a^b;//无进位和 赋给a
b = c;
}
return a;
}
}
T66: 构建乘积数组
- 题目:

- 思路:
如下图红框等式,计算B[i]可分解为两部分,
1)先计算左边的乘积和,即 A[0]*A[1]…*A[i-1]
2)再计算右边的乘积和,即 A[i+1]*A[i+2]…*A[n-1]
3)把1)2)结果相乘,即 A[0] *…A[i-1] * A[i+1]…*A[n-1]
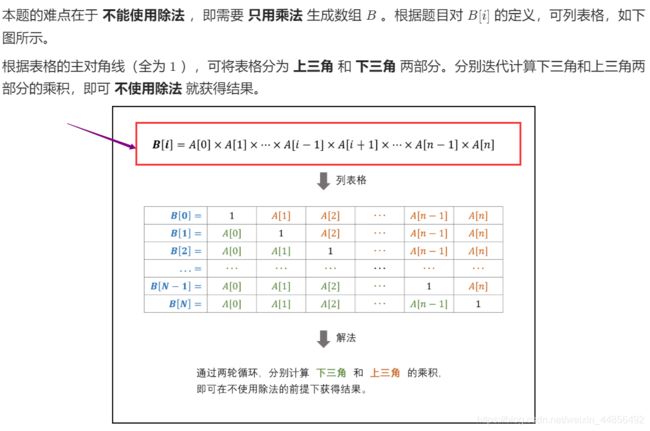

- 代码:
class Solution {
public int[] constructArr(int[] a) {
int n = a.length;
if(n==0) return new int[0];
int[] b = new int[n];
b[0] = 1;
int tmp =1;
for(int i=1;i<b.length;i++){
b[i] = b[i-1]*a[i-1];//左边的乘积和,即a[0]*a[1]...*a[i-1]
}
for(int i = b.length-2;i>=0;i--){
//从倒数第2个开始,
//即先算a[n-2]*a[n-1],再算a[n-3]*a[n-2]*a[n-1],再a[n-4]*a[n-3]*a[n-2]*a[n-1]
tmp *= a[i+1];//右边的乘积和,即a[i+1]*a[i+2]...*a[n-1]
b[i] *= tmp;//让左左边 * 右边,即a[0]*...*a[i-1] * a[i+1]*...*a[n-1]
}
return b;
}
}
T67:把字符串转换成整数
类似的溢出问题:LeetCodeT7
可解释溢出位 >7 ?
因为本题要求>MAX_VALUE,输出MAX_VALUE;

如果这一轮的结果res溢出了,res会变为其他的小于MAX_VALUE的数,不会报错但是结果发生紊乱,使得在后面的循环中根据这个错误的res一错再错;因此为了避免本轮结果溢出,用上一轮的拼接结果res和这一轮的数字联合比较本轮拼接是否溢出

代码:
class Solution {
public int strToInt(String str) {
char[] num = str.trim().toCharArray(); //trim()函数移除字符串两侧的空白字符或其他预定义字符
int n = num.length;
if(n == 0) return 0;
int res = 0;//记录当前转换后的数字
int sign = 1;//记录第一位的符号:-:-1;+:+1
int binary = Integer.MAX_VALUE/10;
//如果当前数已经超过MAX_VALUE,那么他就会溢出报错,而我们是要判断当期数是否溢出,所以将当前数拆为倒数一位和其余各位
int i=1;
if(num[0]=='-') sign = -1;//sign=-1时,第一位是负号,第二位才是数字,所以从i=1开始
else if(num[0] != '+') i=0;//若是+,不用改变sign和i。因为sign和i初始化为1,
//但是是其他字符时需要i=0,即从第一个开始判断
for(int j=i;j<num.length;j++){
if(num[j]>'9' || num[j]<'0') break;
if(res>binary || res==binary && num[j]>'7') return sign == 1 ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : Integer.MIN_VALUE;
res = 10*res + (num[j]-'0');
}
return sign*res;//sign=1返回res,sign=-1,返回-res
}
}
T68-| :二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
while(root != null){
if(root.val>p.val && root.val>q.val){//p,q都在root的左子树
root = root.left;
}else if(root.val<p.val && root.val<q.val){//p,q都在root的右子树
root = root.right;
}else break;//p,q分别在root的作用两侧,直接跳出
}
return root;
}
}
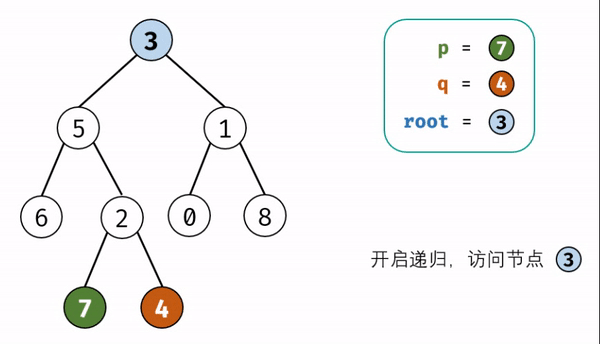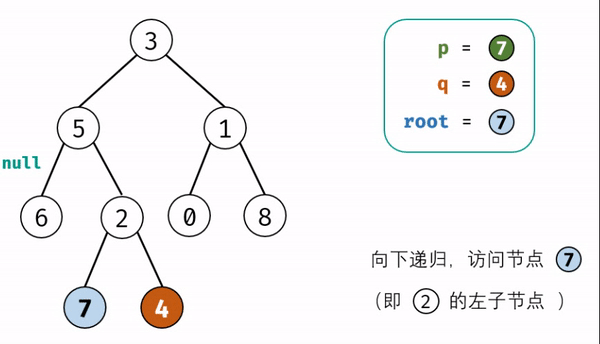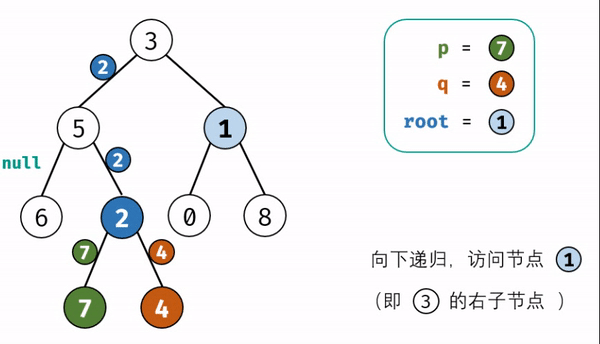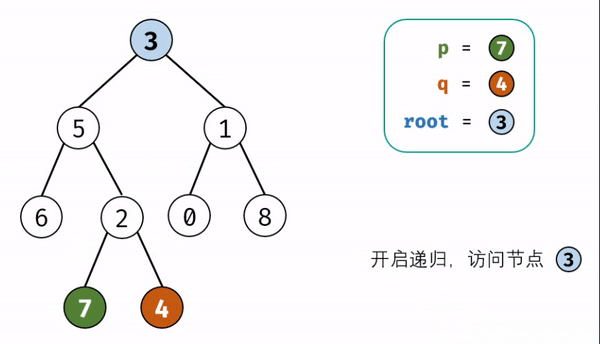
T68-||:二叉树的最近公共祖先
-
思路:先序遍历
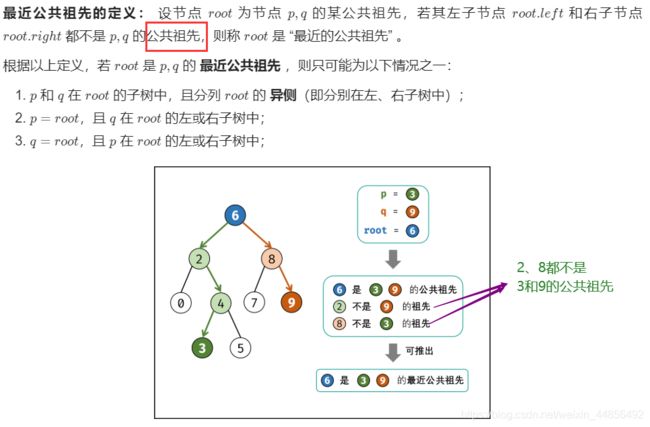
本题和上题的区别:本题是二叉树不是二叉搜索树,无法根据节点值的大小判断在左\右子树,因此,考虑通过递归对二叉树进行先序遍历,当遇到节点 p 或 q 时返回。从底至顶回溯,当节点 p, q在节点 root的异侧时,节点 root 即为最近公共祖先,则向上返回 root 。

-
代码:
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if( root ==null || root == p || root == q) return root;// 如果树为空,直接返回null
//如果p和q中有等于当前root的(先序),那么它们的最近公共祖先即为root(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
// 递归遍历左子树,只要在左子树中找到了p或q,则先找到谁就返回谁
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
// 递归遍历右子树,只要在右子树中找到了p或q,则先找到谁就返回谁
if(left == null && right == null) return null;//1、左右子树都为空,说明不存在p、q
if(left == null) return right;//3、如果在左子树中p和q都找不到,则 p和 q一定都在右子树中
if(right == null) return left;//4、如果在右子树中p和q都找不到,则 p和 q一定都在左子树中
return root;//2、当left和right均不为空,说明 p、q节点分别在root异侧, root是最近公共祖先
}
}