阿里巴巴中间件之Seata
一、在了解Seata之前先简单看一下两阶段提交
1.准备阶段
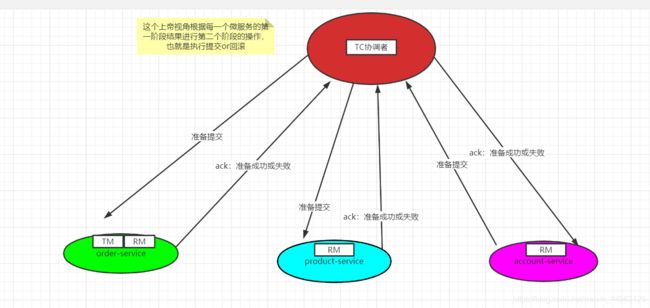
事务协调者(事务管理器)给每个参与者(资源管理器)发送 Prepare消息,每个参与者要么直接返回失败(如权限验证失败),要么在本地执行事务,写本地的redo和undo日志,但不提交。
2.提交阶段

如果协调者收到了参与者的失败消息或者超时,直接给每个参与者发送回滚(Rollback)消息;否则,发送提交(Commit)消息;参与者 根据协调者的指令执行提交或者回滚操作,释放所有事务处理过程中使用 的锁资源。(注意:必须在最后阶段释放锁资源)
TCC会让我们的业务代码进行过多的膨胀,这里不做探讨。
二、Seata简介
Seata提供了AT、TCC、SAGA、XA事务模式,AT是阿里首推的模式,因为AT模式是一个阉割版本,阿里云有上有的GTS。
AT模式很多功能都依赖于SDK的实现,在面向云原生时代,AT 模式方向将是 SDK 的轻量化和标准化,把大部分能力下沉到代理层(Agent 或 Sidecar 的形式),让应用只需要很简单的 SDK 和标准的 SQL 就可以工作。同时AT模式的条件是数据库本身必须支持本地事务,还有表必须定义主键,用来生成前置镜像和后置镜像进行回滚。
以上面的图为例,用户下订单,order-service服务是一个TM,同时它也是一个RM,向seata-server(TC)进行分支事务的注册,同时order-service服务要去调用product-service服务以及account-service服务,被调用的两个服务就是RM,每一个服务都会向Seata-Server注册分支事务,监听每一个服务的事务结果,只要有一个服务异常或者超时,都会对第一个阶段的结果基于前置镜像和后置镜像进行回滚。
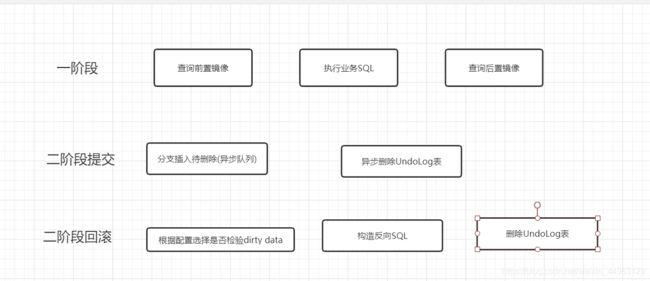
前置镜像,先把执行之前的结果查询出来
SELECT amount FROM account WHERE user_id = 1;
此时假设执行业务sql之前account的值是1000.
执行业务SQL
UPDATE account SET amount = 900 WHERE user_id = 1
后置镜像,把update执行后的结果查询出来
SELECT amount FROM account WHERE user_id = 1;
这时执行完业务sql之后account的值就是900.
三、Seata分布式事务组成部分
-
事务协调者TC:seata的server端,用来保存全局事务、分支事务、全局锁等,决定每个事务参与者的提交与回滚,俗称上帝视角。
-
资源管理器RM:每一个微服务,也就是事务的参与者。
-
事务管理者TM:也是每一个微服务,但是该服务充当带头大哥,决定了全局事务的开启、提交、回滚,凡是该微服务中标有
@GlobalTransaction注解都可以理解为TM,同时它也是一个RM。
四、Seata的demo
1.搭建seata-server端
从github拉取https://github.com/seata/seata/releases,由于Spring Cloud Alibaba我使用的版本是2.2.5.RELEASE,对应的seata客户端依赖是1.3.0,所以我下载的是1.3.0的服务端。下载完解压之后的目录。

进入到解压目录的conf文件夹里面,
 然后编辑
然后编辑registry.conf文件,注册中心我使用Spring Cloud Alibaba的Nacos,所以type就改为nacos,这里是集群模式下的通信进行使用的,当然单机的话你也可以使用file直连的模式。配置的话我使用file模式,type就改为file,对应的文件是跟registry.conf同一个目录下面的file.conf文件。

接下来更改file.conf文件,目前支持三种模式:file、db、redis,这里我使用db模式,同时配置好我们数据库的连接。
 数据库所需要的三张表名我会扔在下面源码的script文件夹里面,也就是
数据库所需要的三张表名我会扔在下面源码的script文件夹里面,也就是seata.sql文件。另外还需要为每个微服务创建数据库对应的业务表以及每个微服务数据库对应的undo_log表。

退出seata服务端的conf目录,进入到bin目录,启动seata
./seata-server.sh -h ip -p port -m db -n 1 >log.out &
- -h:你服务器的ip地址。
- -p:server端的端口号,默认为8091
- -m:全局事务存储模式(file/db/redis)。
- -n:多个server时,用于区分各个节点,避免生成transactionId冲突。
2.微服务代码地址,这里不做过多讲解,有不明白可私聊。https://gogs.tianqingzhao.com/tianqingzhao/seata-demo
五、Seata原理模型

图片地址:https://www.processon.com/view/link/6108ddc3637689310e61f4ed
通过代理数据源拿到数据库连接对象,RM注册到TC,在执行本地事务之前执行前置镜像,也就是执行之前的数据库记录,然后执行业务sql,执行完业务sql之后执行后置镜像,也就是执行完业务sql之后的数据库记录。此时如果有一个分支事务出现异常就进行全局事务的回滚,通过每个微服务下面的unlo_log表的记录进行反向补偿,如果三个分支事务都是正常状态就进行全局提交。需要注意的是Seata默认的AT模式与2PC有一点不同的是:2PC第一阶段只执行不提交,在第二阶段才执行提交,Seata的第一阶段是即执行又提交。
记住seata的几个名词
- 开启全局事务
- 分支事务注册
- 全局事务提交
- 全局事务回滚
六、Seata第一阶段开启全局事务
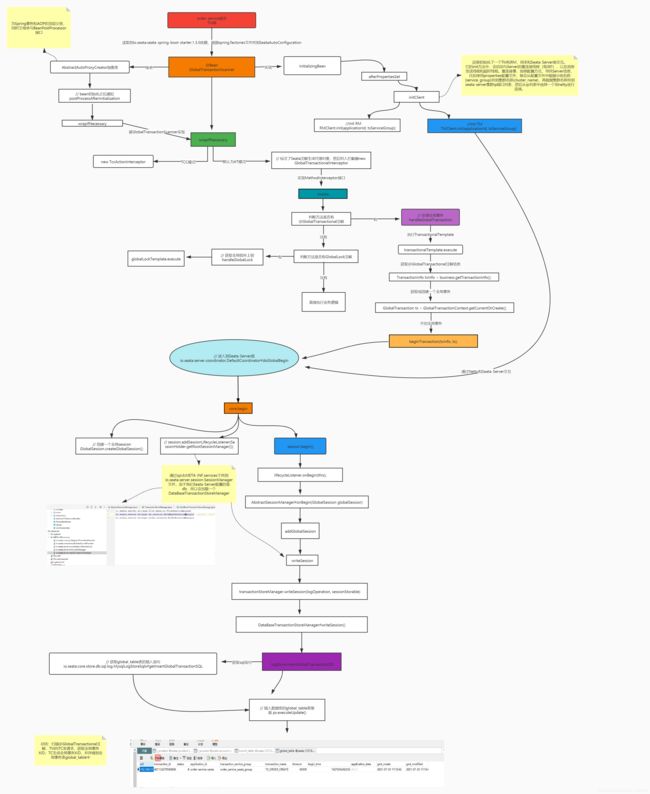
图片地址:https://www.processon.com/view/link/6108de13e0b34d3e35b8e4ef
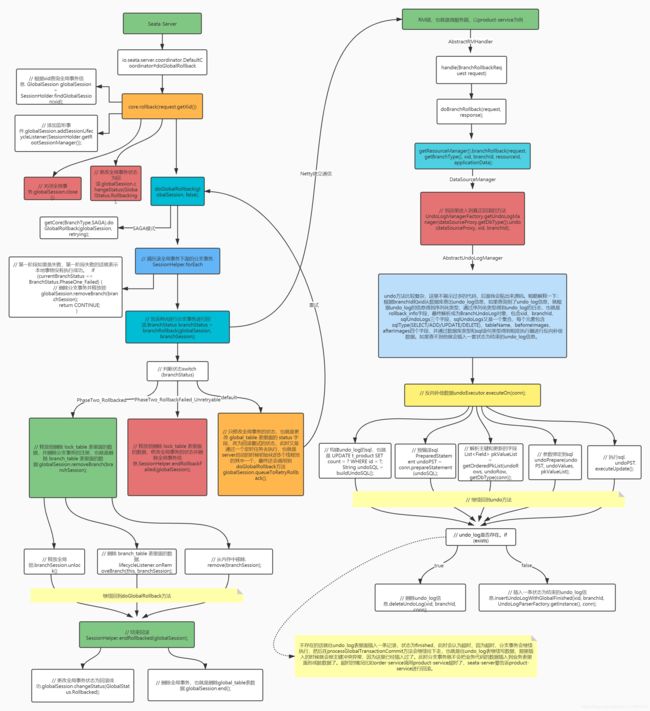
总结:扫描@GlobalTransactional注解,TM向TC通过Netty发送请求,获取全局事务XID;TC生成全局事务XID,并存储到全局事务表global_table中。
七、Seata第一阶段分支事务注册
图片地址:https://www.processon.com/view/link/6108de4be401fd6714ba761d
总结:准备前置镜像;执行目标sql,执行但未提交;准备后置镜像,组装undo_log。向TC注册分支事务,TC端获取全局事务锁,把分支事务信息存储到 branch_table 表,并把全局事务锁信息存储到 lock_table 表中;RM端提交undo_log信息,把前置镜像、后置镜像存储到对应服务下的 undo_log 表中,用于事务回滚;同时RM端提交本地事务。
八、Seata第二阶段全局事务的提交
图片地址:https://www.processon.com/view/link/61079f72e401fd7c4ed48a80
总结:TC先删除对应的lock_table表,并更改全局事务状态为异步提交。根据启动时初始化的异步提交任务去扫描状态为异步提交的全局事务,首先通过Netty向RM发送请求删除undo_log表的记录,RM返回提交成功,并通过同步队列去删除。TC根据RM返回的状态,去删除分支事务,也就是删除branch_table表的数据以及释放锁。最后删除全局事务,也就是删除global_table表的数据。
九、Seata第二阶段全局事务的回滚
图片地址:https://www.processon.com/view/link/6108e656e0b34d3e35b90ed4
总结:TC更改全局状态为回滚,向RM发起回滚数据的请求,RM收到请求进行反向补偿数据,删除undo_log表的信息,并返回回滚成功的状态,然后TC释放分支事务对应的锁资源以及删除分支事务,也就是删除lock_table和branch_table两张表的数据。然后在删除全局事务。
简单看一下 undo 和 executeOn 这两个方法
undo方法:
@Override
public void undo(DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy, String xid, long branchId) throws TransactionException {
Connection conn = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
PreparedStatement selectPST = null;
boolean originalAutoCommit = true;
for (; ; ) {
try {
// 拿到数据库的连接
conn = dataSourceProxy.getPlainConnection();
// The entire undo process should run in a local transaction.
// 设置手动提交
if (originalAutoCommit = conn.getAutoCommit()) {
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
}
// Find UNDO LOG
// 预编译查询语句
selectPST = conn.prepareStatement(SELECT_UNDO_LOG_SQL);
// 设置where条件
selectPST.setLong(1, branchId);
selectPST.setString(2, xid);
rs = selectPST.executeQuery();
boolean exists = false;
while (rs.next()) {
exists = true;
// It is possible that the server repeatedly sends a rollback request to roll back
// the same branch transaction to multiple processes,
// ensuring that only the undo_log in the normal state is processed.
// 查询 undo_log 表的log_status字段的状态
int state = rs.getInt(ClientTableColumnsName.UNDO_LOG_LOG_STATUS);
// 不是正常状态的就不进行回滚
if (!canUndo(state)) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("xid {} branch {}, ignore {} undo_log", xid, branchId, state);
}
return;
}
// 得到context字段的值,也就是系列化的类型,默认为 serializer=jackson
String contextString = rs.getString(ClientTableColumnsName.UNDO_LOG_CONTEXT);
// 处理contextString的值,最终得到的还是 serializer=jackson
Map<String, String> context = parseContext(contextString);
byte[] rollbackInfo = getRollbackInfo(rs);
// 得到序列化的类型为 jackson
String serializer = context == null ? null : context.get(UndoLogConstants.SERIALIZER_KEY);
// 如果为空就是使用默认的,默认的也是 jackson,否则就根据spi去加载对应的解析类型
UndoLogParser parser = serializer == null ? UndoLogParserFactory.getInstance()
: UndoLogParserFactory.getInstance(serializer);
// 解析为 BranchUndoLog 对象,包含xid、branchId、sqlUndoLogs三个字段,
// sqlUndoLogs又是一个集合,每个元素包含sqlType(SELECT/ADD/UPDATE/DELETE)、tableName、befomeImages、afterImages四个字段
BranchUndoLog branchUndoLog = parser.decode(rollbackInfo);
try {
// put serializer name to local
setCurrentSerializer(parser.getName());
List<SQLUndoLog> sqlUndoLogs = branchUndoLog.getSqlUndoLogs();
if (sqlUndoLogs.size() > 1) {
// 用于反转给定list( l )元素的顺序,换句话说,可以说此方法用于从右侧开始更改其元素的顺序。
Collections.reverse(sqlUndoLogs);
}
for (SQLUndoLog sqlUndoLog : sqlUndoLogs) {
TableMeta tableMeta = TableMetaCacheFactory.getTableMetaCache(dataSourceProxy.getDbType()).getTableMeta(
conn, sqlUndoLog.getTableName(), dataSourceProxy.getResourceId());
sqlUndoLog.setTableMeta(tableMeta);
// 通过数据库类型和sql语句的类型得到对应的执行器
AbstractUndoExecutor undoExecutor = UndoExecutorFactory.getUndoExecutor(
dataSourceProxy.getDbType(), sqlUndoLog);
undoExecutor.executeOn(conn);
}
} finally {
// remove serializer name
// 删除序列化类型
removeCurrentSerializer();
}
}
// If undo_log exists, it means that the branch transaction has completed the first phase,
// 如果 undo_log存在,表示分支事务第一阶段已经完成了
// we can directly roll back and clean the undo_log
// 我们可以回滚并且删除 undo_log 表里面的记录
// Otherwise, it indicates that there is an exception in the branch transaction,
// 否则就表示分支事务异常
// causing undo_log not to be written to the database.
// 导致撤销日志不写入数据库。
// For example, the business processing timeout, the global transaction is the initiator rolls back.
// 例如,业务处理超时时,全局事务被启动器回滚。
// To ensure data consistency, we can insert an undo_log with GlobalFinished state
// 为了确保数据一致性,我们可以插入一个GlobalFinished状态的撤消日志,
// to prevent the local transaction of the first phase of other programs from being correctly submitted.
// 以防止其他程序第一阶段的本地事务被正确提交。
// See https://github.com/seata/seata/issues/489
// 这里主要是为了解决一个bug,也就是undo_log不存在的情况,
// 比如客户端向服务端发起分支事务的时候超时了(processGlobalTransactionCommit方法),
// 此时undo_log表就不会存在记录
if (exists) {
deleteUndoLog(xid, branchId, conn);
conn.commit();
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("xid {} branch {}, undo_log deleted with {}", xid, branchId,
State.GlobalFinished.name());
}
} else {
// 不存在的话就往undo_log表里面插入一条记录,状态为finished,此时会认为超时,
// 因为超时,分支事务会继续执行,
// 然后在processGlobalTransactionCommit方法会继续往下走,
// 也就是往undo_log表继续写数据,那里插入的时候就会报主键冲突异常,因为这里已经插入过了。
// 此时分支事务就不会把业务代码的数据插入到业务表里面形成脏数据了。
// 超时的情况比如order-service调用product-service超时了,seata-server要告诉product-service进行回滚。
insertUndoLogWithGlobalFinished(xid, branchId, UndoLogParserFactory.getInstance(), conn);
conn.commit();
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("xid {} branch {}, undo_log added with {}", xid, branchId,
State.GlobalFinished.name());
}
}
return;
} catch (SQLIntegrityConstraintViolationException e) {
// Possible undo_log has been inserted into the database by other processes, retrying rollback undo_log
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("xid {} branch {}, undo_log inserted, retry rollback", xid, branchId);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.rollback();
} catch (SQLException rollbackEx) {
LOGGER.warn("Failed to close JDBC resource while undo ... ", rollbackEx);
}
}
throw new BranchTransactionException(BranchRollbackFailed_Retriable, String
.format("Branch session rollback failed and try again later xid = %s branchId = %s %s", xid,
branchId, e.getMessage()), e);
} finally {
try {
if (rs != null) {
rs.close();
}
if (selectPST != null) {
selectPST.close();
}
if (conn != null) {
if (originalAutoCommit) {
conn.setAutoCommit(true);
}
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException closeEx) {
LOGGER.warn("Failed to close JDBC resource while undo ... ", closeEx);
}
}
}
}
executeOn方法:
public void executeOn(Connection conn) throws SQLException {
if (IS_UNDO_DATA_VALIDATION_ENABLE && !dataValidationAndGoOn(conn)) {
return;
}
try {
// 构建undo_log的sql,也就是 UPDATE t_product SET count = ? WHERE id = ?
String undoSQL = buildUndoSQL();
// 预编译sql
PreparedStatement undoPST = conn.prepareStatement(undoSQL);
// 得到要更新的行数,也就是前置镜像的值,说白了就是更新之前的值
TableRecords undoRows = getUndoRows();
for (Row undoRow : undoRows.getRows()) {
ArrayList<Field> undoValues = new ArrayList<>();
// 解析主键和更新的字段
List<Field> pkValueList = getOrderedPkList(undoRows, undoRow, getDbType(conn));
for (Field field : undoRow.getFields()) {
if (field.getKeyType() != KeyType.PRIMARY_KEY) {
undoValues.add(field);
}
}
// 参数绑定到sql
undoPrepare(undoPST, undoValues, pkValueList);
// 进行反向补偿
undoPST.executeUpdate();
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
if (ex instanceof SQLException) {
throw (SQLException) ex;
} else {
throw new SQLException(ex);
}
}
}
十、浅谈Seata的两个bug
1. bug1
基于file模式的加锁:
io.seata.server.storage.file.session.FileSessionManager#lockAndExecute方法,这里的globalSession对象是每次查询数据库加载出来的,全局事务提交是一个globalSession对象1,分支事务注册式globalSession对象2,两个对象的锁是相互隔离的,所以假设线程1进行全局事务提交的时候并上锁,线程2进行分支事务的注册,在加锁,此时还可以获取到锁资源。
@Override
public <T> T lockAndExecute(GlobalSession globalSession, GlobalSession.LockCallable<T> lockCallable)
throws TransactionException {
globalSession.lock();
try {
return lockCallable.call();
} finally {
globalSession.unlock();
}
}
2.bug2
io.seata.server.coordinator.DefaultCoordinator#doGlobalCommit
io.seata.server.coordinator.DefaultCore#commit
globalSession.closeAndClean();
close();
lifecycleListener.onClose(this);
globalSession.setActive(false);
全局事务提交的时候就行了这么一个操作,就是关闭全局事务,其中禁止分支事务的注册,通过设置 active 字段。
但是回过头去看分支事务的注册的流程:
io.seata.server.coordinator.DefaultCoordinator#doBranchRegister
io.seata.server.coordinator.DefaultCore#branchRegister
io.seata.server.coordinator.AbstractCore#branchRegister
io.seata.server.coordinator.AbstractCore#globalSessionStatusCheck
在 globalSessionStatusCheck 方法进行了检查全局事务的状态,但是要知道分支事务注册的时候,这个全局事务是通过xid实时查询的,会生成一个新的 GlobalSession 对象,但是上面关闭全局事务的时候是设置到内存的,说白了就是两个对象的状态,所以这里的判断是无效的。总体来说和bug1是一样的问题导致的。
if (!globalSession.isActive()) {
throw new GlobalTransactionException(GlobalTransactionNotActive, String.format(
"Could not register branch into global session xid = %s status = %s, cause by globalSession not active",
globalSession.getXid(), globalSession.getStatus()));
}
3.下面用伪代码来模拟一下seata的这两处bug,首先创建 GlobalSession 类,里面有一个内部类 GlobalSessionLock ,也就是锁对象。然后有一个 active 字段,默认值为true。
package com.tqz.seata;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* 全局事务的信息
*
* @autoor tianqingzhao
* @since 2021/7/25 17:40
*/
public class GlobalSession {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(GlobalSession.class);
private GlobalSessionLock globalSessionLock = new GlobalSessionLock();
public boolean isActive() {
return active;
}
public void setActive(boolean active) {
this.active = active;
}
private boolean active = true;
public GlobalSessionLock getGlobalSessionLock() {
return globalSessionLock;
}
public void setGlobalSessionLock(GlobalSessionLock globalSessionLock) {
this.globalSessionLock = globalSessionLock;
}
public void lock() throws InterruptedException {
globalSessionLock.lock();
}
public void unlock() {
globalSessionLock.unlock();
}
private static class GlobalSessionLock {
private Lock globalSessionLock = new ReentrantLock();
public Lock getGlobalSessionLock() {
return globalSessionLock;
}
public void setGlobalSessionLock(Lock globalSessionLock) {
this.globalSessionLock = globalSessionLock;
}
private static final int GLOBAL_SESSION_LOCK_TIME_OUT_MILLS = 2 * 1000;
public void lock() throws InterruptedException {
try {
if (globalSessionLock.tryLock(GLOBAL_SESSION_LOCK_TIME_OUT_MILLS, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
return;
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
logger.error("Interrupted error", e);
}
throw new RuntimeException("锁超时");
}
public void unlock() {
globalSessionLock.unlock();
}
}
}
接下来进行测试,创建并启动两个线程,第一个线程进行全局事务的提交,第二个事务进行分支事务的注册。
package com.tqz.seata;
/**
*
*
* @autoor tianqingzhao
* @since 2021/7/25 17:40
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread commitThread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
commit();
}
});
commitThread.setName("commitThread");
Thread branchRegThread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
branchRegister();
}
});
branchRegThread.setName("branchRegThread");
commitThread.start();
branchRegThread.start();
}
/**
* 提交全局事务
*/
public static void commit() {
// 模拟从数据库查询出来的
GlobalSession globalSession = new GlobalSession();
try {
globalSession.lock();
globalSession.setActive(false);
System.out.println("模拟执行业务方法");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
globalSession.unlock();
}
}
/**
* 注册分支事务
*/
public static void branchRegister() {
// 模拟从数据库拿出来的
GlobalSession globalSession = new GlobalSession();
try {
globalSession.lock();
if(!globalSession.isActive()){
throw new RuntimeException("全局事务关闭 无法注册分支事务");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
globalSession.unlock();
}
}
}
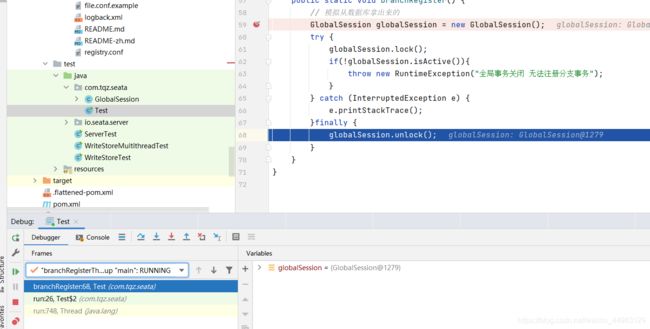
在idea里面使用线程断点进行调试,分别在两个断点处右键,然后选中 Thread。
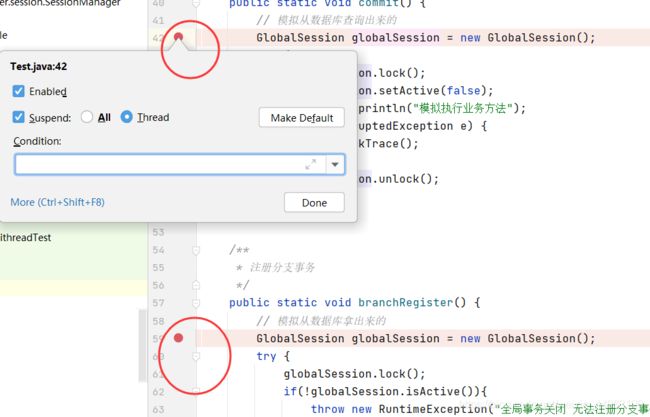
这时候启动main方法,先进入到commitThread,这里我们模拟从数据库查出来了 GlobalSession 对象,然后进行上锁。

再切换回branchRegisterThread,首先第一个bug是基于file模式的加锁,commitThread和branchRegisterThread两个线程是两个对象的锁,所以每个线程都能加锁成功。
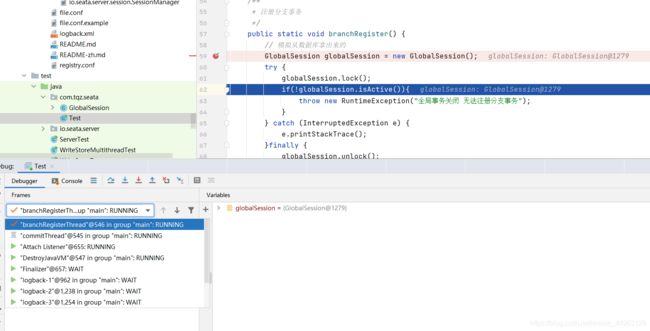
再来看第二个bug,我们再切换成commitThread,然后设置 active 字段为false。

再切换为branchRegisterThread,你commitThread线程的 GlobalSession 对象的 active 状态是在内存中的,管我branchRegisterThread线程的 GlobalSession 对象的 active 状态什么事情,所以这里是判断不住的。印象中这个bug在零点几到目前1.4.x版本也没有进行修复。
十一、分布式事务的BASE理论
BASE理论
- BA:Basically Available(基本可用)
- S:Soft state(软状态)
- E:Eventually consistent(最终一致性)
BASE理论是基于CAP定理演化而来,是对CAP中一致性和可用性权衡的结果。核心思想:即使无法做到强一致性,但每个业务根据自身的特点,采用适当的方式来使系统达到最终一致性,总之要舍弃一个。

分布式事务中同样存在类似的问题。
- SAGA模式满足业务侵入低、性能高。
- Seata的AT模式满足业务侵入低、隔离性强。
- TCC模式满足性能高、隔离性强。
分布式事务一直是业界最大的问题,没有百分之百的解决方案,总之能不用分布式事务尽量不使用!