vuex的实现原理
创建demo
计数器:{{ count }} {{ $store.state.count }}
错误修改
同步修改
异步修改
修改a
修改b
修改c
import {
createStore
} from 'vuex'
export default createStore({
state: {
count: 0
},
getters: {
double (state) {
return state.count * 2
}
},
mutations: {
add (state, payload) {
state.count += payload
}
},
actions: {
asyncAdd ({
commit
}, payload) {
setTimeout(() => {
commit('add', payload)
}, 1000)
}
},
modules: {
aCount: {
namespaced: true,
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
add (state, payload) {
state.count += payload
}
},
modules: {
cCount: {
// namespaced: true,
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
add (state, payload) {
state.count += payload
}
}
}
}
},
bCount: {
namespaced: true,
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
add (state, payload) {
state.count += payload
}
}
}
}
})
// class Store {
// dispatch () {
// console.log(this)
// }
// }
// const { dispatch } = new Store()
// dispatch()
初始化vuex
在store/indexjs和app.vue中,全部换成自己的vuex
import { useStore } from “@/vuex”;
import {createStore} from ‘@/vuex’
在src下添加vuex文件夹,新增index.js,导出两个方法
import { inject } from 'vue'
const storeKey = 'store'
class Store {
constructor (options) {
this.aa = 100
}
install (app, injectKey) {
app.provide(injectKey || storeKey, this)
app.config.globalProperties.$store = this
}
}
export function createStore (options) {
return new Store(options)
}
export function useStore (injectKey = null) {
return inject(injectKey !== null ? injectKey : storeKey)
}
测试功能是否正常
在app.vue中测试{{$store.aa}} 是否输出100
初始化state
把options中的state,挂载到_state上面,使用vue提供的数据响应方法,初始化state
访问 $store._state.data.count,显示0,则说明成功
使用代理,把state代理到_state.data上面
import { inject, reactive } from 'vue'
const storeKey = 'store'
class Store {
constructor (options) {
this._state = reactive({ data: options.state })
}
get state () {
return this._state.data
}
install (app, injectKey) {
app.provide(injectKey || storeKey, this)
app.config.globalProperties.$store = this
}
}
export function createStore (options) {
return new Store(options)
}
export function useStore (injectKey = null) {
return inject(injectKey !== null ? injectKey : storeKey)
}
测试app.vue中的 计数器:{{ count }} {{ $store.state.count }} 是否正常显示
初始化getters
获取options上的getters
取store.getters.double,store.getters必须是一个对象
创建一个新的store.getters
给store.getters做代理,get的时候,取options上的getters方法,传入参数为store.state
import { inject, reactive } from 'vue'
import { forEachValue } from './utils'
const storeKey = 'store'
class Store {
constructor (options) {
const store = this
store._state = reactive({ data: options.state })
// getters
const _getters = options.getters
store.getters = {}
forEachValue(_getters, function (fn, key) {
// ƒ double(state) {
// return state.count * 2;
// }
// 'double'
Object.defineProperty(store.getters, key, {
enumerable: true,
get: () => fn(store.state)
})
})
}
get state () {
return this._state.data
}
install (app, injectKey) {
app.provide(injectKey || storeKey, this)
app.config.globalProperties.$store = this
}
}
export function createStore (options) {
return new Store(options)
}
export function useStore (injectKey = null) {
return inject(injectKey !== null ? injectKey : storeKey)
}
export function forEachValue (obj, fn) {
Object.keys(obj).forEach(key => fn(obj[key], key))
}
测试app.vue ====> double:{{ double }} {{ $store.getters.double }}
初始化mutation和action
在store上挂载_mutations 和_actions
给_mutations 和_actions这两个对象赋值 key ==》 方法
store调用commit和dispatch时候,就是调用_mutations 和_actions上面挂载的方法。
import { inject, reactive } from 'vue'
import { forEachValue } from './utils'
const storeKey = 'store'
class Store {
constructor (options) {
const store = this
store._state = reactive({ data: options.state })
// getters
const _getters = options.getters
store.getters = {}
forEachValue(_getters, function (fn, key) {
// ƒ double(state) {
// return state.count * 2;
// }
// 'double'
Object.defineProperty(store.getters, key, {
enumerable: true,
get: () => fn(store.state)
})
})
// mutations和actions
const _mutations = options.mutations
const _actions = options.actions
store._mutations = Object.create(null)
store._actions = Object.create(null)
forEachValue(_mutations, function (mutation, key) {
// ƒ add(state, payload) {
// state.count += payload;
// }
// 'add'
store._mutations[key] = payload => {
mutation.call(store, store.state, payload)
}
})
forEachValue(_actions, function (action, key) {
// ƒ asyncAdd({
// commit
// }, payload) {
// setTimeout(() => {
// commit('add', payload);
// }, 1000);
// }
// 'asyncAdd'
store._actions[key] = payload => {
action.call(store, store, payload)
}
})
}
get state () {
return this._state.data
}
commit = (type, payload) => {
const store = this
store._mutations[type](payload)
}
dispatch = (type, payload) => {
const store = this
store._actions[type](payload)
}
install (app, injectKey) {
app.provide(injectKey || storeKey, this)
app.config.globalProperties.$store = this
}
}
export function createStore (options) {
return new Store(options)
}
export function useStore (injectKey = null) {
return inject(injectKey !== null ? injectKey : storeKey)
}
测试点击事件,正常则最简单的vuex已经实现
vuex进阶
上面只是实现了vuex的一部分功能,vuex最重要的module功能未实现,action会返回一个promise也没有是实现
如果只是了解原理,上面的demo就够了
重构项目
拆分目录如下
拆分后的store.js
import { storeKey } from './injectKey'
export default class Store {
constructor (options) {
}
install (app, injectKey) {
app.provide(injectKey || storeKey, this)
app.config.globalProperties.$store = this
}
}
初始化moudles
store.js
在store上面挂载_modules,让数据 state 变为树形结构
import { storeKey } from './injectKey'
import ModuleCollection from './module/module-collection'
export default class Store {
constructor (options) {
const store = this
store._modules = new ModuleCollection(options)
}
install (app, injectKey) {
app.provide(injectKey || storeKey, this)
app.config.globalProperties.$store = this
}
}
module/module-collection
创建树形结构,并在_children中挂载modules的子模块
import { forEachValue } from '../utils'
import Module from './module'
export default class ModuleCollection {
constructor (rootModule) {
this.root = null
this.register(rootModule, [])
}
register (rawModule, path) {
// this.root = {
// _raw: rawModule,
// state: rawModule.state,
// _children: {}
// }
const newMoudule = new Module(rawModule)
if (path.length === 0) {
this.root = newMoudule
} else {
// 往前截一位
const parent = path.slice(0, -1).reduce((module, current) => {
return module.getChild(current)
}, this.root)
parent.addChild(path[path.length - 1], newMoudule)
}
if (rawModule.modules) {
forEachValue(rawModule.modules, (rawChildModule, key) => {
console.log(rawChildModule, key)
// {namespaced: true, state: {…}, mutations: {…}, modules: {…}}modules: {cCount: {…}}mutations: {add: ƒ}namespaced: truestate: {count: 0}[[Prototype]]: Object 'aCount'
this.register(rawChildModule, path.concat(key))
})
}
}
}
module.js
生成树的基本结构,并在原型上添加方法getChild ,addChild 来改变实例的_children属性
export default class Module {
constructor (rawModule) {
this._raw = rawModule
this.state = rawModule.state
this._children = {}
}
getChild (key) {
return this._children[key]
}
addChild (key, module) {
this._children[key] = module
}
}
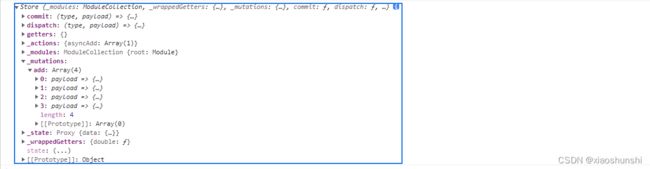
最后挂载到store上的_modules如下图
初始化state
installModule.js
接受四个参数 (store, rootState, path, module)
export function installModule (store, rootState, path, module) {
const isRoot = !path.length
if (!isRoot) {
const parentState = path.slice(0, -1).reduce((state, key) => state[key], rootState)
parentState[path[path.length - 1]] = module.state
}
module.forEachChild((child, key) => {
installModule(store, rootState, path.concat(key), child)
})
}
module.js 添加forEachChild方法
forEachChild (fn) {
forEachValue(this._children, fn)
}
这时store上的state
展示state的数据
这时候,页面还是报错找不到count
添加 resetStoreState(store,state)方法
import { reactive } from 'vue'
export function resetStoreState (store, state) {
store._state = reactive({ data: state })
}
import { storeKey } from './injectKey'
import ModuleCollection from './module/module-collection'
import { installModule } from './installModule'
import { resetStoreState } from './resetStoreState'
export default class Store {
constructor (options) {
const store = this
// 初始化installModule
store._modules = new ModuleCollection(options)
// 初始化state
const state = store._modules.root.state
installModule(store, state, [], store._modules.root)
resetStoreState(store, state)
}
get state () {
return this._state.data
}
install (app, injectKey) {
app.provide(injectKey || storeKey, this)
app.config.globalProperties.$store = this
}
}
页面展示正常,点击事件可用,则说明正常运行
初始化getters
和基础版一样,需要在store上面添加一个_wrappedGetters属性
做代理访问store.getters
store.js
constructor (options) {
const store = this
// 初始化installModule
store._modules = new ModuleCollection(options)
store._wrappedGetters = Object.create(null)
// 初始化state
const state = store._modules.root.state
installModule(store, state, [], store._modules.root)
resetStoreState(store, state)
console.log(store)
}
installModule.js 中初始化getters
function getNestedState(state,path){
return path.reduce((state,key)=>state[key],state)
}
// getters
module.forEachGetter((getter,key)=>{
store._wrappedGetters[key] = ()=>{
return getter(getNestedState(store.state,path))
}
})
module.js 添加方法forEachGetter
让getter挂载到对应的module上
forEachGetter (fn) {
if (this._raw.getters) {
forEachValue(this._raw.getters, fn)
}
}
参照getters,初始化mutation和action
import { storeKey } from './injectKey'
import ModuleCollection from './module/module-collection'
import { installModule } from './installModule'
import { resetStoreState } from './resetStoreState'
export default class Store {
constructor (options) {
const store = this
// 初始化installModule
store._modules = new ModuleCollection(options)
store._wrappedGetters = Object.create(null)
store._mutations = Object.create(null)
store._actions = Object.create(null)
// 初始化state
const state = store._modules.root.state
installModule(store, state, [], store._modules.root)
resetStoreState(store, state)
console.log(store)
}
commit = (type, payload) => {
const entry = this._mutations[type] || []
entry.forEach(handler => handler(payload))
}
dispatch = (type, payload) => {
const entry = this._actions[type] || []
return Promise.all(entry.map(handler => handler(payload)))
}
get state () {
return this._state.data
}
install (app, injectKey) {
app.provide(injectKey || storeKey, this)
app.config.globalProperties.$store = this
}
}
import { isPromise } from './utils'
export function installModule (store, rootState, path, module) {
const isRoot = !path.length
if (!isRoot) {
const parentState = path.slice(0, -1).reduce((state, key) => state[key], rootState)
parentState[path[path.length - 1]] = module.state
}
// getters
module.forEachGetter((getter, key) => {
store._wrappedGetters[key] = () => {
return getter(getNestedState(store.state, path))
}
})
// mutation
module.forEachMoutation((mutation, key) => {
const entry = store._mutations[key] || (store._mutations[key] = [])
entry.push((payload) => {
mutation.call(store, getNestedState(store.state, path), payload)
})
})
// actions
module.forEachAction((action, key) => {
const entry = store._actions[key] || (store._actions[key] = [])
entry.push((payload) => {
const res = action.call(store, store, payload)
if (!isPromise(res)) {
return Promise.resolve(res)
}
return res
})
})
module.forEachChild((child, key) => {
installModule(store, rootState, path.concat(key), child)
})
}
function getNestedState (state, path) {
return path.reduce((state, key) => state[key], state)
}
import { forEachValue } from '../utils'
export default class Module {
constructor (rawModule) {
this._raw = rawModule
this.state = rawModule.state
this._children = {}
}
getChild (key) {
return this._children[key]
}
addChild (key, module) {
this._children[key] = module
}
forEachChild (fn) {
forEachValue(this._children, fn)
}
forEachGetter (fn) {
if (this._raw.getters) {
forEachValue(this._raw.getters, fn)
}
}
forEachMoutation (fn) {
if (this._raw.mutations) {
forEachValue(this._raw.mutations, fn)
}
}
forEachAction (fn) {
if (this._raw.actions) {
forEachValue(this._raw.actions, fn)
}
}
}
import { reactive } from 'vue'
import { forEachValue } from './utils'
export function resetStoreState (store, state) {
store._state = reactive({ data: state })
const wrappedGetters = store._wrappedGetters
store.getters = {}
forEachValue(wrappedGetters, function (getter, key) {
Object.defineProperty(store.getters, key, {
get: () => getter(),
enumerable: true
})
})
}
代码验证 store,页面正常,点击按钮无error,可进行下一步
namespaced的实现
上面的代码,点击后,执行了多个add的方法
这时候需要namespaced对方法的key进行按照path分类
module-collection.js 添加 getNamespaced方法
getNamespaced (path) {
let module = this.root
return path.reduce((namespace, key) => {
module = module.getChild(key)
return namespace + (module.namespaced ? key + '/' : '')
}, '')
}
module.js上面添加 this.namespaced = rawModule.namespaced
在installModule.js中,给每次便利循环的方法添加namespaced
// getters
module.forEachGetter((getter,key)=>{
store._wrappedGetters[namespaced + key] = ()=>{
return getter(getNestedState(store.state,path))
}
})
// mutation
module.forEachMoutation((mutation,key)=>{
const entry = store._mutations[namespaced+key] || (store._mutations[namespaced + key] = [])
entry.push((payload)=>{
mutation.call(store,getNestedState(store.state,path),payload)
})
})
// actions
module.forEachAction((action,key)=>{
const entry = store._actions[namespaced + key] || (store._actions[namespaced + key] = [])
entry.push((payload)=>{
let res = action.call(store,store,payload)
if(!isPromise(res)){
return Promise.resolve(res)
}
return res
})
})