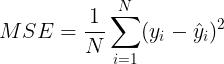机器学习(8)sklearn画决策树(回归树)
目录
一、DecisionTreeRegressor
1、criterion
2、接口
3、交叉验证
二、用sklearn画回归树(基于波士顿房价训练模型)
1、导入库
2、训练模型
3、用Graphviz画回归树
三、回归树对正弦函数上的噪音点降噪
1、导入库
2、生成带噪音点的正弦函数
3、训练模型
4、画plt图
一、DecisionTreeRegressor
sklearn.tree._classes.DecisionTreeRegressor
def __init__(self,
*,
criterion: Any = "squared_error",
splitter: Any = "best",
max_depth: Any = None,
min_samples_split: Any = 2,
min_samples_leaf: Any = 1,
min_weight_fraction_leaf: Any = 0.0,
max_features: Any = None,
random_state: Any = None,
max_leaf_nodes: Any = None,
min_impurity_decrease: Any = 0.0,
ccp_alpha: Any = 0.0) -> None
1、criterion
criterion作为回归树的衡量分枝的指标,也是衡量回归树回归质量的指标,有三种标准:
(1)“mse”:均方误差,父节点和叶子节点之间的均方误差的差额来作为特征选择的标准,这种方法通过叶子节点的的均值来最小化L2损失
(2)“friedman_mse”:费尔德曼均方误差,针对潜在分枝问题改进后的均方误差
(3)“mae”:绝对平均误差,这种方法通过使用叶子节点的中值来最小化L1损失
计算机中默认用负均方误差(neg_mean_squared_error)来进行运算与存储。
2、接口
回归树中的重要接口仍然是apply,fit,score,predict,feature_importance_。
但是score返回的是R^2,即相关系数,而非MSE。
可以通过参数scoring来指定负均方误差返回。
score=cross_val_score(dtg
,boston.data
,boston.target
,cv=10
,scoring='neg_mean_squared_error')3、交叉验证
交叉验证:通过将数据划分为n份,依次使用其中一份作为测试集,其他n-1份作为训练集,多次计算模型的精确性来评估模型的平均准确程度。由于训练集和测试集的划分会存在干扰模型的结果,因此多次进行交叉验证来求出平均值,能提升模型准确率。
二、用sklearn画回归树(基于波士顿房价训练模型)
1、导入库
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston #导入波士顿房价数据集
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score #交叉验证函数
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor #回归树
from sklearn import tree #导入tree2、训练模型
boston=load_boston()
dtg=DecisionTreeRegressor(random_state=0) #criterion默认为MSE
score=cross_val_score(dtg #十次交叉验证
,boston.data
,boston.target
,cv=10
,scoring='neg_mean_squared_error')
print(score) #输出负均方误差3、用Graphviz画回归树
import graphviz #导入graphviz库
feature_names=boston.feature_names #标签使用boston房价特征
data_graph=tree.export_graphviz(dtg.fit(boston.data,boston.target) #第一个参数是训练好的模型,不是回归树类
,feature_names=feature_names
,filled=True
,rounded=True)
graph=graphviz.Source(data_graph)
graph.view()回归树的图太庞大的,不便在此处演示。
三、回归树对正弦函数上的噪音点降噪
1、导入库
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np2、生成带噪音点的正弦函数
rng=np.random.RandomState(1) #随机数种子
x=np.sort(10*rng.rand(80,1),axis=0) #生成0-10之间随机数x取值
y=np.sin(x).ravel() #生成正弦曲线y值
y[::5]+=1*(0.5-rng.rand(16)) #正弦函数上每过五个点生成一个随机噪音,共16个点3、训练模型
regr_1=DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=5) #分别生成深度为5和8的回归树
regr_2=DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=8)
regr_1=regr_1.fit(x,y) #训练模型
regr_2=regr_2.fit(x,y)4、画plt图
x_test=np.arange(0,10,0.01)[:,np.newaxis] #对x_test进行升维,其中':'在的位置为原始维度,np.newaxis为补充维度
y_1=regr_1.predict(x_test)
y_2=regr_2.predict(x_test)
plt.figure() #展开画布
plt.scatter(x,y,s=20,color='r')
plt.plot(x_test,y_1,color='b',label='max_depth=5')
plt.plot(x_test,y_2,color='g',label='max_depth=8') #过拟合
plt.legend() #坐标显示
plt.show()从图中可以看出max_depth=8时,过于依赖数据(包括噪音点),造成过拟合。