pytorch迁移学习载入部分权重
载入权重是迁移学习的重要部分,这个权重的来源可以是官方发布的预训练权重,也可以是你自己训练的权重并载入模型进行继续学习。使用官方预训练权重,这样的权重包含的信息量大且全面,可以适配一些小数据的任务,即小数据在使用迁移学习后仍然能够保持良好的性能,避免的小数据带来的数据不足,模型训练不充分的问题。载入自己的训练的权重在模型测试和继续训练时使用较多,模型测试载入权重就不说了,继续训练是指假设设置epoch为500,训练接受后,发现模型仍然没有收敛,那么你就可以载入epoch为500时的训练权重,再训练500的epoch,这样你对模型就总共训练了1000个epoch,而不需要在发现模型未收敛时,又重头去训练1000个epoch。
壹.载入全部权重
假设模型定义如下,以VGG为例:权重文件为.pth后缀文件:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class VGG(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, features,num_classes=1000):
super(VGG, self).__init__()
self.features = features
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(512 * 7 * 7, 4096),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, num_classes)
)
def forward(self, x):
x5 = self.features(x)
x5= torch.flatten(x5, start_dim=1)
x5= self.classifier(x5)
return x5
def make_features(cfg: list):
layers = []
in_channels = 3
for v in cfg:
if v == "M":
layers += [nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)]
else:
conv2d = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, v, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
layers += [conv2d, nn.ReLU(True)]
in_channels = v
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
cfgs = {
'vgg16': [64,64,'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M'],
}
def vgg(model_name="vgg16", **kwargs):
assert model_name in cfgs, "Warning: model number {} not in cfgs dict!".format(model_name)
cfg = cfgs[model_name]
model = VGG(make_features(cfg) ,**kwargs)
return model
if __name__=='__main__':
device=torch.device('cuda:0')
net=vgg()
net.to(device)
summary(net,(3,224,224))
x=torch.rand(1,3,224,224).to(device)
out=net(x)
print(out.shape)载入模型权重:
model_name = "vgg16"
net = vgg(model_name=model_name, num_classes=102)
weight_path='./vgg16_12_BNsig_1_best.pth'
net.load_state_dict(torch.load(weight_path,map_location=device))这样模型就载入了全部的权重,文中的权重是我自己训练的。
贰.载入部分权重
在很多情况下我们根据实际情况修改了部分网络结构,导致官方的预训练权重或者自己以前训练的权重报错。
假设在现有模型上增加一个模块:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class VGG(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, features,num_classes=1000):
super(VGG, self).__init__()
self.rnn3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, 3, 1, 1),
nn.Tanh())
self.features = features
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(512 * 7 * 7, 4096),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, num_classes)
)
def forward(self, x):
x1=self.rnn3(x)
x5 = self.features(x1)
x5= torch.flatten(x5, start_dim=1)
x5= self.classifier(x5)
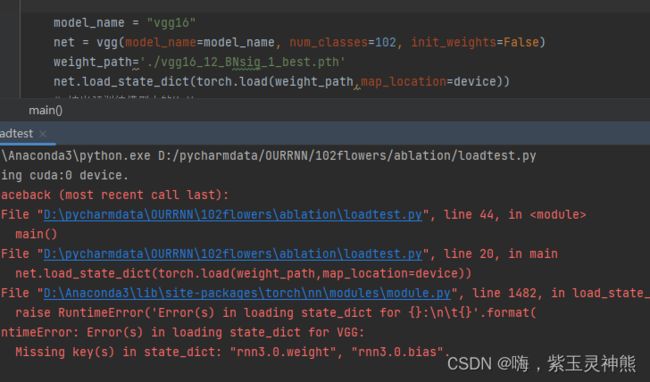
return x5再次载入模型时就会报错:
因为在预训练权重文件中并没有rnn3的权重,所以报错为missing key。
解决方法,从预训练权重中挑出现有模型的权重,并使用预训练权重初始化现有模型的权重,即完成现有模型的权重初始化。
假设现有模型的权重key值有{conv1,conv2,conv3,conv44,conv5},预训练权重的key值有{conv1,conv2,conv3,conv4,conv5}
那么我们新建一个权重字典,将key值在现有模型和预训练模型中都存在的保存下来,然后用新建的权重字典载入现有模型,即完成模型的初始化。
model_name = "vgg16"
net = vgg(model_name=model_name, num_classes=102)
weight_path='./vgg16_12_BNsig_1_best.pth'
# 抽出预训练模型中的K,V
pretrain_model=torch.load(weight_path,map_location=device)
# 抽出现有模型中的K,V
model_dict=net.state_dict()
# 新建权重字典,并更新
state_dict={k:v for k,v in pretrain_model.items() if k in model_dict.keys()}
# 更新现有模型的权重字典
model_dict.update(state_dict)
# 载入更新后的权重字典
net.load_state_dict(model_dict)叁.载入部分权重并冻结载入权重的部分
载入部分和2是一样,冻结权重即意味着权重在训练过程中不更新,那么将权重的requires_grad = False即可。
沿用2的部分,即我们现在载入的权重中只有rnn3是预训练权重中没有,那么我们就冻结其余的权重,只训练rnn3即可。
model_name = "vgg16"
net = vgg(model_name=model_name, num_classes=102, init_weights=False)
weight_path='./vgg16_12_BNsig_1_best.pth'
# 抽出预训练模型中的K,V
pretrain_model=torch.load(weight_path,map_location=device)
# 抽出现有模型中的K,V
model_dict=net.state_dict()
print(model_dict.keys())
# 新建权重字典,并更新
state_dict={k:v for k,v in pretrain_model.items() if k in model_dict.keys()}
print(state_dict.keys())
# 更新现有模型的权重字典
model_dict.update(state_dict)
# 载入更新后的权重字典
net.load_state_dict(model_dict)
# 冻结权重,即设置该训练参数为不可训练即可
for name,para in net.named_parameters():
if name in state_dict:
para.requires_grad=False
# 更新可训练参数
para=[para for para in net.parameters() if para.requires_grad]
# 更新后的可训练参数就只有rnn,权重有两个,一个是weight,一个是bias
print(para)