定义
获取感兴趣的区域(Area Of Interest)的算法。主要用于常用的游戏服务器压力,降低网络风暴的可能。
常见的AOI算法有九宫格,四叉树,灯塔,十字链表等算法。本文主要举例九宫格和四叉树两种算法的golang版本实现。
九宫格
九宫格可以说是最容易理解的一种AOI兴趣算法。
举例: 世界坐标是X[20,200],Y[50,230],划分成6×6的网格为: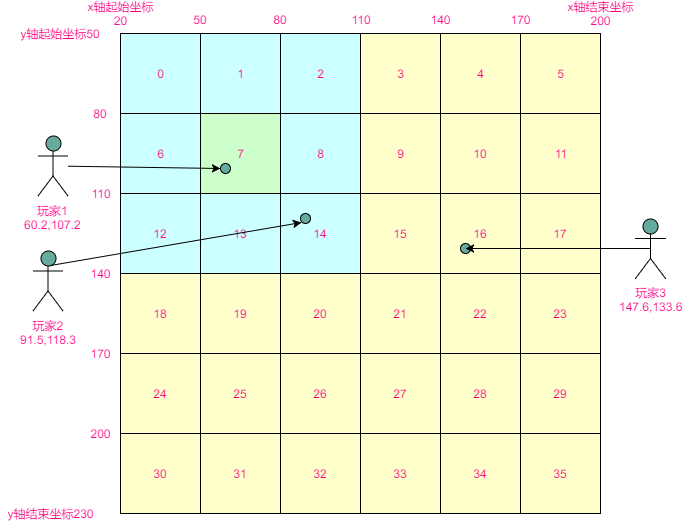
从图可看出,九宫格是把地图根据x,y轴坐标划分为等比例的一张网格地图,每个格子带有一个id编号,当玩家每次移动后根据玩家坐标将玩家置入到相应的格子中,通过把玩家在内的九个格子 的所有玩家数据取出得到兴趣用户。
数据结构
type Grid struct {
GID int //格子ID
Entities sync.Map //当前格子内的实体
}
type GridManger struct {
StartX int // X区域左边界坐标
StartY int // Y区域上边界坐标
AreaWidth int // 格子宽度(长=宽)
GridCount int // 格子数量
grids map[int]*Grid
pool sync.Pool
}通过横纵坐标获取对应的格子ID
func (g *GridManger) getGIDByPos(x, y float64) int {
gx := (int(x) - g.StartX) / g.gridWidth()
gy := (int(y) - g.StartY) / g.gridWidth()
return gy*g.GridCount + gx
}根据格子的gID得到当前周边的九宫格信息
func (g *GridManger) getSurroundGrids(gID int) []*Grid {
grids := g.pool.Get().([]*Grid)
defer func() {
grids = grids[:0]
g.pool.Put(grids)
}()
if _, ok := g.grids[gID]; !ok {
return grids
}
grids = append(grids, g.grids[gID])
// 根据gID, 得到格子所在的坐标
x, y := gID%g.GridCount, gID/g.GridCount
for i := 0; i < 8; i++ {
newX := x + dx[i]
newY := y + dy[i]
if newX >= 0 && newX < g.GridCount && newY >= 0 && newY < g.GridCount {
grids = append(grids, g.grids[newY*g.GridCount+newX])
}
}
return grids
}增删查
func (g *GridManger) Add(x, y float64, key string) {
entity := entityPool.Get().(*Entity)
entity.X = x
entity.Y = y
entity.Key = key
ID := g.getGIDByPos(x, y)
grid := g.grids[ID]
grid.Entities.Store(key, entity)
}
func (g *GridManger) Delete(x, y float64, key string) {
ID := g.getGIDByPos(x, y)
grid := g.grids[ID]
if entity, ok := grid.Entities.Load(key); ok {
grid.Entities.Delete(key)
entityPool.Put(entity)
}
}
func (g *GridManger) Search(x, y float64) []string {
result := resultPool.Get().([]string)
defer func() {
result = result[:0]
resultPool.Put(result)
}()
ID := g.getGIDByPos(x, y)
grids := g.getSurroundGrids(ID)
for _, grid := range grids {
grid.Entities.Range(func(_, value interface{}) bool {
result = append(result, value.(*Entity).Key)
return true
})
}
return result
}四叉树
可以明显看到九宫格算法需要一次性开辟出所有的网格,无论格子中是否存在一定数量的玩家。当一次性出现陈千上万的网格,对服务端的资源浪费可想而知。类似的算法与灯塔算法亦是如此。当然也有一些算法对此做了优化但终有取舍。
四叉树算是一种比较完备的AOI算法。四叉树也是在二维图片中定位像素的唯一适合的算法。
数据结构
type Node struct {
Leaf bool // 是否为叶子节点
Deep int // 深度
AreaWidth float64 // 格子宽度(长=宽)
XStart float64 // 起始范围
YStart float64 // 起始范围
Tree *QuadTree // 树指针
Child [4]*Node // 子节点
Entities *sync.Map // 实体
}
type QuadTree struct {
maxCap, maxDeep int
radius float64
mPool sync.Pool
*Node
}检查节点是否可以分割
func (n *Node) canCut() bool {
if n.XStart+n.AreaWidth/2 > 0 && n.YStart+n.AreaWidth/2 > 0 {
return true
}
return false
}检查节点是否需要分割
func (n *Node) needCut() bool {
lens := 0
n.Entities.Range(func(key, value interface{}) bool {
lens++
return true
})
return lens+1 > n.Tree.maxCap && n.Deep+1 <= n.Tree.maxDeep && n.canCut()
}分割节点
func (n *Node) cutNode() {
n.Leaf = false
half := n.AreaWidth / 2
n.Child[leftUp] = NewSonNode(n.XStart, n.YStart, n)
n.Child[rightUp] = NewSonNode(n.XStart+half, n.YStart, n)
n.Child[leftDown] = NewSonNode(n.XStart, n.YStart+half, n)
n.Child[rightDown] = NewSonNode(n.XStart+half, n.YStart+half, n)
// 将实体迁移到对应子节点
n.Entities.Range(func(k, v interface{}) bool {
entity := v.(*Entity)
for _, node := range n.Child {
if node.intersects(entity.X, entity.Y) {
node.Entities.Store(entity.Key, entity)
}
}
n.Entities.Delete(k)
return true
})
n.Tree.mPool.Put(n.Entities)
n.Entities = nil
}增删查
func (n *Node) Add(x, y float64, name string) {
// 判断是否需要分割
if n.Leaf && n.needCut() {
n.cutNode()
}
// 非叶子节点往下递归
if !n.Leaf {
n.Child[n.findSonQuadrant(x, y)].Add(x, y, name)
return
}
entity := entityPool.Get().(*Entity)
entity.X = x
entity.Y = y
entity.Key = name
// 叶子节点进行存储
n.Entities.Store(entity.Key, entity)
}
func (n *Node) Delete(x, y float64, name string) {
if !n.Leaf {
n.Child[n.findSonQuadrant(x, y)].Delete(x, y, name)
return
}
if entity, ok := n.Entities.Load(name); ok {
n.Entities.Delete(name)
entityPool.Put(entity)
}
}
func (n *Node) Search(x, y float64) []string {
result := resultPool.Get().([]string)
defer func() {
result = result[:0]
resultPool.Put(result)
}()
n.search(x, y, &result)
return result
}
func (n *Node) search(x, y float64, result *[]string) {
if !n.Leaf {
minX, maxX := x-n.Tree.radius, x+n.Tree.radius
minY, maxY := y-n.Tree.radius, y+n.Tree.radius
for _, son := range n.Child {
if son.intersects(minX, minY) || son.intersects(maxX, minY) ||
son.intersects(minX, maxY) || son.intersects(maxX, maxY) {
son.search(x, y, result)
}
}
return
}
n.Entities.Range(func(key, value interface{}) bool {
*result = append(*result, value.(*Entity).Key)
return true
})
return
}总结
四叉树的优势相比九宫格应该有两点
1.当玩家数量比较少的时候,节省了节点的分配的内存
2.当玩家数量比较多的时候能保持每个节点内的玩家数量均衡 但当玩家数量比较多的时候,整个树的内存体积和九宫格体积应该是差不多的,因为一样要存那么多个玩家数据进去
另外四叉树和九宫格都能通过控制视野半径去防止网络风暴
完整代码实例:
https://github.com/knight0zh/aoi
欢迎大家来我的github点小星星,留言提出宝贵意见
