第一章 C++编程基础——1.7文件读写
文章目录
-
-
- 1、写入操作
- 2、读文件
- 3、同时读写
- 4、案例更新
- 5、习题
-
本文是这一章的最后一小节,主要学习C++中文件的读写操作,最后案例依旧是上几个文章的更新。
【代码已上传至自己github,供参考: github】
本文的主要目的是学习文件读写,案例具体来说:(1)每次执行结束,将用户的姓名及程序(会话)的某些数据写入文件;(2)在程序打开另一个会话时,能够将数据从文件中读回。
首先对文件读写时,要包含的头文件是:
fstream
1、写入操作
若是写文件,则创建ofstream对象,例如:
ofstream outfile(“seq_data.txt”);//以覆盖的方式写文件
ofstream outfile(“seq_data.txt”,ios_base::app);//以追加的方式进行写文件
案例:
int main() {
string name;
int num_tries = 0;
int num_rights = 0;
///追加模式
ofstream outfile("seq_data.txt",ios_base::app);
cout << "please enter your name: ";
cin >> name;
cout << "please input num_tries、num_rights: ";
cin >> num_tries>>num_rights;
if (!outfile) //无法打开文件
cerr << "Sorry!Unable to save session data!";
else
outfile << name << " "
<< num_tries << " "
<< num_rights
<< endl;
return 0;
}
2、读文件
若是读文件,则创建ifstream对象,例如:
ifstream infile(“seq_data.txt”);//读文件
案例:
int main(){
string name;
int num_tries = 0;
int num_rights = 0;
int nt;//用户猜过的总次数
int nc;//用户猜对的总次数
string usr_name;
cout << "Please input your name: ";
cin >> usr_name;
ifstream infile("seq_data.txt");
if (!infile)//无法打开文件
cerr << "Sorry,the file can not open!";
else
{
while (infile>>name)
{
infile >> nt >> nc;
if (name==usr_name)
cout << "Welcome back " << usr_name
<< "\n Your current score is " << nc
<< " out of " << nt << "\n Good luck!\n";
num_tries = nt;
num_rights = nc;
}
}
return 0;
}
3、同时读写
若是读写文件,则创建fstream对象,例如:
fstream iofile("seq_data.txt",ios_base::in|ios_base::app);
案例:
int main(){
fstream iofile("seq_data.txt",ios_base::in|ios_base::app);
if (!iofile)
cerr << "Sorry,the file can not open!";
else
{
//写入
int num_tries = 0;
int num_rights = 0;
string usr_name;
iofile << "cqy2 " << 10 << ' '<< 7 << endl;
//由于ios_base::app的原因,开始读取前将文件位置定位到起始
iofile.seekg(0);
//读
iofile >> usr_name >> num_tries >> num_rights;
cout << "name: " << usr_name << endl;
cout << "num_tries: " << num_tries << endl;
cout << "num_rightes: " << num_rights;
}
return 0;
}
注意:其中由于ios_base::app的原因,开始读取前应该要将文件位置定位到起始位置,seekg()可以将iofile重新定位至文件起始处。
4、案例更新
int main() {
int usr_guess; //用户猜测的数字
bool num_seq = true; //显示下一组数列
bool guess_again = true; //用户想再猜一次
int guess_num = 0; //用户猜的总次数
int guess_right = 0;//用户猜对次数
char usr_rsp; //用户的回答 内循环用
char try_again; //用户的回答 外循环用
double usr_score = 0.0;//评分比值,采用double双精度类型
const int max_tries = 3;//设置最多猜测次数
const int seq_size = 18;//设置数列最大长度
int elem_seq[seq_size] = { //每个数列存储前三个数字进行猜测
1,2,3, //Fibonacci(斐波那契)
3,4,7, //Lucas(卢卡斯)
2,5,12, //Pell
3,6,10, //Triangular
4,9,16, //Square
5,12,22 //Pentagonal
};
//将每个数列前三个数存入vector
vector<int> fibonacci(elem_seq, elem_seq + 3);
vector<int> lucas(elem_seq + 3, elem_seq + 6);
vector<int> pell(elem_seq + 6, elem_seq + 9);
vector<int> Triangular(elem_seq + 9, elem_seq + 12);
vector<int> Square(elem_seq + 12, elem_seq + 15);
vector<int> Pentagonal(elem_seq + 15, elem_seq + 18);
const int max_seq = 6;
string seq_names[seq_size] = {
"Fibonacci",
"Lucas",
"Pell",
"Triangular",
"Square",
"Pentagonal"
};
//将每个数列地址存入seq_addrs数组
vector<int> *seq_addrs[max_seq] = {
&fibonacci,&lucas,&pell,&Triangular,&Square,&Pentagonal
};
vector<int> *current_vec = 0;
int seq_index;
srand(max_seq);
//========================更新部分========================
int nt = 0;//猜测总次数
int nc = 0;//猜测对的次数
string usr_name;
cout << "Please input your name: ";
cin >> usr_name;
//读数据
ifstream infile("seq_data.txt");
if (!infile)
cout << "Sorry,the file can not open!" << endl;
else
{
int find=0;
string name;
while (infile >> name)
{
infile >> nt >> nc;
if (name==usr_name)
{
find = 1;
guess_num = nt;
guess_right = nc;
}
}
if (find == 1)
cout << "Welcome back!" << usr_name
<< "\n TOT [" << nt << "] "
<< " of [" << nc << "]"
<< "\n Good luck!\n";
else
cout << "Welcome," << usr_name << "!" << endl;
}
//===================================================
while (num_seq == true) {
int try_cnt = 0;//猜的次数与最多次数比较
bool got_it = false; //用户是否猜对
//对数列进行随机化
seq_index = rand() % max_seq;
current_vec = seq_addrs[seq_index];//获取数列
//开始猜测数字
cout << "The first two elements of the squence are: "
<< (*current_vec)[0] << ","
<< (*current_vec)[1] << "."
<< "\nWhat is the next element?\n";
//用户猜错且想再次猜
while (guess_again == true && got_it == false && (try_cnt++ <= max_tries))
{
std::cout << "please input your num:" << endl;
std::cin >> usr_guess;
guess_num++;
//如果猜正确
if (usr_guess == (*current_vec)[2]) {
std::cout << "Your guess is right!"
<< (*current_vec)[2]
<< " is the next element in the "
<< seq_names[seq_index]
<< " sequence.\n";
got_it = true;
guess_right++;
}
//用户猜错
else {
//判断猜的次数 switch
switch (try_cnt)
{
case(1):
std::cout << "Oops!Nice guess but not quiye it! \n" << endl;
break;
case(2):
std::cout << "Hmm.Sorry.Wrong a second time.\n" << endl;
break;
case(3):
std::cout << "Ah,this is harder than it looks.\n" << endl;
break;
default:
std::cout << "It must be getting pretty frustrating by now! \n" << endl;
break;
}
//是否再试一次
std::cout << "Error!Want to try again?(y/n):";
std::cin >> usr_rsp;
if (usr_rsp == 'N' || usr_rsp == 'n')
guess_again = false;
}
}//内层循环结束
std::cout << "want to try another sequence again?(y/n):";
std::cin >> try_again;
if (try_again == 'N' || try_again == 'n')
num_seq = false;
}//外循环结束
//=======================更新部分======================
//将信息写入文件
ofstream outfile("seq_data.txt", ios_base::app);
outfile << usr_name << " "
<< guess_num << " "
<< guess_right << endl;
//====================================================
return 0;
}
5、习题
(1) 编写一个程序,能够询问用户的姓名,并读取用户所输人的内容。请确保用户输入的名称长度大于两个字符。如果用户的确输人了有效名称,就响应一些信息。请以两种方式实现:第一种使用C-style字符串,第二种使用string对象。
第一种:C-style字符串
int main() {
const int size = 18;
char name[size];
cout << "please input your name:" << endl;
cin >> name;
if (strlen(name) < 3)
cout << "sorry,your name's size <3";
else
cout << "Welcome," << name << "!" << endl;
return 0;
}
第二种:string对象
int main(){
string name;
cout << "please input your name:"<<endl;
cin >> name;
if (name.size() < 3)
cout << "sorry,your name's size <3";
else
cout << "Welcome," << name<<"!"<<endl;
return 0;
}
(2)编写一个程序,从标准输人设备读取一串整数,并将读人的整数依次放到array及vector,然后遍历这两种容器,求取数值总和。将总和及平均值输出至标准输出设备。
int main() {
vector<int> vec_num;
int num;
int sum = 0;
cout << "please input the num: "<<endl;
while (cin>>num ){
vec_num.push_back(num);
//=============这部分可以不要,设置输入数字最多个数 =============
if (vec_num.size() > 5)
break;
//=======================================================
}
for (int i = 0; i < vec_num.size(); i++)
{
sum += vec_num[i];
}
cout << "sum=" << sum << endl;
cout << "average=" << sum / vec_num.size() << endl;
return 0;
}
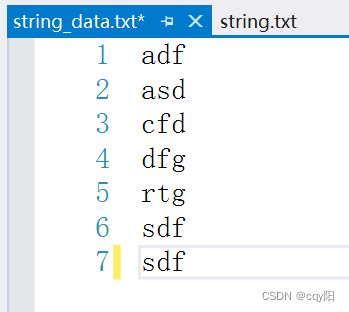
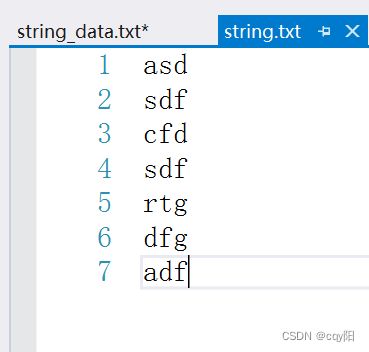
(3)使用你最称手的编辑工具,输入两行(或更多)文字并存盘。然后编写-一个程序,打开该文本文件,将其中每个字都读取到一个vector对象中。遍历该vector, 将内容显示到cout。然后利用泛型算法sort(),对所有文字排序,再将排序后的结果输出到另一个文件。
注意: sort()算法使用
#include int main() {
vector<string> my_string;
ifstream infile("string.txt");
ofstream outfile("string_data.txt", ios_base::app);
if (!infile || !outfile)
cout << "Error,the file can not open!" << endl;
else
{
string txt;
while (infile >> txt)
my_string.push_back(txt);
cout << "Unsorted text:" << endl;
for (int index = 0; index < my_string.size(); index++)
cout << my_string[index] << endl;
sort(my_string.begin(), my_string.end());
for (int i = 0; i < my_string.size(); i++)
outfile << my_string[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}