Netty学习(六)-- Handler & Pipeline
Handler & Pipeline
ChannelHandler 用来处理 Channel 上的各种事件,分为入站和出站两种。所有的 ChannelHandler 被连成一串,即 Pipeline。
- 入站处理器通常是
ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter的子类,主要用来读取客户端数据,写回结果。 - 出站处理器通常是
ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter的子类,主要对写回结果进行加工。
每个 Channel 是一个产品的加工车间,Pipeline 是车间中的流水线,ChannelHandler 就是流水线上的各道工序,而后面要讲的 ByteBuf 是原材料,经过很多工序加工:先经过一道道入站工序,再经过一道道出站工序最终变成产品
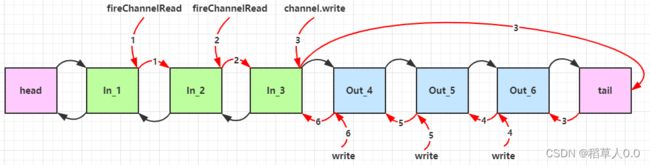
执行顺序:
@Slf4j
public class TestPipelineServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ServerBootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
// 1、通过 Channel 获取 pipeline
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
// 2、添加处理器 head -> 添加的handler -> tail
// head -> h1 -> h2 -> h3 -> h4 -> h5 -> h6 -> tail
// 入站处理 head -> h1 -> h2 -> h3
pipeline.addLast("h1", new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
log.debug("h1");
// 第一个 handler 将 ByteBuf 转成 String
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
String name = buf.toString(Charset.defaultCharset());
super.channelRead(ctx, name);
}
});
pipeline.addLast("h2", new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object name) throws Exception {
log.debug("h2");
// 第二个 handler 将 String 转成 Stu 对象
Student student = new Student(name.toString());
// 将数据传递给下一个 handler,如果不调用,调用链会断开
super.channelRead(ctx, student); // ctx.fireChannelRead(student);
}
});
pipeline.addLast("h3", new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
log.debug("h3, 结果{}, class:{}", msg, msg.getClass());
// super.channelRead(ctx, msg); 再往后没有入站 handler 了
// 向客户端写数据
// 这个是从 tail 往前找有没有出站处理器
// ch.writeAndFlush(ctx.alloc().buffer().writeBytes("server...".getBytes()));
// 这个是从 h3 往前找有没有出站处理器
ctx.writeAndFlush(ctx.alloc().buffer().writeBytes("server...".getBytes()));
}
});
// 出站处理 (只有向客户端写数据才会触发) tail -> h6 -> h5 -> h4
pipeline.addLast("h4", new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
log.debug("h4");
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
});
pipeline.addLast("h5", new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
log.debug("h5");
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
});
pipeline.addLast("h6", new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
log.debug("h6");
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
});
}
})
.bind(8888);
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
static class Student{
private String name;
}
}
ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter 是按照 addLast 的顺序执行的,而 ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter 是按照 addLast 的逆序执行的。ChannelPipeline 的实现是一个 ChannelHandlerContext(包装了 ChannelHandler) 组成的双向链表
服务端 pipeline 触发的原始流程,图中数字代表了处理步骤的先后次序
1)EmbeddedChannel
用来测试出站和入站处理器,省略编写服务端和客户端代码的繁杂步骤,方便开发测试。
@Slf4j
public class TestEmbeddedChannel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 入站处理器
ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter h1 = new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
log.debug("h1");
super.channelRead(ctx, msg);
}
};
ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter h2 = new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
log.debug("h2");
super.channelRead(ctx, msg);
}
};
// 出站处理器
ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter h3 = new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
log.debug("h3");
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
};
ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter h4 = new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
log.debug("h4");
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
};
EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel(h1, h2, h3, h4);
// 模拟入站
channel.writeInbound(ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer().writeBytes("hello".getBytes()));
// 模拟出站
channel.writeOutbound(ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer().writeBytes("hello".getBytes()));
}
}