深度学习目标检测——AP以及MAP
AP计算概述
知道了AP 的定义,下一步就是理解AP计算的实现,理论上可以通过积分来计算AP,公式如下:
A P = ∫ 0 1 P ( r ) d r AP=\int_0^1 P(r) dr AP=∫01P(r)dr
但通常情况下都是使用近似或者插值的方法来计算 AP。
近似计算AP
A P = ∑ k = 1 N P ( k ) Δ r ( k ) AP = \sum_{k=1}^{N}P(k)\Delta r(k) AP=k=1∑NP(k)Δr(k)
- 近似计算 AP(
approximated average precision),这种计算方式是 approximated 形式的; - 很显然位于一条竖直线上的点对计算AP没有贡献;
- 这里
N为数据总量,k为每个样本点的索引, Δ r ( k ) = r ( k ) − r ( k − 1 ) Δr(k)=r(k)−r(k−1) Δr(k)=r(k)−r(k−1)。
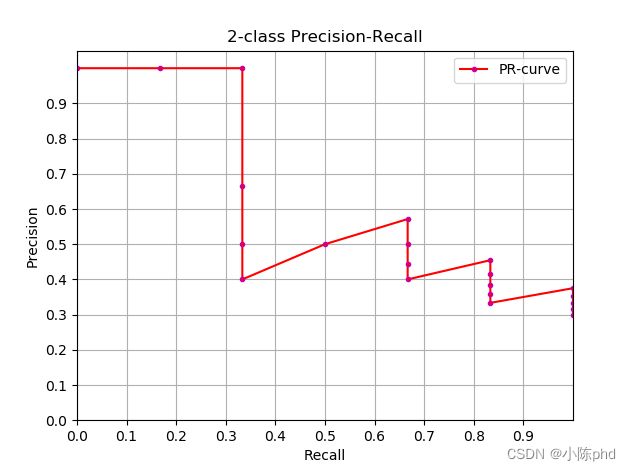
近似计算AP和绘制PR曲线代码如下:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class_names = ["car", "pedestrians", "bicycle"]
def draw_PR_curve(predict_scores, eval_labels, name, cls_idx=1):
"""calculate AP and draw PR curve, there are 3 types
Parameters:
@all_scores: single test dataset predict scores array, (-1, 3)
@all_labels: single test dataset predict label array, (-1, 3)
@cls_idx: the serial number of the AP to be calculated, example: 0,1,2,3...
"""
# print('sklearn Macro-F1-Score:', f1_score(predict_scores, eval_labels, average='macro'))
global class_names
fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=1, figsize=(15, 10))
# Rank the predicted scores from large to small, extract their corresponding index(index number), and generate an array
idx = predict_scores[:, cls_idx].argsort()[::-1]
eval_labels_descend = eval_labels[idx]
pos_gt_num = np.sum(eval_labels == cls_idx) # number of all gt
predict_results = np.ones_like(eval_labels)
tp_arr = np.logical_and(predict_results == cls_idx, eval_labels_descend == cls_idx) # ndarray
fp_arr = np.logical_and(predict_results == cls_idx, eval_labels_descend != cls_idx)
tp_cum = np.cumsum(tp_arr).astype(float) # ndarray, Cumulative sum of array elements.
fp_cum = np.cumsum(fp_arr).astype(float)
precision_arr = tp_cum / (tp_cum + fp_cum) # ndarray
recall_arr = tp_cum / pos_gt_num
ap = 0.0
prev_recall = 0
for p, r in zip(precision_arr, recall_arr):
ap += p * (r - prev_recall)
# pdb.set_trace()
prev_recall = r
print("------%s, ap: %f-----" % (name, ap))
fig_label = '[%s, %s] ap=%f' % (name, class_names[cls_idx], ap)
ax.plot(recall_arr, precision_arr, label=fig_label)
ax.legend(loc="lower left")
ax.set_title("PR curve about class: %s" % (class_names[cls_idx]))
ax.set(xticks=np.arange(0., 1, 0.05), yticks=np.arange(0., 1, 0.05))
ax.set(xlabel="recall", ylabel="precision", xlim=[0, 1], ylim=[0, 1])
fig.savefig("./pr-curve-%s.png" % class_names[cls_idx])
plt.close(fig)
插值计算AP
插值计算(Interpolated average precision) AP 的公式的演变过程这里不做讨论,详情可以参考这篇文章,我这里的公式和图也是参考此文章的。11点插值计算方式计算AP公式如下:
A P = 1 11 ∑ r ∈ { 0 , 0.1 , 0.2 , … , 1.0 } P intep ( r ) P interp ( r ) = M A X r ^ : r ^ ≥ r P ( r ^ ) \begin{gathered} A P=\frac{1}{11} \sum_{r \in\{0,0.1,0.2, \ldots, 1.0\}} P_{\text {intep }}(r) \\ P_{\text {interp }}(r)=M A X_{\hat{r}: \hat{r} \geq r} P(\hat{r}) \end{gathered} AP=111r∈{0,0.1,0.2,…,1.0}∑Pintep (r)Pinterp (r)=MAXr^:r^≥rP(r^)
- 这是通常意义上的 11 points_Interpolated 形式的 AP,选取固定的 {0,0.1,0.2,…,1.0} 11个阈值,这个在PASCAL2007中有使用
- 这里因为参与计算的只有11个点,所以 K=11,称为11points_Interpolated,k为阈值索引
- P i n t e r p ( k ) P_{interp}(k) Pinterp(k) 取第 k 个阈值所对应的样本点之后的样本中的最大值,只不过这里的阈值被限定在了 {0,0.1,0.2,…,1.0} 范围内。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-KaGONv2a-1662646748371)(…/…/images/插值计算AP的PR曲线图.png)]
从曲线上看,真实 AP< approximated AP < Interpolated AP,11-points Interpolated AP 可能大也可能小,当数据量很多的时候会接近于 Interpolated AP,与 Interpolated AP 不同,前面的公式中计算 AP 时都是对 PR 曲线的面积估计,PASCAL的论文里给出的公式就更加简单粗暴了,直接计算11 个阈值处的 precision 的平均值。PASCAL 论文给出的 11 点计算 AP 的公式如下。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-AF2dVFBg-1662646748371)(…/…/images/11点计算AP公式.png)]
三,AP计算实现
1, 在给定 recal 和 precision 的条件下计算 AP:
def voc_ap(rec, prec, use_07_metric=False):
"""
ap = voc_ap(rec, prec, [use_07_metric])
Compute VOC AP given precision and recall.
If use_07_metric is true, uses the
VOC 07 11 point method (default:False).
"""
if use_07_metric:
# 11 point metric
ap = 0.
for t in np.arange(0., 1.1, 0.1):
if np.sum(rec >= t) == 0:
p = 0
else:
p = np.max(prec[rec >= t])
ap = ap + p / 11.
else:
# correct AP calculation
# first append sentinel values at the end
mrec = np.concatenate(([0.], rec, [1.]))
mpre = np.concatenate(([0.], prec, [0.]))
# compute the precision envelope
for i in range(mpre.size - 1, 0, -1):
mpre[i - 1] = np.maximum(mpre[i - 1], mpre[i])
# to calculate area under PR curve, look for points
# where X axis (recall) changes value
i = np.where(mrec[1:] != mrec[:-1])[0]
# and sum (\Delta recall) * prec
ap = np.sum((mrec[i + 1] - mrec[i]) * mpre[i + 1])
return ap
2,给定目标检测结果文件和测试集标签文件 xml 等计算 AP:
def parse_rec(filename):
""" Parse a PASCAL VOC xml file
Return : list, element is dict.
"""
tree = ET.parse(filename)
objects = []
for obj in tree.findall('object'):
obj_struct = {}
obj_struct['name'] = obj.find('name').text
obj_struct['pose'] = obj.find('pose').text
obj_struct['truncated'] = int(obj.find('truncated').text)
obj_struct['difficult'] = int(obj.find('difficult').text)
bbox = obj.find('bndbox')
obj_struct['bbox'] = [int(bbox.find('xmin').text),
int(bbox.find('ymin').text),
int(bbox.find('xmax').text),
int(bbox.find('ymax').text)]
objects.append(obj_struct)
return objects
def voc_eval(detpath,
annopath,
imagesetfile,
classname,
cachedir,
ovthresh=0.5,
use_07_metric=False):
"""rec, prec, ap = voc_eval(detpath,
annopath,
imagesetfile,
classname,
[ovthresh],
[use_07_metric])
Top level function that does the PASCAL VOC evaluation.
detpath: Path to detections result file
detpath.format(classname) should produce the detection results file.
annopath: Path to annotations file
annopath.format(imagename) should be the xml annotations file.
imagesetfile: Text file containing the list of images, one image per line.
classname: Category name (duh)
cachedir: Directory for caching the annotations
[ovthresh]: Overlap threshold (default = 0.5)
[use_07_metric]: Whether to use VOC07's 11 point AP computation
(default False)
"""
# assumes detections are in detpath.format(classname)
# assumes annotations are in annopath.format(imagename)
# assumes imagesetfile is a text file with each line an image name
# cachedir caches the annotations in a pickle file
# first load gt
if not os.path.isdir(cachedir):
os.mkdir(cachedir)
cachefile = os.path.join(cachedir, '%s_annots.pkl' % imagesetfile)
# read list of images
with open(imagesetfile, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
imagenames = [x.strip() for x in lines]
if not os.path.isfile(cachefile):
# load annotations
recs = {}
for i, imagename in enumerate(imagenames):
recs[imagename] = parse_rec(annopath.format(imagename))
if i % 100 == 0:
print('Reading annotation for {:d}/{:d}'.format(
i + 1, len(imagenames)))
# save
print('Saving cached annotations to {:s}'.format(cachefile))
with open(cachefile, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(recs, f)
else:
# load
with open(cachefile, 'rb') as f:
try:
recs = pickle.load(f)
except:
recs = pickle.load(f, encoding='bytes')
# extract gt objects for this class
class_recs = {}
npos = 0
for imagename in imagenames:
R = [obj for obj in recs[imagename] if obj['name'] == classname]
bbox = np.array([x['bbox'] for x in R])
difficult = np.array([x['difficult'] for x in R]).astype(np.bool)
det = [False] * len(R)
npos = npos + sum(~difficult)
class_recs[imagename] = {'bbox': bbox,
'difficult': difficult,
'det': det}
# read dets
detfile = detpath.format(classname)
with open(detfile, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
splitlines = [x.strip().split(' ') for x in lines]
image_ids = [x[0] for x in splitlines]
confidence = np.array([float(x[1]) for x in splitlines])
BB = np.array([[float(z) for z in x[2:]] for x in splitlines])
nd = len(image_ids)
tp = np.zeros(nd)
fp = np.zeros(nd)
if BB.shape[0] > 0:
# sort by confidence
sorted_ind = np.argsort(-confidence)
sorted_scores = np.sort(-confidence)
BB = BB[sorted_ind, :]
image_ids = [image_ids[x] for x in sorted_ind]
# go down dets and mark TPs and FPs
for d in range(nd):
R = class_recs[image_ids[d]]
bb = BB[d, :].astype(float)
ovmax = -np.inf
BBGT = R['bbox'].astype(float)
if BBGT.size > 0:
# compute overlaps
# intersection
ixmin = np.maximum(BBGT[:, 0], bb[0])
iymin = np.maximum(BBGT[:, 1], bb[1])
ixmax = np.minimum(BBGT[:, 2], bb[2])
iymax = np.minimum(BBGT[:, 3], bb[3])
iw = np.maximum(ixmax - ixmin + 1., 0.)
ih = np.maximum(iymax - iymin + 1., 0.)
inters = iw * ih
# union
uni = ((bb[2] - bb[0] + 1.) * (bb[3] - bb[1] + 1.) +
(BBGT[:, 2] - BBGT[:, 0] + 1.) *
(BBGT[:, 3] - BBGT[:, 1] + 1.) - inters)
overlaps = inters / uni
ovmax = np.max(overlaps)
jmax = np.argmax(overlaps)
if ovmax > ovthresh:
if not R['difficult'][jmax]:
if not R['det'][jmax]:
tp[d] = 1.
R['det'][jmax] = 1
else:
fp[d] = 1.
else:
fp[d] = 1.
# compute precision recall
fp = np.cumsum(fp)
tp = np.cumsum(tp)
rec = tp / float(npos)
# avoid divide by zero in case the first detection matches a difficult
# ground truth
prec = tp / np.maximum(tp + fp, np.finfo(np.float64).eps)
ap = voc_ap(rec, prec, use_07_metric)
return rec, prec, ap
四,map计算方法
因为 mAP 值的计算是对数据集中所有类别的 AP 值求平均,所以我们要计算 mAP,首先得知道某一类别的 AP 值怎么求。不同数据集的某类别的 AP 计算方法大同小异,主要分为三种:
(1)在 VOC2007,只需要选取当Recall >= 0, 0.1, 0.2, …, 1共11个点时的Precision最大值,然后AP就是这11个Precision的平均值,map就是所有类别AP值的平均。VOC 数据集中计算 AP 的代码(用的是插值计算方法,代码出自py-faster-rcnn仓库)
(2)在 VOC2010 及以后,需要针对每一个不同的 Recall 值(包括0和1),选取其大于等于这些 Recall 值时的 Precision 最大值,然后计算PR曲线下面积作为 AP 值,map 就是所有类别 AP 值的平均。
(3)COCO 数据集,设定多个 IOU 阈值(0.5-0.95,0.05为步长),在每一个IOU阈值下都有某一类别的 AP 值,然后求不同 IOU 阈值下的 AP 平均,就是所求的最终的某类别的AP值。