《动手学深度学习》笔记
相关笔记
李沐的《动手学深度学习v2》 PyTorch版
笔记
- 相关笔记
-
- 李沐的《动手学深度学习v2》 PyTorch版
- 前言
-
- 相关笔记随笔
- 04 数据预处理
- 05 线性代数
-
- 基础概念
-
- 1. 标量 scalar
- 2. 向量
- 3. 矩阵
- 4. 张量
- 5. 降维
- randn函数——torch内置函数
- 练习1:证明一个矩阵的转置的转置是,即 (⊤)⊤=
- 练习2:给出两个矩阵 和 ,证明“它们转置的和”等于“它们和的转置”,即 ⊤+⊤=(+)⊤ 。
- 练习3:给定任意方阵 , +⊤ 总是对称的吗?为什么?
- 练习4:形状 (2,3,4) 的张量X。len(X)的输出结果是什么?
- 练习5:对于任意形状的张量X,len(X)是否总是对应于X特定轴的长度?这个轴是什么?
- 练习6:运行A/A.sum(axis=1),看看会发生什么。你能分析原因吗?
- 练习7:考虑一个具有形状 (2,3,4) 的张量,在轴0、1、2上的求和输出是什么形状?
- 练习8:为linalg.norm函数提供3个或更多轴的张量,并观察其输出。对于任意形状的张量这个函数计算得到什么?
- 06 矩阵计算
-
- 课程概念
-
- 1. 标量对向量求导
- 2. 向量对标量求导
- 3. 向量对向量求导
- 07 自动求导
-
- 向量链式求导法
- 计算图
-
- 正向计算
- 反向累计
- 正反对比
- 练习2:在运行反向传播函数之后,立即再次运行它,看看会发生什么。
- 练习3:在控制流的例子中,我们计算d关于a的导数,如果我们将变量a更改为随机向量或矩阵,会发生什么?
- 08 线性回归 (有较多概念)
-
- 相关基础概念
-
- 1. 线性回归
-
- 基本元素
- 2. 线性模型
- 3. 损失函数
- 4. 解析解 / 显示解 数学过程不理解
- 5. 随机梯度下降
- 6. 矢量化加速
- 7. 正态分布与平方损失
- 没看懂的点:
- 8. 从线性回归到深度网络
-
- 将线性回归模型描述为一个神经网络
- 习题未做(数学相关性太大)
- 线性回归的从零开始实现 ?
- 09 Softmax回归
-
- 1
- 04 数据操作 数据预处理
-
- 1.引入库
- 2.读入数据
- 总结
前言
相关笔记随笔
04 数据预处理
chapter_preliminaries / pandas
使用pandas预处理原始数据,并将原始数据转换为张量格式
import os
os.makedirs(os.path.join('..', 'data'), exist_ok=True)
data_file = os.path.join('..', 'data', 'house_tiny.csv')
with open(data_file, 'w') as f:
f.write('NumRooms,Alley,Price\n') # 列名
f.write('NA,Pave,127500\n') # 每行表示一个数据样本
f.write('2,NA,106000\n')
f.write('4,NA,178100\n')
f.write('NA,NA,140000\n')
不理解os.path.join()的作用
05 线性代数
chapter_preliminaries / linear-algerbra
基础概念
1. 标量 scalar
用只有一个元素的张量 tensor表示
tensor(3.)
2. 向量
- 概念
可以将其视为标量组成的列表,并且将这些标量值称为向量的元素或分量
用一维张量处理向量
tensor( [ 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 ] ) - 定义
x = torch.arange(4)
x
tensor( [ 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 ] ) - 长度
len(x)
4
向量或轴的维度:向量或轴的长度
张量的维度:张量具有的轴数
x.shape
torch.Size( [ 4 ] )
形状(shape)是一个元素组,列出了张量沿每个轴的长度
对于只有一个轴的张量,形状只有一个元素
3. 矩阵
- 定义
A = torch.arange(16).reshape(16, 4)
A
tensor([[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7], [ 8, 9, 10, 11], [12, 13, 14, 15]]) - 转置
A.T
tensor([[ 0, 4, 8, 12], [ 1, 5, 9, 13], [ 2, 6, 10, 14], [ 3, 7, 11, 15]])
A == A.T
tensor([[ True, False, False, False], [False, True, False, False], [False, False, True, False], [False, False, False, True]])
4. 张量
- 定义
X = torch.arange(24).reshape(2, 3, 4)
X
tensor([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7], [ 8, 9, 10, 11]], [[12, 13, 14, 15], [16, 17, 18, 19], [20, 21, 22, 23]]]) - 算法的基本性质
给定具有相同形状的任意两个张量,任何按元素二元运算的结果都将是相同形状的张量
A = torch.arange(20, dtype=torch.float32).reshape(5, 4)
B = A.clone() # 通过分配新内存,将A的一个副本分配给B
A, A + B, A * B # 两个矩阵的按元素乘法称为Hadamard积(Hadamard product)(数学符号 ⊙ )
将张量乘以或加上一个标量不会改变张量的形状,其中张量的每个元素都将与标量相加或相乘
5. 降维
randn函数——torch内置函数
help(torch.randn)
"""
Help on built-in function randn:
randn(...)
randn(*size, *, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False) -> Tensor
Returns a tensor filled with random numbers from a normal distribution
with mean `0` and variance `1` (also called the standard normal
distribution).
.. math::
\text{out}_{i} \sim \mathcal{N}(0, 1)
The shape of the tensor is defined by the variable argument :attr:`size`.
Args:
size (int...): a sequence of integers defining the shape of the output tensor.
Can be a variable number of arguments or a collection like a list or tuple.
Keyword args:
generator (:class:`torch.Generator`, optional): a pseudorandom number generator for sampling
out (Tensor, optional): the output tensor.
dtype (:class:`torch.dtype`, optional): the desired data type of returned tensor.
Default: if ``None``, uses a global default (see :func:`torch.set_default_tensor_type`).
layout (:class:`torch.layout`, optional): the desired layout of returned Tensor.
Default: ``torch.strided``.
device (:class:`torch.device`, optional): the desired device of returned tensor.
Default: if ``None``, uses the current device for the default tensor type
(see :func:`torch.set_default_tensor_type`). :attr:`device` will be the CPU
for CPU tensor types and the current CUDA device for CUDA tensor types.
requires_grad (bool, optional): If autograd should record operations on the
returned tensor. Default: ``False``.
Example::
>>> torch.randn(4)
tensor([-2.1436, 0.9966, 2.3426, -0.6366])
>>> torch.randn(2, 3)
tensor([[ 1.5954, 2.8929, -1.0923],
[ 1.1719, -0.4709, -0.1996]])
"""
A = torch.randn(3, 4)
a = torch.randn(size=())
练习1:证明一个矩阵的转置的转置是,即 (⊤)⊤=
A = torch.randn(3, 4)
AT = A.T
ATT = AT.T
A, AT, ATT
练习2:给出两个矩阵 和 ,证明“它们转置的和”等于“它们和的转置”,即 ⊤+⊤=(+)⊤ 。
A, B = torch.randn(3, 4), torch.randn(3, 4)
AT, BT = A.T, B.T
AB, ATBT = A + B , AT + BT
AB, ATBT
练习3:给定任意方阵 , +⊤ 总是对称的吗?为什么?
练习4:形状 (2,3,4) 的张量X。len(X)的输出结果是什么?
X = torch.arange(24).reshape(2, 3, 4)
len(X)
2
练习5:对于任意形状的张量X,len(X)是否总是对应于X特定轴的长度?这个轴是什么?
import torch
x, y, z = torch.arange(24).reshape(2,3,4), torch.arange(12).reshape(3,4), torch.arange(4)
len(x),len(y),len(z)
# (2, 3, 4)
对应axis=0这个轴
练习6:运行A/A.sum(axis=1),看看会发生什么。你能分析原因吗?
A = torch.arange(20, dtype=torch.float32).reshape(5, 4)
A,A.sum(axis = 1),A.sum(axis=0),A.sum(axis = 1, keepdim = True)
"""
(tensor([[ 0., 1., 2., 3.],
[ 4., 5., 6., 7.],
[ 8., 9., 10., 11.],
[12., 13., 14., 15.],
[16., 17., 18., 19.]]),
tensor([ 6., 22., 38., 54., 70.]),
tensor([40., 45., 50., 55.]),
tensor([[ 6.],
[22.],
[38.],
[54.],
[70.]]))
"""
结果是报错:
RuntimeError: The size of tensor a (4) must match the size of tensor b (5) at non-singleton dimension 1
原因是:sum(axis = 1)会压缩张量维度,将此处的54的二维矩阵压缩(坍缩)为15的一维矩阵(行向量),
而sum(axis = 1, keepdim = True)则会保存axis = 1的维度,将A矩阵压缩为5*1的一维矩阵(列向量)
练习7:考虑一个具有形状 (2,3,4) 的张量,在轴0、1、2上的求和输出是什么形状?
[3,4], [2,4], [2,3]
copy大佬的解释:

练习8:为linalg.norm函数提供3个或更多轴的张量,并观察其输出。对于任意形状的张量这个函数计算得到什么?
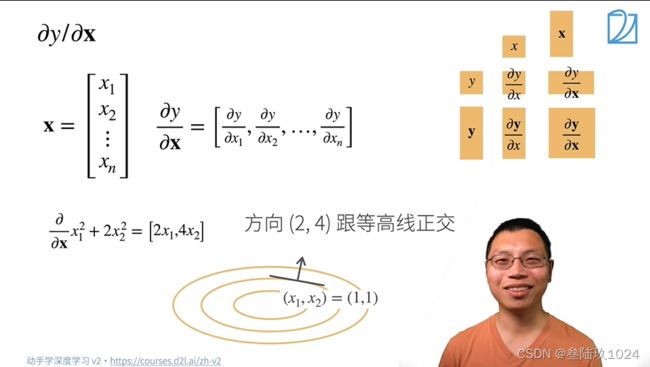
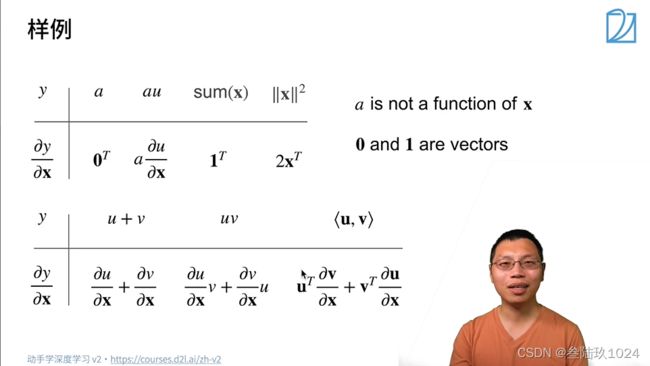
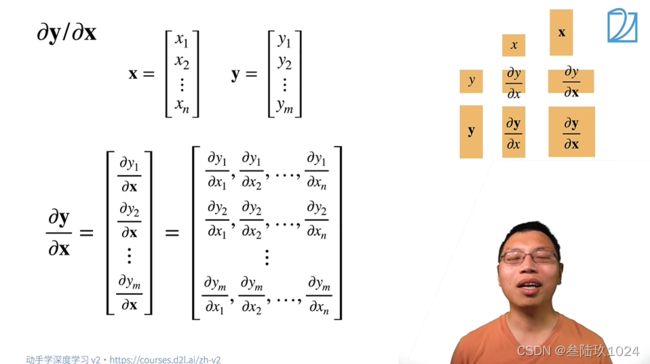
06 矩阵计算
课程概念
1. 标量对向量求导
2. 向量对标量求导
3. 向量对向量求导
相关知识:
矩阵论 BV1xk4y1B7RQ?p=3
分子布局
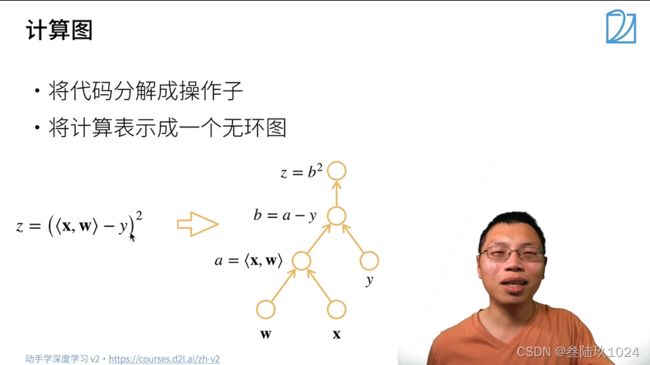
07 自动求导
autograd
向量链式求导法
计算图
正向计算
反向累计
正反对比
练习2:在运行反向传播函数之后,立即再次运行它,看看会发生什么。
import torch
x = torch.arange(4.0,requires_grad=True)
y = 2 * torch.dot(x, x)
y.backward()
x.grad
y.backward()
x.grad
"""
RuntimeError: Trying to backward through the graph a second time (or directly access saved tensors after they have already been freed). Saved intermediate values of the graph are freed when you call .backward() or autograd.grad(). Specify retain_graph=True if you need to backward through the graph a second time or if you need to access saved tensors after calling backward.
"""
修改:
import torch
x = torch.arange(4.0,requires_grad=True)
y = 2 * torch.dot(x, x)
y.backward(retain_graph=True)
x.grad
y.backward(retain_graph=True)
x.grad
"""
tensor([ 0., 8., 16., 24.])
"""
练习3:在控制流的例子中,我们计算d关于a的导数,如果我们将变量a更改为随机向量或矩阵,会发生什么?
def f(a):
b = a * 2
while b.norm() < 1000:
b = b * 2
if b.sum() > 0:
c = b
else:
c = 100 * b
return c
a = torch.randn(size=(3,4), requires_grad=True)
d = f(a)
d.backward()
# grad can be implicitly created only for scalar outputs
08 线性回归 (有较多概念)
chapter_linear-networks / linear_regression
线性神经网络基础知识 :神经网络的整个训练过程,包括:定义简单的神经网络架构、数据处理、指定损失函数和如何训练模型 (包括08 09)
从简单的线性神经网络开始
相关基础概念
1. 线性回归
预测任务的一类,除了回归问题还有分类问题
基本元素
**训练数据集 / 训练集:**真实的数据集,包括试图预测的目标和预测所依据的自变量
**样本 / 数据点 / 数据样本:**每行数据
**标签 / 目标:**试图预测的目标
**特征 / 协变量:**预测所依据的自变量
2. 线性模型
-
示例表达式:
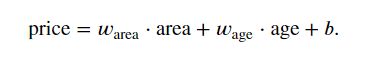
其中
Warea和Wage为权重,权重决定了每个特征对我们预测值的影响
b为偏置(bias)、偏移量(offset)或截距(intercept)
严格来说:该表达式是输入特征的一个仿射变换(affine transformation),仿射变换的特点是通过加权和对特征进行线性变换(linear transformation),并通过偏置项来进行平移(translation) -
机器学习领域
由于我们通常使用的是高维数据集,建模时采用线性代数表示法会比较方便:

其中,上述表达式中的向量x 对应于单个数据样本的特征,使用矩阵X可以很方便的引用整个数据集的样本,其中,行数代表了一个样本的特征数量,而列数代表了样本数
上述表达式可表示为:
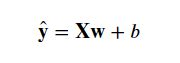
线性回归的目的找到一组权重向量w和偏置b:当给定从X的同分布中取样的新样本特征时,这组权重向量和偏置能够使得新样本预测标签的误差尽可能小
在确定模型参数(model parameters),还需要两个东西:
- 模型质量的度量方式
- 通过更新模型以提高模型预测质量的方法
3. 损失函数
定义:量化目标的实际值与预测值之间的差距

损失均值:

找到一组参数(w*, b*),使在所有训练样本上的**总损失:**最小化

4. 解析解 / 显示解 数学过程不理解
线性回归是一个很简单的优化问题,线性回归的解可以用一个公式简单地表达出来,此类解叫做解析解

虽然解析解可以进行很好的数学分析,但是解析解对问题的限制很严格,导致他无法广泛应用在深度学习中
5. 随机梯度下降
即使在无法得到解析解的情况下,仍可以有效的训练模型
在许多任务上,那些难以优化的模型效果要更好。 因此,弄清楚如何训练这些难以优化的模型是非常重要的
方法:通过不断在损失函数递减的方向上 更新参数 来降低误差
梯度下降最简单的用法:计算损失函数(数据集中所有样本的损失均值)关于模型参数的导数
但是,该方法执行时会很慢,因为在每一次更新参数前,都必须遍历整个数据集
因此,我们通常会在每次需要计算更新时,随机抽取一小批样本,这种变体就叫做 小批量随机梯度下降(minibatch stochastic gradient descent)

ppt图解:


6. 矢量化加速
对比for循环可带来数量级的加速
7. 正态分布与平方损失
正态分布的概率密度函数:

改变均值会产生沿 轴的偏移,增加方差将会分散分布、降低其峰值
没看懂的点:
8. 从线性回归到深度网络
将线性回归模型描述为一个神经网络

该图只显示连接模式,即只显示每个输入如何连接到输出,隐去了权重和偏置的值。
输入为 1,…, , 因此输入层中的输入数(或称为特征维度,feature dimensionality)为 。 网络的输出为 1 ,因此输出层中的输出数是1。需要注意的是,输入值都是已经给定的,并且只有一个计算神经元。
由于模型重点在发生计算的地方,所以通常我们在计算层数时不考虑输入层。我们可以将线性回归模型视为仅由单个人工神经元组成的神经网络,或称为单层神经网络。
习题未做(数学相关性太大)
线性回归的从零开始实现 ?
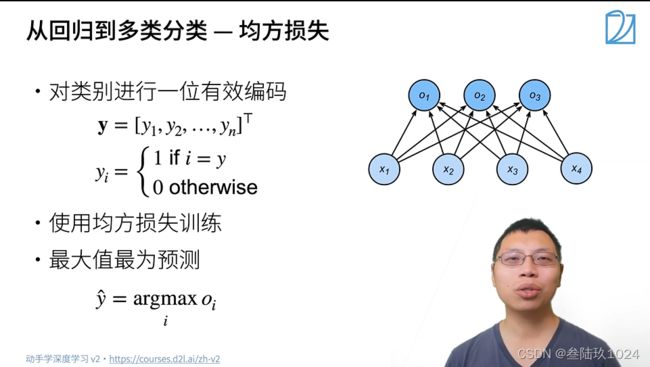
09 Softmax回归
1
04 数据操作 数据预处理
1.引入库
代码如下(示例):
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
import ssl
ssl._create_default_https_context = ssl._create_unverified_context
2.读入数据
代码如下(示例):
data = pd.read_csv(
'https://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/1283/adult.data.csv')
print(data.head())
该处使用的url网络请求的数据。