SpringBoot异常处理及其原理——源码学习
SpringBoot版本:2.3.4
应用
SpringBoot默认的异常处理机制是:
- 对于浏览器客户端,返回一个白页(whiteLable)

- 对于机器客户端,返回一个json,包含错误信息
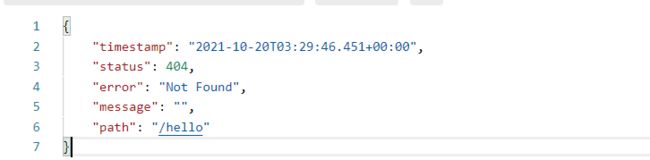
- 自定义错误页面页很简单,只要在静态资源路径里放置我们的页面,并用4xx.html和5xx.html命名,就把相应状态码的异常映射到相应的页面。
原理
下面来探究一下原理
在控制器方法中设置一个除零错。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public void handle(){
int a = 1 / 0;
}
}
请求到来的时候会交由DispatchServlet的doDispatch()方法处理
1、和正常请求一致,先获得它的handlermappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);,再获得它的适配器,HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());, 调用处理器方法 mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());,其中会先处理参数,再调用业务方法
2、 业务方法中的错误会被抛出,一直到doDispacth()被catch捕获,然后传入processDispatchResult方法处理返回的视图。
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
//
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv,dispatchException);
3、processDispatchResult方法会先判断异常是否为空,然后调用mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);处理。
4、在processHandlerException方法中选择一个能够处理该异常的异常解析器(HandlerExceptionResolver)
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView processHandlerException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
// Success and error responses may use different content types
request.removeAttribute(HandlerMapping.PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE);
// 选择已经配置了的异常解析器
ModelAndView exMv = null;
if (this.handlerExceptionResolvers != null) {
for (HandlerExceptionResolver resolver : this.handlerExceptionResolvers) {
exMv = resolver.resolveException(request, response, handler, ex);
if (exMv != null) {
break;
}
}
}
//...
//后面代码略去
SpringBoot默认为我们配置了四个异常解析器
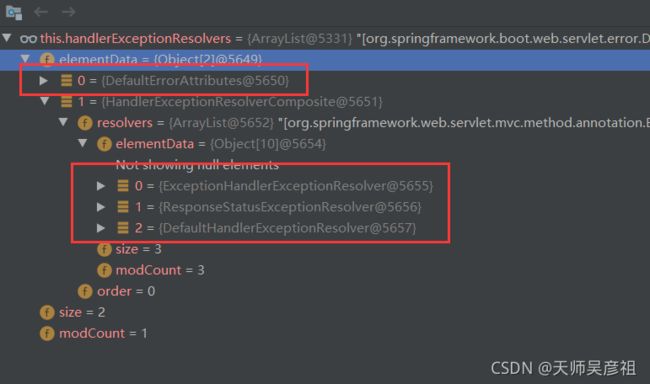
DefaultErrorAttributes,只为我们在request中保存错误信息。
//DefaultErrorAttributes
public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) {
this.storeErrorAttributes(request, ex);
return null;
}
默认情况下四个异常处理器都不能够处理,都是返回null,异常被接着抛出。
5、doDispacth()方法对于这个请求其实已经处理完了,总的看除了记录错误信息,什么都没做。但框架底层会为我们发送一个/error请求,这时候又会来到doDispacth()处理。
6、/error请求会交由BasicErrorController#errorHtml(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse)处理,这个类也是SpringBoot为我们自动装配的。具体的配置类为org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,异常处理的类都在这个配置类中配置。
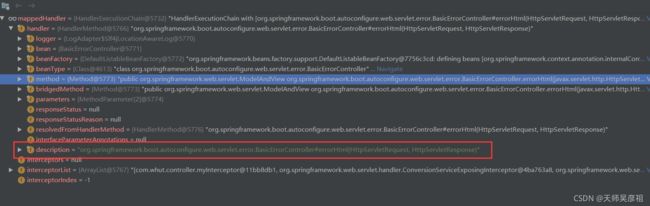
进到BasicErrorController中我们发现这个类是如何处理异常的,也解释了文章开头框架能根据不同的客户端对象返回不同类型的数据。
//BasicErrorController
@RequestMapping(produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE)
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
//获得错误状态码
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
Map<String, Object> model = Collections
.unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(request, getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
//解析错误视图
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
//ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration中会自动配置一个名为error的view,就是我们默认的百页。
return (modelAndView != null) ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
@RequestMapping
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
if (status == HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT) {
return new ResponseEntity<>(status);
}
Map<String, Object> body = getErrorAttributes(request, getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.ALL));
return new ResponseEntity<>(body, status);
}
在解析错误视图时,默认只有一个错误视图解析器

有趣的是,DefaultErrorViewResolver在解析错误视图的时候,会将状态码作为视图名传入。

接下来会根据状态码和已存在的静态资源做一个匹配,先是直接匹配,再是模糊匹配,最后创建一个异常处理的模型视图在BasicErrorController中返回。
7、经过一些后续的处理后,返回我们得到的错误处理视图。
自定义错误处理
在清楚了原理后,我们就可以根据自己的需求做出一些自定义操作。
自定义错误页
静态资源中添加我们的错误页, error/404.html error/5xx.html;有精确的错误状态码页面就匹配精确,没有就找 4xx.html;如果都没有就触发白页。
@ControllerAdvice+@ExceptionHandler处理全局异常
@ControllerAdvice
public class MyExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(value = {ArithmeticException.class})
public void handleException(Exception ex){
//处理异常
}
}
这个方法其实就是对应了之前没有生效的ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver,由它支持。
/**
* Find an {@code @ExceptionHandler} method for the given exception. The default
* implementation searches methods in the class hierarchy of the controller first
* and if not found, it continues searching for additional {@code @ExceptionHandler}
* methods assuming some {@linkplain ControllerAdvice @ControllerAdvice}
* Spring-managed beans were detected.
* @param handlerMethod the method where the exception was raised (may be {@code null})
* @param exception the raised exception
* @return a method to handle the exception, or {@code null} if none
*/
@Nullable
protected ServletInvocableHandlerMethod getExceptionHandlerMethod(
@Nullable HandlerMethod handlerMethod, Exception exception) {
Class<?> handlerType = null;
if (handlerMethod != null) {
// Local exception handler methods on the controller class itself.
// To be invoked through the proxy, even in case of an interface-based proxy.
handlerType = handlerMethod.getBeanType();
ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver resolver = this.exceptionHandlerCache.get(handlerType);
if (resolver == null) {
resolver = new ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver(handlerType);
this.exceptionHandlerCache.put(handlerType, resolver);
}
Method method = resolver.resolveMethod(exception);
if (method != null) {
return new ServletInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod.getBean(), method);
}
// For advice applicability check below (involving base packages, assignable types
// and annotation presence), use target class instead of interface-based proxy.
if (Proxy.isProxyClass(handlerType)) {
handlerType = AopUtils.getTargetClass(handlerMethod.getBean());
}
}
for (Map.Entry<ControllerAdviceBean, ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver> entry : this.exceptionHandlerAdviceCache.entrySet()) {
ControllerAdviceBean advice = entry.getKey();
if (advice.isApplicableToBeanType(handlerType)) {
ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver resolver = entry.getValue();
Method method = resolver.resolveMethod(exception);
if (method != null) {
return new ServletInvocableHandlerMethod(advice.resolveBean(), method);
}
}
}
return null;
}
@ResponseStatus+自定义异常
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN, reason = "用户名和密码不匹配")
public class UsernameNotMatchPasswordException extends RuntimeException {
}
这个异常就会被前面没有生效的ResponseStatusExceptionResolver处理,最后底层调用response.sendError(statusCode, resolvedReason),我们自定义的错误信息会被带入,让tomcat发送/error。
//ResponseStatusExceptionResolver
protected ModelAndView applyStatusAndReason(int statusCode, @Nullable String reason, HttpServletResponse response)
throws IOException {
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(reason)) {
response.sendError(statusCode);
}
else {
String resolvedReason = (this.messageSource != null ?
this.messageSource.getMessage(reason, null, reason, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale()) :
reason);
response.sendError(statusCode, resolvedReason);
}
return new ModelAndView();
}
}
自定义实现 HandlerExceptionResolver 处理异常
/**
* Interface to be implemented by objects that can resolve exceptions thrown during
* handler mapping or execution, in the typical case to error views. Implementors are
* typically registered as beans in the application context.
*
* Error views are analogous to JSP error pages but can be used with any kind of
* exception including any checked exception, with potentially fine-grained mappings for
* specific handlers.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 22.11.2003
*/
public interface HandlerExceptionResolver {
/**
* Try to resolve the given exception that got thrown during handler execution,
* returning a {@link ModelAndView} that represents a specific error page if appropriate.
* The returned {@code ModelAndView} may be {@linkplain ModelAndView#isEmpty() empty}
* to indicate that the exception has been resolved successfully but that no view
* should be rendered, for instance by setting a status code.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @param response current HTTP response
* @param handler the executed handler, or {@code null} if none chosen at the
* time of the exception (for example, if multipart resolution failed)
* @param ex the exception that got thrown during handler execution
* @return a corresponding {@code ModelAndView} to forward to,
* or {@code null} for default processing in the resolution chain
*/
@Nullable
ModelAndView resolveException(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex);
}
注意设置order,让其优先于默认的解析器,这样可以根据我们自己的逻辑自定义处理过程。
ErrorViewResolver 实现自定义处理异常
当然我们也可以自定义错误视图的解析过程。
/**
* Interface that can be implemented by beans that resolve error views.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @since 1.4.0
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ErrorViewResolver {
/**
* Resolve an error view for the specified details.
* @param request the source request
* @param status the http status of the error
* @param model the suggested model to be used with the view
* @return a resolved {@link ModelAndView} or {@code null}
*/
ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model);
}
文章比较粗糙,细节不够,还望指教。