Leetcode刷题06-位运算
位运算
基础知识
原码、反码和补码
二进制有三种不同的表示形式:原码、反码和补码,计算机内部使用补码来表示
原码:就是其二进制表示,(其中第一位为符号位)
反码:正数的反码就是原码,负数的反码是符号位不变,其余位取反。
补码:正数的补码就是原码,负数的补码是反码+1
符号位:最高位为符号位,0表示正数,1表示负数,在位运算中符号位也参与位运算
位运算操作
1.按位非操作
整数的二进制每一位都取反(0变成1,1变成0)
00 00 01 01 -> 5
~
11 11 10 10 -> -6 (反码是11 11 10 01, 原码是10 00 01 10,因此是-6)
2.按位与操作
只有二进制中两个对应位是1才为1
00 00 01 01 -> 5
&
00 00 01 10 -> 6
---
00 00 01 00 -> 4
3.按位或操作
二进制中有一个对应位是1就为1,全为0结果才为0
00 00 01 01 -> 5
|
00 00 01 10 -> 6
---
00 00 01 11 -> 7
4.按位异或操作
只有对应位不同结果为1,否则为0
00 00 01 01 -> 5
^
00 00 01 10 -> 6
---
00 00 00 11 -> 3
异或的操作满足交换律和结合律,即:
A^B = B^A
ABC = A(BC)
A^A = 0
A^0 = A
ABA = AAB = 0^B = B
5.按位左移操作
num << i将num的二进制表示向左移动i位,右边补0得到的值,左移1位表示十进制的数值加倍。
00 00 10 11 -> 11
11 << 3
01 01 10 00 -> 88
6.按位右移操作
num >> i将num的二进制表示向右移动i位得到的值
00 00 10 11 -> 11
11 >> 3
00 00 00 10 -> 2
题目解析
只出现一次的数字
1.题目描述
题目链接
2.解析思路及代码
对每个数进行异或即可得到答案,因为任何数异或自己等于0,题目中说了只有一个数出现一次,其他都出现两次,因此出现两次的数字异或结果都为0,0异或只出现一次的数等于只出现一次的数,时间复杂度为O(n)
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i ++ ) {
res = res ^ nums[i];
}
return res;
}
class Solution:
def singleNumber(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
res = 0
for item in nums:
res = res ^ item
return res
只出现一次的数字 III
1.题目描述
题目链接
2.解题思路及代码
思路:
- 使用哈希表存储每个数字出现的次数,然后将出现次数为1的结果返回
- 使用异或操作和与操作,假设出现一次的数字为x1、x2,首先将所有数异或,根据上一题可得最后的结果为 x = x 1 ⊕ x 2 x = x1 \oplus x2 x=x1⊕x2,然后取x的最后一个1,即使用x & -x,因为该位的结果为1,因此可以得出x1和x2的该位一定是不相同的,使用与运算可以将原数组所有数的该位分成两组,x1和x2一定不在同一组,那么每组都只会有一个出现一次的数,即可得到最后的结果。
public int[] singleNumber(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length < 2) return new int[2];
int res = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
res ^= num;
}
res = res & (-res);
int num1 = 0, num2 = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
if ((res & num) == 0) {
num1 ^= num;
} else {
num2 ^= num;
}
}
return new int[]{num1, num2};
}
class Solution:
def singleNumber(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
if len(nums) < 2:
return []
res = 0
for num in nums:
res ^= num
res = res & (-res)
num1, num2 = 0, 0
for num in nums:
if res & num == 0:
num1 ^= num
else:
num2 ^= num
return [num1, num2]
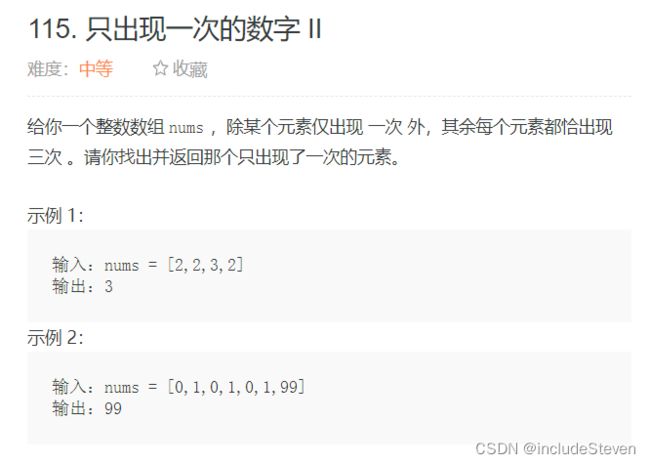
只出现一次的数字 II
1.题目描述
题目链接
2.解题思路及代码
- 使用哈希表映射每个数字的出现次数,然后找出只出现一次的元素
- 获取答案的每一位上的数字,因为其他数都出现三次,因此答案的每一位数字等于所有数字出现的结果和模3,注意如果目标语言不区分有符号数和无符号数,最高位需要特判。
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 32; i ++ ) {
int total = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
total += ((num >> i) & 1);
}
if ((total % 3) == 1) {
res |= (1 << i);
}
}
return res;
}
class Solution:
def singleNumber(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
res = 0
for i in range(32):
total = sum((num >> i) & 1 for num in nums)
if total % 3:
if i == 31:
res -= (1 << i)
else:
res |= (1 << i)
return res
2 的幂
1.题目描述
题目链接
2.解题思路及代码
- 使用n & (n - 1)可以移除n的最低位,判断该结果是否为0即可
- 使用n & (-n)可以取出n的最后一个1,判断该结果是否与n相等即可
public boolean isPowerOfTwo(int n) {
return n > 0 && ((n & (n - 1)) == 0);
}
class Solution:
def isPowerOfTwo(self, n: int) -> bool:
return n > 0 and (n == (n & (-n)))
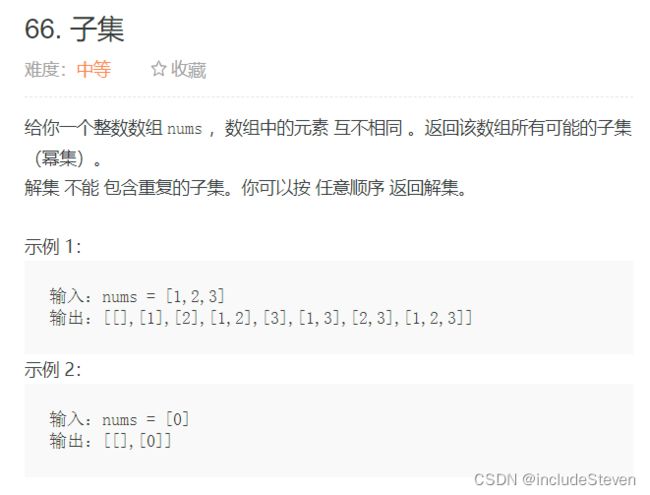
子集
1.题目描述
题目链接
2.解题思路及代码
- 迭代得到结果,数组中出现的每一个结果都可以用二进制对应的位数表示,假设数组有3个元素,那么100表示第一个元素出现,第二个元素不出现,第三个元素不出现,最终的二进制最大值为111。
- 递归求解,对于数组的每一个位置的值,可以选择包含或不包含
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < (1 << nums.length); i ++ ) {
tmp.clear();
for (int j = 0; j < nums.length; j ++ ) {
if ((i & (1 << j)) != 0) {
tmp.add(nums[j]);
}
}
// 注意这里必须重新初始化一个List,否则ans的最后结果都会指向同一个值
ans.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(tmp));
}
return ans;
}
class Solution {
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
dfs(0, nums);
return ans;
}
public void dfs(int cur, int[] nums) {
if (cur == nums.length) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));
return ;
}
// 不选择该位
dfs(cur + 1, nums);
// 选择该位
tmp.add(nums[cur]);
dfs(cur + 1, nums);
tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);
}
}
class Solution:
def subsets(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
res = [[]]
for i in nums:
# 在每一个现有的结果前加上当前数字
res = res + [[i] + num for num in res]
return res