一、 概述
1、 简介
HTTPX 是 Python 3 的全功能 HTTP 客户端,它提供同步和异步 API,并支持 HTTP/1.1 和 HTTP/2。
官方文档位置:https://www.python-httpx.org/
该库的特性:
HTTPX 建立在公认的可用性之上requests,并为您提供:
- 广泛兼容请求的 API。
- 标准同步接口,但如果需要,可以支持异步。
- HTTP/1.1和 HTTP/2 支持。
- 能够直接向WSGI 应用程序或ASGI 应用程序发出请求。
- 到处都是严格的超时。
- 完全类型注释。
- 100% 的测试覆盖率。
加上requests…的所有标准功能
- 国际域名和 URL
- 保持活动和连接池
- 具有 Cookie 持久性的会话
- 浏览器式 SSL 验证
- 基本/摘要认证
- 优雅的键/值 Cookie
- 自动减压
- 自动内容解码
- Unicode 响应体
- 多部分文件上传
- HTTP(S) 代理支持
- 连接超时
- 流式下载
- .netrc 支持
- 分块请求
安装方式:
pip install httpx # 安装库 pip install httpx[http2] # 获取http2的支持 pip install httpx[brotli] # 包括可选的 brotli 解码器支持
2、 命令行模式
安装: pip install 'httpx[cli]'
现在允许我们直接从命令行使用 HTTPX…
发送请求…
3、 快速开始
3.1 get请求
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
__author__ = "A.L.Kun"
__file__ = "demo01.py"
__time__ = "2022/9/9 7:55"
import httpx
from fake_useragent import UserAgent
headers = {
"user-agent": UserAgent().random,
}
params = {
"wd": "python" # 输入百度搜索的内容
}
resp = httpx.get("https://www.baidu.com/s", params=params, headers=headers, cookies=None, proxies=None) # 和原来requests的使用方法类似
resp.encoding = resp.charset_encoding # 根据文档的编码还对文档进行编码
print(resp.text) # 获取数据信息
requests中的参数和httpx中的参数大部分类似
3.2 post请求
3.2.1 表单
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
__author__ = "A.L.Kun"
__file__ = "demo01.py"
__time__ = "2022/9/9 7:55"
import httpx
data = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'}
r = httpx.post("https://httpbin.org/post", data=data)
print(r.text)
3.2.2 文件
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
__author__ = "A.L.Kun"
__file__ = "demo01.py"
__time__ = "2022/9/9 7:55"
import httpx
files = {'upload-file': open('a.jpg', 'rb')}
# 也可以通过元组来指定数据类型
# files = {'upload-file': ('report.xls', open('report.xls', 'rb'), 'application/vnd.ms-excel')}
r = httpx.post("https://httpbin.org/post", files=files)
print(r.text)
3.2.3 JSON
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
__author__ = "A.L.Kun"
__file__ = "demo01.py"
__time__ = "2022/9/9 7:55"
import httpx
data = {'integer': 123, 'boolean': True, 'list': ['a', 'b', 'c']}
r = httpx.post("https://httpbin.org/post", json=data)
print(r.text)
3.2.4 二进制
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
__author__ = "A.L.Kun"
__file__ = "demo01.py"
__time__ = "2022/9/9 7:55"
import httpx
content = b'Hello, world'
r = httpx.post("https://httpbin.org/post", content=content, headers={
"Content-Type": "application/octet-stream",
})
print(r.text)
Content-Type在上传二进制数据时设置自定义标头
常见的媒体格式类型如下:
- text/html : HTML格式
- text/plain :纯文本格式
- text/xml : XML格式
- image/gif :gif图片格式
- image/jpeg :jpg图片格式
- image/png:png图片格式
以application开头的媒体格式类型:
- application/xhtml+xml :XHTML格式
- application/xml: XML数据格式
- application/atom+xml :Atom XML聚合格式
- application/json: JSON数据格式
- application/pdf:pdf格式
- application/msword : Word文档格式
- application/octet-stream : 二进制流数据(如常见的文件下载)
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded :
另外一种常见的媒体格式是上传文件之时使用的:
- multipart/form-data : 需要在表单中进行文件上传时,就需要使用该格式
3.3 响应处理
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
__author__ = "A.L.Kun"
__file__ = "demo01.py"
__time__ = "2022/9/9 7:55"
import httpx
resp = httpx.request("GET", "https://www.baidu.com")
if resp.status_code == httpx.codes.OK:
print(resp.text) # 如果请求成功
print(resp.raise_for_status()) # 判断响应是否成功,成功返回None,失败则报错
3.4 流式响应
对于大型下载,您可能希望使用不会一次将整个响应主体加载到内存中的流式响应。
您可以流式传输响应的二进制内容…
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
__author__ = "A.L.Kun"
__file__ = "demo01.py"
__time__ = "2022/9/9 7:55"
import httpx
with httpx.stream("GET", "https://www.example.com") as r:
for data in r.iter_bytes(): # 流式传输响应的二进制内容
# for text in r.iter_text(): # 获取全部的文本内容
# for line in r.iter_lines(): # 逐行获取传输响应的文本内容
# for chunk in r.iter_raw(): # 获取编码前的原始数据
# if r.headers['Content-Length'] < TOO_LONG: # 有条件的加载内容
print(data)
注意:
如果您以任何这些方式使用流式响应,则response.contentandresponse.text属性将不可用
3.5 cookie
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
__author__ = "A.L.Kun"
__file__ = "demo01.py"
__time__ = "2022/9/9 7:55"
import httpx
# 获取cookie
r = httpx.get('https://httpbin.org/cookies/set?chocolate=chip')
print(r.cookies['chocolate']) # 获取请求中的cookie
# 设置cookie
cookies_1 = {"peanut": "butter"}
cookies_2 = httpx.Cookies()
cookies_2.set('cookie_on_domain', 'hello, there!', domain='httpbin.org')
cookies_2.set('cookie_off_domain', 'nope.', domain='example.org')
r = httpx.get('http://httpbin.org/cookies', cookies=cookies_2)
print(r.json())
3.6 重定向
默认情况下,HTTPX不会跟随所有 HTTP 方法的重定向,尽管这可以显式启用。
如,GitHub 将所有 HTTP 请求重定向到 HTTPS。
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
__author__ = "A.L.Kun"
__file__ = "demo01.py"
__time__ = "2022/9/9 7:55"
import httpx
r = httpx.get('http://github.com/')
print(r.status_code)
print(r.history) # 查看重定向的记录
print(r.next_request) # 获取到重定向以后的请求对象
resp = httpx.Client().send(r.next_request) # 对请求对象发送请求
print(resp.text)
那么,我们可不可以跟踪这个重定向呢?其实是可以的:
您可以使用参数修改默认重定向处理follow_redirects
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
__author__ = "A.L.Kun"
__file__ = "demo01.py"
__time__ = "2022/9/9 7:55"
import httpx
r = httpx.get('http://github.com/', follow_redirects=True)
print(r.history) # 查看重定向记录
print(r.url) # 获取请求的url
print(r.text) # 获取请求数据
3.7 超时和验证
HTTPX 默认包含所有网络操作的合理超时,这意味着如果连接没有正确建立,那么它应该总是引发错误而不是无限期挂起。
网络不活动的默认超时为五秒。您可以将值修改为或多或少严格:
httpx.get('https://github.com/', timeout=0.001) # 同时也可以禁止超时行为
httpx.get('https://github.com/', timeout=None)
HTTPX 支持基本和摘要 HTTP 身份验证。
要提供基本身份验证凭据,请将纯文本str或bytes对象的 2 元组作为auth参数传递给请求函数:
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
__author__ = "A.L.Kun"
__file__ = "demo01.py"
__time__ = "2022/9/9 7:55"
import httpx
httpx.get("https://example.com", auth=("my_user", "password123")) # 验证方法一
auth = httpx.DigestAuth("my_user", "password123") # 验证方法二
httpx.get("https://example.com", auth=auth)
二、 客户端
1、 特性
如果您来自 Requests,httpx.Client()您可以使用它来代替requests.Session().
其功能:
当您使用快速入门指南中记录的顶级 API 发出请求时,HTTPX 必须为每个请求建立一个新连接(连接不被重用)。随着对主机的请求数量增加,这很快就会变得低效。
另一方面,Client实例使用HTTP 连接池。这意味着当您向同一主机发出多个请求时,Client将重用底层 TCP 连接,而不是为每个请求重新创建一个。
与使用顶级 API 相比,这可以带来显着的性能提升,包括:
- 减少请求之间的延迟(无握手)。
- 减少 CPU 使用率和往返次数。
- 减少网络拥塞。
额外功能:
Client实例还支持顶级 API 中不可用的功能,例如:
- 跨请求的 Cookie 持久性。
- 跨所有传出请求应用配置。
- 通过 HTTP 代理发送请求。
- 使用HTTP/2。
# 使用方法1
with httpx.Client() as client:
...
# 使用方法2
client = httpx.Client()
try:
...
finally:
client.close()
2、 发出请求
一旦有了,就可以使用,等Client发送请求。例如:.get() .post() ,其传递参数的方法都一样,要注意一点的是,在实例化Client的时候,可以传入请求参数,使得这个局部作用域内可以共享这些参数,跨请求共享配置:
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
__author__ = "A.L.Kun"
__file__ = "demo01.py"
__time__ = "2022/9/9 7:55"
import httpx
# 共用请求头
url = 'http://httpbin.org/headers'
headers = {'user-agent': 'my-app/0.0.1'}
with httpx.Client(headers=headers) as client:
# 这里面的所有请求的请求头都包含{'user-agent': 'my-app/0.0.1'}
r = client.get(url)
print(r.json()['headers']['User-Agent'])
# 共用 + 私有
headers = {'X-Auth': 'from-client'}
params = {'client_id': 'client1'}
with httpx.Client(headers=headers, params=params) as client:
headers_ = {'X-Custom': 'from-request'}
params_ = {'request_id': 'request1'}
r = client.get('https://example.com', headers=headers_,
params=params_) # 这个参数结合了headers+headers_ , params+params_,但是只限于params和headers,对于所有其他参数,内部请求级别的值优先
print(r.request.url)
print(r.request.headers['X-Auth'])
print(r.request.headers['X-Custom'])
# 优先级
with httpx.Client(auth=('tom', 'mot123')) as client:
r = client.get('https://example.com', auth=('alice', 'ecila123'))
_, _, auth = r.request.headers['Authorization'].partition(' ')
import base64
print(base64.b64decode(auth))
3、 其他配置
此外,Client接受一些在请求级别不可用的配置选项。
例如,base_url允许您为所有传出请求添加 URL:
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
__author__ = "A.L.Kun"
__file__ = "demo01.py"
__time__ = "2022/9/9 7:55"
import httpx
with httpx.Client(base_url='http://httpbin.org') as client:
r = client.get('/headers')
print(r.request.url)
设置编码:
import httpx
import chardet # pip install chardet
def autodetect(content):
return chardet.detect(content).get("encoding") # 对html的编码进行自动的检测
# Using a client with character-set autodetection enabled.
client = httpx.Client(default_encoding=autodetect)
response = client.get(...)
print(response.encoding) # This will either print the charset given in
# the Content-Type charset, or else the auto-detected
# character set.
print(response.text)
4、 python_web
您可以将httpx客户端配置为使用 WSGI 协议直接调用 Python Web 应用程序。
这对于两个主要用例特别有用:
- 在测试用例
httpx中用作客户端。 - 在测试期间或在开发/登台环境中模拟外部服务。
下面是一个针对 Flask 应用程序集成的示例:
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
__author__ = "A.L.Kun"
__file__ = "demo01.py"
__time__ = "2022/9/9 7:55"
from flask import Flask
import httpx
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route("/")
def hello():
return "Hello World!"
with httpx.Client(app=app, base_url="http://localhost") as client:
# base_url:指定app的根路由
r = client.get("/") # 获取根路由下的响应数据
print(r.text)
assert r.status_code == 200 # 断言
assert r.text == "Hello World!"
对于一些更复杂的情况,您可能需要自定义 WSGI 传输。这使您可以:
- 通过设置检查 500 个错误响应而不是引发异常
raise_app_exceptions=False。 script_name通过设置(WSGI)将 WSGI 应用程序挂载到子路径。remote_addr通过设置(WSGI)为请求使用给定的客户端地址。
# Instantiate a client that makes WSGI requests with a client IP of "1.2.3.4".
transport = httpx.WSGITransport(app=app, remote_addr="1.2.3.4")
with httpx.Client(transport=transport, base_url="http://testserver") as client:
...
5、 Request对象
为了最大限度地控制通过网络发送的内容,HTTPX 支持构建显式Request实例:
request = httpx.Request("GET", "https://example.com")
要将Request实例分派到网络,请创建一个Client实例并使用.send():
with httpx.Client() as client:
response = client.send(request)
...
如果您需要以默认Merging of parameters不支持的方式混合客户端级别和请求级别选项,您可以使用.build_request()然后对Request实例进行任意修改。例如:
headers = {"X-Api-Key": "...", "X-Client-ID": "ABC123"}
with httpx.Client(headers=headers) as client:
request = client.build_request("GET", "https://api.example.com")
print(request.headers["X-Client-ID"]) # "ABC123"
# Don't send the API key for this particular request.
del request.headers["X-Api-Key"]
response = client.send(request)
...
6、 钩子函数
HTTPX 允许您向客户端注册“事件挂钩”,每次发生特定类型的事件时都会调用这些挂钩。
目前有两个事件挂钩:
request- 在请求完全准备好之后,但在它被发送到网络之前调用。通过request实例。response- 在从网络获取响应之后但在返回给调用者之前调用。通过response实例。
这些允许您安装客户端范围的功能,例如日志记录、监视或跟踪。
def log_request(request):
print(f"Request event hook: {request.method} {request.url} - Waiting for response")
def log_response(response):
request = response.request
print(f"Response event hook: {request.method} {request.url} - Status {response.status_code}")
client = httpx.Client(event_hooks={'request': [log_request], 'response': [log_response]}) # 绑定钩子函数
您还可以使用这些挂钩来安装响应处理代码,例如这个示例,它创建了一个总是httpx.HTTPStatusError 在 4xx 和 5xx 响应时引发的客户端实例。
def raise_on_4xx_5xx(response):
response.raise_for_status()
client = httpx.Client(event_hooks={'response': [raise_on_4xx_5xx]})
钩子也允许修改request和response对象。
def add_timestamp(request):
request.headers['x-request-timestamp'] = datetime.now(tz=datetime.utc).isoformat()
client = httpx.Client(event_hooks={'request': [add_timestamp]})
事件挂钩必须始终设置为可调用列表,并且您可以为每种类型的事件注册多个事件挂钩。
除了能够在实例化客户端时设置事件挂钩外,还有一个.event_hooks属性允许您检查和修改已安装的挂钩。
client = httpx.Client() client.event_hooks['request'] = [log_request] client.event_hooks['response'] = [log_response, raise_on_4xx_5xx]
如果您使用 HTTPX 的异步支持,那么您需要注意注册的钩子
httpx.AsyncClient必须是异步函数,而不是普通函数。
7、 进度条
如果您需要监控大型响应的下载进度,您可以使用响应流并检查response.num_bytes_downloaded属性。
此接口是正确确定下载进度所必需的,因为如果使用 HTTP 响应压缩,则返回的总字节数response.content或response.iter_content()不会总是与响应的原始内容长度相对应。
例如,tqdm在下载响应时使用库显示进度条可以这样完成……
import tempfile
import httpx
from tqdm import tqdm
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile() as download_file: # 创建一个临时文件。程序结束就删除
url = "https://speed.hetzner.de/100MB.bin"
with httpx.stream("GET", url) as response: # 使用流发送请求
total = int(response.headers["Content-Length"])
with tqdm(total=total, unit_scale=True, unit_divisor=1024, unit="B") as progress:
num_bytes_downloaded = response.num_bytes_downloaded
for chunk in response.iter_bytes():
download_file.write(chunk)
progress.update(response.num_bytes_downloaded - num_bytes_downloaded)
num_bytes_downloaded = response.num_bytes_downloaded
8、 .netrc 支持
HTTPX 支持 .netrc 文件。在trust_env=True某些情况下,如果未定义 auth 参数,HTTPX 会尝试将 auth 从 .netrc 文件添加到请求的标头中。
NETRC 文件在客户端发出的请求之间进行缓存。如果您需要刷新缓存(例如,因为 NETRC 文件已更改),您应该创建一个新客户端或重新启动解释器。
默认trust_env为真。设置为假:
httpx.get('https://example.org/', trust_env=False)
如果NETRCenvironment 为空,HTTPX 会尝试使用默认文件。( ~/.netrc, ~/_netrc)
改变NETRC环境:
import os os.environ["NETRC"] = "my_default_folder/.my_netrc"
.netrc 文件内容示例:
machine netrcexample.org login example-username password example-password ...
使用Client实例时,trust_env应该在客户端本身上设置,而不是在请求方法上:
client = httpx.Client(trust_env=False)
三、 代理
1、 简介
HTTPX 支持通过在proxies客户端初始化或顶级 API 函数(如httpx.get(..., proxies=...).
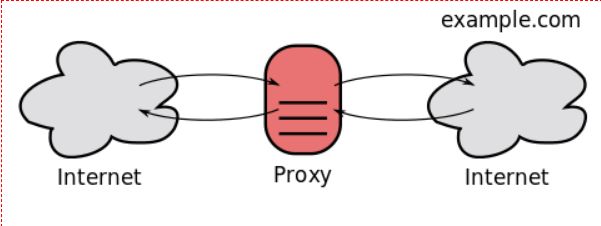
代理如何工作的图表(来源:维基百科)。左侧的“Internet”blob 可能是example.com通过代理请求的 HTTPX 客户端。
2、 使用方法
2.1 简单使用
要将所有流量(HTTP 和 HTTPS)路由到位于 的代理http://localhost:8030,请将代理 URL 传递给客户端…
with httpx.Client(proxies="http://localhost:8030") as client:
...
对于更高级的用例,传递一个 proxies dict。例如,要将 HTTP 和 HTTPS 请求路由到 2 个不同的代理,分别位于http://localhost:8030和http://localhost:8031,传递一个dict代理 URL:
proxies = {
"http://": "http://localhost:8030",
"https://": "http://localhost:8031",
}
with httpx.Client(proxies=proxies) as client:
...
2.2 验证
代理凭据可以作为userinfo代理 URL 的部分传递。例如:
proxies = {
"http://": "http://username:password@localhost:8030",
# ...
}
2.3 路由
HTTPX 提供了细粒度的控制来决定哪些请求应该通过代理,哪些不应该。此过程称为代理路由。
该proxies字典将 URL 模式(“代理键”)映射到代理 URL。HTTPX 将请求的 URL 与代理密钥进行匹配,以决定应该使用哪个代理(如果有)。从最具体的代理密钥(例如https://:)到最不具体的代理密钥(例如 )进行匹配https://。
HTTPX 支持基于scheme、domain、port或这些的组合的路由代理。
2.3.1 通配符路由
通过代理路由所有内容…
proxies = {
"all://": "http://localhost:8030",
}
2.3.2 方案路由
通过一个代理路由 HTTP 请求,通过另一个代理路由 HTTPS 请求…
proxies = {
"http://": "http://localhost:8030",
"https://": "http://localhost:8031",
}
2.3.3 域路由
# 代理域“example.com”上的所有请求,让其他请求通过...
proxies = {
"all://example.com": "http://localhost:8030",
}
# 代理域“example.com”上的 HTTP 请求,让 HTTPS 和其他请求通过...
proxies = {
"http://example.com": "http://localhost:8030",
}
# 将所有请求代理到“example.com”及其子域,让其他请求通过...
proxies = {
"all://*example.com": "http://localhost:8030",
}
# 代理所有请求到“example.com”的严格子域,让“example.com”等请求通过...
proxies = {
"all://*.example.com": "http://localhost:8030",
}
2.3.4 端口路由
将端口 1234 上的 HTTPS 请求代理到“example.com”…
proxies = {
"https://example.com:1234": "http://localhost:8030",
}
代理端口 1234 上的所有请求…
proxies = {
"all://*:1234": "http://localhost:8030",
}
2.3.5 无代理支持
也可以定义不应通过代理路由的请求。
为此,请None作为代理 URL 传递。例如…
proxies = {
# Route requests through a proxy by default...
"all://": "http://localhost:8031",
# Except those for "example.com".
"all://example.com": None,
}
3、 区别
3.1 前言
有细心的朋友就发现了,我前面不是说大部分参数requests库一样么?怎么代理的有点不一样呢?注意啊,我的意思是大部分一样,这样便于大家理解和记忆。
那么,这个代理的区别在哪呢?
我们来看一下requests的代理的使用
3.2 requests代理
使用 proxies任何请求方法的参数配置单个请求, 确保在存在环境代理的情况下使用代理:
# 普通的代理
import requests
proxies = {
'http': 'http://10.10.1.10:3128',
'https': 'http://10.10.1.10:1080',
}
requests.get('http://example.org', proxies=proxies)
# 权限认证
proxies = {'http': 'http://user:[email protected]:3128/'}
# 给特定的方案和主机提供代理,这将匹配对给定方案和确切主机名的任何请求。
proxies = {'http://example.org': 'http://10.10.1.10:5323'} # 其为一个简单的路由功能,进行简单的代理分发
3.3 总结
通过回顾requests代理,相信大家就发现了区别了:
在代理字典中,httpx代理的键最后面有两个斜杆,而requests代理没有
我的理解是,这应该是各自第三方库的语法没有一致的标准,这造成了代理ip的语法不一
比如,aiohttp的代理是这样使用的:
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
proxy_auth = aiohttp.BasicAuth('user', 'pass')
async with session.get("http://python.org",
proxy="http://proxy.com",
proxy_auth=proxy_auth) as resp:
print(resp.status)
注意:
proxy_auth = aiohttp.BasicAuth('your_user', 'your_password')其为权限认证,当然,权限认证的方法还可以在urlStr中,proxy = 'http://your_proxy_url:your_proxy_port'
以及scrapy框架的代理是这样使用的:
def start_requests(self):
for url in self.start_urls:
return Request(url=url, callback=self.parse,
headers={"User-Agent": "scrape web"},
meta={"proxy": "http:/154.112.82.262:8050"})
# 权限认证:
# request.headers["Proxy-Authorization"] = basic_auth_header("", "")
它是给request中的meta对象添加代理:
request.meta["proxy"] = "http://192.168.1.1:8050"
当然,如果大家有更好的看法的话,可以私信我哦!
同时,httpx的代理功能更为全面,其可以让我们的代码更加优雅!
四、 异步客户端
1、 简介
HTTPX 默认提供标准的同步 API,但如果需要,还可以选择异步客户端。
异步是一种比多线程更高效的并发模型,并且可以提供显着的性能优势并支持使用长寿命的网络连接,例如 WebSockets。
如果您使用的是异步 Web 框架,那么您还需要使用异步客户端来发送传出的 HTTP 请求。
发送异步请求:
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
__author__ = "A.L.Kun"
__file__ = "demo01.py"
__time__ = "2022/9/9 7:55"
import asyncio
import httpx
async def test():
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
r = await client.get("https://www.baidu.com")
print(r)
tasks = [test() for i in range(100)]
asyncio.run(asyncio.wait(tasks))
2、 API 差异
如果您使用的是异步客户端,那么有一些 API 使用异步方法。
2.1 发出请求
请求方法都是异步的,因此您应该response = await client.get(...)对以下所有内容使用样式:
- AsyncClient.get(url, ...)
- AsyncClient.options(url, ...)
- AsyncClient.head(url, ...)
- AsyncClient.post(url, ...)
- AsyncClient.put(url, ...)
- AsyncClient.patch(url, ...)
- AsyncClient.delete(url, ...)
- AsyncClient.request(method, url, ...)
- AsyncClient.send(request, ...)
2.2 打开和关闭客户
async with httpx.AsyncClient()如果您需要上下文管理的客户端,请使用…
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
...
或者,await client.aclose()如果您想明确关闭客户端,请使用:
client = httpx.AsyncClient() ... await client.aclose()
2.3 流式响应
该AsyncClient.stream(method, url, ...)方法是一个异步上下文块
client = httpx.AsyncClient()
async with client.stream('GET', 'https://www.example.com/') as response:
async for chunk in response.aiter_bytes():
...
异步响应流方法是:
- Response.aread()- 用于有条件地读取流块内的响应。
- Response.aiter_bytes()- 用于将响应内容作为字节流式传输。
- Response.aiter_text()- 用于将响应内容作为文本流式传输。
- Response.aiter_lines()- 用于将响应内容流式传输为文本行。
- Response.aiter_raw()- 用于流式传输原始响应字节,而不应用内容解码。
- Response.aclose()- 用于关闭响应。你通常不需要这个,因为.streamblock 在退出时会自动关闭响应。
对于上下文块使用不实例的情况,可以通过使用 发送实例来进入“手动模式Request”client.send(..., stream=True)。
import httpx
from starlette.background import BackgroundTask
from starlette.responses import StreamingResponse
client = httpx.AsyncClient()
async def home(request):
req = client.build_request("GET", "https://www.example.com/")
r = await client.send(req, stream=True)
return StreamingResponse(r.aiter_text(), background=BackgroundTask(r.aclose))
使用这种“手动流模式”时,作为开发人员,您有责任确保
Response.aclose()最终调用它。不这样做会使连接保持打开状态,很可能导致资源泄漏。
2.4 流式传输请求
async def upload_bytes():
... # yield byte content
await client.post(url, content=upload_bytes())
3、 异步环境
3.1 asyncio
AsyncIO 是 Python 的内置库 ,用于使用 async/await 语法编写并发代码。
import asyncio
import httpx
async def main():
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
response = await client.get('https://www.example.com/')
print(response)
asyncio.run(main())
3.2 trio
Trio 是一个替代异步库,围绕结构化并发原则设计。
import httpx
import trio
async def main():
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
response = await client.get('https://www.example.com/')
print(response)
trio.run(main)
trio必须安装该软件包才能使用 Trio 后端。
3.3 anyio
AnyIO 是一个异步网络和并发库,可在asyncio或trio. 它与您选择的后端的本机库融合在一起(默认为asyncio)。
import httpx
import anyio
async def main():
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
response = await client.get('https://www.example.com/')
print(response)
anyio.run(main, backend='trio')
4、 python_web
正如httpx.Client允许您直接调用 WSGI Web 应用程序一样,httpx.AsyncClient该类允许您直接调用 ASGI Web 应用程序。
我们以这个 Starlette 应用为例:
from starlette.applications import Starlette
from starlette.responses import HTMLResponse
from starlette.routing import Route
async def hello(request):
return HTMLResponse("Hello World!")
app = Starlette(routes=[Route("/", hello)])
我们可以直接向应用程序发出请求,如下所示:
import httpx
async with httpx.AsyncClient(app=app, base_url="http://testserver") as client:
r = await client.get("/")
assert r.status_code == 200
assert r.text == "Hello World!"
对于一些更复杂的情况,您可能需要自定义 ASGI 传输。这使您可以:
- 通过设置检查 500 个错误响应而不是引发异常
raise_app_exceptions=False。 - 通过设置将 ASGI 应用程序挂载到子路径
root_path。 - 通过设置为请求使用给定的客户端地址
client。
例如:
# Instantiate a client that makes ASGI requests with a client IP of "1.2.3.4",
# on port 123.
transport = httpx.ASGITransport(app=app, client=("1.2.3.4", 123))
async with httpx.AsyncClient(transport=transport, base_url="http://testserver") as client:
...
其余更多内容,请到官方文档查看!https://www.python-httpx.org/
总结
到此这篇关于python新一代网络请求库之python-httpx库操作指南的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关新一代网络请求库python-httpx库内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!