【Android进阶】6、多 Activity 的 APP
文章目录
-
- 6.1 启动子Activity
- 6.2 从子Activity返回结果
- 6.3 父Activity处理返回的结果
- 6.4 Activity的管理和使用
多 Activity 的 APP,主要涉及启动一个新的 Activity, 并向其传递数据
我们添加一个新的Activity, 可看到题目答案, 效果如下:

6.1 启动子Activity
首先在 strings.xml 中添加字符串资源
<string name="warning_text">您确定要这样吗?string>
<string name="show_answer_button">查看答案string>
<string name="cheat_button">您在作弊!string>
<string name="judgment_toast">作弊是不对的.string>
创建新的 CheatActivity 布局如下:

AndroidStudio会自动在AndroidManifest.xml中添加CheatActivity的声明
<activity
android:name=".CheatActivity"
android:exported="false" />
添加一个按钮如下:
<Button
android:id="@+id/cheat_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="24dp"
android:text="@string/cheat_button" />
调用按钮
private lateinit var cheatButton: Button
cheatButton = findViewById(R.id.cheat_button)
cheatButton.setOnClickListener {
// Start Cheat Activity
}
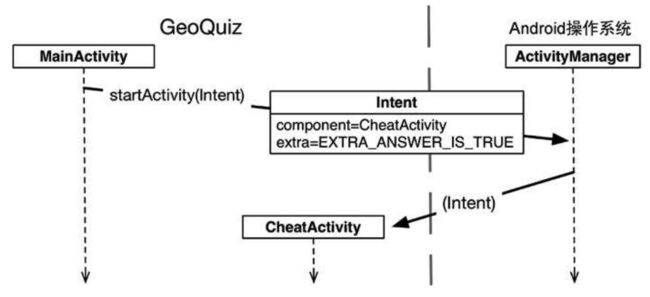
当调用StartActivity(Intent)时, 会发请求给操作系统的ActivityManager, 其会创建Activity实例并调用起onCreate(Bundle?)函数:
Intent的构造函数是Intent(packageContext: Context, class: Class), 调用方式如下
cheatButton.setOnClickListener {
// Start CheatActivity
val intent = Intent(this, CheatActivity::class.java)
startActivity(intent)
}
传入Intent构造函数的Class类型参数告诉ActivityManager应该启动哪个activity。Context参数告诉ActivityManager在哪里可以找到它。
在启动activity前,ActivityManager会确认指定的Class是否已在manifest配置文件中声明。如果已完成声明,则启动activity,应用正常运行。反之,则抛出ActivityNotFoundException异常,应用崩溃。这就是必须在manifest配置文件中声明应用的全部activity的原因。
class CheatActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
...
}
companion object {
fun newIntent(packageContext: Context, answerIsTrue: Boolean):
Intent {
return Intent(packageContext,CheatActivity::class.java).apply {
putExtra(EXTRA_ANSWER_IS_TRUE, answerIsTrue)
}
}
}
}
调用方式如下:
cheatButton.setOnClickListener {
val answerIsTrue = quizViewModel.currentQuestionAnswer
val intent = CheatActivity.newIntent(this@MainActivity, answerIsTrue)
startActivity(intent)
}
根据传入的参数显示对应的TextView的逻辑如下:
class CheatActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private var answerIsTrue = false
private lateinit var answerTextView: TextView
private lateinit var showAnswerButton: Button
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_cheat)
answerIsTrue = intent.getBooleanExtra(
EXTRA_ANSWER_IS_TRUE,
false
)
answerTextView = findViewById(R.id.answer_text_view)
showAnswerButton = findViewById(R.id.show_answer_button)
showAnswerButton.setOnClickListener {
val answerText = when {
answerIsTrue -> R.string.true_button
else -> R.string.false_button
}
answerTextView.setText(answerText)
}
}
companion object {
fun newIntent(packageContext: Context, answerIsTrue: Boolean):
Intent {
return Intent(packageContext, CheatActivity::class.java).apply {
putExtra(EXTRA_ANSWER_IS_TRUE, answerIsTrue)
}
}
}
}
6.2 从子Activity返回结果
Activity.startActivityForResult(Intent, Int)函数的第一个参数同前述的intent。第二个参数是请求代码。
请求代码是先发送给子activity,然后再返回给父activity的整数值,由用户定义。在一个activity启动多个不同类型的子activity且需要判断消息回馈方时,就会用到该请求代码。
虽然MainActivity只启动一种类型的子activity,但为应对未来的需求变化,现在就应设置请求代码常量。
private const val REQUEST_CODE_CHEAT = 0
startActivityForResult(intent, REQUEST_CODE_CHEAT)
子Activity可通过如下两种方式返回给父Activity, 其中resultCode可为一下常量之一(Activity.RESULT_OK和Activity.RESULT_CANCELED)
setResult(resultCode: Int)
setResult(resultCode: Int, data: Intent)
按如下返回给父Activity
showAnswerButton.setOnClickListener {
val answerText = when {
answerIsTrue -> R.string.true_button
else -> R.string.false_button
}
answerTextView.setText(answerText)
setAnswerShownButton(true)
}
private fun setAnswerShownButton(isAnswerShown: Boolean) {
val data = Intent().apply{
putExtra(EXTRA_ANSWER_SHOWN, isAnswerShown)
}
setResult(Activity.RESULT_OK, data)
}
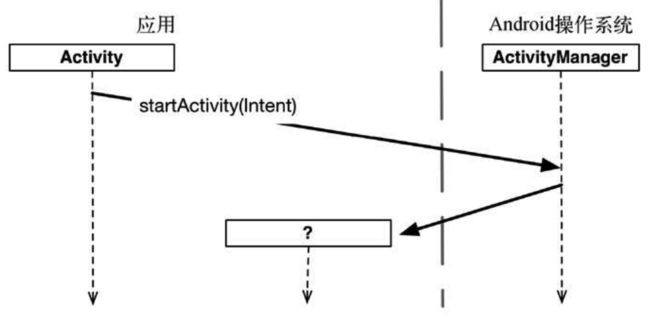
当按Back键返回桌面时, ActivityManager会调用父Activity的onActivityResult(requestCode: Int, resultCode: Int, data: Intent)函数, 如下图:
6.3 父Activity处理返回的结果
override fun onActivityResult(
requestCode: Int,
resultCode: Int,
data: Intent?
) {
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data)
if (resultCode != Activity.RESULT_OK) {
return
}
if (requestCode == REQUEST_CODE_CHEAT) {
quizViewModel.isCheater =
data?.getBooleanExtra(EXTRA_ANSWER_SHOWN, false) ?: false
}
}
private fun checkAnswer(userAnswer: Boolean) {
val correctAnswer = quizViewModel.currentQuestionAnswer
val messageResId = when {
quizViewModel.isCheater -> R.string.judgment_toast
userAnswer == correctAnswer -> R.string.correct_toast
else -> R.string.incorrect_toast
}
Toast.makeText(this, messageResId, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show()
}
效果如下
6.4 Activity的管理和使用
来看看当我们在各activity间往返的时候,操作系统层面到底发生了什么。首先,在桌面启动器中点击GeoQuiz应用时,操作系统并没有启动应用,而只是启动了应用中的一个activity。确切地说,它启动了应用的launcher activity。在GeoQuiz应用中,MainActivity就是它的launcher activity。
使用应用向导创建GeoQuiz应用以及MainActivity时,MainActivity默认被设置为launcher activity。配置文件中,MainActivity声明的intent-filter元素节点下,可看到MainActivity被指定为launcher activity. AndroidManifest.xml如下
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
package="com.bignerdranch.android.geoquiz">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:dataExtractionRules="@xml/data_extraction_rules"
android:fullBackupContent="@xml/backup_rules"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme.GeoQuiz"
tools:targetApi="31">
<activity
android:name=".CheatActivity"
android:exported="false" />
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
intent-filter>
activity>
application>
manifest>
各Activity的栈关系如下图:
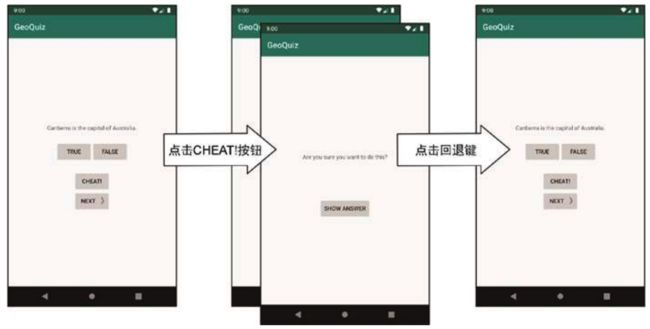
按回退键,CheatActivity实例被弹出栈外,MainActivity重新回到栈顶部。在CheatActivity中调用Activity.finish()函数同样可以将CheatActivity从栈里弹出。
如果运行GeoQuiz应用,在MainActivity界面按回退键,MainActivity将从栈里弹出,我们将退回到GeoQuiz应用运行前的画面, 如下两张图
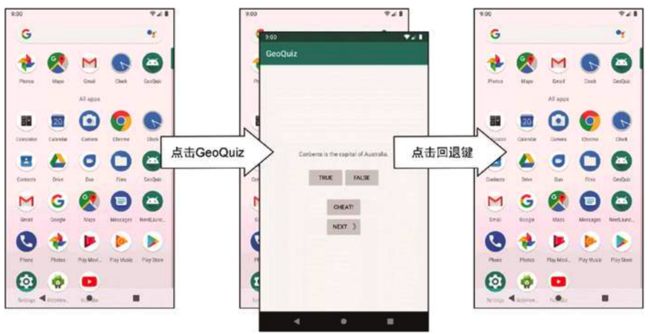
其实, ActivityManager维护着一个非特定应用独享的后退栈。所有应用的activity都共享该后退栈。这也是将ActivityManager设计成操作系统级的activity管理器来负责启动应用activity的原因之一。显然,后退栈是作为一个整体共享于操作系统及设备,而不单单用于某个应用。