unittest和pytest测试框架基础
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45912307/article/details/124078581
unittest和pytest测试框架基础
-
- 01 单元测试
- 02 unittest
-
- 2.1 unittest编写规范
- 2.2 测试框架结构
-
- 2.2.1 前后置
- 2.2.2 命名方法
- 2.2.3 断言&断言结果
- 2.2.4.加载测试用例
- 2.2.5 unittest报告
- 2.2.6 运行方式
- 2.2.7 执行顺序
- 2.3 测试用例执行过程
- 2.3 unittestdemo
- 03 pytest
-
- 3.1 pytest 介绍
- 3.2 pytest安装依赖包
- 3.3 pytest用例的识别和运行
- 3.4 pytest 常用插件及用法
-
- 3.4.1 pytest-rerunfailures 失败重运行
- 3.4.2 pytest-assume 支持执行多条失败断言
- 3.4.3 pytest.fixture()
- 3.4.4 pytest.mark.skip()
- 3.4.5 pytest.mark.xfail()
- 3.4.6 pytest.mark.标签名 打标签
- 3.4.7 pytest-html 测试报告
- 3.4.8 pytest-allure 测试报告
- 3.4.9 pytest-ordering
- 3.4.10 pytest-xdist 多线程与分布式执行
- 3.5 pytest框架结构
- 03 unittest和pytest和区别
- git demo地址:
01 单元测试
1. 什么是单元测试?
- 单元测试是开发者编写的一小段代码,用于检验被测代码的一个很小的、很明确的功能是否正确。通常而言,一个单元测试是用于判断某个特定条件(或者场景)下某个特定函数的行为。
2. 单元测试什么时候执行?
- 开发阶段,单元测试介入越早后续集成测试遇到的问题越少
3. 单元测试由谁负责?
- 由程序员负责
4. python的主要单元测试框架?
Unittest:python内置的标准类库;Pytest:丰富、灵活的测试框架,语法简单,可以结合allure生成一个炫酷的测试报告;Nose:是对unittest的扩展,使得python的测试更加简单。Mock:unittest.mock是用来测试python的库
02 unittest
2.1 unittest编写规范
1. Unittest提供了了test cases、test suites、test fixtures、test runner相关的组件
2. 编写规范
- 测试模块首先
import unittest - 测试类必须继承
unittest.TestCase - 测试方法必须以"test_"开头
- 模块名字,类名没有特殊要求
2.2 测试框架结构
2.2.1 前后置
1. 类方法
setUpClass()只会在测试用例类执行执行一次tearDownClass()只会在测试用例类执行后执行一次- 如果想要在所有case执行之前准备一次环境,并在所有case执行结束之后再清理环境,可以用
setUpClass()与tearDownClass()。比如:数据库连接及销毁、cookie获取
2. 函数方法
setUp(): 每次测试用例方法执行之前都会执行的方法。tearDown():每次用例方法执行之后都会自动执行的方法setUp用来为测试准备环境;tearDown用来清理环境。
2.2.2 命名方法
1. 模块名:以test开头
2. 类名:以Test开头
3. 方法名:以test开头
- 如果想有些方法不在本次执行使用
@unittest.skip
2.2.3 断言&断言结果
1.断言
self.assertEqual(expected, actual):提示更加具体,会把预期结果和实际结果打印出来self.assertTrue(expected == actual):预期结果和实际结果没有具体提示
2. 断言结果
- “.”表示通过
- “F” False 表示断言没有通过
- “E” Error 表示程序内部发生了错误
2.2.4.加载测试用例
1.方式1:
- suite = loader.discover(start_dir=‘./test_case’,pattern=‘test*.py’)
- suite = unittest.defaultTestLoader.discover(start_dir=‘./test_case’,pattern=‘test*.py’)
- 参数解析
discover可以一次调用多个脚本start_dir被测试脚本的路径pattern脚本名称匹配规则
2.方式2: 只测试某个具体的模块、功能,使用 loaderTestsFromTestCase、loaderTestsFromModule
3.方式3:加载指定测试类 loader.loadTestsFromTestCase(测试用例类名)
import os
import time
import unittest
# 1. 初始化testloader(加载器)
loader = unittest.TestLoader()
# 2.1 加载方式1: 加载全部测试用例
# 2.1 suite = testloader.discover(文件夹路径,'test_*.py) 发现(加载)用例
# 2.2 加载方式2:加载多个模块测试用例
# 加载多个模块的测试用例,保存到测试套件当中
suite1 = loader.loadTestsFromModule(模块名)
suite2= loader.loadTestsFromTestCase(类名)
suite3 = loader.loadTestsFromName(name,模块名) # name:传入一个模块或测试用例类或测试方法,或一个可调用的对象
suite_list = [suite1,suite2,suite3]
# 将多个测试套件合并添加第一个总的测试套件中,初始化一个空的测试套件
total_suite = unittest.TestSuite()
total_suite.addTests(suite_list)
# suite.addTests([类名1('函数名1'),类名1('函数名2'),类名1('函数名3'),类名2,模块名1,模块名2,....])
# 加载方式3:加载指定测试类
# suite = loader.loadTestsFromTestCase(测试用例类名)
# 3. 初始化运行器
runner = unittest.TextTestRunner()
# 4. 运行测试用例 runner.run(suite)
runner.run(total_suite)
2.2.5 unittest报告
# 模块导入
from unittestreport.HTMLTestRunnerNew import HTMLTestRunner
# 报告存放路径
report_path = os.path.join(root_path,'report')
if not os.path.exists(report_path):
os.mkdir(report_path)
# 报告名称
ts = time.strftime('%Y%m%d%H%M%S',time.localtime(time.time()))
file_name = 'api_test_{}.html'.format(ts)
file_path = os.path.join(report_path,file_name)
with open(file_path,'w',encoding='utf8') as f:
# 初始化运行器,以普通文本生成测试报告 TextTestRunner
runner = HTMLTestRunner(
stream=f,
verbosity=2,
title='xxx系统测试报告',
description='接口自动化测试报告',
tester='jsonLiu'
# 6.运行测试用例 runner.run(suite)
runner.run(total_suite)
)
2.2.6 运行方式
1. unittest 右键 --> run ‘模块名|方法名|类名’,pycharm自带
- pycharm运行注意事项:
- 在空行处右击,执行单个模块
- 在类名上,执行单个测试类
- 在方法名上,执行单个测试用例
- tips:注意在指定的位置运行,空行的地方运行
2. python 代码 main方式:unittest.main()
3. 命令行方式运行python -m unittest
- python -m unittest test_module1 test_module2
- python -m unittest test_module.TestClass
- python -m unittest test_module.TestClass.test_method
- python -m unittest tests/test_*.py
2.2.7 执行顺序
1. 遵循 ascii 编码排序:
- unittest默认顺序是:根据ASCII码的顺序加载测试用例,数字与字母的顺序为:0-9,A-Z,a-z。所以以A开头的测试用例方法会优先执行,以a开头会后执行
- pytest执行基本原则:根据名称的字母逐一进行ASCII比较,越小越先执行。
- 多个测试模块(.py文件)时,根据基本原则执行。
- 一个测试模块(.py文件)中,先执行测试函数,后执行测试类。多个测试类则遵循基本原则,类中的测试方法遵循基本原则。
2. 如果想手工调整测试用例的执行顺序,不同的字母加数字
2.3 测试用例执行过程
- 首先是要写好
TestCase - 然后由
TestLoader加载TestCase到TestSuite - 然后由
TextTestRunner来运行TestSuite - 运行的结果保存在
TextTestResult中 - 整个过程集成在
unittest.main模块中
2.3 unittestdemo
import unittest
class TestUnittestDemo(unittest.TestCase):
@classmethod
def setUpClass(cls) -> None:
print("setUpClass")
def setUp(self) -> None:
print("setUp method")
def tearDown(self) -> None:
print("tearDown method")
@classmethod
def tearDownClass(cls) -> None:
print("tearDownClass")
def test_add(self):
a = 1
b = 2
print("%s-> %s" % (self.__repr__, a + b))
def test_subtraction(self):
a = 1
b = 2
print("%s-> %s" % (self.__repr__, a - b))
def test_sum(self):
print("%s-> %s" % (self.__repr__, sum([i for i in range(100)])))
class TestUnittestDemo02(unittest.TestCase):
def test_mul(self):
print("%s-> %s" % (self.__repr__, 10*20))
if __name__ == '__main__':
# import unittest
import os
import time
from unittestreport.HTMLTestRunnerNew import HTMLTestRunner
# suite = unittest.defaultTestLoader.discover('./test_case', 'test*.py')
loader = unittest.TestLoader()
suite1 = loader.loadTestsFromName('test_add','test_unittest_demo')
suite2 = loader.loadTestsFromModule("test_unittest_demo",pattern='test_subtraction')
suite3 = loader.loadTestsFromTestCase(TestUnittestDemo02)
suite = [suite1,suite2,suite3]
local = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
report_path = os.path.join(local, 'report')
if not os.path.exists(report_path):
os.mkdir(report_path)
ts = time.strftime('%Y%m%d%H%M%S', time.localtime(time.time()))
file_name = 'api_test_{}.html'.format(ts)
file_path = os.path.join(report_path, file_name)
with open(file=file_path, mode='w', encoding='utf8') as f:
runner = HTMLTestRunner(stream=f, verbosity=2, title='xxx项目接口测试报告', description='xxx接口用例', tester='jsonLiu')
runner.run(suite)
03 pytest
3.1 pytest 介绍
1. pytest是一个非常成熟的全功能的Python测试框架
- 简单灵活,容易上手;
- 支持参数化;
- 测试用例的skip和xfail,自动失败重试等处理;
- 能够支持简单的单元测试和复杂的功能测试,还可以用来做selenium /appnium等自动化测试、接口自动化测试(pytest+requests);
- pytest具有很多第三方插件,并且可以自定义扩展,比较好用的如 pytest-allure(完美html测试报告生成),pytest-xdist(多CPU任务并发执行)等;
- 可以很好的和jenkins集成;
2. 官方文档: https://docs.pytest.org/en/7.1.x/index.html
3.2 pytest安装依赖包
pip install -U pytest U升级并安装pip install pytest-sugar运行界面美化pip install pytest-rerunfailures用例失败重试运行pip install pytest-xdist多任务并发执行测试用例pip install pytest-assume允许pytest测试用例中执行多个失败的断言pip intall pytest-html生成html报告pip list查看pytest -h帮助
3.3 pytest用例的识别和运行
1. 测试文件
test_* .py*_test.py
2. 用例识别
Test*类包含的所有test_*的方法(测试类不能带有__init__方法);- 不在class中的所有的
test_*方法
3. pytest也可以执行unittest框架写的用例和方法
4. 终端执行
pytest /py.testpytest -v: (最高级别信息–verbose)打印详细运行日志信息pytest -v -s 文件名:s是带控制台输出结果,也是输出详细pytest 文件名.py:执行单独一个pytest模块pytest 文件名.py::类名:运行某个模块里面某个类pytest 文件名.py::类名:方法名:运行某个模块里面某个类里面的方法pytest -v -k "类名 and not 方法名":跳过运行某个用例- 运行打上这个标记的测试用例:
pytest -m [标记名]@pytest.mark.[标记名]
pytest -x 文件名.py:一旦运行到报错就停止运行pytest --maxfail=[num]:当运行错误达到num的时候就停止运行
5. pycharm方式执行
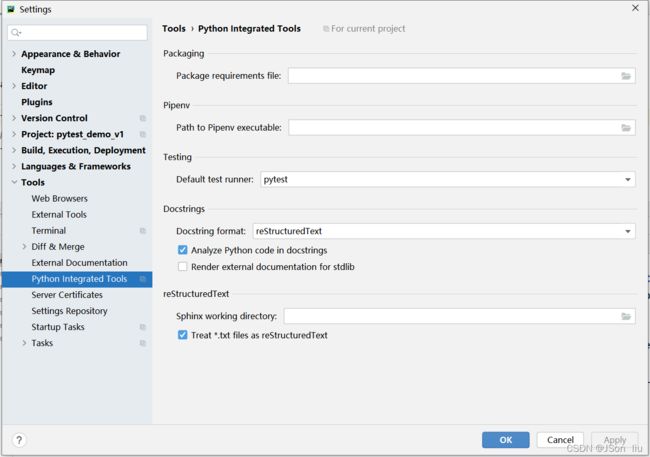
- 打开PyCharm,依次打开
Preferences--->Tools--->Python Integrated Tools,将Testing里的Default test runner选择项选为pytest,保存即可。
- 终端运行:
pytest -v -s 文件名.py::测试类名::测试函数名 - pycharm命令行参数运行
pytest.main()运行所有用例pytest.main("-v -s 模块名::类名")参数和终端方式一样pytest.main(["-v", "模块名", "类名","函数名"])- pytest.main([“-v”, “-m”, “标签名1”,“标签名n”]) # 运行指定的用例
- pycharm 右键运行
3.4 pytest 常用插件及用法
3.4.1 pytest-rerunfailures 失败重运行
1. 场景:
- 测试失败后要重新运行n次,要在重新运行之间添加延迟时间,间隔n秒再运行。
2. 安装`:
- pip install pytest-rerunfailures
3. 执行方式:
- 命令行方式执行:
pytest --reruns 失败重运行次数 -v -s 模块名.pypytest -v --reruns 失败重运行次数 --reruns-delay 延时时间(单位:s)
pytest.main()- 配置文件:修改
pytest.ini文件,添加失败重试参数,即:addopts = -s --reruns 2 --html=./report.html - 参数解释:
-s:是输出程序运行信息
--rerun n: 失败重试n次
html=./report.html: 在当前目录下生成report.html文件
- 配置文件:修改
3.4.2 pytest-assume 支持执行多条失败断言
1. 场景:
- 一个方法中写多条断言,通常第一条过不去,下面就不执行了。我们想报错也都执行一下。
2. 安装:
- pip install pytest-assume
3. 执行:
- pytest.assume(a==b)
- pytest.assume(a in b)
- pytest.assume(a not in b)
3.4.3 pytest.fixture()
1. 作用
- 初始化与清理工作:装饰器函数
@pytest.fixture(),它是在声明一个函数是fixture,如果测试函数参数列表中含有fixture名,那么pytest执行的时候就会检测到,并在测试函数运行之前执行该fixture - 网站登录退出
- 完成setup和teardown操作,处理数据库或文件的打开、关闭操作
- 准备测试数据:将数据提前写入数据库或通过params返回给测试用例
2.用法: 在方法前面加@pytest.fixture()
@pytest.fixture()默认函数级别@pytest.fixture(autouse=True)# 设置为默认启动形式@pytest.fixture(scope="function|class|module", autouse=True)自定义作用范围
3.语法:
@pytest.fixture(scope ="function",params=None,autouse=False,ids=None,name=None)
4.参数解读:
scope:被标记方法的作用域- function :默认值,表示每个测试方法都要执行一次
- class:作用于整个类, 表示每个类的所有测试方法只运行一次
- module:作用于整个模块, 每个module的所有测试方法只运行一次
- package:整个包下都可用
- session:会话级 每次会话只需要运行一次,会话内所有方法、类、模块都共享这个方法
autouse:默认False,若为True,刚每个测试函数都会自动调用该fixture,无需传入fixture函数名params:可选形参列表,支持列表传入,默认None,每个param的值fixture都会去调用执行一次ids:用例标识id,默认为空,如果没有提供id,它们将从参数中自动生成。name:fixture的重命名,通常来说使用 fixture 的测试函数会将 fixture 的函数名作为参数传递,但是 pytest 也允许将fixture重命名,如果使用了name,函数名不再生效
5.fixture调用
- fixture调用方式:
- 方式1:
@pytest.mark.usefixtures("定义的fixture名称")作为函数应用 - 方式2:直接在测试用例中传入定义的fixture名称
- 方式1:
- 接收返回值的方式:
- 方式1:
@pytest.mark.usefixtures("fixture函数名称")将fixture函数名称作为用例参数 - 方式2:
def test_case(fixture函数名称)fixture函数名称作为用例参数 - 用例的参数有两种:1)数据驱动 2)fixture
- 注意:
- 如果需要使用fixture返回值,一定要传参,可以不用
@pytetst.mark.usefixtures - 如果fixture没有返回值,测试要使用,必须申明:
@pytest.mark.usefixtures
- 如果需要使用fixture返回值,一定要传参,可以不用
- 方式1:
6.1 应用场景1:fixture
测试用例执行时,有的用例需要登陆才能执行,有些用例不需要登陆。setup和teardown无法满足。fixture可以。默认scope(范围)
- 步骤:
- 导入pytest
- 在登陆的函数上面加
@pytest.fixture() - 在要使用的测试方法中传入(登陆函数名称),就先登陆
- 不传入的就不登陆直接执行测试方法
6.2 应用场景2: conftest.py 配置文件
与其他测试工程师合作一起开发时,公共模块要在不同文件中,要在大家都能访问到的地方。
-
解决:
conftest.py这个文件进行数据共享,并且可以放在不同位置起着不同的范围共享作用。
-
执行:
- 系统执行到参数login时先从本文件中查找是否有这个名字的变量,之后再从conftest.py中找是否有
-
步骤:
- 将登陆模块带
@pytest.fixture写在conftest.py
- 将登陆模块带
-
注意事项:conftest固定文件名,不能替换conftest.py与运行的用例需在同一个package下,并且有_init__.py文件。- 不需要
import conftset,直接调用fixture名称就可以 - 全局的配置和前期工作都可以写在这里,放在某个包下,就是这个包数据共享的地方。
- 作用域(哪些范围内的用例可以使用):conftest.py所在文件夹内的用例都可以使用
6.3 应用场景3: yield关键字
测试方法后销毁清除数据或环境清理工作
- 解决:
- 通过在同一模块中加入yield关键字,yield是调用第一次返回结果,第二次执行它下面的语句返回。
- 步骤:
@pytest.fixture(scope=module)- 在测试的方法中加yield,之后加销毁清除的步骤处理
- tips:这种方式没有返回值,如果希望有返回使用
addfinalizer
6.4 应用场景4:autouse=True 自动调用
不想原测试方法有任何改动,或全部都自动实现自动应用,没特例,也都不需要返回值时可以选择自动应用
- 解决:使用fixture中的参数
autouse=True实现。 - 步骤:
- 在方法上面加
@pytest.fixture(autouse=True) - 在测试方法上加
@pytest.mark.usefixtures("函数名")
- 在方法上面加
6.5 应用场景5 params 数据参数化
- 作用: 方便测试函数对测试属性的获取
- 基本语法:
parametrize(argnames, argvalues, indirect=False, ids=None, scope=None) - 常用参数:
- argnames:要参数化的变量,string(逗号分割),list,tuple
- argvalues:
- 参数对应值,类型必须为list,list[tuple]
- 当参数为一个时,参数格式:[value]
- 当参数个数大于一个时,格式为:[(param_value1,param_value2…),(param_value1,param_value2…)]
- 传参方式:
-
参数方式
- 单参数:
@pytest.mark.parametrize('参数名',list) - 多参数:
@pytest.mark.parametrize('参数名1,参数名2',[(参数1_data[0], 参数2_data[0]),(参数1_data[1], 参数2_data[1])]) - 组合参数化:
@pytest.mark.parametrize("params1", ["user01"]) @pytest.mark.parametrize("params2", [["value_p2","value_p3"],["value_pp2,value_pp3"]]) def test_func01(params1,params2): d = {} d[params1] = params2
- 单参数:
-
函数方式
@pytest.fixture(scope='作用范围') def 函数名(request): data = request.param # 获取对象属性 return request 参数 = [{'user': 'admin01', 'password': '123456'}, {'user': 'admin02', 'password': 'abc123'}] @pytest.mark.parametrize('函数名',参数,indirect=True) # indirect默认为False,需要设置成Ture以函数方式传参 def test_函数名(函数名): a = login print(a)
-
3.4.4 pytest.mark.skip()
1. 使用场景
- 调试时不想运行这个用例
- 标记无法在某些平台上运行的测试功能
- 在某些版本中执行,其他版本中跳过
- 当前的外部资源不可用时跳过(如果测试数据是从数据库中取到的,连接数据库的功能如果返回结果未成功就跳过,因为执行也都报错)
2. 解决:
- 用法1:
@pytest.mark.skip("注释说明") - 用法2:
@pytest.mark.skipif(condition, reason=None)在满足某些条件下才希望通过,否则跳过这个测试。condition: 跳过的条件,必传参数reason: 标注原因
3.4.5 pytest.mark.xfail()
1. 使用场景:
- 功能测试尚未实施或尚未修复的错误,当测试通过时尽管预计会失败(标记为
pytest.mark.xfail),它是一个xpass,将在测试摘要中报告。 - 希望测试由于某种情况而期望执行失败
2. 解决:
@pytest.mark.xfail(condition=None, reason=None, raises=None, run=True, strict=False)
3. 常用参数:
condition:预期失败的条件,必传参数reason:失败的原因
3.4.6 pytest.mark.标签名 打标签
1. 注册标签名
-
方式1:创建
pytest.ini文件,在文件中按如下形式添加标签名:###################### 打标签 ####################### [pytest] markers= 标签名: The explanation must be in Chinese 标签名1 标签名2 # : 代表解释,必须为英文 ############## 配置pytest命令行运行参数 ################## [pytest] addopts = -v -s --reruns 失败次数 --html=./report.html # 空格分隔,可添加多个命令行参数 -所有参数均为插件包的参数 ################### 配置测试搜索的路径 #################### [pytest] testpaths = ./scripts # 当前目录下的scripts文件夹 可自定义 ################### 配置测试搜索的文件名 #################### [pytest] python_files = test_*.py # 当前目录下的scripts文件夹下,以test_开头,以.py结尾的所有文件 -可自定义 ################### 配置测试搜索的测试类名 #################### [pytest] python_classes = Test_* # 当前目录下的scripts文件夹下,以test_开头,以.py结尾的所有文件中,以Test_开头的类 ################### 配置测试搜索的测试函数名 #################### [pytest] python_functions = test_* # 当前目录下的scripts文件夹下,以test_开头,以.py结尾的所有文件中,以Test_开头的类内,以test_开头的⽅法 -可自定义 -
方式2:创建
conftest.py文件# 注册标签方式2: def pytest_configure(config): marker_list = ["标签名1","标签名2",...] for markers in marker_list: config.addinivalue_line( "markers",markers )
2. 打标记
- 在测试用例/测试类上面加:
@pytest.mark.已注册的标记名 - 更多标签方法:
- 打标记范围:测试用例、测试类、模块文件
- 在测试类里,使用以下声明(测试类下,所有用例都被打上该标签):
class TestClass(object): pytestmark = pytest.mark.已注册标签名 pytestmark = [pytest.mark.标签1, pytest.mark.标签2] # 多标签模式 - 在模块文件里,同理(py文件下,所有测试函数和测试类里的测试函数,都有该标签):
import pytest pytestmark = pytest.mark.webtest pytestmark = [pytest.mark.标签1, pytest.mark.标签2] # 多标签模式
3. 运行过滤:pytest.main(['-m','标签名'])
3.4.7 pytest-html 测试报告
1. 安装
pip install pytest-html -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple/ --trusted-host pypi.douban.com
2. 使用方式
- 命令行方式:
pytest --html=存储路径/report.html - 添加到*.ini配置
- 修改
pytest.ini文件,添加报告参数,即:addopts = -s --html=./report.html - 参数解释:
-s是输出程序运行信息
--html=./report.html在当前目录下生成report.html文件
⚠若要生成xml文件,可将--html=./report.html改成--html=./report.xml
- 修改
3.4.8 pytest-allure 测试报告
1. allure安装链接:
https://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2/io/qameta/allure/allure-commandline/
2. 与pytest集成:需要pytest执行用例后,生成allure能够解析的测试结果文件
- 安装:
pip install allure-pytest
3. 使用:
pytest --alluredir=测试报告目录- 使用allure命令,生成html样式的报告
allure serve alluredir的路径
3.4.9 pytest-ordering
1. 默认情况:根据ASCII码的顺序加载测试用例,数字与字母的顺序为:0-9,A-Z,a-z
pytest用例执行基本原则:根据名称的字母逐一进行ASCII比较,越小越先执行。
- 多个测试模块(.py文件)时,根据基本原则执行。
- 一个测试模块(.py文件)中,先执行测试函数,后执行测试类。
- 多个测试类则遵循基本原则,类中的测试方法遵循基本原则。
2. 作用: 以函数修饰符的方式标记被测函数,通过参数控制函数执行顺序
3. 安装:
pip install pytest-ordering -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple/ --trusted-host pypi.douban.com
4. 使用方法:
- 标记于被测函数,
@pytest.mark.run(order=x)
- 根据order传入参数来决定运行顺序:- order值全为正数或全为负数时, 值越小,优先级越高
- 正数和负数同时存在,正数优先级高
- 总结: 0 > 较小整数> 较大的整数 > 无标记 > 较小的负数 > 较大的负数
3.4.10 pytest-xdist 多线程与分布式执行
1. 使用场景:
- 当测试用例非常多的时候,一条条按顺序执行测试用例,很浪费测试时间。这时候就可以用到 pytest-xdist,让自动化测试用例可以分布式执行,从而大大节省测试时间。
2. 解决:
- pytest分布式执行插件:pytest-xdist,多个CPU或主机执行
- 前提:用例之间都是独立的,没有先后顺序,随机都能执行,可重复运行不影响其他用例。
3. 安装:
pip install pytest-xdist -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple/ --trusted-host pypi.douban.com
4. 执行
- 多个CPU并行执行用例,直接加
pytest -n 并行数 - 在多个终端下一起执行
3.5 pytest框架结构
1. setup,teardown
- 模块级(
setup_module/teardown_module):模块始末,全局的(优先最高) - 函数级(
setup_function/teardown_function):只对函数用例生效(不在类中) - 类级(
setup_class/teardown_class):只在类中前后运行(在类中)。 - 方法级(
setup_method/teardown_methond):开始于方法始末(在类中) - 类里面的(
setup/teardown):运行在调用方法的前后
2. conftest.py 文件:存放
3. pytest.ini 文件
4. run.py :项目入口文件
03 unittest和pytest和区别
| unittest | pytest | |
|---|---|---|
| 用例编写规则 | 1)测试文件必须先import unittest2)测试类必须继承 unittest.TestCase3)测试方法必须以“test_”开头 4)测试类必须要有 unittest.main()方法 |
1)测试文件名必须以“test_”开头或者"test"结尾(如:test_ab.py) 2)测试方法必须以“test”开头 3)测试类命名以"Test"开头 |
| 用例分类执行 | 默认执行全部用例,也可以通过加载testsuit,执行部分用例 | 可以通过@pytest.mark来标记类和方法,pytest.main()加入参数(“-m”)可以只运行标记的类和方法 |
| 用例前置和后置 | 提供了setUp/tearDown,只能针对所有用例 | pytest中的fixture显然更加灵活。可以任意自定义方法函数,只要加上@pytest.fixture()这个装饰器,那么被装饰的方法就可以被使用 |
| 参数化 | 需依赖ddt库 | 使用@pytest.mark.parametrize()装饰器 |
| 断言 | 很多断言格式(assertEqual、assertIn、assertTrue、assertFalse) | 1)assert 表达式 2) pytest.assume(断言) 支持运行多条失败断言 |
| 报告 | 使用HTMLTestRunnerNew库 | 有pytest-HTML、allure插件 |
| 失败重跑 | 无此功能 | pytest支持用例执行失败重跑,pytest-rerunfailures插件 |
git demo地址:
https://github.com/JSonliuJ/pytestdemo_v1