Linux常用C函数---字符串转换篇
函数讲解部分参考http://net.pku.edu.cn/~yhf/linux_c/

|
|
atof(将字符串转换成浮点型数) |
|
相关函数
|
atoi,atol,strtod,strtol,strtoul |
|
表头文件
|
#include <stdlib.h> |
|
定义函数
|
double atof(const char *nptr); |
|
函数说明
|
atof()会扫描参数nptr字符串,跳过前面的空格字符,直到遇上数字或正负符号才开始做转换,而再遇到非数字或字符串结束时('\0')才结束转换,并将结果返回。参数nptr字符串可包含正负号、小数点或E(e)来表示指数部分,如123.456或123e-2。 |
|
返回值
|
返回转换后的浮点型数。 |
|
附加说明
|
atof()与使用strtod(nptr,(char**)NULL)结果相同。 |
|
范例
|
/* 将字符串a 与字符串b转换成数字后相加*/ #include<stdlib.h> main() { char *a=”-100.23”; char *b=”200e-2”; float c; c=atof(a)+atof(b); printf(“c=%.2f\n”,c); } |
|
执行
|
c=-98.23 |
|
|
atoi(将字符串转换成整型数) |
|
相关函数
|
atof,atol,atrtod,strtol,strtoul |
|
表头文件
|
#include<stdlib.h> |
|
定义函数
|
int atoi(const char *nptr); |
|
函数说明
|
atoi()会扫描参数nptr字符串,跳过前面的空格字符,直到遇上数字或正负符号才开始做转换,而再遇到非数字或字符串结束时('\0')才结束转换,并将结果返回。 |
|
返回值
|
返回转换后的整型数。 |
|
附加说明
|
atoi()与使用strtol(nptr,(char**)NULL,10);结果相同。 |
|
范例
|
/* 将字符串a 与字符串b转换成数字后相加*/ #include<stdlib.h> mian() { char a[]=”-100”; char b[]=”456”; int c; c=atoi(a)+atoi(b); printf(c=%d\n”,c); } |
|
执行
|
c=356 |
|
|
atol(将字符串转换成长整型数) |
|
相关函数
|
atof,atoi,strtod,strtol,strtoul |
|
表头文件
|
#include<stdlib.h> |
|
定义函数
|
long atol(const char *nptr); |
|
函数说明
|
atol()会扫描参数nptr字符串,跳过前面的空格字符,直到遇上数字或正负符号才开始做转换,而再遇到非数字或字符串结束时('\0')才结束转换,并将结果返回。 |
|
返回值
|
返回转换后的长整型数。 |
|
附加说明
|
atol()与使用strtol(nptr,(char**)NULL,10);结果相同。 |
|
范例
|
/*将字符串a与字符串b转换成数字后相加*/ #include<stdlib.h> main() { char a[]=”1000000000”; char b[]=” 234567890”; long c; c=atol(a)+atol(b); printf(“c=%d\n”,c); } |
|
执行
|
c=1234567890 |
|
|
gcvt(将浮点型数转换为字符串,取四舍五入) |
|
相关函数
|
ecvt,fcvt,sprintf |
|
表头文件
|
#include<stdlib.h> |
|
定义函数
|
char *gcvt(double number,size_t ndigits,char *buf); |
|
函数说明
|
gcvt()用来将参数number转换成ASCII码字符串,参数ndigits表示显示的位数。gcvt()与ecvt()和fcvt()不同的地方在于,gcvt()所转换后的字符串包含小数点或正负符号。若转换成功,转换后的字符串会放在参数buf指针所指的空间。 |
|
返回值
|
返回一字符串指针,此地址即为buf指针。 |
|
附加说明
|
|
|
范例
|
#include<stdlib.h> main() { double a=123.45; double b=-1234.56; char *ptr; int decpt,sign; gcvt(a,5,ptr); printf(“a value=%s\n”,ptr); ptr=gcvt(b,6,ptr); printf(“b value=%s\n”,ptr); } |
|
执行
|
a value=123.45 b value=-1234.56 |
|
|
strtod(将字符串转换成浮点数) |
|
相关函数
|
atoi,atol,strtod,strtol,strtoul |
|
表头文件
|
#include<stdlib.h> |
|
定义函数
|
double strtod(const char *nptr,char **endptr); |
|
函数说明
|
strtod()会扫描参数nptr字符串,跳过前面的空格字符,直到遇上数字或正负符号才开始做转换,到出现非数字或字符串结束时('\0')才结束转换,并将结果返回。若endptr不为NULL,则会将遇到不合条件而终止的nptr中的字符指针由endptr传回。参数nptr字符串可包含正负号、小数点或E(e)来表示指数部分。如123.456或123e-2。 |
|
返回值
|
返回转换后的浮点型数。 |
|
附加说明
|
参考atof()。 |
|
范例
|
/*将字符串a,b,c 分别采用10,2,16 进制转换成数字*/ #include<stdlib.h> mian() { char a[]=”1000000000”; char b[]=”1000000000”; char c[]=”ffff”; printf(“a=%d\n”,strtod(a,NULL,10)); printf(“b=%d\n”,strtod(b,NULL,2)); printf(“c=%d\n”,strtod(c,NULL,16)); } |
|
执行
|
a=1000000000 b=512 c=65535 |
|
|
strtol(将字符串转换成长整型数) |
|
相关函数
|
atof,atoi,atol,strtod,strtoul |
|
表头文件
|
#include<stdlib.h> |
|
定义函数
|
long int strtol(const char *nptr,char **endptr,int base); |
|
函数说明
|
strtol()会将参数nptr字符串根据参数base来转换成长整型数。参数base范围从2至36,或0。参数base代表采用的进制方式,如base值为10则采用10进制,若base值为16则采用16进制等。当base值为0时则是采用10进制做转换,但遇到如'0x'前置字符则会使用16进制做转换。一开始strtol()会扫描参数nptr字符串,跳过前面的空格字符,直到遇上数字或正负符号才开始做转换,再遇到非数字或字符串结束时('\0')结束转换,并将结果返回。若参数endptr不为NULL,则会将遇到不合条件而终止的nptr中的字符指针由endptr返回。 |
|
返回值
|
返回转换后的长整型数,否则返回ERANGE并将错误代码存入errno中。 |
|
附加说明
|
ERANGE指定的转换字符串超出合法范围。 |
|
范例
|
/* 将字符串a,b,c 分别采用10,2,16进制转换成数字*/ #include<stdlib.h> main() { char a[]=”1000000000”; char b[]=”1000000000”; char c[]=”ffff”; printf(“a=%d\n”,strtol(a,NULL,10)); printf(“b=%d\n”,strtol(b,NULL,2)); printf(“c=%d\n”,strtol(c,NULL,16)); } |
|
执行
|
a=1000000000 b=512 c=65535 |
|
|
strtoul(将字符串转换成无符号长整型数) |
|
相关函数
|
atof,atoi,atol,strtod,strtol |
|
表头文件
|
#include<stdlib.h> |
|
定义函数
|
unsigned long int strtoul(const char *nptr,char **endptr,int base); |
|
函数说明
|
strtoul()会将参数nptr字符串根据参数base来转换成无符号的长整型数。参数base范围从2至36,或0。参数base代表采用的进制方式,如base值为10则采用10进制,若base值为16则采用16进制数等。当base值为0时则是采用10进制做转换,但遇到如'0x'前置字符则会使用16进制做转换。一开始strtoul()会扫描参数nptr字符串,跳过前面的空格字符串,直到遇上数字或正负符号才开始做转换,再遇到非数字或字符串结束时('\0')结束转换,并将结果返回。若参数endptr不为NULL,则会将遇到不合条件而终止的nptr中的字符指针由endptr返回。 |
|
返回值
|
返回转换后的长整型数,否则返回ERANGE并将错误代码存入errno中。 |
|
附加说明
|
ERANGE指定的转换字符串超出合法范围。 |
|
范例
|
参考strtol() |
|
|
toascii(将整型数转换成合法的ASCII 码字符) |
|
相关函数
|
isascii,toupper,tolower |
|
表头文件
|
#include<ctype.h> |
|
定义函数
|
int toascii(int c) |
|
函数说明
|
toascii()会将参数c转换成7位的unsigned char值,第八位则会被清除,此字符即会被转成ASCII码字符。 |
|
返回值
|
将转换成功的ASCII码字符值返回。 |
|
范例
|
#include<stdlib.h> main() { int a=217; char b; printf(“before toascii () : a value =%d(%c)\n”,a,a); b=toascii(a); printf(“after toascii() : a value =%d(%c)\n”,b,b); } |
|
执行
|
before toascii() : a value =217() after toascii() : a value =89(Y) |
|
|
tolower(将大写字母转换成小写字母) |
|
相关函数
|
isalpha,toupper |
|
表头文件
|
#include<stdlib.h> |
|
定义函数
|
int tolower(int c); |
|
函数说明
|
若参数c为大写字母则将该对应的小写字母返回。 |
|
返回值
|
返回转换后的小写字母,若不须转换则将参数c值返回。 |
|
附加说明
|
|
|
范例
|
/* 将s字符串内的大写字母转换成小写字母*/ #include<ctype.h> main() { char s[]=”aBcDeFgH12345;!#$”; int i; printf(“before tolower() : %s\n”,s); for(i=0;I<sizeof(s);i++) s[i]=tolower(s[i]); printf(“after tolower() : %s\n”,s); } |
|
执行
|
before tolower() : aBcDeFgH12345;!#$ after tolower() : abcdefgh12345;!#$ |
|
|
toupper(将小写字母转换成大写字母) |
|
相关函数
|
isalpha,tolower |
|
表头文件
|
#include<ctype.h> |
|
定义函数
|
int toupper(int c); |
|
函数说明
|
若参数c为小写字母则将该对映的大写字母返回。 |
|
返回值
|
返回转换后的大写字母,若不须转换则将参数c值返回。 |
|
附加说明
|
|
|
范例
|
/* 将s字符串内的小写字母转换成大写字母*/ #include<ctype.h> main() { char s[]=”aBcDeFgH12345;!#$”; int i; printf(“before toupper() : %s\n”,s); for(i=0;I<sizeof(s);i++) s[i]=toupper(s[i]); printf(“after toupper() : %s\n”,s); } |
|
执行
|
before toupper() : aBcDeFgH12345;!#$ after toupper() : ABCDEFGH12345;!#$ |
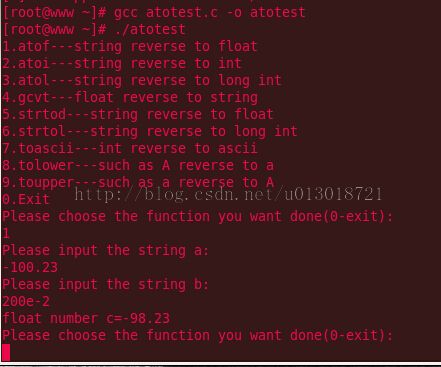
linux实例代码如下:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 5 6 7 void atof_fun();//string reverse to float 8 9 void atoi_fun();//string reverse to int 10 11 void atol_fun();//string reverse to long int 12 13 void gcvt_fun();//float reverse to string 14 15 void strtod_fun();//string reverse to float 16 17 void strtol_fun();//string reverse to long int 18 19 void toascii_fun();//int reverse to ascii 20 21 void tolower_fun();//such as A reverse a; 22 23 void toupper_fun();//such as a reverse A; 24 25 26 int main() 27 28 { 29 30 int Index; 31 32 33 printf("1.atof---string reverse to float\n"); 34 35 printf("2.atoi---string reverse to int\n"); 36 37 printf("3.atol---string reverse to long int\n"); 38 39 printf("4.gcvt---float reverse to string\n"); 40 41 printf("5.strtod---string reverse to float\n"); 42 43 printf("6.strtol---string reverse to long int\n"); 44 45 printf("7.toascii---int reverse to ascii\n"); 46 47 printf("8.tolower---such as A reverse to a\n"); 48 49 printf("9.toupper---such as a reverse to A\n"); 50 51 printf("0.Exit\n"); 52 53 while(1) 54 55 { 56 57 printf("Please choose the function you want done(0-exit):\n"); 58 59 scanf("%d",&Index); 60 61 if(Index==0) 62 63 { 64 65 printf("Bye Bye\n"); 66 67 break; 68 69 } 70 71 else 72 73 { 74 75 switch(Index) 76 77 { 78 79 case 1:atof_fun(); 80 81 break; 82 83 case 2:atoi_fun(); 84 85 break; 86 87 case 3:atol_fun(); 88 89 break; 90 91 case 4:gcvt_fun(); 92 93 break; 94 95 case 5:strtod_fun(); 96 97 break; 98 99 case 6:strtol_fun(); 100 101 break; 102 103 case 7:toascii_fun(); 104 105 break; 106 107 case 8:tolower_fun(); 108 109 break; 110 111 case 9:toupper_fun(); 112 113 break; 114 115 default: 116 117 break; 118 119 } 120 121 } 122 123 } 124 125 return 0; 126 127 } 128 129 130 131 //string reverse to float 132 133 void atof_fun() 134 135 { 136 137 char a[20]; 138 139 char b[20]; 140 141 142 printf("Please input the string a:\n"); 143 144 scanf("%s",a); 145 146 printf("Please input the string b:\n"); 147 148 scanf("%s",b); 149 150 151 float c; 152 153 c=atof(a)+atof(b); 154 155 printf("float number c=%.2f\n",c); 156 157 } 158 159 160 161 //string reverse to int 162 163 void atoi_fun() 164 165 { 166 167 char a[20]; 168 169 char b[20]; 170 171 printf("Please input the string a:\n"); 172 173 scanf("%s",a); 174 175 printf("Please input the string b:\n"); 176 177 scanf("%s",b); 178 179 180 181 int c; 182 183 c=atoi(a)+atoi(b); 184 185 printf("int number c=%d\n",c); 186 } 187 188 189 190 //string reverse to long int 191 192 void atol_fun() 193 194 { 195 196 char a[20]; 197 198 char b[20]; 199 200 printf("Please input the string a:\n"); 201 202 scanf("%s",a); 203 204 printf("Please input the string b:\n"); 205 206 scanf("%s",b); 207 208 209 210 long c; 211 212 c=atol(a)+atol(b); 213 214 215 printf("long int number c=%ld\n",c); 216 217 } 218 219 220 221 //float reverse to string 222 223 void gcvt_fun() 224 225 { 226 227 double a; 228 229 int aIndex; 230 231 double b; 232 233 int bIndex; 234 235 printf("Please input a and aIndex:\n"); 236 237 scanf("%lf,%d",&a,&aIndex); 238 239 printf("Please input b and bIndex:\n"); 240 241 scanf("%lf,%d",&b,&bIndex); 242 243 244 char str[20]; 245 246 gcvt(a,aIndex,str); 247 248 printf("%lf reverse to string---%s\n",a,str); 249 250 gcvt(b,bIndex,str); 251 252 printf("%lf reverse to string---%s\n",b,str); 253 254 } 255 256 257 258 //string reverse to float 259 260 void strtod_fun() 261 262 { 263 264 char a[20],*ptr; 265 266 double value; 267 268 269 printf("Please input a string:\n"); 270 271 scanf("%s",a); 272 273 274 value=strtod(a,&ptr); 275 276 printf("The string is %s the number is %lf\n",a,value); 277 278 } 279 280 //string reverse to long int 281 282 void strtol_fun() 283 284 { 285 286 char a[20],*ptr; 287 288 long int value; 289 290 291 printf("Please input a string\n"); 292 293 scanf("%s",a); 294 295 value=strtol(a,&ptr,10); 296 297 printf("The string is %s the number is %ld\n",a,value); 298 299 } 300 301 302 303 //int reverse to ascii 304 void toascii_fun() 305 306 { 307 308 int a; 309 310 char b; 311 312 313 printf("Please input the non-ascii number a:\n"); 314 315 scanf("%d",&a); 316 317 b=toascii(a); 318 319 320 printf("Before ascii---(%d)to(%c)\n",a,a); 321 322 printf("After ascii---(%d)to(%c)\n",a,b); 323 324 } 325 326 327 328 //A reverse to a 329 330 void tolower_fun() 331 332 { 333 char a[40]; 334 335 int i; 336 337 printf("Please input the string of a:\n"); 338 339 scanf("%s",a); 340 341 342 printf("Before tolower:%s\n",a); 343 344 345 for(i=0;a[i]!=0;i++) 346 347 { 348 349 a[i]=tolower(a[i]); 350 351 } 352 353 354 355 printf("After tolower:%s\n",a); 356 357 } 358 359 360 361 //a reverse to A 362 363 void toupper_fun() 364 365 { 366 char a[40]; 367 368 int i; 369 370 printf("Please input the string of a:\n"); 371 372 373 scanf("%s",a); 374 375 376 printf("Before toupper:%s\n",a); 377 378 379 for(i=0;a[i]!=0;i++) 380 381 { 382 383 a[i]=toupper(a[i]); 384 385 } 386 387 388 printf("After toupper:%s\n",a); 389 390 }
运行结果: