一个.net客户端通讯框架的设计(二)---准备FastBuffer和BOConverter
在网络编程中,我们会频繁用到两个东西,一个是buffer。一个是bit-order。把数据填充到buffer中,然后通过buffer读写我们所需要的基本数据,还好.NET为我们提供了BitConverter这个非常好用的util,方便我们编写自己的Buffer和字节序转换器。
IBuffer
通常Buffer会有如下几个概念;position,limit,capacity,flip,mark,reset,free
position:即将读/写的位置
limit:有效读/写的极限位置
capacity:buffer的最大长度
flip:limit设为置position,position设为0
mark:记录当前的position,对应reset操作
reset:将position设置为之前mark的位置
free:将缓冲标识为空闲,可在入池前调用。
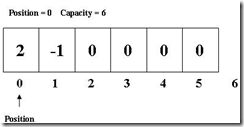
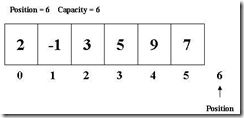
比如,一个capacity为6的缓冲区,加入当前position为0,那么下次读/写操作都将从0位置开始。
我read 2个字节,读出的是2和-1,此时position会变成2,再write 4个字节的数据,将从位置2开始,将这4个字节的数据写到byte[2]-byte[5]中,最后position为6,如果再继续读/写,除非缓冲设置为AutoExpand否则将会发生缓冲区益处。
下面是我自己的IBuffer接口和一个IBuffer的实现,如果您没用过BitConverter、Buffer建议您查阅MSDN,这里就不再复述。
使用说明:a.将AutoExtend设置为true,FastBuffer会在预知缓冲大小不够的情况下自动扩展,如果设置为false,一旦读/写操作超出capacity大小会抛出BufferOverflowException。b.如果想预分配n个字节的缓冲,只需:FastBuffer.Allocate(n)。c.如果想将一个byte[] data放在FastBuffer中只需调用FastBuffer.Wrap(data)。
FastBuffer:
IBuffer
public interface IBuffer
: IDataReader, IDataWriter
{
int Position { get ; set ; }
int Limit { get ; set ; }
int Capacity { get ; set ; }
void Flip();
void Rewind();
void Clear();
void Reset();
void Free();
long Remaining { get ; }
byte [] toAllBytes();
byte [] copyAvaliableBytes();
bool AutoExtend { get ; set ; }
void Append( byte [] p, int start, int length);
}
IDataReader;IDataWriter
public interface IDataReader
{
byte ReadByte();
byte [] ReadBytes( int n);
short ReadShort();
Int16 ReadInt16();
Int32 ReadInt32();
Int64 ReadInt64();
long ReadLong();
float ReadFloat();
double ReadDouble();
}
public interface IDataWriter
{
void WriteByte( byte b);
void WriteBytes( byte [] data);
void WriteShort( short data);
void WriteInt16(Int16 data);
void WriteInt32(Int32 data);
void WriteInt64(Int64 data);
void WriteLong( long data);
void WriteFloat( float data);
void WriteDouble( double data);
}
FastBuffer
public class FastBuffer : IBuffer
{
#region basic data type sizes
public static readonly int SIZE_SHORT = sizeof ( short );
public static readonly int SIZE_INT16 = sizeof (Int16);
public static readonly int SIZE_INT32 = sizeof (Int32);
public static readonly int SIZE_INT64 = sizeof (Int64);
public static readonly int SIZE_LONG = sizeof ( long );
public static readonly int SIZE_FLOAT = sizeof ( float );
public static readonly int SIZE_DOUBLE = sizeof ( double );
#endregion
#region
private byte [] _data;
private int _position;
private int _limit;
private int _capacity;
private Boolean isAutoExtend = false ;
#endregion
#region static create methods
public static FastBuffer Allocate( int size)
{
var buffer = new FastBuffer();
buffer._data = Array.CreateInstance( typeof (Byte), size) as byte [];
buffer.Capacity = size;
return buffer;
}
public static FastBuffer Wrap( byte [] data)
{
var buffer = new FastBuffer();
buffer._data = data;
buffer.Capacity = data.Length;
return buffer;
}
#endregion
#region IBuffer Members
public long Remaining
{
get
{
return _limit - _position;
}
}
public int Position
{
get
{
return _position;
}
set
{
if (value > _capacity)
throw new BufferOverflowException();
_position = value;
if (_position > Limit)
{
Limit = _position;
}
}
}
public int Limit
{
get
{
return _limit;
}
set
{
if (value > _capacity)
throw new BufferOverflowException();
if (value < _position)
_position = value;
_limit = value;
}
}
public int Capacity
{
get
{
return _capacity;
}
set
{
if (value < _limit)
_limit = value;
if (value < _position)
_position = value;
_capacity = value;
}
}
public void Flip()
{
Limit = Position;
Position = 0 ;
}
public void Rewind()
{
Position = 0 ;
}
public void Clear()
{
Position = 0 ;
Limit = Capacity;
}
public void Reset()
{
Position = 0 ;
Limit = 0 ;
}
public void Free()
{
_data = null ;
Position = 0 ;
Limit = 0 ;
Capacity = 0 ;
}
public byte [] toAllBytes()
{
return _data;
}
public byte [] copyAvaliableBytes()
{
var ret = new byte [_limit];
Array.Copy(_data, 0 , ret, 0 , _limit);
return ret;
}
#endregion
#region IDataReader Members
public byte ReadByte()
{
return Buffer.GetByte(_data, Position ++ );
}
public byte [] ReadBytes( int n)
{
byte [] ret = new byte [n];
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++ )
{
ret[i] = Buffer.GetByte(_data, Position ++ );
}
return ret;
}
public short ReadShort()
{
var ret = BitConverter.ToInt16(_data, Position);
Position += SIZE_SHORT;
return ret;
}
public short ReadInt16()
{
var ret = BitConverter.ToInt16(_data, Position);
Position += SIZE_INT16;
return ret;
}
public int ReadInt32()
{
var ret = BitConverter.ToInt32(_data, Position);
Position += SIZE_INT32;
return ret;
}
public long ReadInt64()
{
var ret = BitConverter.ToInt64(_data, Position);
Position += SIZE_INT64;
return ret;
}
public long ReadLong()
{
var ret = BitConverter.ToInt64(_data, Position);
Position += SIZE_LONG;
return ret;
}
public float ReadFloat()
{
var ret = BitConverter.ToSingle(_data, Position);
Position += SIZE_FLOAT;
return ret;
}
public double ReadDouble()
{
var ret = BitConverter.ToDouble(_data, Position);
Position += SIZE_DOUBLE;
return ret;
}
#endregion
#region IDataWriter Members
public void WriteByte( byte b)
{
if (_position + 1 > this .Capacity)
{
if (isAutoExtend)
{
var dest = new byte [_capacity + _capacity / 2 + 1 ];
Buffer.BlockCopy(_data, 0 , dest, 0 , _data.Length);
}
else
throw new BufferOverflowException();
}
Buffer.SetByte(_data, Position ++ , b);
}
public void WriteBytes( byte [] data, int start, int length)
{
if (_position + length > this .Capacity)
{
if (isAutoExtend)
{
_capacity = _capacity + _capacity / 2 + length;
var dest = new byte [_capacity];
Buffer.BlockCopy(_data, 0 , dest, 0 , _data.Length);
_data = dest;
}
else
throw new BufferOverflowException();
}
for ( int i = start; i < start + length; i ++ )
{
Buffer.SetByte(_data, Position ++ , data[i]);
}
}
public void WriteBytes( byte [] data)
{
WriteBytes(data, 0 , data.Length);
}
public void WriteShort( short data)
{
WriteBytes(BitConverter.GetBytes(data));
}
public void WriteInt16( short data)
{
WriteBytes(BitConverter.GetBytes(data));
}
public void WriteInt32( int data)
{
WriteBytes(BitConverter.GetBytes(data));
}
public void WriteInt64( long data)
{
WriteBytes(BitConverter.GetBytes(data));
}
public void WriteLong( long data)
{
WriteBytes(BitConverter.GetBytes(data));
}
public void WriteFloat( float data)
{
WriteBytes(BitConverter.GetBytes(data));
}
public void WriteDouble( double data)
{
WriteBytes(BitConverter.GetBytes(data));
}
public void Append( byte [] data, int start, int length)
{
if (_position + length > this ._capacity)
{
_capacity = _capacity + _capacity / 2 + data.Length;
var dest = new byte [_capacity];
Buffer.BlockCopy(_data, 0 , dest, 0 , _data.Length);
_data = dest;
}
WriteBytes(data, start, length);
}
public bool AutoExtend
{
get
{
return isAutoExtend;
}
set
{
isAutoExtend = true ;
}
}
#endregion
}
我们来测试一下这个FastBuffer(PS:为了方便我就不贴那堆测试用例了,仅作简单的演示)
测试一下
static void Main( string [] arg)
{
Console.ReadKey();
var buffer = FastBuffer.Allocate( 1 ); // 这里故意将预分配的长度缩小
buffer.AutoExtend = true ; // 测试是否能够自动延展缓冲区大小
buffer.WriteByte( 5 );
buffer.WriteShort( 51 );
buffer.WriteInt64( 91923 );
buffer.WriteFloat( 1.203f );
buffer.Flip();
Console.WriteLine(buffer.ReadByte());
Console.WriteLine(buffer.ReadShort());
Console.WriteLine(buffer.ReadInt64());
Console.WriteLine(buffer.ReadFloat());
}
结果是一致的。
字节序转换
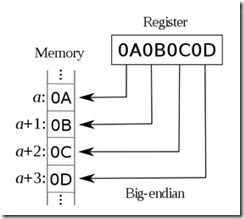
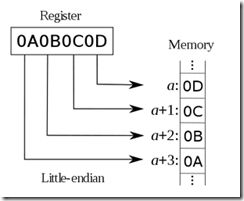
字节序其实是计算机的一个常识性的概念,我在这里简单讲解一下。我们知道CPU有个概念叫字长,现在的大部分CPU都是64位(bit)的,也就支持每次将是64字长=8字节的数据对齐写入到内存中,不过绝大多数人使用的操作系统和软件都是32位的。对于32位的操作系统而言,即便CPU是64位,其运行效率与32CPU无异。拿32位系统来说,假如CPU要将寄存器中起始地址为a的数据0x0A0B0C0D写入到内存中,此时会有两种选择:其一是将0A0B0C0D依次写入到内存中的a,a+1,a+2,a+3这四个位置上;其二是将其依次写入到a+3,a+2,a+1,a这四个位置上。前者就是little-endian的方式,后者是big-endian。
对于大小字节序嘛通过位运算将各种基本数据类型的前后位颠倒一下即可。
首先判断当前运行平台的字节序(这里有个常识:win32、clr使用小字节序,java平台、mac系统使用大字节序):对于.NET我们无需自己去判断BitConverter.IsLittleEndian即可返回字节序的结果。
其次是掉转顺序:对于一个byte而言当然就不用掉转了。我们拿int32和float开刀。
.NET提供的基础库真的很方便,很多基础性的东西我们无需自己去写或者去找什么第三方的代码。用C#来写字节序转换是非常之简单的。不过还是讲两种方法。
第一种:“万金油”:
无论你是几个字节,通吃int16/int32/int63/uint16/ushort/flost/double……。
对于一个基本类型,我们可以用System.BitConverter来将其转换为byte[],然后用Array.Reverse来将其反序,再用BitConverter.ToXXX将其重新构造为一个数值即可。
public static UInt32 swapByteOrder(UInt32 value)
{
Byte[] buffer = BitConverter.GetBytes(value);
Array.Reverse(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
return BitConverter.ToUInt32(buffer, 0);
}
第二种方法:
为什么要介绍第二种方法呢?因为前一种方法固然简单,但是性能上相比还是要逊色一些。其实我们弄清了原理,只需要简单的位运算即可完成大小字节序转换而无需借助BitConverter和Array这两个util。比如UInt32,用位运算将4位上的数分离后移位再重新组合即可。
public static UInt32 swapByteOrder(UInt32 value)
{
UInt32 swap = ((0x000000FF) & (value >> 24)
| (0x0000FF00) & (value >> 8)
| (0x00FF0000) & (value << 8)
| (0xFF000000) & (value << 24));
return swap;
}
至此,我们已经有了自己的buffer和字节序转换器,无论对应的通信是什么平台都能得心应手。下篇将介绍IOService、decoder、encoder、协议的设计。
代码下载