Spring Boot v2.4.4源码解析(四)事件机制篇下
Spring Boot事件发布及监听机制
一、 事件驱动模型
1. 面向事件编程在Spring下实践
事件驱动模型可以最大程度减少耦合度,而Spring拥有一套完善的事件发布与处理机制。在Spring中想完成一个完整的面向事件编程,需要以下三个步骤:
- 自定义一个事件,该事件需要继承
ApplicationEvent,参考Spring Boot v2.4.4源码解析(三)事件机制篇一; - 事件发布者注入
ApplicationEventPublisher对象,用于发布事件; - 事件监听者实现
ApplicationListener接口,或者使用@EventListener注解(Spring 4.1引入);
具体实现细节可以参考文档Better application events in Spring Framework 4.2。
调试时会发现注入事件发布者ApplicationEventPublisher 其实是Spring Boot应用上下文AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext。
看下应用上下文接口ApplicationContext UML类图:
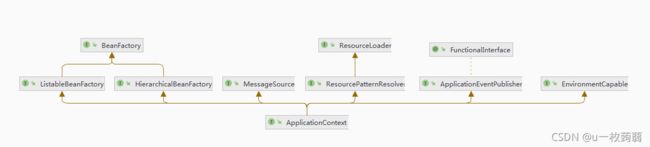
可以看出,ApplicationContext继承接口ApplicationEventPublisher提供事件发布功能。
2. 拓展面试题:BeanFactory和ApplicationContext的区别
这里可以衍生出一道经典面试题:Spring中 BeanFactory和ApplicationContext的区别。
从上面接口继承关系可以看出ApplicationContext继承至接口BeanFactory,所以BeanFactory提供的功能ApplicationContext均支持,并且ApplicationContext扩展了如下功能:
- 扩展
MessageResource接口,支持消息国际化; - 扩展
ApplicationEventPublisher接口,支持事件发布; - 扩展
ResourcePatternResolver接口,支持资源加载;
ApplicationContext提供自动BeanPostProcessor注册功能;ApplicationContext提供自动BeanFactoryPostProcessor注册功能;BeanFactroy采用的是延迟加载形式注入bean,ApplicationContext则相反,它是在容器启动时,一次性创建了所有的bean;
具体细节可以参考Chapter 3. The IoC container
3. 事件发布者真面目
看下AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext发布事件时序图:
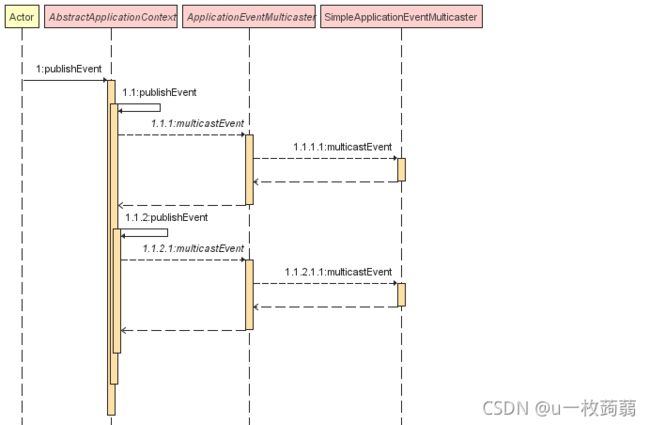
可以看出,AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext发布事件最终也是委托给SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster。
二、 事件广播器
看下SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster UML类图:
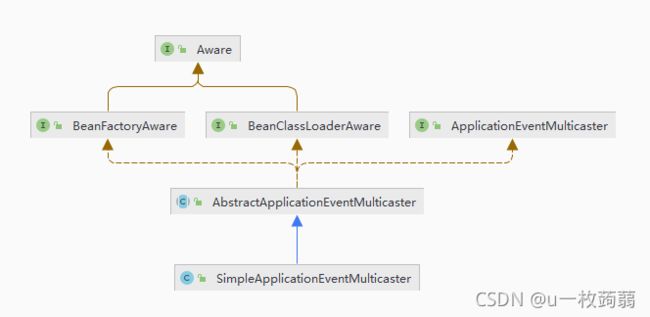
1. 顶级接口ApplicationEventMulticaster规定事件广播器功能
除了Aware接口,SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster顶级接口为ApplicationEventMulticaster,ApplicationEventMulticaster定义了管理ApplicationListener事件监听者和向这些监听者广播事件的一些方法。并且官方注释明确指出,ApplicationEventPublisher(特别是ApplicationContext)可以将实际事件发布功能委托给ApplicationEventMulticaster实现类。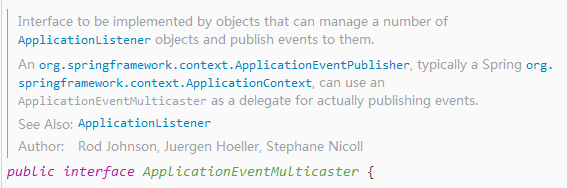
ApplicationEventMulticaster 接口规定事件广播器需要具备如下功能:
- 注册事件监听器功能,支持通过实例和bean名称方式注册;
void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener); void addApplicationListenerBean(String listenerBeanName); - 移除已经注册的事件监听器功能,不仅支持通过实例和bean名称方式移除,还能通过Predicate断言方式批量移除;
void removeApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener); void removeApplicationListenerBean(String listenerBeanName); // 注意, 这里只能移除通过实例注册的事件监听器, 不能移除通过bean名称注册的事件监听器 void removeApplicationListeners(Predicate<ApplicationListener<?>> predicate); // 注意, 这里只能移除通过bean名称注册的事件监听器, 不能移除通过实例注册的事件监听器 void removeApplicationListenerBeans(Predicate<String> predicate); - 事件广播功能;
void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event); void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType);
2. AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster管理事件监听器
抽象类AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster实现了ApplicationEventMulticaster管理事件监听器功能,这就不难理解为什么AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster要实现BeanFactoryAware接口,因为ApplicationEventMulticaster支持通过bean名称方式注册和移除监听器,所以需要beanFactory根据bean名称获取事件监听器实例。
2.1 内部类与缓存
AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster中定义了几个内部类:
DefaultListenerRetriever,封装已经注册的事件监听器,注册和移除时都是对该类进行操作。成员变量applicationListeners和applicationListenerBeans分别代表通过实例和bean名称注册的事件监听器;private class DefaultListenerRetriever { public final Set<ApplicationListener<?>> applicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(); public final Set<String> applicationListenerBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(); // 获取所有事件监听器 public Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> getApplicationListeners() { List<ApplicationListener<?>> allListeners = new ArrayList<>( this.applicationListeners.size() + this.applicationListenerBeans.size()); allListeners.addAll(this.applicationListeners); if (!this.applicationListenerBeans.isEmpty()) { BeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); for (String listenerBeanName : this.applicationListenerBeans) { try { ApplicationListener<?> listener = beanFactory.getBean(listenerBeanName, ApplicationListener.class); // 从beanFactory中获取 if (!allListeners.contains(listener)) { // 去重 allListeners.add(listener); } } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { } } } AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(allListeners); return allListeners; } }CachedListenerRetriever,DefaultListenerRetriever封装所有已经注册的事件监听器,但是一个监听器只能监听一种事件,当事件发生时需要从DefaultListenerRetriever筛选出能够处理该种事件的监听器。这样当同一类型事件发生多次时,势必会造成重复筛选;为了避免重复筛选,AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster将已经筛选出来的事件监听器封装成CachedListenerRetriever进行缓存。CachedListenerRetriever和DefaultListenerRetriever类似,只不过applicationListeners和applicationListenerBeans由volatile修饰,保证线程可见性,并且在调用getApplicationListeners()方法获取事件监听器需要判断缓存是否已加载(applicationListeners或applicationListenerBeans是否为null)。这里不贴CachedListenerRetriever源码。ListenerCacheKey,事件监听器缓存键,成员变量eventType和sourceType分别表示事件类型和事件源类型。从这里可以看出DefaultListenerRetriever是根据事件类型和事件源类型对事件监听器进行缓存的。ListenerCacheKey还重写了equals方法:只有eventType和sourceType都相同时,才认为两个ListenerCacheKey相同。
AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster内部变量如下:
// 已经注册的事件监听器
private final DefaultListenerRetriever defaultRetriever = new DefaultListenerRetriever();
// 缓存, 数据源是defaultRetriever
final Map<ListenerCacheKey, CachedListenerRetriever> retrieverCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64);
private ClassLoader beanClassLoader; // 通过BeanClassLoaderAware接口注入
private ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory; // 通过BeanFactoryAware接口注入
2.2 Cache-Aside 缓存模式
retrieverCache为ConcurrentHashMap类型,线程安全。但是DefaultListenerRetriever非线程安全类,考虑到线程安全性,所有对defaultRetriever 的读(保证线程可见性)写操作都要加锁。
AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster缓存使用Cache-Aside(旁路缓存)模式,所有对数据源defaultRetriever 的修改操作,都会清空缓存。
例如:
// 省略beanClassLoader和beanFactory的set/get方法
@Override
public void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener) {
synchronized (this.defaultRetriever) {
// 移除代理, 防止同一个事件监听器多次添加
Object singletonTarget = AopProxyUtils.getSingletonTarget(listener);
if (singletonTarget instanceof ApplicationListener) {
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners.remove(singletonTarget);
}
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners.add(listener);
this.retrieverCache.clear(); // 清空缓存
}
}
// addApplicationListenerBean(String), removeApplicationListener(ApplicationListener)
// removeApplicationListenerBean(String), removeApplicationListeners(Predicate>)
// removeApplicationListenerBeans(Predicate )
// removeAllListeners()方法类似addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener)方法
// 都是先对defaultRetriever的applicationListeners或者applicationListenerBeans进行操作
// 然后清除retrieverCache缓存, 这里省略
// 获取所有事件监听器
protected Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> getApplicationListeners() {
synchronized (this.defaultRetriever) { // synchronized保证其他线程对defaultRetriever的修改, 线程可见
return this.defaultRetriever.getApplicationListeners();
}
}
2.3 获取指定类型监听器
getApplicationListeners(ApplicationEvent , ResolvableType)是AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster比较重要的方法,用于获取指定事件类型的事件监听器。
protected Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> getApplicationListeners(
ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {
Object source = event.getSource();
Class<?> sourceType = (source != null ? source.getClass() : null);
ListenerCacheKey cacheKey = new ListenerCacheKey(eventType, sourceType); // 计算缓存键
// 需要填充属性值的CachedListenerRetriever, 如果newRetriever为null, 表示不需要属性填充
CachedListenerRetriever newRetriever = null;
// 快速检查是否缓存中命中
CachedListenerRetriever existingRetriever = this.retrieverCache.get(cacheKey);
if (existingRetriever == null) {
// 缓存安全?
if (this.beanClassLoader == null ||
(ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(event.getClass(), this.beanClassLoader) &&
(sourceType == null || ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(sourceType, this.beanClassLoader)))) {
newRetriever = new CachedListenerRetriever();
// 注意, 此时放进去的newRetriever是CachedListenerRetriever属性
// 未赋值(applicationListeners和applicationListenerBeans均为null)的空壳子
existingRetriever = this.retrieverCache.putIfAbsent(cacheKey, newRetriever);
// 在retrieverCache.get和etrieverCache.putIfAbsent之间可能已经有其他线程将该类型事件监听器放入缓存
// 所以这里还需要检测, 避免重复属性赋值
if (existingRetriever != null) {
newRetriever = null;
}
}
}
if (existingRetriever != null) {
Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> result = existingRetriever.getApplicationListeners();
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
// 如果result为null, 表示在retrieverCache.get和etrieverCache.putIfAbsent之间有其他线程将该类型事件监听器放入缓存
// 但放入的还是个没来得及属性赋值的CachedListenerRetriever空壳子
// 还需要调用函数retrieveApplicationListeners获取
}
// 从defaultRetriever中获取事件类型为eventType, 事件源类型为sourceType的事件监听器
// 如果newRetriever非null, 还需要将获取事件监听器赋值给newRetriever的applicationListeners和applicationListenerBeans属性
return retrieveApplicationListeners(eventType, sourceType, newRetriever);
}
如果缓存未命中,AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster会立即新建一个未属性赋值的CachedListenerRetriever空壳子放入缓存,随后在retrieveApplicationListeners(ResolvableType, Class, CachedListenerRetriever)函数中再对放入缓存的CachedListenerRetriever属性赋值。
考虑多线程环境:如果多个线程同时缓存未命中,都将新建的CachedListenerRetriever放入缓存这一步没有问题(ConcurrentHashMap线程安全,putIfAbsent只会将第一次调用CachedListenerRetriever放入缓存),但是如果每个线程都将自己新建的CachedListenerRetriever在retrieveApplicationListeners函数中属性赋值这不就没有必要吗。所以在缓存未命中,将新建的CachedListenerRetriever放入缓存,如果发现有返回(其他线程放入)时,需要将newRetriever置为null,后续不需要再对其属性赋值。
看下retrieveApplicationListeners函数源码:
private Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> retrieveApplicationListeners(
ResolvableType eventType, @Nullable Class<?> sourceType, @Nullable CachedListenerRetriever retriever) {
List<ApplicationListener<?>> allListeners = new ArrayList<>(); // 返回的所有过滤后的事件监听器
// 已经根据eventType和sourceType过滤的事件监听器, 用于给retriever属性赋值
Set<ApplicationListener<?>> filteredListeners = (retriever != null ? new LinkedHashSet<>() : null);
Set<String> filteredListenerBeans = (retriever != null ? new LinkedHashSet<>() : null);
Set<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners;
Set<String> listenerBeans;
synchronized (this.defaultRetriever) { // 使用synchronized保证其他线程对defaultRetriever的修改本线程可见
listeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners);
listenerBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.defaultRetriever.applicationListenerBeans);
}
// 从所有事件监听器中筛选能支持eventType和sourceType的事件监听器
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : listeners) {
if (supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType)) {
if (retriever != null) {
filteredListeners.add(listener);
}
allListeners.add(listener);
}
}
// 通过bean名称筛选
if (!listenerBeans.isEmpty()) {
ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeans) {
try {
// 初始筛选, 避免在getBean时提前实例化
if (supportsEvent(beanFactory, listenerBeanName, eventType)) {
ApplicationListener<?> listener = // 根据bean名称从beanFactory获取实例
beanFactory.getBean(listenerBeanName, ApplicationListener.class);
// 可能已经通过实例注册过
if (!allListeners.contains(listener) && supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType)) {
if (retriever != null) {
if (beanFactory.isSingleton(listenerBeanName)) {
filteredListeners.add(listener);
}
else {
filteredListenerBeans.add(listenerBeanName);
}
}
allListeners.add(listener);
}
}
else {
// 不支持, 移除通过实例方式注册的事件监听器
Object listener = beanFactory.getSingleton(listenerBeanName);
if (retriever != null) {
filteredListeners.remove(listener);
}
allListeners.remove(listener);
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // 未找到单例bean, 可能位于bean销毁阶段
}
}
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(allListeners); // 排序
if (retriever != null) {
// retriever属性赋值
if (filteredListenerBeans.isEmpty()) {
retriever.applicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(allListeners);
retriever.applicationListenerBeans = filteredListenerBeans;
}
else {
retriever.applicationListeners = filteredListeners;
retriever.applicationListenerBeans = filteredListenerBeans;
}
}
return allListeners;
}
从上面源码可以看出,retrieveApplicationListeners(ResolvableType eventType , Class sourceType , CachedListenerRetriever retriever)函数实现两个功能:
- 获取指定事件类型
eventType和事件源类型sourceType的监听器实例集合(通过bean名称注册的需要通过beanFactory获取); - 如果
retriever非null,将获取到监听器的实例集合和bean名称集合给retriever属性赋值;
2.4 筛选监听器
从defaultRetriever中筛选特定事件类型和事件源类型事件监听器工作主要由supportsEvent函数实现,supportsEvent函数有两种重载形式:
supportsEvent( ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory, String listenerBeanName, ResolvableType eventType)形式,前文已经介绍,beanFactory采用的是延迟加载形式注入bean,在第一次调用getBean方法时才会实例化bean,对于不满足条件的bean,如果直接调用getBean的话会造成不必要的实例化操作,该方法通过检查bean定义事件泛型避免不必要实例化操作,但不能精确判断。private boolean supportsEvent( ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory, String listenerBeanName, ResolvableType eventType) { Class<?> listenerType = beanFactory.getType(listenerBeanName); // GenericApplicationListener继承SmartApplicationListener // SmartApplicationListener又继承ApplicationListener// listenerType为null, 或者SmartApplicationListener是SmartApplicationListener\ApplicationListener 返回true if (listenerType == null || GenericApplicationListener.class.isAssignableFrom(listenerType) || SmartApplicationListener.class.isAssignableFrom(listenerType)) { return true; } // 判断listenerType实现ApplicationListener接口时, 泛型是否继承eventType if (!supportsEvent(listenerType, eventType)) { return false; } try { BeanDefinition bd = beanFactory.getMergedBeanDefinition(listenerBeanName); ResolvableType genericEventType = bd.getResolvableType().as(ApplicationListener.class).getGeneric(); // 没有实现ApplicationListener接口返回true // 实现ApplicationListener且泛型继承eventType也返回true return (genericEventType == ResolvableType.NONE || genericEventType.isAssignableFrom(eventType)); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // 手工注入bean名称 return true; } }supportsEvent(Class listenerType, ResolvableType eventType), 判断listenerType实现ApplicationListener接口时,ApplicationListener接口泛型是否继承eventType。但如果listenerType没有实现ApplicationListener接口,该方法也会返回true;protected boolean supportsEvent(Class<?> listenerType, ResolvableType eventType) { ResolvableType declaredEventType = GenericApplicationListenerAdapter.resolveDeclaredEventType(listenerType); return (declaredEventType == null || declaredEventType.isAssignableFrom(eventType)); }supportsEvent(ApplicationListener listener, ResolvableType eventType, @Nullable Class sourceType), 精确判断listener能否监听事件类型eventType且事件源类型sourceType;protected boolean supportsEvent( ApplicationListener<?> listener, ResolvableType eventType, @Nullable Class<?> sourceType) { GenericApplicationListener smartListener = (listener instanceof GenericApplicationListener ? (GenericApplicationListener) listener : new GenericApplicationListenerAdapter(listener)); return (smartListener.supportsEventType(eventType) && smartListener.supportsSourceType(sourceType)); }
3. SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster事件广播
AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster实现了ApplicationEventMulticaster接口管理事件监听器功能, 所以其子类SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster只需要实现ApplicationEventMulticaster接口事件广播功能(由multicastEvent方法定义)即可。AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster定义了获取特定事件类型所有事件监听器方法getApplicationListeners(ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType),那广播事件也简单了,只需要调用该方法获取所有事件监听器,然后循环调用这些事件监听器的onApplicationEvent方法处理事件逻辑即可;在事件发布线程中循环执行事件监听者处理逻辑,虽然开销比较小,但会面临一个风险:流氓监听器可能会阻塞整个应用程序。
为了解决这个问题,SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster定义了一个Executor类型的taskExecutor,如果Executor不为空,则让监听程序在Executor中执行,可以实现异步监听。
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster广播事件核心方法源码如下:
@Override
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
multicastEvent(event, resolveDefaultEventType(event));
}
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
// 循环调用
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
private ResolvableType resolveDefaultEventType(ApplicationEvent event) {
return ResolvableType.forInstance(event);
}
// 同步/异步调用监听器
protected void invokeListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
ErrorHandler errorHandler = getErrorHandler();
if (errorHandler != null) {
try {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
catch (Throwable err) { // 处理错误
errorHandler.handleError(err);
}
}
else {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked"})
private void doInvokeListener(ApplicationListener listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
try {
// 调用监听器监听逻辑
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
catch (ClassCastException ex) {
String msg = ex.getMessage();
if (msg == null || matchesClassCastMessage(msg, event.getClass()) ||
(event instanceof PayloadApplicationEvent &&
matchesClassCastMessage(msg, ((PayloadApplicationEvent) event).getPayload().getClass()))) {
// Possibly a lambda-defined listener which we could not resolve the generic event type for
// -> let's suppress the exception.
Log loggerToUse = this.lazyLogger;
if (loggerToUse == null) {
loggerToUse = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
this.lazyLogger = loggerToUse;
}
if (loggerToUse.isTraceEnabled()) {
loggerToUse.trace("Non-matching event type for listener: " + listener, ex);
}
}
else {
throw ex;
}
}
}
也可以使用Spring提供的@EnableAsync + @Asnc 方式实现异步监听。
4. 事件监听器注册时机
这里还有一个问题:在发布事件调用getApplicationListeners(ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType)获取事件监听器时,要确保所有监听器已经注册完成,那这些事件监听器什么时候注册的呢?
EventPublishingRunListener(将Spring Boot启动时间节点封装成时间并发布,参考Spring Boot v2.4.4源码解析(三)事件机制篇一)内部的SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster,在创建时,就注册通过SPI机制加载的事件监听器;public EventPublishingRunListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args) { this.application = application; this.args = args; this.initialMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(); for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : application.getListeners()) { this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener); } }- 实现
ApplicationListener接口,或者使用@EventListener注解的事件监听器,Spring Boot会在刷新上下文时调用registerListeners()注册。
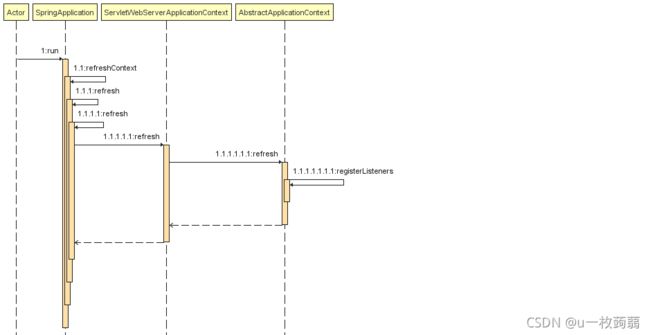
protected void registerListeners() { // Register statically specified listeners first. for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) { getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener); } // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans // uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them! String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false); for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) { getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName); } // Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster... Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents; this.earlyApplicationEvents = null; if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(earlyEventsToProcess)) { for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) { getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent); } } } - 手动调用
AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster的addApplicationListenerBean系列方法注册;