前端训练营学习笔记——工程化实践一:创建自己的脚手架工具
目录
- 0 引言
- 1 什么是工程化
- 2 初始化与构建
-
- 2.1 初始化工具Yeoman
- 2.2 利用yeoman创建脚手架的简单用法
-
- 2.2.1 通过yeoman进行命令行交互
- 2.2.2 通过yeoman进行HTML模板填充
- 2.2.3 通过yeoman管理依赖
- 2.3 webpack基本知识
-
- 2.3.1 webpack的设计初衷和基本理解
- 2.3.2 webpack安装使用的两种方式
- 2.3.3 webpack的基础概念
- 2.4 babel基本知识
-
- 2.4.1 babel的作用
- 2.4.2 babel安装和使用
- 2.4.3 在webpack中通过babel-loader使用babel
- 2.5 利用yeoman搭建一个vue脚手架
-
- 2.5.1 创建generator-vue项目
- 2.5.2 配置webpack
- 2.5.3 拷贝相关模板文件
- 3 单元测试
-
- 3.1 单元测试的适用场景
- 3.2 前端单测工具
- 3.3 Mocha的安装和简单使用
-
- 3.3.1 安装
- 3.3.2 简单使用
- 3.3.3 将require/exports改成import/export语法
- 3.4 单元测试的核心概念code coverage
-
- 3.4.1 code coverage含义
- 3.4.2 code coverage插件nyc用法
- 3.4.3 code covrage测试结果示例
- 3.5 实例:对parseHTML函数进行单元测试
- 3.6 将单测集成到工具链中
- 4 利用集成了单测的脚手架搭建vue项目
- 5 小结
0 引言
前面几篇博客介绍的是组件化知识和实践,组件化是从架构的角度解决如何通过程序复用将项目做大的问题,而本篇博客将要介绍的工程化则是解决如何通过制作工具、搭建系统等方式带领一个团队把项目做好。
1 什么是工程化
- 工具、流程、系统:从没有到有,从少到多
- 质量和效率:由低到高
2 初始化与构建
2.1 初始化工具Yeoman
Yeoman是社区流行的一个初始化工具,可以用来创建脚手架工具,相当于generator的generator
利用Yeoman创建generator的方法:
- 利用
npm init新建一个模块 - 安装
yeoman-generator包并全局安装yo命令
npm install yeoman-generator
npm install -g yo
- 在index.js中参考Yeoman官网的例子编写一个Generator类
var Generator = require('yeoman-generator');
module.exports = class extends Generator {
// The name `constructor` is important here
constructor(args, opts) {
// Calling the super constructor is important so our generator is correctly set up
super(args, opts);
}
method1() {
this.log('method 1 just ran');
}
method2() {
this.log('method 2 just ran');
}
};
- 修改package.json中的name(generator-模块名)和main路径(指向index.js的路径)
- 利用
npm link将本地的模块链接到标准全局模块中去 - 最后执行
yo 模块名启动脚手架
2.2 利用yeoman创建脚手架的简单用法
2.2.1 通过yeoman进行命令行交互
// 在Generator中增加prompting异步方法
async prompting() {
this.answers = await this.prompt([
{
type: "input",
name: "name",
message: "Your project name",
default: this.appname // Default to current folder name
},
{
type: "confirm",
name: "cool",
message: "Would you like to enable the Cool feature?"
},
{
type: "input",
name: "title",
message: "Your project title"
}
]);
this.log("app name", this.answers.name);
this.log("cool feature", this.answers.cool);
}
2.2.2 通过yeoman进行HTML模板填充
// 在Generator中增加writing方法并执行this.fs.copyTpl
writing() {
this.fs.copyTpl(
this.templatePath('index.html'), // templatePath在与当前文件同级的templates文件夹下
this.destinationPath('public/index.html'), // 相对于根目录
{ title: this.answers.title } // 使用2.2.1中用户输入的`title`
);
}
2.2.3 通过yeoman管理依赖
利用this.fs.extendJSON()函数更改package.json并执行npmInstall自动安装依赖
class extends Generator {
writing() {
const pkgJson = {
devDependencies: {
eslint: '^3.15.0'
},
dependencies: {
react: '^16.2.0'
}
};
// Extend or create package.json file in destination path
this.fs.extendJSON(this.destinationPath('package.json'), pkgJson);
}
install() {
this.npmInstall();
}
};
2.3 webpack基本知识
2.3.1 webpack的设计初衷和基本理解
- 设计初衷:webpack最初是为Node设计的打包工具,提供的能力是将node代码打包成浏览器可用的代码
- 基本理解:webpack能够进行多文件合并,在合并过程中通过各种loader和plugin去控制合并的规则以及对文本进行一些转换
2.3.2 webpack安装使用的两种方式
- 全局安装webpack-cli和webpack
- 本地安装webpack-cli然后使用
npx webpack命令执行webpack
2.3.3 webpack的基础概念
- entry:用于设置入口文件
- output:用于设置输出文件路径
- loader:一种文件格式转换工具,用于将其它形式语言书写的文件转译成能被webpack识别的json或js格式,常见的loader有css-loader,vue-loader
- plugin: 用于完成除Loader之外的其它功能,如打包优化、拷贝文件等
2.4 babel基本知识
2.4.1 babel的作用
将新版本的js文件转换成老版本的js文件,以便能够运行在老版本的浏览器中
2.4.2 babel安装和使用
需要全局安装@babel/core和@babel/cli和用来设定默认配置的@babel/preset-env,并在.babelrc文件中配置@babel/preset-env
{
"presets": ["@babel/preset-env"]
}
安装好后执行babel filename.js即可
2.4.3 在webpack中通过babel-loader使用babel
作用是能够在webpack打包过程中,自动利用babel对js文件进行处理
rules: [
{
test: /\.js$/,
use: {
loader: "babel-loader",
options: {
presets: ["@babel/preset-env"],
plugins: [...]
}
}
}
]
2.5 利用yeoman搭建一个vue脚手架
2.5.1 创建generator-vue项目
按照2.1中介绍的步骤创建一个generator-vue项目,注意package.json中的name(需要以generator-开头,执行脚手架时会被用户输入的项目名覆盖)和main路径要正确,入口文件index.js如下
var Generator = require('yeoman-generator');
module.exports = class extends Generator {
// The name `constructor` is important here
constructor(args, opts) {
// Calling the super constructor is important so our generator is correctly set up
super(args, opts);
}
async prompting() {
this.answers = await this.prompt([
{
type: "input",
name: "name",
message: "Your project name",
default: this.appname // Default to current folder name
}
])
this.log("app name", this.answers.name);
}
async initPackages() {
const pkgJson = {
"name": this.answers.name,
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "generators/app/index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"dependencies": {
"yeoman-generator": "^4.11.0"
},
}
// Extend or create package.json file in destination path
this.fs.extendJSON(this.destinationPath('package.json'), pkgJson);
this.npmInstall(["vue"], {"save-dev": false}); // 如果要装vue3,改成vue@next
this.npmInstall(["webpack", "vue-loader"], {"save-dev": true})
}
copyFiles() {
this.fs.copyTpl(
this.templatePath('HelloVue.vue'),
this.destinationPath('src/HelloVue.vue'),
{}
);
}
};
2.5.2 配置webpack
在templates文件夹中新建一个webpack配置文件webpack.config.js,配置vue-loader,vue-stytle-loader,css-loader以及webpack的copy-plugin插件, 如下
const webpack = require('webpack'); // 访问内置的插件
const VueLoaderPlugin = require("vue-loader/lib/plugin")
const CopyPlugin = require("copy-webpack-plugin");
module.exports = {
entry: './src/main.js',
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.vue$/,
use: 'vue-loader', // 实现将vue文件转换成webpack能识别的js或json文件
},
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: ['vue-style-loader', 'css-loader'], // css-loader要在后面,否则会报错
}
],
},
plugins: [
new VueLoaderPlugin(), // VueLoader插件
new CopyPlugin({ // 拷贝插件
patterns: [
{ from: "src/*.html", to: "[name].[ext]" },
],
})
],
mode: "development"
};
2.5.3 拷贝相关模板文件
在template中添加index.html、main.js文件,并在index.js中将它们和webpack.config.js一同copy到src内
3 单元测试
3.1 单元测试的适用场景
- 可能会被很多人使用的开源项目
- 复用度比较高的商业项目
- 其它需要保证已有功能正确不受影响的复杂大型项目
3.2 前端单测工具
- Mocha:有趣、简单且灵活的JavaScript测试框架
- Jest:一个令人愉快的 JavaScript 测试框架,专注于简洁明快
3.3 Mocha的安装和简单使用
3.3.1 安装
- 全局安装:
npm install -g mocha - 项目安装:
npm install --save-dev mocha
3.3.2 简单使用
add.js
function add(a, b) {
return a+b
}
module.exports = add
test.js
let add = require("./add")
var assert = require('assert');
describe('test add function', function() {
it('1 + 2 should return 3', function() {
assert.equal(add(1, 2), 3);
});
});
最后在test.js目录下执行mocha即可运行单元测试
3.3.3 将require/exports改成import/export语法
在3.3.2中引入和导出模块使用的是node的require/exports,如果想改成import/export语法,需要借助babel
- 本地安装mocha
- 本地安装@babel/core,@babel/preset-env,@babel-register
- 配置.babelrc的presets
{
"presets": ["@babel/preset-env"],
}
- 在package.json中的test字段添加运行mocha的脚本
mocha --require @babel/register
{
"name": "unit-test",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "mocha --require @babel/register",
},
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"devDependencies": {
"@babel/core": "^7.14.6",
"@babel/preset-env": "^7.14.7",
"@babel/register": "^7.14.5",
"@istanbuljs/nyc-config-babel": "^3.0.0",
"babel-plugin-istanbul": "^6.0.0",
"mocha": "^9.0.1"
}
}
- 最后执行
npm run test即可
3.4 单元测试的核心概念code coverage
3.4.1 code coverage含义
code coverage是用来检测编写的单元测试用例是否完整覆盖了项目代码,可以使用nyc插件。
单测应达到的目标:函数覆盖率100%,行覆盖率>90%
3.4.2 code coverage插件nyc用法
将nyc应用于使用了babel的mocha项目的方法:
- 本地安装nyc
npm i --save-dev nyc - 安装两个插件:
npm i --save-dev babel-plugin-istanbul @istanbuljs/nyc-config-babel - 在.babelrc中添加
"plugins": ["istanbul"]然后在.nycrc配置文件中添加如下配置
{
"extends": "@istanbuljs/nyc-config-babel"
}
- 在package.json中的test字段添加coverage的脚本
"coverage": "nyc mocha" - 最后执行
npm run coverage命令即可
3.4.3 code covrage测试结果示例
| File | % Stmts | % Branch | % Funcs | % Lines | Uncovered Line #s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All files | 90.43 | 82.04 | 100 | 90.29 | |
| parser.js | 90.43 | 82.04 | 100 | 90.29 | 25,80,105,170-171,227,237,249,260,265,271,273,293,297,316,356,362-365,373,392 |
3.5 实例:对parseHTML函数进行单元测试
详见HTML-parser/test/test.js,几点注意:
- 为方便对babel处理过的代码跟踪调试,需要在调试的配置文件launch.json中加入两个额外的配置,并在.babelrc中加入配置
"sourceMaps": "inline" /*不会产生额外的输出文件*/
"runtimeArgs": ["--require", "@babel/register"],
"sourceMaps": true, // 开启源映射,以便调试的时候能够映射到真实的代码而非babel转译的代码
- launch.json中的program配置要指定到
node_modules/bin/mocha目录
3.6 将单测集成到工具链中
参考2.5.1在pkgJson中添加test和coverage命令,安装单测相关依赖并将.babelrc,.nycrc和单测模板文件test.js拷贝到destinationPath中,详细请参考generator-vuetool/generators/app/index.js
4 利用集成了单测的脚手架搭建vue项目
- 在脚手架项目根目录下创建新的项目文件夹my_vue_app
- 在my_vue_app文件夹中执行
yo vuetool命令 - 按照命令行提示依次输入相关设置等待项目搭建完成
yo vuetool
? Your project name my_vue_app
app name my_vue_app
create package.json
create src\HelloVue.vue
create src\main.js
create webpack.config.js
create src\index.html
create .babelrc
create .nycrc
create test\test.js
npm notice created a lockfile as package-lock.json. You should commit this file.
npm WARN [email protected] No description
npm WARN [email protected] No repository field.
+ [email protected]
added 14 packages from 41 contributors in 3.095s
+ [email protected]
+ [email protected]
+ [email protected]
+ [email protected]
+ @babel/[email protected]
+ @babel/[email protected]
+ [email protected]
+ @vue/[email protected]
+ [email protected]
+ @babel/[email protected]
+ [email protected]
+ [email protected]
+ [email protected]
+ [email protected]
+ @istanbuljs/[email protected]
+ [email protected]
added 520 packages from 257 contributors in 71.987s
48 packages are looking for funding
run `npm fund` for details
生成的项目目录结构如下图所示
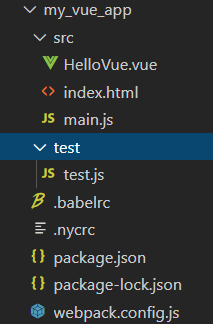
4. 等项目搭建好后便可以愉快地进行开发和测试了
- 运行
npm run test可以执行单测 - 运行
npm run coverage可以执行单测覆盖率检查 - 运行
npm run build可以打包构建项目生成dist目标代码
5 小结
本篇博客首先阐述了对前端工程化的基本理解:前端工程化体现在工具、规范、系统等从无到有,由少到多,目标是提升项目开发的效率和质量。然后以一个实际的项目——创建自己的脚手架工具为例,分项目初始化和构建以及单元测试两部分介绍如何创建自己的脚手架工具。最后利用创建的脚手架工具快速搭建一个包含测试模块的vue项目。希望读者能从中体会到工程化是如何提升项目开发效率和质量的,当然笔者目前也还处在工程化刚学习入门阶段,后续需要通过不断地实践加深认识和理解。
ps:如果觉得此文对你有帮助或启发,请不要吝惜你的点赞和分享,如有疑问,请留言或私信交流