springboot源码系列-HandlerMapping
1,DispatcherServlet转发流程
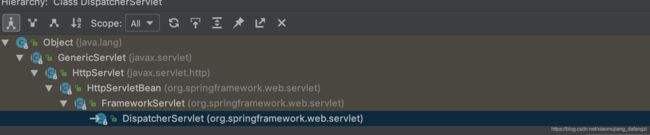
先看一下springmvc这个核心类DispatcherServlet的继承关系
我们知道HttpServlet是处理doGet/doPost/doPut/doDelete 去完成一段业务逻辑的处理。但是spring是怎么将这些doX请求变成一个controller或者一个controller的method的去处理的呢。我们通过看FrameworkServelet的方法栈发现实际上FrameworkServelet已经实现了Do系列方法。我们以doGet为例进入代码。
 跟进doGet方法 发现doGet并没有做什么处理只是简单的调用了processRequest()去处理请求。进入processRequest方法。
跟进doGet方法 发现doGet并没有做什么处理只是简单的调用了processRequest()去处理请求。进入processRequest方法。
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
doService(request, response);
...略....
}我们注意看doService方法 这个方法在FrameworkServlet是一个抽象方法,而实现者正是我们所熟知的DispatcherServlet。继续进入该方法。发现doService方法也没有做什么事情 只是简单的调用自身的doDispatch方法。由于doDispatch方法代码比较多 我们只是把有关我们主题的代码摘录出来。
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
...略...
}
可以看出 dispatch方法主要的功能是选择一个HandlerExecutionChain 然后通过对应的HandlerAdapter对象执行处理逻辑。继续跟进getHandler()方法
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(
"Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
return null;
}这个方法主要是遍历自身持有的HandlerMapping对象 根据请求的request找到合适的HandlerExecutionChain。具体的查找的动作是在我们的HandlerMapping对象中去做的处理。下面看一下HandlerMapping是如何工作的。
2,HandlerMapping
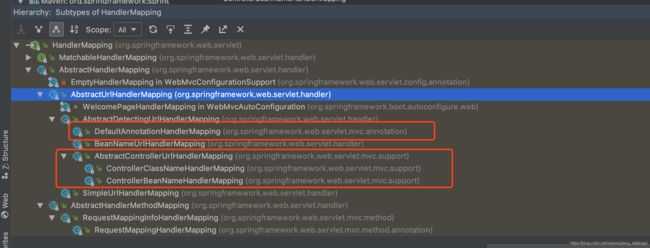
还是一样 我们先来看一下类的继承关系。
我们可以看到HandlerMapping有众多的实现类(在spring5.0以下版本中) 我演示的版本是基于spring4.3.11。在当前版本中已经有一批实现类 官方已经不建议使用了。例如:DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping,AbstractControllerUrlHandlerMapping,ControllerClassNameHandlerMapping,ControllerBeanNameHandlerMapping。也就是图像红框标注出来的。在spring5.x之后已经不存在了。谨慎使用。这么多的实现类 我们主要分为两种。AbstractUrlHandlerMapping所带领的整个控制器为一个请求和AbstractHandlerMethodMapping方法级别的映射。下面我们接着上面的(1)中的HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);继续跟进HandlerMapping的getHandler方法。我们以AbstractUrlHandlerMapping代表的实现为例走一遍查找流程。
我们进入一级抽象类AbstractHandlerMapping通用实现。
@Override
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.corsConfigSource.getCorsConfiguration(request);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
主要看第一句,getHandlerInternal方法 我们点进去 发现父类是一个抽象方法 实现分别由我们上诉讲到的两个抽象子类实现。继续跟进getHandlerInternal方法。
protected Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
Object handler = lookupHandler(lookupPath, request);
if (handler == null) {
// We need to care for the default handler directly, since we need to
// expose the PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE for it as well.
Object rawHandler = null;
if ("/".equals(lookupPath)) {
rawHandler = getRootHandler();
}
if (rawHandler == null) {
rawHandler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (rawHandler != null) {
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (rawHandler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) rawHandler;
rawHandler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
validateHandler(rawHandler, request);
handler = buildPathExposingHandler(rawHandler, lookupPath, lookupPath, null);
}
}
if (handler != null && logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Mapping [" + lookupPath + "] to " + handler);
}
else if (handler == null && logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No handler mapping found for [" + lookupPath + "]");
}
return handler;
}跟进lookupHandler
protected Object lookupHandler(String urlPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// Direct match?
Object handler = this.handlerMap.get(urlPath);
if (handler != null) {
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
validateHandler(handler, request);
return buildPathExposingHandler(handler, urlPath, urlPath, null);
}
// Pattern match?
List matchingPatterns = new ArrayList<>();
for (String registeredPattern : this.handlerMap.keySet()) {
if (getPathMatcher().match(registeredPattern, urlPath)) {
matchingPatterns.add(registeredPattern);
}
else if (useTrailingSlashMatch()) {
if (!registeredPattern.endsWith("/") && getPathMatcher().match(registeredPattern + "/", urlPath)) {
matchingPatterns.add(registeredPattern +"/");
}
}
}
...略...
} 可以看到这个方法先从自身拥有的handlerMap中精确匹配 如果找到返回 找不到 再正则匹配。最终返回handler。最后在AbstractHandlerMapping类中包装HandlerExecutionChain返回。HandlerExecutionChain 可以简单理解为一个逻辑处理器和多个拦截器组成的一组请求执行器。每一个请求都会有一个HandlerExecutionChain 去执行响应。
到此查找HandlerExecutionChain 的流程结束。而针对另一个分支的HandlerMapping(AbstractHandlerMethodMapping)是如何实现查找功能 由于篇幅关系就不一一列举。仔细阅读上诉流程 会有几个问题
- DispatcherServlet中的handlerMappings(所有HandlerMapping实例的集合)是在何时被赋值的
- AbstractUrlHandlerMapping中的handlerMap是何时被初始化的。
- springboot中的HandlerMapping实例是谁帮我们实例化的。因为我们在开发过程中好像并没有手动实例化一个HandlerMapping实例给到springIoc容器
我们先看第一个问题。 DispatcherServlet中的handlerMappings是在何时被赋值的
仔细查看DispatcherServlet的父类FrameworkServlet时发现 该类里面有一个内部类
private class ContextRefreshListener implements ApplicationListener {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
FrameworkServlet.this.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
} 当然这个类的实例化是在父类的configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext中实例化的。 我们可以看到ContextRefreshListener 是一个事件监听器。IOC容器刷新完成之后 该监听器会调用父类的onApplicationEvent方法。继续跟进该方法,发现该方法调用了一个空方法onRefresh ,这个方法是由DispatcherServlet重写。我们直接进入主干方法。
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.
Map matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order.
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
}
// Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering
// a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found.
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No HandlerMappings found in servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default");
}
}
} 可以发现 handlerMappings的初始化是在springIoc容器刷新完成之后 通过容器类型查找 找到所有的HandlerMapping类型赋值给handlerMappings。
第二个问题AbstractUrlHandlerMapping中的handlerMap是何时被初始化的。我们以SimpleUrlHandlerMapping为例。直接定位到registerHandlers 至于这个方法在何时调用 读者可自行阅读。
protected void registerHandlers(Map urlMap) throws BeansException {
if (urlMap.isEmpty()) {
logger.trace("No patterns in " + formatMappingName());
}
else {
urlMap.forEach((url, handler) -> {
// Prepend with slash if not already present.
if (!url.startsWith("/")) {
url = "/" + url;
}
// Remove whitespace from handler bean name.
if (handler instanceof String) {
handler = ((String) handler).trim();
}
registerHandler(url, handler);
});
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
List patterns = new ArrayList<>();
if (getRootHandler() != null) {
patterns.add("/");
}
if (getDefaultHandler() != null) {
patterns.add("/**");
}
patterns.addAll(getHandlerMap().keySet());
logger.debug("Patterns " + patterns + " in " + formatMappingName());
}
}
} 最终会调用父类的 registerHandler方法。
protected void registerHandler(String urlPath, Object handler) throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
Assert.notNull(urlPath, "URL path must not be null");
Assert.notNull(handler, "Handler object must not be null");
Object resolvedHandler = handler;
// Eagerly resolve handler if referencing singleton via name.
if (!this.lazyInitHandlers && handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
ApplicationContext applicationContext = obtainApplicationContext();
if (applicationContext.isSingleton(handlerName)) {
resolvedHandler = applicationContext.getBean(handlerName);
}
}
Object mappedHandler = this.handlerMap.get(urlPath);
if (mappedHandler != null) {
if (mappedHandler != resolvedHandler) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot map " + getHandlerDescription(handler) + " to URL path [" + urlPath +
"]: There is already " + getHandlerDescription(mappedHandler) + " mapped.");
}
}
else {
if (urlPath.equals("/")) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Root mapping to " + getHandlerDescription(handler));
}
setRootHandler(resolvedHandler);
}
else if (urlPath.equals("/*")) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Default mapping to " + getHandlerDescription(handler));
}
setDefaultHandler(resolvedHandler);
}
else {
this.handlerMap.put(urlPath, resolvedHandler);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Mapped [" + urlPath + "] onto " + getHandlerDescription(handler));
}
}
}
}那么问题三:springboot中的HandlerMapping实例是谁帮我们实例化的。为了说明第三个问题 我们做一个小例子
@Bean
public SimpleUrlHandlerMapping getHandlerMapping(){
SimpleUrlHandlerMapping simpleUrlHandlerMapping = new SimpleUrlHandlerMapping();
Properties properties = new Properties();
simpleUrlHandlerMapping
.setUrlMap(Collections.singletonMap("test.html", testUrlMappingController()));
simpleUrlHandlerMapping.setMappings(properties);
//simpleUrlHandlerMapping.setOrder(1);
return simpleUrlHandlerMapping;
}
@Bean
public TestUrlMappingController testUrlMappingController(){
return new TestUrlMappingController();
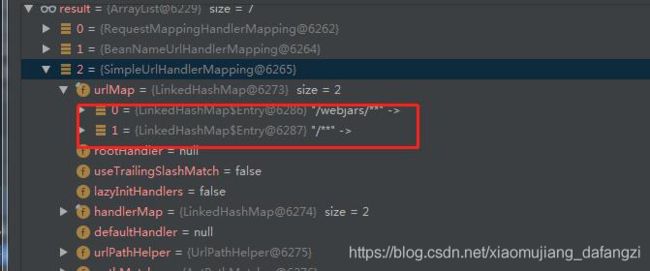
}我们像容器中注入了一个SimpleUrlHandlerMapping 当然我们注释了simpleUrlHandlerMapping.setOrder(1); 这句代码。我们并未设置当前HandlerMapping的优先级。启动容器 访问test.html 发现404. 我们把注释打开 设置优先级为1 访问却发现可以成功。放回。带着疑问 断点跟入了请求。
惊奇的发现 我们系统中除了我们定义的HandlerMapping之外 还有6个。并且有一个SimpleUrlHandlerMapping排在我们的SimpleUrlHandlerMapping之前 更可气的是 它竟然有一个路径为/**的匹配器。 所以只要它这个HandlerMapping在我们之前 那基本上没我们定义的HandlerMapping什么事了。所以出现404很正常。
通过刚才的例子我们发现spring帮我们向容器中注入了很多handlerMapping 这些handlerMapping各司其职。 但是在哪注入的,很多人想到了springboot的自动注入。我也打开了autoconfiure包找到了嫌疑人 WebMvcAutoConfiguration。仔细阅读发现这个类里面有一个内部类 EnableWebMvcConfiguration 这个内部类 继承了DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration 而间接继承了WebMvcConfigurationSupport 这个类这么熟悉??? 打开这个类发现这么一段代码:
@Bean
@Nullable
public HandlerMapping resourceHandlerMapping() {
Assert.state(this.applicationContext != null, "No ApplicationContext set");
Assert.state(this.servletContext != null, "No ServletContext set");
ResourceHandlerRegistry registry = new ResourceHandlerRegistry(this.applicationContext,
this.servletContext, mvcContentNegotiationManager(), mvcUrlPathHelper());
addResourceHandlers(registry);
AbstractHandlerMapping handlerMapping = registry.getHandlerMapping();
if (handlerMapping == null) {
return null;
}
handlerMapping.setPathMatcher(mvcPathMatcher());
handlerMapping.setUrlPathHelper(mvcUrlPathHelper());
handlerMapping.setInterceptors(getInterceptors());
handlerMapping.setCorsConfigurations(getCorsConfigurations());
return handlerMapping;
}进入getHandlerMapping方法确实发现 new了一个SimpleUrlHandlerMapping并且优先级设置为Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 1。 不仅如此 这个类还加入了其余的一些HandlerMapping的实现 有兴趣的可以进一步阅读。