React项目构建及页面路由
目录
- React项目构建
-
- React脚手架的构建
- React 页面路由
-
- hash模式
- history模式
- React路由
-
- 路由组件
- Route
- Link和NavLink
- Redirect页面重定向
- Switch
- history对象
- 案例
React项目构建
在React框架的使用中,常使用react脚手架来简化react项目的创建。
React脚手架的构建
(1)全局安装React脚手架:
npm install -g create-react-app
(2)构建react项目——myapp:
npx create-react-app myapp
其他方法:
yarn create react-app myapp
(4)程序运行:
npm start
React 页面路由
从用户角度看,前端路由主要实现了两个功能:
- 记录当前页面的状态(保存当前页面的URL,再次打开该URL时,网页还是保存时的状态)
- 可以使用浏览器的前进和后退功能
常用的路由方式有两种:hash模式和history模式
hash模式
hash是指URL地址后面“#”以及其后面的字符。hash也称为描点,本身是用来做页面定位的,它可以使“#”后面的字符对应的内容显示在可视区域内。
hash值的变化不会导致浏览器向服务器发送请求,并且hash的改变会触发hashchange事件,浏览器的前进后退也能对其进行控制,所以在html5的history出现之前,常使用hash实现路由跳转。
使用到的API:
window.location.hash = 'qq' // 设置 url 的 hash,会在当前url后加上 '#qq'
var hash = window.location.hash // '#qq'
window.addEventListener('hashchange', function(){
// 监听hash变化,点击浏览器的前进后退会触发
})
history模式
使用hash做为路由的话,具有一定的局限性:
- hash本来是用来做页面定位的,如果用作路由,原来的描点功能就不能使用了。
- hash的传参是基于URL的,传递参数会有体积限制,而history就不一样了。
history模式不仅可以再url里面放参数,还可以将数据存放在一个特定的对象中。即history模式路由可以传递复杂的数据。
相关API:
window.history.pushState(state, title, url)
- state是需要保存的数据,这个数据在触发popstate事件时,可以再event.state里面获取
- title是标题
- url是设定新的历史记录的url.
例如:
假设当前url是:https://www.baidu.com/a/
执行history.pushState(null,null,'./b/')后,url就变成了https://www.baidu.com/a/b/.
执行history.pushState(null,null,’/b/’),url就变成了https://www.baidu.com/b/
其他API:
window.history.back() //后退
window.history.forward() //前进
window.history.go(1) //前进1步,若为-2,是后退两步
//window.history.length可以查看当前历史堆栈中页面的数量
React路由
react实现页面路由的模块:react-router-dom
下载模块:
yarn add react-router-dom
路由组件
(1)react-router-dom有两种路由组件:HashRouter(hash模式)和BrowserRouter(history模式)
这两种组件是路由的容器,必须在最外层。
例如:
history模式:
React.render(
<BrowserRouter>
<Route path="/" component={Home}/>
</BrowserRouter>
)
Route
Route是路由的一个原材料,用于控制路径和组件之间的对应关系。
相关参数:
- path:路由路径
- component:组件
- exact:用于精确定位
例如:
<Route exact path="/" component={Home}/>
//即只在路径最后是“/”时,才显示Home组件的内容(exact的作用)
如果不使用exact:
<Route path="/" component={Home}/>
<Route path="/login" component={Login}/>
//即使路径最后是"/login",页面显示的也是Home组件的内容,因为该路径中包含了"/"。
注意:以上写法是^ 5.2.0版本以及^5.3.0版本的路由写法。
如果是升级后的版本(^ 6.0.2版本),则使用以下方式:
<Routes>
<Route path='/' element={<Home/>}/>
</Routes>
Link和NavLink
Link和NavLink都用于实现路由跳转,但NavLink的参数更多一些。
搭配to实现路由跳转。
<NavLink to='/'>点我换页</NavLink>
Redirect页面重定向
(1)基本的重定向
<Redirect to="/else" />
(2)对象形式
<Redirect
to={{
pathname: "/login",
search: "?utm=your+face",
state: { referrer: currentLocation }
}}
/>
(3)采用push生成新的记录
<Redirect push to="/else" />
(4) 配合Switch组件使用,form表示重定向之前的路径,如果匹配则重定向,不匹配则不重定向
<Switch>
<Redirect from='/old-path' to='/new-path'/>
<Route path='/new-path' component={Place}/>
</Switch>
Switch
路由切换,只会匹配第一个路由,可以想象成tab栏
Switch内部只能包含Route、Redirect、Router
<Switch>
<Route exact path="/" component={Login}/>
<Route path="/home" component={Home}/>
</Switch>
history对象
在每个路由组件中我们可以使用this.props.history获取到history对象。
在history中封装了push,replace,go等方法。
History {
length: number;
action: Action;
location: Location;
push(path: Path, state?: LocationState): void; // 调用push前进到一个地址,可以接受一个state对象,就是自定义的路由数据
push(location: LocationDescriptorObject): void; // 接受一个location的描述对象
replace(path: Path, state?: LocationState): void; // 用页面替换当前的路径,不可再goBack
replace(location: LocationDescriptorObject): void; // 同上
go(n: number): void; // 往前走多少页页面
goBack(): void; // 返回一个页面
goForward(): void; // 前进一个页面
}
使用: this.props.history.push('/home')
案例
(PS:这里使用的是react-router-dom老的版本)
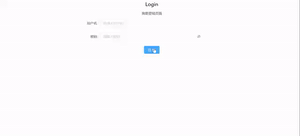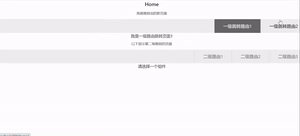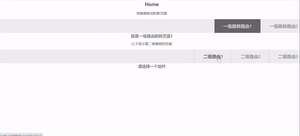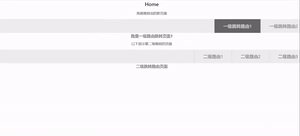
Login组件:
export default class Login extends Component{
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
login=()=>{
console.log(this.props.history)
this.props.history.push('/home') //将home组件的url压入地址栏
console.log(this.props.history)
}
render(){
return(
<div>
<h2>Login</h2>
<p>我是登陆页面</p>
<Form
labelCol={{
span: 8,
}}
wrapperCol={{
span: 8,
}}
>
<Form.Item label={'用户名'}>
<Input placeholder={'请输入用户名'}/>
</Form.Item>
<Form.Item label={'密码'}>
<Input.Password placeholder={'请输入密码'}/>
</Form.Item>
</Form>
<Button type={'primary'} onClick={this.login}>登陆</Button>
</div>
)
}
}
Home组件:
export default class Home extends Component{
render() {
return(
<BrowserRouter>
<h2>Home</h2>
<p>我是跳转出的新页面</p>
<div>
<ul>
<li>
<NavLink to={'/home1'}>一级跳转路由1</NavLink>
</li>
<li>
<NavLink to={'/home2'}>一级跳转路由2</NavLink>
</li>
</ul>
<Route path={'/home1'} component={Home1}/>
<Route path={'/home2'} component={Home2}/>
</div>
</BrowserRouter>
)
}
}
Home1组件:
export default class Home1 extends Component{
render() {
return(
<>
<h3>我是一级路由跳转页面1</h3>
<p>以下显示第二级跳转的页面</p>
<div>
<ul>
<li>
<Link to={`${this.props.match.url}/homes1`}>二级路由1</Link>
</li>
<li>
<Link to={`${this.props.match.url}/homes2`}>二级路由2</Link>
</li>
<li>
<Link to={`${this.props.match.url}/homes3`}>二级路由3</Link>
</li>
</ul>
<Route path={`${this.props.match.url}/homes1`} component={Homes}/>
<Route path={`${this.props.match.url}/homes2`} component={Homes2}/>
<Route path={`${this.props.match.url}/homes3`} component={Homes}/>
<Route exact path={this.props.match.url} render={()=> (
<h3>请选择一个组件</h3>)
}/>
</div>
</>
)
}
}
Homes组件:
export default class Homes extends Component{
render() {
return(
<div>
<h3>二级跳转路由页面</h3>
</div>
)
}
}
Homes2组件:
export default class Homes2 extends Component{
render() {
return(
<div>
<h3>二级跳转路由页面homes2</h3>
</div>
)
}
}