1110. Delete Nodes And Return Forest
Given the root of a binary tree, each node in the tree has a distinct value.
After deleting all nodes with a value in to_delete, we are left with a forest (a disjoint union of trees).
Return the roots of the trees in the remaining forest. You may return the result in any order.
Example 1:
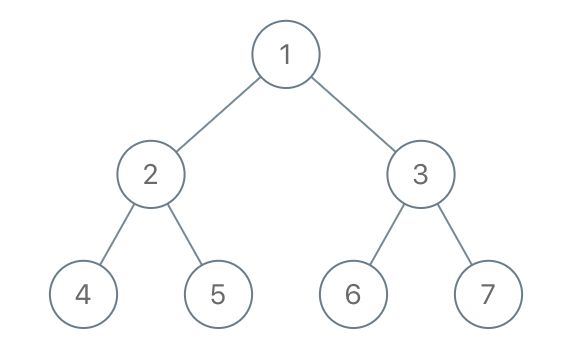
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], to_delete = [3,5] Output: [[1,2,null,4],[6],[7]]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,4,null,3], to_delete = [3] Output: [[1,2,4]]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the given tree is at most
1000. - Each node has a distinct value between
1and1000. to_delete.length <= 1000to_deletecontains distinct values between1and1000.
题目: 给定一棵二叉树,和一个数组。删除树中值等于数组元素值的节点。
思路:
方法一:BFS。用queue来保存所有节点
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector delNodes(TreeNode* root, vector& to_delete) {
vector res;
unordered_set del(to_delete.begin(), to_delete.end());
queue q;
q.push(root);
if(!del.count(root->val)) res.push_back(root);
while(!q.empty()){
TreeNode* node = q.front();
q.pop();
if(del.count(node->val)){
if(node->left && !del.count(node->left->val))
res.push_back(node->left);
if(node->right && !del.count(node->right->val))
res.push_back(node->right);
}
if(node->left){
q.push(node->left);
if(del.count(node->left->val))
node->left = NULL;
}
if(node->right){
q.push(node->right);
if(del.count(node->right->val))
node->right = NULL;
}
}
return res;
}
}; 方法二,DFS
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void DFS(TreeNode* node, unordered_set& del, vector& res){
if(!node) return;
DFS(node->left, del, res);
DFS(node->right, del, res);
if(node->left && del.count(node->left->val))
node->left = NULL;
if(node->right && del.count(node->right->val))
node->right = NULL;
if(del.count(node->val)){
if(node->left) res.push_back(node->left);
if(node->right) res.push_back(node->right);
}
}
vector delNodes(TreeNode* root, vector& to_delete) {
vector res;
unordered_set del(to_delete.begin(), to_delete.end());
if(root && !del.count(root->val)) res.push_back(root);
DFS(root, del, res);
return res;
}
};