863. All Nodes Distance K in Binary Tree
Given the root of a binary tree, the value of a target node target, and an integer k, return an array of the values of all nodes that have a distance k from the target node.
You can return the answer in any order.
Example 1:
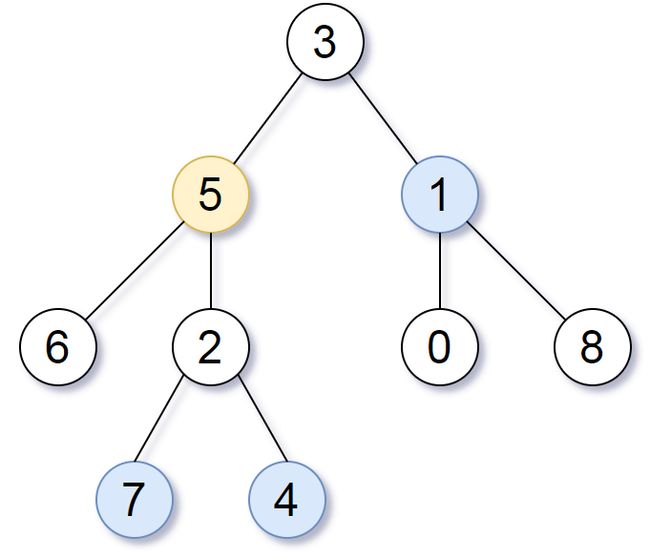
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], target = 5, k = 2 Output: [7,4,1] Explanation: The nodes that are a distance 2 from the target node (with value 5) have values 7, 4, and 1.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1], target = 1, k = 3 Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 500]. 0 <= Node.val <= 500- All the values
Node.valare unique. targetis the value of one of the nodes in the tree.0 <= k <= 1000
题目: 给定一个二叉树,和其中一个节点。求与给定节点距离为k的所有节点的值。路径不一定要过根节点。
思路:首先需要找到给定的节点位置。距离给定节点target 为k的节点可能在target之下(子孙辈节点),也可能在target之上(祖辈节点),也可能在target旁边。因此需要两种操作,一种向下寻找距离给定节点为k,一种向上寻找。向下寻找比较简单,只找到距离为k的节点并放入结果中即可。向上寻找需要逐层寻找,比如向上一层找到target的parent后,需要再找到旁支与partent距离为k-1的所有节点。再向上二层找到parent的parent……以此类推。
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void getDownNode(TreeNode* node, int k, vector& res){
if(!node || k < 0) return;
if(k == 0){
res.push_back(node->val);
return;
}
getDownNode(node->left, k-1, res);
getDownNode(node->right, k-1, res);
}
int getUpNode(TreeNode* node, TreeNode* target, int k, vector& res){
if(!node) return -1;
if(node == target){
getDownNode(node, k, res);
return 0;
} else {
int left = getUpNode(node->left, target, k, res);
int right = getUpNode(node->right, target, k, res);
if(left == -1 && right == -1) return -1;
else if(left != -1){
if(left == k-1) res.push_back(node->val);
getDownNode(node->right, k-left-2, res);
return left+1;
} else if(right != -1){
if(right == k-1) res.push_back(node->val);
getDownNode(node->left, k-right-2, res);
return right+1;
}
}
return -1;
}
vector distanceK(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* target, int k) {
vector res;
getUpNode(root, target, k, res);
return res;
}
};