Entity Framework中的DataAnnotations
Model使用DataAnnotations定义数据库和验证
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema
注意这里的验证会在web客户端和EF端同时验证。
[Key]
数据库: 定义主键
[Required]
数据库: 会把字段设置成not null
验证: 会要求必须输入
是否可以为null [Required(AllowEmptyStrings = false)] 不能为null和空字符串
[MaxStringLegth]
数据库: 字段长度
验证: 验证是否超出长度
[MinStringLegth]
验证: 验证是否长度不够
[NotMapped]
不和数据库匹配的字段,比如数据库存了First Name, Last Name, 我们可以创建一个属性Full Name, 数据库中没有,但是可以使用到其它地方。
[ComplexType]
复杂类型,当你想用一个表,但是表中其它的列做成另外一个类,这个时候可以使用.
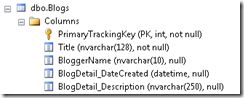
比如这里BlogDetails是Blog表的一部分,在Blog类中有个属性是BlogDetails
[ComplexType] public class BlogDetails { public DateTime? DateCreated { get; set; } [MaxLength(250)] public string Description { get; set; } }
实际的表结构就会是这样:
[ConcurrencyCheck]
表示并发标识, 标记为ConcurrencyCheck的列,会在更新数据前,检查有没有改变,如果改变了,说明期间发生过数据修改。这个时候会导致操作失败,出现DbUpdateConcurrencyException
[Timestamp]
这种数据类型表现自动生成的二进制数,确保这些数在数据库中是唯一的。timestamp 一般用作给表行加版本戳的机制。存储大小为 8 字节. 所以对应的.net 类型是Byte[]
一个表只能有一个 timestamp 列.
[Table] [Column]
用来表示数据库匹配的细节
[Table("InternalBlogs")] public class Blog [Column("BlogDescription", TypeName="ntext")] public String Description {get;set;}
[DatabaseGenerated]
数据库中有些字段是触发器类似的创造的数据,这些不希望在更新的时候使用, 但是又想在读取出来,可以用这个标记
[DatabaseGenerated(DatabaseGenerationOption.Computed)] public DateTime DateCreated { get; set; }
[ForeignKey]
public class Post { public int Id { get; set; } public string Title { get; set; } public DateTime DateCreated { get; set; } public string Content { get; set; } public int BlogId { get; set; } [ForeignKey("BlogId")] public Blog Blog { get; set; } public ICollection<Comment> Comments { get; set; } }
[InverseProperty]
如果子表使用了ForeignKey, 父表又使用字表的Collection对象会导致,在子表中生成多个外键
这个时候,需要在父表类中的子表Collection对象上添加上这个Attribute表明会重用子对象的哪个属性作为外键。