C | C控制语句:分支和跳转
目录
一、if语句
二、if else语句
2.1 另一个示例:介绍getchar()和putchar()
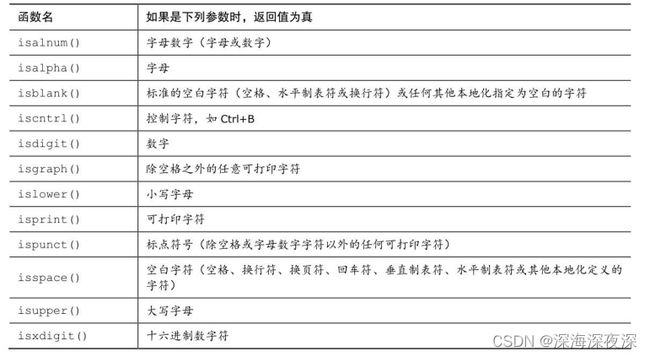
2.2 ctype.h系列的字符函数
2.3 多重选择else if
2.4 else与if配对
2.5 多层嵌套的if语句
三、逻辑运算符
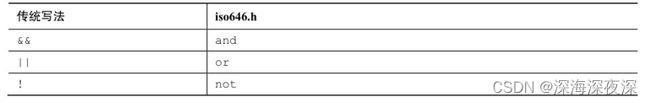
3.1 备选拼写:iso646.h头文件
3.2 优先级
3.3 求值顺序
3.4 范围
四、一个统计单词的程序
五、条件运算符:?:
六、循环辅助:continue和break
6.1 continue语句
6.2 break语句
七、多重选择:switch和break
7.1 switch语句
7.2 只读每行的首字符
7.3 多重标签
7.4 switch和if else
八、goto语句
一、if语句
if语句被称为分支语句(branching statement)或选择语句(selection statement)。
通用形式如下:
if ( expression )
statement
expression使用任意表达式,表达式的值为0则为假,通常为关系表达式。statement部分可以是一条简单语句或复合语句。
// colddays.c -- 找出0℃以下的天数占总天数的百分比
#include
int main(void)
{
const int FREEZING = 0;
float temperature;
int cold_days = 0;
int all_days = 0;
printf("Enter the list of daily low temperatures.\n");
printf("Use Celsius, and enter q to quit.\n");
while (scanf("%f", &temperature) == 1)
{
all_days++;
if (temperature < FREEZING)
cold_days++;
}
if (all_days != 0)
printf("%d days total: %.1f%% were below freezing.\n",
all_days, 100.0 * (float)cold_days / all_days);
if (all_days == 0)
printf("No data entered!\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
} 运行结果:
Enter the list of daily low temperatures.
Use Celsius, and enter q to quit.
12 5 -2.5 0 6 8 -3 -10 5 10 q
10 days total: 30.0% were below freezing.
(float)cold_days强制类型转换可以明确表达转换类型的意图,保护程序免受不同版本编译器的影响。
二、if else语句
C还提供了if else形式,可以在两条语句之间作选择。
if else语句的通用形式是:
if ( expression )
statement1
else
statement2
如果expression为真(非0),则执行statement1;如果expression为假或0,则执行else后面的statement2。statement1和statement2可以是一条简单语句或复合语句。
- C并不要求一定要缩进,但这是标准风格。
- 在if和else之间只允许有一条语句(简单语句或复合语句),否则,编译器发现else并没有所属的if,这是错误的。
if (x > 0)
printf("Incrementing x:\n");
x++;
else // 将产生一个错误
printf("x <= 0 \n");
2.1 另一个示例:介绍getchar()和putchar()
getchar()函数不带任何参数,它从输入队列中返回下一个字符。
ch = getchar();
等价于
scanf("%c", &ch);
putchar()函数打印它的参数。
putchar(ch);
等价于
printf("%c", ch);
- 由于这些函数只处理字符,所以它们比更通用的scanf()和printf()函数更快、更简洁。
- getchar()和 putchar()不需要转换说明,因为它们只处理字符。
- 这两个函数通常定义在 stdio.h头文件中(而且,它们通常是预处理宏,而不是真正的函数)。
// cypher1.c -- 更改输入,空格不变
#include
#define SPACE ' ' // SPACE表示单引号-空格-单引号
int main(void)
{
char ch;
ch = getchar(); // 读取一个字符
while (ch != '\n') // 当一行未结束时
{
if (ch == SPACE) // 留下空格
putchar(ch); // 该字符不变
else
putchar(ch + 1); // 改变其他字符
ch = getchar(); // 获取下一个字符
}
putchar(ch); // 打印换行符
system("pause");
return 0;
} 运行结果:
CALL ME HAL.
DBMM NF IBM/
!=运算符的优先级比=高
2.2 ctype.h系列的字符函数
如果程序只转换字母,保留所有的非字母字符(不只是空格)会更好。C 有一系列专门处理字符的函数,ctype.h头文件包含了这些函数的原型。
#include
#include // 包含isalpha()的函数原型
int main(void)
{
char ch;
while ((ch = getchar()) != '\n')
{
if (isalpha(ch)) // 如果是一个字符,
putchar(ch + 1); // 显示该字符的下一个字符
else // 否则,
putchar(ch); // 原样显示
}
putchar(ch); // 显示换行符
system("pause");
return 0;
} 运行结果:
Look! It's a programmer!
Mppl! Ju't b qsphsbnnfs!
- 有些函数涉及本地化,指的是为适应特定区域的使用习惯修改或扩展 C 基本用法的工具。
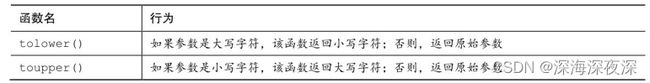
- 字符映射函数不会修改原始的参数。
ctype.h头文件中的字符测试函数
ctype.h头文件中的字符映射函数
2.3 多重选择else if
if (expression1)
statement1
else if (expression2)
statement2
else
statement3
如果expression1为真,执行statement1部分;如果expression2为真,执行statement2部分;否则,执行statement3部分。
// electric.c -- 计算电费
#include
#define RATE1 0.13230 // 首次使用 360 kwh 的费率
#define RATE2 0.15040 // 接着再使用 108 kwh 的费率
#define RATE3 0.30025 // 接着再使用 252 kwh 的费率
#define RATE4 0.34025 // 使用超过 720kwh 的费率
#define BREAK1 360.0 // 费率的第1个分界点
#define BREAK2 468.0 // 费率的第2个分界点
#define BREAK3 720.0 // 费率的第3个分界点
#define BASE1 (RATE1 * BREAK1)
// 使用360kwh的费用
#define BASE2 (BASE1 + (RATE2 * (BREAK2 - BREAK1)))
// 使用468kwh的费用
#define BASE3 (BASE1 + BASE2 + (RATE3 *(BREAK3 -\
BREAK2)))
// 使用720kwh的费用
int main(void)
{
double kwh; // 使用的千瓦时
double bill; // 电费
printf("Please enter the kwh used.\n");
scanf("%lf", &kwh); // %lf对应double类型
if (kwh <= BREAK1)
bill = RATE1 * kwh;
else if (kwh <= BREAK2) // 360~468 kwh
bill = BASE1 + (RATE2 * (kwh - BREAK1));
else if (kwh <= BREAK3) // 468~720 kwh
bill = BASE2 + (RATE3 * (kwh - BREAK2));
else // 超过 720 kwh
bill = BASE3 + (RATE4 * (kwh - BREAK3));
printf("The charge for %.1f kwh is $%1.2f.\n", kwh, bill);
system("pause");
return 0;
} 运行结果:
Please enter the kwh used.
999
The charge for 999.0 kwh is $282.09.
- 符号常量表示不同的费率和费率分界点,更新数据非常方便。
- 实际上,else if 是已学过的 if else 语句的变式, 是if else的嵌套结构。
- 整个if else语句被视为一条语句。
- C99标准要求编译器最少支持127层套嵌。
2.4 else与if配对
如果没有花括号,else与离它最近的if匹配,除非最近的if被花括号括起来。
编译器是忽略缩进的。
2.5 多层嵌套的if语句
// divisors.c -- 使用嵌套if语句显示一个数的约数
#include
#include
int main(void)
{
unsigned long num; // 待测试的数
unsigned long div; // 可能的约数
bool isPrime; // 素数标记
printf("Please enter an integer for analysis; ");
printf("Enter q to quit.\n");
while (scanf("%lu", &num) == 1)
{
for (div = 2, isPrime = true; (div * div) <= num; div++)
{
if (num % div == 0)
{
if ((div * div) != num)
printf("%lu is divisible by %lu and %lu.\n",
num, div, num / div);
else
printf("%lu is divisible by %lu.\n",
num, div);
isPrime = false; // 该数不是素数}
}
}
if (isPrime)
printf("%lu is prime.\n", num);
printf("Please enter another integer for analysis; ");
printf("Enter q to quit.\n");
}
printf("Bye.\n");
return 0;
system("pause");
}
//该程序会把1认为素数 运行结果:
Please enter an integer for analysis; Enter q to quit.
123456789
123456789 is divisible by 3 and 41152263.
123456789 is divisible by 9 and 13717421.
123456789 is divisible by 3607 and 34227.
123456789 is divisible by 3803 and 32463.
123456789 is divisible by 10821 and 11409.
Please enter another integer for analysis; Enter q to quit.
32
32 is divisible by 2 and 16.
32 is divisible by 4 and 8.
Please enter another integer for analysis; Enter q to quit.
3
3 is prime.
Please enter another integer for analysis; Enter q to quit.
- 整数乘法比求平方根快。
- 从技术角度看,if else语句作为一条单独的语句,不必使用花括号。当语句太长时,使用花括号能提高代码的可读性,而且还可防止今后在if循环中添加其他语句时忘记加花括号。
- 在外层循环把一个变量设置为某个值(如,1),然后在if语句中把该变量重新设置为0。这样的变量通常称为标记(flag)。
- 在程序中包含了stdbool.h头文件,便可用bool代替_Bool类型,用true和false分别代替1和0。
三、逻辑运算符
// chcount.c -- 使用逻辑与运算符
#include
#define PERIOD '.'
int main(void)
{
char ch;
int charcount = 0;
while ((ch = getchar()) != PERIOD)
{
if (ch != '"' && ch != '\'')
charcount++;
}
printf("There are %d non-quote characters.\n", charcount);
system("pause");
return 0;
} 运行结果:
I didn't read the "I'm a Programming Fool" best seller.
There are 50 non-quote characters.
- 字符‘,用 '\''表示。
- 逻辑运算符的优先级比关系运算符低,所以不必在子表达式两侧加圆括号。
3.1 备选拼写:iso646.h头文件
C99标准新增了可代替逻辑运算符的拼写,它们被定义在ios646.h头文件中。如果在程序中包
含该头文件,便可用and代替&&、or代替||、not代替!。
为何C不直接使用and、or和not?因为C一直坚持尽量保持较少的关键字。
3.2 优先级
- !运算符的优先级很高,比乘法运算符还高,与递增运算符的优先级相同,只比圆括号的优先级低。&&运算符的优先级比||运算符高,但是两者的优先级都比关系运算符低,比赋值运算符高。
- 建议带圆括号,这能使表达式含义很清楚。
3.3 求值顺序
apples = (5 + 3) * (9 + 6);
- C 把先计算哪部分的决定权留给编译器的设计者,以便针对特定系统优化设计。但是,对于逻辑运算符是个例外,C保证逻辑表达式的求值顺序是从左往右。
- &&和||运算符都是序列点,所以程序在从一个运算对象执行到下一个运算对象之前,所有的副作用都会生效。
while ((c = getchar()) != ' ' && c != '\n')
读取字符直至遇到第1 个空格或换行符。第1 个子表达式把读取的值赋给c,后面的子表达式会用到c的值。如果没有求值循序的保证,编译器可能在给c赋值之前先对后面的表达式求值。
3.4 范围
&&运算符可用于测试范围。
if (range >= 90 && range <= 100)
错误示例:
if (90 >= range <= 100)
这样写的问题是代码有语义错误,而不是语法错误,所以编译器不会捕获这样的问题.
编译器把测试表达式解释为:
(90 <= range) <= 100
四、一个统计单词的程序
// wordcnt.c -- 统计字符数、单词数、行数
#include
#include // 为isspace()函数提供原型
#include // 为bool、true、false提供定义
#define STOP '|'
int main(void)
{
char c; // 读入字符
char prev; // 读入的前一个字符
long n_chars = 0L;// 字符数
int n_lines = 0; // 行数
int n_words = 0; // 单词数
int p_lines = 0; // 不完整的行数
bool inword = false; // 如果c在单词中,inword 等于 true
printf("Enter text to be analyzed (| to terminate):\n");
prev = '\n'; // 用于识别完整的行
while ((c = getchar()) != STOP)
{
n_chars++; // 统计字符
if (c == '\n')
n_lines++; // 统计行
if (!isspace(c) && !inword)
{
inword = true;// 开始一个新的单词
n_words++; // 统计单词
}
if (isspace(c) && inword)
inword = false; // 打到单词的末尾
prev = c; // 保存字符的值
}
if (prev != '\n')
p_lines = 1;
printf("characters = %ld, words = %d, lines = %d, ",
n_chars, n_words, n_lines);
printf("partial lines = %d\n", p_lines);
system("pause");
return 0;
} 运行结果:
Enter text to be analyzed (| to terminate):
Reason is a
powerful servant but
an inadequate master.
|
characters = 55, words = 9, lines = 3, partial lines = 0
- 伪代码:
如果c不是空白字符,且inword为假
设置inword为真,并给单词计数
如果c是空白字符,且inword为真
设置inword为假
- 如果使用布尔类型的变量,通常习惯把变量自身作为测试条件。
用if (inword)代替if (inword == true)
用if (!inword)代替if (inword == false)
五、条件运算符:?:
C提供条件表达式(conditional expression)作为表达if else语句的一种便捷方式,该表达式使用?:条件运算符。
条件运算符是C语言中唯一的三元运算符。
条件表达式的通用形式如下:
expression1 ? expression2 : expression3
如果 expression1 为真(非 0),那么整个条件表达式的值与expression2 的值相同;如果expression1为假(0),那么整个条件表达式的值与expression3的值相同。
- 需要把两个值中的一个赋给变量时,就可以用条件表达式。
- 通常,条件运算符完成的任务用 if else 语句也可以完成。但是,使用条件运算符的代码更简洁,而且编译器可以生成更紧凑的程序代码。
/* paint.c -- 使用条件运算符 */
#include
#define COVERAGE 350 // 每罐油漆可刷的面积(单位:平方英尺)
int main(void)
{
int sq_feet;
int cans;
printf("Enter number of square feet to be painted:\n");
while (scanf("%d", &sq_feet) == 1)
{
cans = sq_feet / COVERAGE;
cans += ((sq_feet % COVERAGE == 0)) ? 0 : 1;
printf("You need %d %s of paint.\n", cans,
cans == 1 ? "can" : "cans");
printf("Enter next value (q to quit):\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 运行结果:
Enter number of square feet to be painted:
349
You need 1 can of paint.
Enter next value (q to quit):
350
You need 1 can of paint.
Enter next value (q to quit):
351
You need 2 cans of paint.
Enter next value (q to quit):
q
六、循环辅助:continue和break
6.1 continue语句
3种循环都可以使用continue语句。执行到该语句时,会跳过本次迭代的剩余部分,并开始下一轮迭代。如果continue语句在嵌套循环内,则只会影响包含该语句的内层循环。
/* skippart.c -- 使用continue跳过部分循环 */
#include
int main(void)
{
const float MIN = 0.0f;
const float MAX = 100.0f;
float score;
float total = 0.0f;
int n = 0;
float min = MAX;
float max = MIN;
printf("Enter the first score (q to quit): ");
while (scanf("%f", &score) == 1)
{
if (score < MIN || score > MAX)
{
printf("%0.1f is an invalid value.Try again: ", score);
continue; // 跳转至while循环的测试条件
}
printf("Accepting %0.1f:\n", score);
min = (score < min) ? score : min;
max = (score > max) ? score : max;
total += score;
n++;
printf("Enter next score (q to quit): ");
}
if (n > 0)
{
printf("Average of %d scores is %0.1f.\n", n, total / n);
printf("Low = %0.1f, high = %0.1f\n", min, max);
}
else
printf("No valid scores were entered.\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
} 运行结果:
Enter the first score (q to quit): 188
188.0 is an invalid value.Try again: 19
Accepting 19.0:
Enter next score (q to quit): q
Average of 1 scores is 19.0.
Low = 19.0, high = 19.0
有两种方法可以避免使用continue
1、省略continue,把剩余部分放在一个else块中。这种情况下,使用continue的好处是减少主语句组中的一级缩进。当语句很长或嵌套较多时,紧凑简洁的格式提高了代码的可读性。
2、把if的测试条件的关系反过来便可避免使用continue。
while ((ch = getchar() ) != '\n')
{
if (ch == '\t')
continue;
putchar(ch);
}
改为:
while ((ch = getchar()) != '\n')
if (ch != '\t')
putchar(ch);
- 如果用了continue没有简化代码反而让代码更复杂,就不要使用continue。
- continue还可用作占位符。下面的循环读取并丢弃输入的数据,直至读到行末尾。
while (getchar() != '\n')
;
改为以下,可读性更高。
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
- 对于while和 do while 循环,执行 continue 语句后的下一个行为是对循环的测试表达式求值。
- 对于for循环,执行continue后的下一个行为是对更新表达式求值,然后是对循环测试表达式求值。
6.2 break语句
程序执行到循环中的break语句时,会终止包含它的循环,并继续执行下一阶段。如果break语句位于嵌套循环内,它只会影响包含它的当前循环。
/* break.c -- 使用 break 退出循环 */
#include
int main(void)
{
float length, width;
printf("Enter the length of the rectangle:\n");
while (scanf("%f", &length) == 1)
{
printf("Length = %0.2f:\n", length);
printf("Enter its width:\n");
if (scanf("%f", &width) != 1)
break;
printf("Width = %0.2f:\n", width);
printf("Area = %0.2f:\n", length * width);
printf("Enter the length of the rectangle:\n");
}
printf("Done.\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
} 运行结果:
Enter the length of the rectangle:
20
Length = 20.00:
Enter its width:
30
Width = 30.00:
Area = 600.00:
Enter the length of the rectangle:
q
Done.
- 如果用了break代码反而更复杂,就不要使用break。
- break语句对于switch语句而言至关重要。
- 在for循环中的break和continue的情况不同,执行完break语句后会直接执行循环后面的第1条语句,连更新部分也跳过。嵌套循环内层的break只会让程序跳出包含它的当前循环,要跳出外层循环还需要一个break。
七、多重选择:switch和break
使用条件运算符和 if else 语句很容易编写二选一的程序。然而,有时程序需要在多个选项中进行选择。可以用if else if...else来完成。但是,大多数情况下使用switch语句更方便。
/* animals.c -- 使用switch语句 */
#include
#include
int main(void)
{
char ch;
printf("Give me a letter of the alphabet, and I will give ");
printf("an animal name\nbeginning with that letter.\n");
printf("Please type in a letter; type # to end my act.\n");
while ((ch = getchar()) != '#')
{
if ('\n' == ch)
continue;
if (islower(ch)) /* 只接受小写字母*/
switch (ch)
{
case 'a':
printf("argali, a wild sheep of Asia\n");
break;
case 'b':
printf("babirusa, a wild pig of Malay\n");
break;
case 'c':
printf("coati, racoonlike mammal\n");
break;
case 'd':
printf("desman, aquatic, molelike critter\n");
break;
case 'e':
printf("echidna, the spiny anteater\n");
break;
case 'f':
printf("fisher, brownish marten\n");
break;
default:
printf("That's a stumper!\n");
} /* switch结束 */
else
printf("I recognize only lowercase letters.\n");
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue; /* 跳过输入行的剩余部分 */
printf("Please type another letter or a #.\n");
} /* while循环结束 */
printf("Bye!\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
} 运行结果:
Give me a letter of the alphabet, and I will give an animal name
beginning with that letter.
Please type in a letter; type # to end my act.
a
argali, a wild sheep of Asia
Please type another letter or a #.
abc
argali, a wild sheep of Asia
Please type another letter or a #.
#
Bye!
注:如果上述程序把下面的代码注释掉,结果有所不同。
//while (getchar() != '\n')
// continue; /* 跳过输入行的剩余部分 */
Give me a letter of the alphabet, and I will give an animal name
beginning with that letter.
Please type in a letter; type # to end my act.
a
argali, a wild sheep of Asia
Please type another letter or a #.
abc
argali, a wild sheep of Asia
Please type another letter or a #.
babirusa, a wild pig of Malay
Please type another letter or a #.
coati, racoonlike mammal
Please type another letter or a #.
7.1 switch语句
- 程序扫描标签(这里指,case 'a' :、case 'b' :等)列表,直到发现一个匹配的值为止。然后程序跳
- 转至那一行。如果没有匹配的标签怎么办?如果有default :标签行,就跳转至该行;否则,程序继续执行在switch后面的语句。
- 如果没有break语句,就会从匹配标签开始执行到switch末尾。
- break语句可用于循环和switch语句中,但是continue只能用于循环中。
- 如果switch语句在一个循环中,continue便可作为switch语句的一部分。continue让程序跳出循环的剩余部分,包括switch语句的其他部分。
- C语言的case一般都指定一个值,不能使用一个范围。
- switch在圆括号中的测试表达式的值应该是一个整数值(包括char类型)。case标签必须是整数类型(包括char类型)的常量或整型常量表达式(即,表达式中只包含整型常量)。不能用变量作为case标签。
switch的构造如下:
switch ( 整型表达式)
{
case 常量1:
语句
case 常量2:
语句
default:
语句
}
7.2 只读每行的首字符
当输入dab时,只处理了第1个字符。这种丢弃一行中其他字符的行为,经常出现在响应单字符的交互程序中。
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue; /* 跳过输入行的其余部分 */
循环从输入中读取字符,包括按下Enter键产生的换行符。注意,函数的返回值并没有赋给ch,以上代码所做的只是读取并丢弃字符。
假设用户一开始就按下Enter键,那么程序读到的首个字符就是换行符。下面的代码处理这种情况。
if (ch == '\n')
continue;
7.3 多重标签
#include
int main(void)
{
char ch;
int a_ct, e_ct, i_ct, o_ct, u_ct;
a_ct = e_ct = i_ct = o_ct = u_ct = 0;
printf("Enter some text; enter # to quit.\n");
while ((ch = getchar()) != '#')
{
switch (ch)
{
case 'a':
case 'A': a_ct++;
break;
case 'e':
case 'E': e_ct++;
break;
case 'i':
case 'I': i_ct++;
break;
case 'o':
case 'O': o_ct++;
break;
case 'u':
case 'U': u_ct++; break;
default: break;
} // switch结束
} // while循环结束
printf("number of vowels: A E I O U\n");
printf(" %4d %4d %4d %4d %4d\n",
a_ct, e_ct, i_ct, o_ct, u_ct);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//或者
#include
#include
int main(void)
{
char ch;
int a_ct, e_ct, i_ct, o_ct, u_ct;
a_ct = e_ct = i_ct = o_ct = u_ct = 0;
printf("Enter some text; enter # to quit.\n");
while ((ch = getchar()) != '#')
{
switch (toupper(ch))
{
case 'A': a_ct++;
break;
case 'E': e_ct++;
break;
case 'I': i_ct++;
break;
case 'O': o_ct++;
break;
case 'U': u_ct++; break;
default: break;
} // switch结束
} // while循环结束
printf("number of vowels: A E I O U\n");
printf(" %4d %4d %4d %4d %4d\n",
a_ct, e_ct, i_ct, o_ct, u_ct);
system("pause");
return 0;
} 运行结果:
Enter some text; enter # to quit.
I see under the overseer.#
number of vowels: A E I O U
0 7 1 1 1
- 可以把case 'U'的break语句去掉以缩短代码。但是从另一方面看,保留这条break语句可以防止以后在添加新的case。
- 使用ctype.h系列的toupper()函数可以精简代码。
7.4 switch和if else
如果是根据浮点类型的变量或表达式来选择,就无法使用 switch。如果根据变量在某范围内决定程序流的去向,使用 switch 就很麻烦,这种情况用if就很方便。
如果使用switch,程序通常运行快一些,生成的代码少一些。
八、goto语句
goto语句使程序控制跳转至相应标签语句。冒号用于分隔标签和标签语句。标签名遵循变量命名规则。标签语句可以出现在goto的前面或后面。
形式:
goto label ;
label : statement
- 没有goto语句C程序也能运行良好。Kernighan和Ritchie提到goto语句“易被滥用”,并建议“谨慎使用,或者根本不用”。
- C程序员可以接受一种goto的用法——出现问题时从一组嵌套循环中跳出(一条break语句只能跳出当前循环)。
- 程序中使用其他形式比使用goto的条理更清晰。C允许在标签中使用描述性的单词而不是数字。