golang map 并发读写 sync.Map 实现原理
一. map并发读写不安全
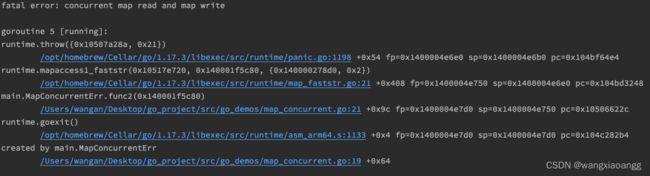
Go map 是不支持并发写操作的,当 Goroutine 操作同一个 map,会产生报错:fatal error: concurrent map writes。
1. map 并发读写
//map 并发读写 产生错误
//fatal error: concurrent map read and map write
func MapConcurrentErr() {
c := make(map[string]int)
go func() { //开一个goroutine写map
for j := 0; j < 1000000; j++ {
c[fmt.Sprintf("%d", j)] = j
}
}()
go func() { //开一个goroutine读map
for j := 0; j < 1000000; j++ {
fmt.Println(c[fmt.Sprintf("%d", j)])
}
}()
time.Sleep(time.Second * 20)
}2.使用sync map 解决并发安全问题
//sync map 并发读写安全
func SyncMapConcurrent() {
c := sync.Map{}
go func() { //开一个goroutine写map
for j := 0; j < 1000000; j++ {
c.Store(j, j)
fmt.Println("store", j)
}
}()
go func() { //开一个goroutine读map
for j := 0; j < 1000000; j++ {
load, ok := c.Load(j)
fmt.Println("load", load, ok)
}
}()
time.Sleep(time.Second * 20)
}
二.sync map实现
2.1 结构体
1.Map结构体
type Map struct {
//锁,用于保护 dirty 和 read。读写dirty、将dirty copy到 read时需要持有该锁。
mu Mutex
//实际结构为 readOnly
// read contains the portion of the map's contents that are safe for
// concurrent access (with or without mu held).
//
// The read field itself is always safe to load, but must only be stored with
// mu held.
//
// Entries stored in read may be updated concurrently without mu, but updating
// a previously-expunged entry requires that the entry be copied to the dirty
// map and unexpunged with mu held.
read atomic.Value // readOnly
// dirty contains the portion of the map's contents that require mu to be
// held. To ensure that the dirty map can be promoted to the read map quickly,
// it also includes all of the non-expunged entries in the read map.
//
// Expunged entries are not stored in the dirty map. An expunged entry in the
// clean map must be unexpunged and added to the dirty map before a new value
// can be stored to it.
//
// If the dirty map is nil, the next write to the map will initialize it by
// making a shallow copy of the clean map, omitting stale entries.
dirty map[interface{}]*entry
//misses 字段来统计 read 被穿透的次数(被穿透指需要读 dirty 的情况),超过一定次数则将
//dirty 数据同步到 read 上
// misses counts the number of loads since the read map was last updated that
// needed to lock mu to determine whether the key was present.
//
// Once enough misses have occurred to cover the cost of copying the dirty
// map, the dirty map will be promoted to the read map (in the unamended
// state) and the next store to the map will make a new dirty copy.
misses int
}2.readOnly
// readOnly is an immutable struct stored atomically in the Map.read field.
type readOnly struct {
m map[interface{}]*entry
//标记ditry中是否包含元素
amended bool // true if the dirty map contains some key not in m.
} 3.entry
entry 用来存储值的地址属性 p 有三种状
p == nil: 键值已经被删除,且m.dirty == nilp == expunged: 键值已经被删除,但m.dirty!=nil且m.dirty不存在该键值(expunged 实际是空接口指针)- 否则键值对存在,存在于
m.read.m中,如果m.dirty!=nil则也存在于m.dirty
// expunged is an arbitrary pointer that marks entries which have been deleted
// from the dirty map.
var expunged = unsafe.Pointer(new(interface{}))
2.2 map结构体的方法
1.Load
Load方法用于获取map中的值
// Load returns the value stored in the map for a key, or nil if no
// value is present.
// The ok result indicates whether value was found in the map.
func (m *Map) Load(key interface{}) (value interface{}, ok bool) {
read, _ := m.read.Load().(readOnly)
e, ok := read.m[key]
if !ok && read.amended {
m.mu.Lock()
// Avoid reporting a spurious miss if m.dirty got promoted while we were
// blocked on m.mu. (If further loads of the same key will not miss, it's
// not worth copying the dirty map for this key.)
read, _ = m.read.Load().(readOnly)
e, ok = read.m[key]
if !ok && read.amended {
e, ok = m.dirty[key]
//触发miss逻辑, 符合条件时会将dirty数据copy 到readOnly
// Regardless of whether the entry was present, record a miss: this key
// will take the slow path until the dirty map is promoted to the read
// map.
m.missLocked()
}
m.mu.Unlock()
}
if !ok {
return nil, false
}
// 读取entry中值
return e.load()
}
2.Store
store用户设置key的值
// Store sets the value for a key.
func (m *Map) Store(key, value interface{}) {
read, _ := m.read.Load().(readOnly)
if e, ok := read.m[key]; ok && e.tryStore(&value) {
return
}
m.mu.Lock()
read, _ = m.read.Load().(readOnly)
if e, ok := read.m[key]; ok {
if e.unexpungeLocked() {
// The entry was previously expunged, which implies that there is a
// non-nil dirty map and this entry is not in it.
m.dirty[key] = e
}
e.storeLocked(&value)
} else if e, ok := m.dirty[key]; ok {
e.storeLocked(&value)
} else {
if !read.amended {
// We're adding the first new key to the dirty map.
// Make sure it is allocated and mark the read-only map as incomplete.
m.dirtyLocked()
m.read.Store(readOnly{m: read.m, amended: true})
}
m.dirty[key] = newEntry(value)
}
m.mu.Unlock()
}
3.Delete
// Delete deletes the value for a key.
func (m *Map) Delete(key interface{}) {
m.LoadAndDelete(key)
}
// LoadAndDelete deletes the value for a key, returning the previous value if any.
// The loaded result reports whether the key was present.
func (m *Map) LoadAndDelete(key interface{}) (value interface{}, loaded bool) {
read, _ := m.read.Load().(readOnly)
e, ok := read.m[key]
if !ok && read.amended {
m.mu.Lock()
read, _ = m.read.Load().(readOnly)
e, ok = read.m[key]
if !ok && read.amended {
e, ok = m.dirty[key]
delete(m.dirty, key)
// Regardless of whether the entry was present, record a miss: this key
// will take the slow path until the dirty map is promoted to the read
// map.
m.missLocked()
}
m.mu.Unlock()
}
if ok {
return e.delete()
}
return nil, false
}三 总结
- 通过 read 和 dirty 两个字段将读写分离,读的数据存在只读字段 read 上,将最新写入的数据则存在 dirty 字段上
- 读取时会先查询 read,不存在再查询 dirty,写入时则只写入 dirty
- 读取 read 并不需要加锁,而读或写 dirty 需要加锁,cory dirty到read时需要加锁
- 另外有 misses 字段来统计 read 被穿透的次数(被穿透指需要读 dirty 的情况),超过一定次数则将 dirty 数据同步到 read 上
- 对于删除数据则直接通过标记来延迟删除