![]()
背景
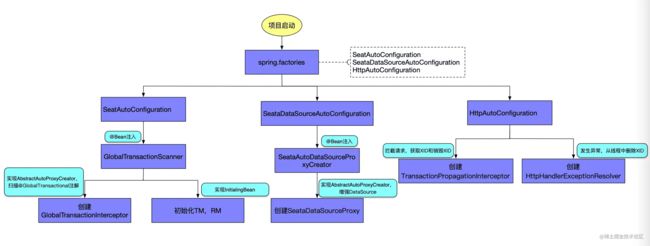
为了了解Seata AT模式的原理,我通过源码解读的方式画出了Seata AT模式启动的图示:
如果是基于Springboot项目的话,项目启动的使用,一般约定会先查看spring.factories文件,配置了哪些类是需要自动装配的。Seata也是利用了这个约定,在项目启动的时候,默认会装配指定的类,以完成Seata相关组件的初始化。
下面我们来一起根据源码解读Seata AT模式启动流程。
由上图可知,Seata AT模式可大概分成以下三部分:
1.与底层数据库打交道的DataSource,这部分功能处理交给了SeataDataSourceAutoConfiguration。
2.处理@GlobalTransactional注解,实现分布式事务管理功能,这部分交给SeataAutoConfiguration处理。
3.分支事务获取、销毁全局事务XID,这部分功能交给HttpAutoConfiguration。
SeataDataSourceAutoConfiguration
首先,我们来看看Seata是如何处理DataSource的。
// 依赖DataSource
@ConditionalOnBean(DataSource.class)
// 三个配置都要为true
@ConditionalOnExpression("${seata.enabled:true} && ${seata.enableAutoDataSourceProxy:true} && ${seata.enable-auto-data-source-proxy:true}")
@AutoConfigureAfter({SeataCoreAutoConfiguration.class})
public class SeataDataSourceAutoConfiguration {
/**
* The bean seataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator.
*/
@Bean(BEAN_NAME_SEATA_AUTO_DATA_SOURCE_PROXY_CREATOR)
// 可替换
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator.class)
public SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator seataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator(SeataProperties seataProperties) {
return new SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator(seataProperties.isUseJdkProxy(),
seataProperties.getExcludesForAutoProxying(), seataProperties.getDataSourceProxyMode());
}
}
1.@ConditionalOnBean(DataSource.class)意味着我们的项目中一定要有DataSource这个Bean。
2.@ConditionalOnExpression里面表示要满足以下三个条件才会创建SeataDataSourceAutoConfiguration:
seata.enabled=true
seata.enableAutoDataSourceProxy=true
seata.enable-auto-data-source-proxy=true
3.@AutoConfigureAfter表示当前Bean创建一定在指定的SeataCoreAutoConfiguration之后。
根据以上分析,我们在引入Seata AT模式的时候,一定要先创建项目的DataSource Bean对象,其次保证相关的配置满足要求,那么才能正确地保证DataSource被Seata代理。
下面继续看SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator的创建:
@ConditionalOnMissingBean表示这个Bean的创建其实是可以开发人员自定义的,如果开发人员没有自定义,那么就由Seata自己创建。
在SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator类中,它继承了AbstractAutoProxyCreator,也就是AOP功能的标准实现。这个时候,我们主要关注wrapIfNecessary方法的实现:
public class SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator extends AbstractAutoProxyCreator {
@Override
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
// 不是DataSource对象不代理
if (!(bean instanceof DataSource)) {
return bean;
}
// 如果是DataSource对象,但是不是SeataDataSourceProxy对象
if (!(bean instanceof SeataDataSourceProxy)) {
// 先调用父类包装一层
Object enhancer = super.wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
// 如果代理后的对象和代理前的对象是同一个对象
// 说明要么这个对象之前已经被代理过
// 要么SeataDataSourceProxy被开发人员excluded
if (bean == enhancer) {
return bean;
}
// 如果是正常的DataSource对象的话,那么就会被自动构建成SeataDataSourceProxy,并返回
DataSource origin = (DataSource) bean;
SeataDataSourceProxy proxy = buildProxy(origin, dataSourceProxyMode);
DataSourceProxyHolder.put(origin, proxy);
return enhancer;
}
/*
* things get dangerous when you try to register SeataDataSourceProxy bean by yourself!
* if you insist on doing so, you must make sure your method return type is DataSource,
* because this processor will never return any subclass of SeataDataSourceProxy
*/
// Seata是不建议用户自己构建SeataDataSourceProxy对象的,即使用户自己构建了SeataDataSourceProxy对象,Seata也会重新处理
LOGGER.warn("Manually register SeataDataSourceProxy(or its subclass) bean is discouraged! bean name: {}", beanName);
// 获取用户包装好的代理对象
SeataDataSourceProxy proxy = (SeataDataSourceProxy) bean;
// 获取原生DataSource
DataSource origin = proxy.getTargetDataSource();
// 重新包装,并返回
Object originEnhancer = super.wrapIfNecessary(origin, beanName, cacheKey);
// this mean origin is either excluded by user or had been proxy before
if (origin == originEnhancer) {
return origin;
}
// else, put to holder and return originEnhancer
DataSourceProxyHolder.put(origin, proxy);
// 返回包装好的代理对象SeataDataSourceProxy
return originEnhancer;
}
}
1.通过以上代码解读,有一个点我们需要注意,就是开发人员不需要自己的构建SeataDataSourceProxy对象,使用原生的DataSource即可,Seata会帮助我们构建SeataDataSourceProxy对象。
SeatAutoConfiguration
SeatAutoConfiguration主要功能就是创建GlobalTransactionScanner对象,所以核心功能全部在GlobalTransactionScanner里面。
// 配置seata.enabled=true
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = SEATA_PREFIX, name = "enabled", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
// 装配顺序
@AutoConfigureAfter({SeataCoreAutoConfiguration.class})
public class SeataAutoConfiguration {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SeataAutoConfiguration.class);
@Bean(BEAN_NAME_FAILURE_HANDLER)
// 失败处理器,可替换
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(FailureHandler.class)
public FailureHandler failureHandler() {
return new DefaultFailureHandlerImpl();
}
@Bean
@DependsOn({BEAN_NAME_SPRING_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_PROVIDER, BEAN_NAME_FAILURE_HANDLER})
// 开发人员可自定义GlobalTransactionScanner
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(GlobalTransactionScanner.class)
public GlobalTransactionScanner globalTransactionScanner(SeataProperties seataProperties, FailureHandler failureHandler,
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory,
@Autowired(required = false) List scannerCheckers) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Automatically configure Seata");
}
// set bean factory
GlobalTransactionScanner.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// add checkers
// '/META-INF/services/io.seata.spring.annotation.ScannerChecker'
GlobalTransactionScanner.addScannerCheckers(EnhancedServiceLoader.loadAll(ScannerChecker.class));
// spring beans
GlobalTransactionScanner.addScannerCheckers(scannerCheckers);
// add scannable packages
GlobalTransactionScanner.addScannablePackages(seataProperties.getScanPackages());
// add excludeBeanNames
GlobalTransactionScanner.addScannerExcludeBeanNames(seataProperties.getExcludesForScanning());
//set accessKey and secretKey
GlobalTransactionScanner.setAccessKey(seataProperties.getAccessKey());
GlobalTransactionScanner.setSecretKey(seataProperties.getSecretKey());
// create global transaction scanner
return new GlobalTransactionScanner(seataProperties.getApplicationId(), seataProperties.getTxServiceGroup(), failureHandler);
}
}
1.装配SeataAutoConfiguration要求配置中seata.enabled=true;
2.我们可以自定义FailureHandler;这个失败处理器是专门给TM使用的;
3.同样我们也可以自定义GlobalTransactionScanner,不过基本上不会这么做,除非有特殊需求;
GlobalTransactionScanner里面基本上做两个事情:
- 代理所有被
@GlobalTransactional或@GlobalLock注解的方法; - 使用Neety初始化
TM Client和RM Client,以便实现和TC通信;TC也就是我们的Seata Server;
public class GlobalTransactionScanner extends AbstractAutoProxyCreator
implements ConfigurationChangeListener, InitializingBean, ApplicationContextAware, DisposableBean {
}
AbstractAutoProxyCreator:通过wrapIfNecessary方法代理所有被@GlobalTransactional或@GlobalLock注解的方法;
ConfigurationChangeListener:通过onChangeEvent方法监听配置service.disableGlobalTransaction的变化;InitializingBean:通过afterPropertiesSet方法初始化TM Client和RM Client;ApplicationContextAware:通过setApplicationContext方法获取IOC容器;DisposableBean:当GlobalTransactionScanner被销毁时,通过destroy方法来回收资源;
我们重点关注wrapIfNecessary和afterPropertiesSet方法:
@Override
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
// 检查Bean是否符合被代理的要求
// 1. 不能是配置类,比如以Configuration、Properties、Config结尾的Bean名称
// 2. Bean所在的包名在扫描范围内
// 3. 不能被@Scope注解
if (!doCheckers(bean, beanName)) {
return bean;
}
try {
synchronized (PROXYED_SET) {
// 如果已经被代理,就跳过
if (PROXYED_SET.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
interceptor = null;
// 检查是否被TCC注解
if (TCCBeanParserUtils.isTccAutoProxy(bean, beanName, applicationContext)) {
// 初始化TCC Fence Clean Task
TCCBeanParserUtils.initTccFenceCleanTask(TCCBeanParserUtils.getRemotingDesc(beanName), applicationContext);
// 创建TCC代理类
interceptor = new TccActionInterceptor(TCCBeanParserUtils.getRemotingDesc(beanName));
ConfigurationCache.addConfigListener(ConfigurationKeys.DISABLE_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION,
(ConfigurationChangeListener)interceptor);
} else {
// 如果不是TCC代理,那么先获取当前类和它实现的接口
Class serviceInterface = SpringProxyUtils.findTargetClass(bean);
Class[] interfacesIfJdk = SpringProxyUtils.findInterfaces(bean);
// 判断当前类及相关方法是否被@GlobalTransactional或@GlobalLock注解
if (!existsAnnotation(new Class[]{serviceInterface})
&& !existsAnnotation(interfacesIfJdk)) {
// 没有被注解,不代理
return bean;
}
// 准备创建方法拦截器
if (globalTransactionalInterceptor == null) {
globalTransactionalInterceptor = new GlobalTransactionalInterceptor(failureHandlerHook);
ConfigurationCache.addConfigListener(
ConfigurationKeys.DISABLE_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION,
(ConfigurationChangeListener)globalTransactionalInterceptor);
}
// 拦截器创建完毕
interceptor = globalTransactionalInterceptor;
}
LOGGER.info("Bean[{}] with name [{}] would use interceptor [{}]", bean.getClass().getName(), beanName, interceptor.getClass().getName());
// 如果bean不是代理对象,那么不做方法拦截,直接返回
if (!AopUtils.isAopProxy(bean)) {
bean = super.wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
} else {
// 准备把方法拦截器插入进去
AdvisedSupport advised = SpringProxyUtils.getAdvisedSupport(bean);
// 获取所有的方法拦截器,包括GlobalTransactionalInterceptor
Advisor[] advisor = buildAdvisors(beanName, getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(null, null, null));
int pos;
// 依次添加进目标对象中
for (Advisor avr : advisor) {
// Find the position based on the advisor's order, and add to advisors by pos
pos = findAddSeataAdvisorPosition(advised, avr);
advised.addAdvisor(pos, avr);
}
}
PROXYED_SET.add(beanName);
// 返回被代理的bean
return bean;
}
} catch (Exception exx) {
throw new RuntimeException(exx);
}
}
通过上述源码分析可知:Seata是根据类、接口和方法上的@GlobalTransactional或@GlobalLock注解来判断是否需要针对目标方法做拦截的。
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
// 如果不允许全局事务
if (disableGlobalTransaction) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Global transaction is disabled.");
}
// 添加监听器,监听配置的变化
ConfigurationCache.addConfigListener(ConfigurationKeys.DISABLE_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION,
(ConfigurationChangeListener)this);
return;
}
if (initialized.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
// 准备初始化TM Client、RM Client
initClient();
}
}
private void initClient() {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Initializing Global Transaction Clients ... ");
}
if (DEFAULT_TX_GROUP_OLD.equals(txServiceGroup)) {
LOGGER.warn("the default value of seata.tx-service-group: {} has already changed to {} since Seata 1.5, " +
"please change your default configuration as soon as possible " +
"and we don't recommend you to use default tx-service-group's value provided by seata",
DEFAULT_TX_GROUP_OLD, DEFAULT_TX_GROUP);
}
if (StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(applicationId) || StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(txServiceGroup)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("applicationId: %s, txServiceGroup: %s", applicationId, txServiceGroup));
}
//初始化TM Client
TMClient.init(applicationId, txServiceGroup, accessKey, secretKey);
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Transaction Manager Client is initialized. applicationId[{}] txServiceGroup[{}]", applicationId, txServiceGroup);
}
//初始化RM Client
RMClient.init(applicationId, txServiceGroup);
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Resource Manager is initialized. applicationId[{}] txServiceGroup[{}]", applicationId, txServiceGroup);
}
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Global Transaction Clients are initialized. ");
}
registerSpringShutdownHook();
}
至此,SeatAutoConfiguration的工作处理完毕;
HttpAutoConfiguration
HttpAutoConfiguration的工作比较简单,我们想象一下,RM如何知道它属于哪一个分布式事务?这就需要一个统一的标识来决定所有的分支事务都属于同一个分布式事务,这个标识在Seata中叫做XID;
XID由TM开启分布式事务时生成,通过RPC的方式从一个分支事务传递到另一个分支事务,所以我们在RM端需要一个从RPC中解析获取XID的功能,以及在业务逻辑处理完毕后,销毁当前线程中XID的功能。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
public class HttpAutoConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
// 注册拦截器
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new TransactionPropagationInterceptor());
}
// 添加异常解析处理器
@Override
public void extendHandlerExceptionResolvers(List exceptionResolvers) {
exceptionResolvers.add(new HttpHandlerExceptionResolver());
}
}
public class TransactionPropagationInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(TransactionPropagationInterceptor.class);
// 前置处理逻辑
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) {
// 获取当前线程XID
String xid = RootContext.getXID();
// 从rpc中获取XID
String rpcXid = request.getHeader(RootContext.KEY_XID);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("xid in RootContext[{}] xid in HttpContext[{}]", xid, rpcXid);
}
// 如果线程中没有XID,并且从请求中拿到了XID,那么把请求中的XID绑定到当前线程
if (StringUtils.isBlank(xid) && StringUtils.isNotBlank(rpcXid)) {
RootContext.bind(rpcXid);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("bind[{}] to RootContext", rpcXid);
}
}
return true;
}
// 后置处理逻辑
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
// 业务逻辑处理完毕,从当前线程中删除XID
if (RootContext.inGlobalTransaction()) {
XidResource.cleanXid(request.getHeader(RootContext.KEY_XID));
}
}
}
public class HttpHandlerExceptionResolver extends AbstractHandlerExceptionResolver {
// 发生异常后,删除当前线程中的XID
@Override
protected ModelAndView doResolveException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o, Exception e) {
XidResource.cleanXid(request.getHeader(RootContext.KEY_XID));
return null;
}
}
小结
通过以上源码分析和图解Seata AT模式,我们可以了解到以下几点:
1.GlobalTransactionInterceptor属于TM侧,它主要负责通过TM Client开启分布式事务、提交分布式事务以及回滚分布式事务;属于大总管。
2.SeataDataSourceProxy属于RM侧,它主要负责分支事务的开启,提交以及回滚,属于真正干活的小兵。
3.TM Client和RM Client纯属于两个通信工具,负责与TC端建立通信。
4.TransactionPropagationInterceptor和HttpHandlerExceptionResolver服务于分支事务,负责全局事务XID的获取以及业务逻辑处理完毕的善后事宜。
以上就是Seata AT模式启动过程图文示例详解的详细内容,更多关于Seata AT模式启动过程的资料请关注脚本之家其它相关文章!