笔试强训(十七)
目录
- 一、选择题
- 二、编程题
-
- 2.1 杨辉三角的变形
-
- 2.1.1 题目
- 2.1.2 题解
- 2.2 计算字符出现的次数
-
- 2.2.1 题目
- 2.2.2 题解
一、选择题
(1)下列SQL语句中哪条语句可为用户zhangsan分配数据库userdb表userinfo的查询和插入数据权限(A)
A.grant select,insert on userdb.userinfo to ‘zhangsan’@‘localhost’
B.grant ‘zhangsan’@‘localhost’ to select,insert for userdb.userinfo
C.grant select,insert on userdb.userinfo for ‘zhangsan’@‘localhost’
D.grant ‘zhangsan’@‘localhost’ to userdb.userinfo on select,insert
常用的管理权限命令有:
授予用户某张表查询/插入/修改/删除数据的权限:
grant select/insert/update/delete on 数据库名.表名 to 用户名@‘该用户允许访问的ip’
(2)下列关于数据库索引的说法错误的是(B)
A.索引可以提升查询、分组和排序的性能
B.索引不会影响表的更新、插入和删除操作的效率
C.全表扫描不一定比使用索引的执行效率低
D.对于只有很少数据值的列,不应该创建索引
数据量越大,数据更新的操作(插入、修改和删除)对索引的效率影响越大,需要对B+树进行调整
(3)下面哪个SQL命令用来向表中添加列(D)
A.modify table tablename add column colomuName
B.modify table tablename add colomuName
C.alter table tablename add column colomuName
D.alter table tablename add columnName type
修改表结构的关键字都是alter table 表名,再根根据的修改语句
(4)有订单表orders,包含字段用户信息userid,字段产品信息productid,以下语句能返回至少被订购过两次的productid(D)
A.select productid from orders where count(productid)>1
B.select productid from orders where max(productid)>1
C.select productid from orders where having count(productid)>1 group by productid
D.select productid from orders where group by productid having count(productid)>1
(5)在手机开发中常用的数据库是(A)
A.sqlLite
B.Oracle
C.Sql Server
二、编程题
2.1 杨辉三角的变形
2.1.1 题目
2.1.2 题解
import java.util.*;
// 注意类名必须为 Main, 不要有任何 package xxx 信息
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=scanner.nextInt();
if(n<3){
System.out.println(-1);
}else if(n%2==1){
System.out.println(2);
}else if(n%4==0){
System.out.println(3);
}else if(n%4==2){
System.out.println(4);
}
}
}
【常规做法】:按照题目意思,可以发现第n行有2n - 1个元素,第i,j元素等于上一行第j - 2,j - 1,j三列元素之和,每一行的第一列和最后一列都为1,如果是第二列,则只是两个元素之和
代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=scanner.nextInt();
int[][] a=new int[n][2*n-1];
a[0][0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
a[i][0]=a[i][2*i]=1;
for(int j=1;j<2*n-1;j++){
if(j==1){
a[i][j]=a[i-1][j]+a[i-1][j-1];
}else {
a[i][j]=a[i-1][j]+a[i-1][j-1]+a[i-1][j-2];
}
}
}
int j=0;
for(j=0;j<2*n-1;j++){
if(a[n-1][j]%2==0){
System.out.println(j+1);
break;
}
}
if(j==2*n-1){
System.out.println(-1);
}
}
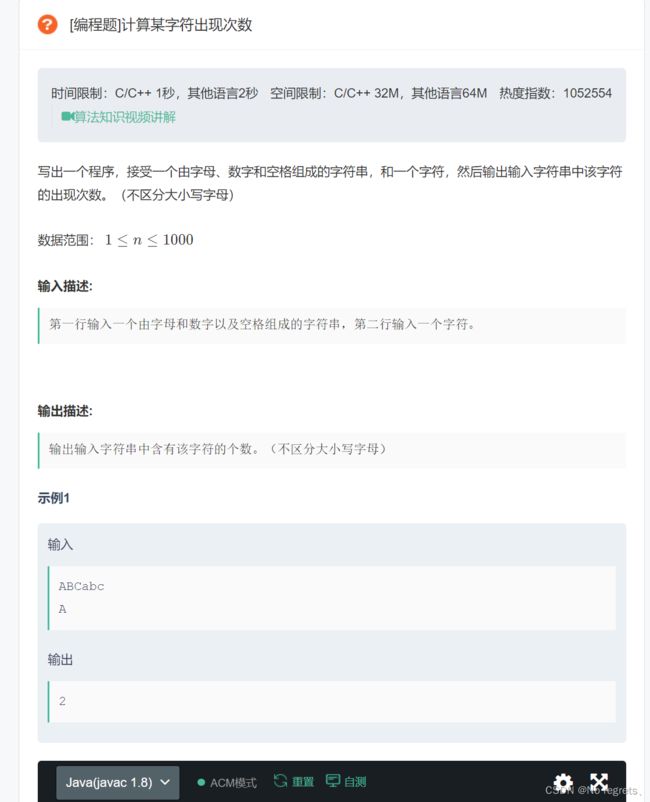
2.2 计算字符出现的次数
2.2.1 题目
2.2.2 题解
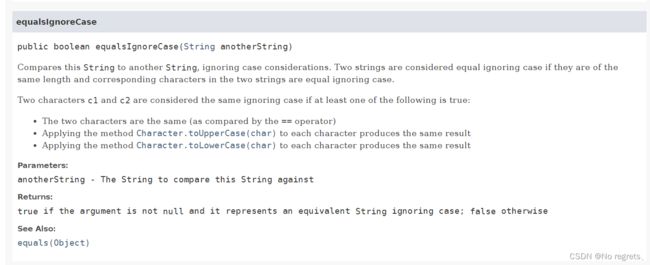
思路:核心方法,equalsIgnoreCase(),遍历str1字符串中的每个字符,看是否和字符str2相等,若相等,count++
代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
String str1= scanner.nextLine();
String str2=scanner.nextLine();
char[] s=str1.toCharArray();
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i<str1.length();i++){
if(str2.equalsIgnoreCase(String.valueOf(s[i]))){
count++;
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}