SpringBoot整合SpringSecurity(通俗易懂)
- 注重版权,转载请注明原作者和原文链接
作者:码农BookSea
原文链接: https://blog.csdn.net/bookssea/article/details/109262109
先看后赞,养成习惯。
点赞收藏,人生辉煌。
基于数据库的身份认证
一、创建项目
创建一个 SpringBoot 模块项目,选择相关依赖:
先搭建项目正常访问,在pom.xml中,先把Spring Security依赖注释
<!--<dependency>-->
<!--<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>-->
<!--<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>-->
<!--</dependency>-->
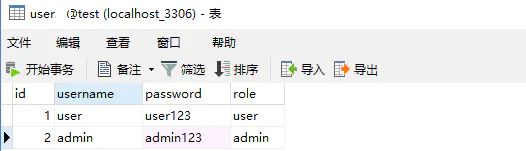
在MySQL数据库中创建一张用户表,id主键自增,并添加两个用户如下:
代码:
创建entity实体
@Data
public class UserInfo {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String role;
}
创建mapper接口
@Mapper
@Repository
public interface UserInfoMapper {
@Select("select * from user where username = #{username}")
UserInfo getUserInfoByUsername(String username);
}
创建UserInfoService.java文件
@Service
public class UserInfoService {
@Autowired
private UserInfoMapper userInfoMapper;
public UserInfo getUserInfo(String username){
return userInfoMapper.getUserInfoByUsername(username);
}
}
创建HelloController.java文件
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
private UserInfoService userInfoService;
@GetMapping("/get-user")
public UserInfo getUser(@RequestParam String username){
return userInfoService.getUserInfoByUsername(username);
}
}
配置文件application.yml中设置MySQL连接配置和MyBatis配置
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/security?useSSL=FALSE&serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
logging:
level:
com.example.bdatabaserole.mapper: debug # 打印sql语句
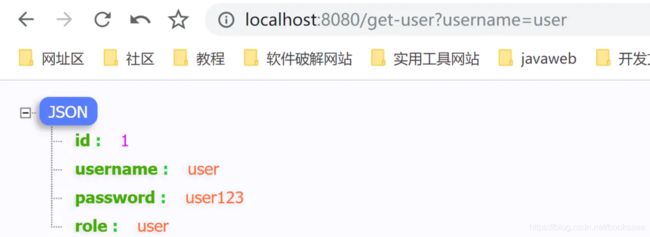
以上配置好后,启动项目,访问localhost:8080/get-user?username=user,正常获取到用户信息:
下面开始使用Spring Security安全验证:
二、Spring Security基于数据库认证
把pom.xml中的Spring Security依赖注释去掉:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
要从数据库读取用户信息进行身份认证,需要新建类实现UserDetailService接口重写loadUserByUsername方法:
@Component
public class CustomUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
private UserInfoService userInfoService;
/**
* 需新建配置类注册一个指定的加密方式Bean,或在下一步Security配置类中注册指定
*/
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
// 通过用户名从数据库获取用户信息
UserInfo userInfo = userInfoService.getUserInfo(username);
if (userInfo == null) {
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("用户不存在");
}
// 得到用户角色
String role = userInfo.getRole();
// 角色集合
List<GrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList<>();
// 角色必须以`ROLE_`开头,数据库中没有,则在这里加
authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_" + role));
return new User(
userInfo.getUsername(),
// 因为数据库是明文,所以这里需加密密码
passwordEncoder.encode(userInfo.getPassword()),
authorities
);
}
}
创建Security的配置类WebSecurityConfig继承WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter,并重写configure(auth)方法:
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private MyUserDatailService userDatailService;
/**
* 指定加密方式
*/
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){
// 使用BCrypt加密密码
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth
// 从数据库读取的用户进行身份认证
.userDetailsService(userDatailService)
.passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
}
}
上面设置完后,重新启动,在登录页面就可以输入数据库中的用户名/密码了。
三、角色访问控制
上面设置后,可以使用数据库中的用户名/密码登录,还获取到了用户的角色。通过用户的角色,可以限制用户的请求访问:
开启方法的访问权限,需要在WebSecurityConfig添加
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity注解
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true) // 开启方法级安全验证
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
...
}
修改UserController.java类,增加方法的访问权限
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
private UserInfoService userInfoService;
@GetMapping("/get-user")
public UserInfo getUser(@RequestParam String username){
return userInfoService.getUserInfo(username);
}
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole('user')") // 只能user角色才能访问该方法
@GetMapping("/user")
public String user(){
return "user角色访问";
}
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole('admin')") // 只能admin角色才能访问该方法
@GetMapping("/admin")
public String admin(){
return "admin角色访问";
}
}
配置完后,重新启动程序,在登录页面中:
输入user/user123登录,该用户角色为user,可以访问localhost:8080/user,不能访问localhost:8080/admin;
再重启程序输入admin/admin123登录,角色为admin,能访问localhost:8080/admin,不能访问localhost:8080/user。
四、密码加密保存
前面的用户密码都是手动添加的,所以数据库中是明文显示,在实际开发中,都是需要加密保存的。
下面模拟简单注册用户,加密保存密码:
UserInfoMapper.java类中添加插入用户
@Mapper
@Repository
public interface UserMapper {
...
// 插入用户
@Insert("insert into user(username, password, role) value(#{username}, #{password}, #{role})")
int insertUserInfo(UserInfo userInfo);
}
UserInfoService.java类中添加插入方法,注意要加密密码
@Service
public class UserInfoService {
...
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
...
public int insertUser(UserInfo userInfo){
// 加密密码
userInfo.setPassword(passwordEncoder.encode(userInfo.getPassword()));
return userInfoMapper.insertUserInfo(userInfo);
}
}
修改HelloController.java,增加添加用户接口
@RestController
public class HelloController {
...
@PostMapping("/add-user")
public int addUser(@RequestBody UserInfo userInfo){
return userInfoService.insertUser(userInfo);
}
}
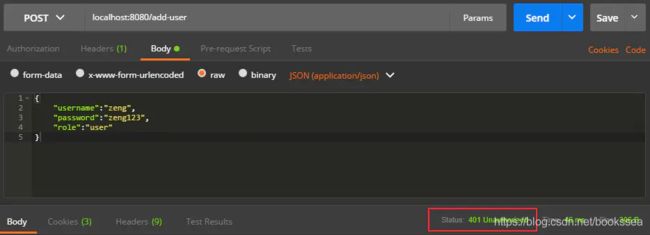
配置完后,启动服务,使用Postman发送POST请求来添加用户:
点击Send按钮后,添加失败,不会返回成功1,看到红框的状态码显示401 Unauthorized,说明无权限,需要登录,但注册用户是不用登录的,所以就需要注册用户的请求无需身份验证:
修改WebSecurityConfig配置类,重写configure(HttpSecurity http)方法,配置允许注册用户的请求访问:
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
...
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.POST, "/add-user").permitAll() // 允许post请求/add-user,而无需认证
.anyRequest().authenticated() // 所有请求都需要验证
.and()
.formLogin() // 使用默认的登录页面
.and()
.csrf().disable();// post请求要关闭csrf验证,不然访问报错;实际开发中开启,需要前端配合传递其他参数
}
}
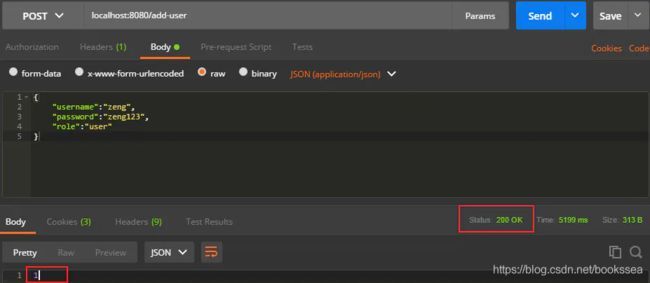
配置允许POST请求/add-user访问后,再在Postman发送请求就可以成功了:
图片
查看数据库数据,添加的用户密码已加密:
使用加密密码登录,需要修改CustomUserDetailsService类,之前从数据库拿到明文密码后需要加密,现在数据库里面的密码已经加密了,就不用加密了:
@Component
public class MyUserDatailService implements UserDetailsService {
//@Autowired
//private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
...
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
...
return new User(
user.getUsername(),
// 数据库密码已加密,不用再加密
user.getPassword(),
authorities
);
}
}
浏览器访问localhost:8080/user,输入zeng/zeng123登录即可。
五、密码修改
UserInfoMapper.java类中添加更新用户密码操作:
@Mapper
@Repository
public interface UserMapper {
...
@Update("update user set password = #{newPwd} where username = #{username}")
int updatePwd(String username, String newPwd);
}
UserInfoService.java类中添加更新密码的操作方法:
@Service
public class UserInfoService {
...
public int updatePwd(String oldPwd, String newPwd) {
// 获取当前登录用户信息(注意:没有密码的)
UserDetails principal = (UserDetails) SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
String username = principal.getUsername();
// 通过用户名获取到用户信息(获取密码)
UserInfo userInfo = userInfoMapper.getUserInfoByUsername(username);
// 判断输入的旧密码是正确
if (passwordEncoder.matches(oldPwd, userInfo.getPassword())) {
// 不要忘记加密新密码
return userInfoMapper.updatePwd(username, passwordEncoder.encode(newPwd));
}
return 0;
}
}
HelloController.java类增加修改用户密码接口:
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@PutMapping("/updatePwd")
public int updatePwd(@RequestBody Map<String, String> map){
return userInfoService.updatePwd(map.get("oldPwd"), map.get("newPwd"));
}
}
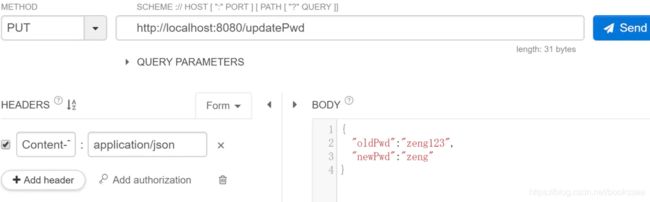
启动程序,因为需要登录,且修改密码请求方式为PUT请求,所以无法使用Postman发起请求,可以使用谷歌浏览器的插件Restlet Client:
先浏览器输入http://localhost:8080/login登录用户zeng/zeng123:
在Restlet Client中进行PUT更新请求:
这里更新后,需要重启后就可以使用新密码登录了。
5.用户角色多对多关系
上面的设置后,能基本实现了身份认证和角色授权了,但还是有一点不足:
我们前面用户表中,用户和角色是绑定一起,用户就只有一个角色了,但实际上,用户可能拥有多个角色,角色拥有多个用户,是多对多的关系,所以需要重新设置用户表和角色表。
创建普通项目运行
IDEA创建一个 Spring Initializr模块项目,名为b-database-manytomany-role,选择Spring Security和web依赖,其他按需选择Lombok、MySQL、JDBC和MyBatis。
先按照普通项目创建起来正常访问,在pom.xml中,先把Spring Security依赖注释
<!--<dependency>-->
<!--<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>-->
<!--<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>-->
<!--</dependency>-->
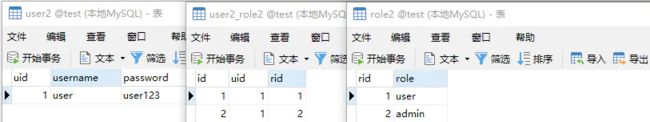
新建表,主键id全部都是自增。
用户user2表
CREATE TABLE
user2(uidint(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
usernamevarchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci
NULL DEFAULT NULL,passwordvarchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8
COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (uid) USING
BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 11 CHARACTER SET = utf8
COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
角色role2表,指定了2个角色
CREATE TABLE
role2(ridint(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
rolevarchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL
DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (rid) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB
AUTO_INCREMENT = 3 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci
ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
用户角色关系user2_role2表
CREATE TABLE
user2_role2(idint(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
uidint(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL,ridint(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 10
CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
初始化数据:
– 添加1个用户 INSERT INTO
user2VALUES (1, ‘user’, ‘user123’);– 添加2个角色 INSERT INTO
role2VALUES (1, ‘user’); INSERT INTOrole2VALUES (2, ‘admin’);– 1个用户,拥有2个角色 INSERT INTO
user2_role2VALUES (1, 1, 1); INSERT INTOuser2_role2VALUES (2, 1, 2);
使用Navicat可视化表的数据结构为:
创建entity实体类
User类
@Data
public class User {
private Integer uid;
private String username;
private String password;
}
Role类
@Data
public class Role {
private Integer rid;
private String role;
}
创建DTO类
因为用户和角色是多对多关系,需要在用户中含有角色的对象,角色中含有用户的对象,创建DTO类而不再entity类中添加,是因为entity类属性是和表字段一一对应的,一般不推荐在entity类中添加与表字段无关的属性。
新建dto包,在包下创建如下类:
UserDTO类
// 注意,多对多不要用@Data,因为ToString会相互调用,导致死循环
@Setter
@Getter
public class UserDTO extends User {
private Set<Role> roles;
}
RoleDTO类(目前用不到,可不建)
// 注意,多对多不要用@Data,因为ToString会相互调用,导致死循环
@Setter
@Getter
public class RoleDTO extends Role {
private Set<User> users;
}
添加UserMapper.java类
@Mapper
@Repository
public interface UserMapper {
// 查询用户
UserDTO selectUserByUsername(@Param("username") String username);
}
UserMapper.xml。因为需要关联查询,所有使用xml方式
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" >
<mapper namespace="com.example.bdatabasemanytomanyrole.mapper.UserMapper">
<resultMap id="userRoleMap" type="com.example.bdatabasemanytomanyrole.dto.UserDTO">
<id property="uid" column="uid"/>
<result property="username" column="username"/>
<result property="password" column="password"/>
<collection property="roles" ofType="com.example.bdatabasemanytomanyrole.dto.RoleDTO">
<id property="rid" column="rid"/>
<result property="role" column="role"></result>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectUserByUsername" resultMap="userRoleMap">
select user2.uid, user2.username, user2.password, role2.rid, role2.role
from user2, user2_role2, role2
where user2.username=#{username}
and user2.uid = user2_role2.uid
and user2_role2.rid = role2.rid
</select>
</mapper>
UserService.java
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
public UserDTO getUser(String username){
return userMapper.selectUserByUsername(username);
}
}
UserController.java
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping("/get-user")
public UserDTO getUser(@RequestParam String username){
return userService.getUser(username);
}
}
上面完成后,启动项目,访问localhost:8080/get-user?username=user,查询到的用户信息为:
引入Spring Security安全验证
把pom.xml中的Spring Security依赖注释去掉:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
此时,再重新启动程序,访问localhost:8080/get-user?username=user时,会跳转到登录页面。此时默认的登录用户名为user,密码在启动时打印在控制台。
从数据库中获取用户、密码进行登录:
添加MyUserDetailsService.java,实现UserDetailsService,重写loadUserByUsername方法:
@Component
public class MyUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
UserDTO user = userService.getUser(username);
if (user == null) {
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("用户不存在");
}
// 添加用户拥有的多个角色
List<GrantedAuthority> grantedAuthorities = new ArrayList<>();
Set<Role> roles = user.getRoles();
for (Role role : roles) {
grantedAuthorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_" + role.getRole()));
}
return new User(
user.getUsername(),
// 数据库中密码没加密,需加密
new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode(user.getPassword()),
grantedAuthorities
);
}
}
添加WebSecurityConfig.java,继承WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter,重写configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth)方法:
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private MyUserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth
.userDetailsService(userDatailService)
.passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
}
}
重新启动,可以使用user/user123登录了。
查看登录用户信息
要查看登录用户信息,我们可以在UserController中添加方法:
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping("/get-user")
public UserDTO getUser(@RequestParam String username){
return userService.getUser(username);
}
/**
* 查看登录用户信息
*/
@GetMapping("/get-auth")
public Authentication getAuth(){
return SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
}
}
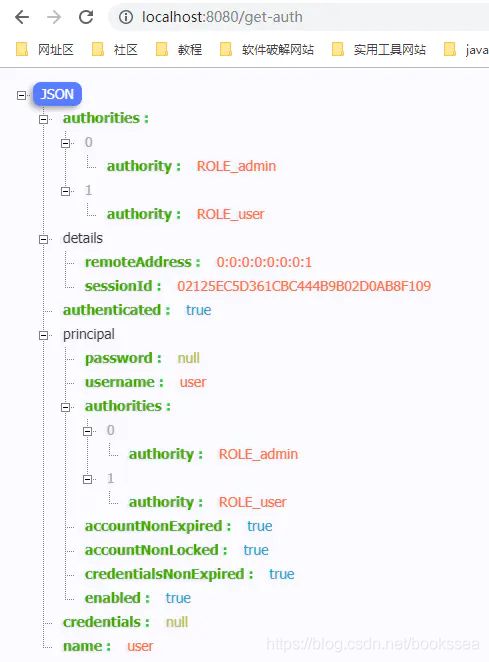
重新启动登录后,访问localhost:8080/get-auth,返回:
以上就是本篇文章的有关内容
给大家放波福利,博主最近在搞阿里云推广,
活动折扣价:全网最低价87元/年,261元/3年,比学生9.9每月还便宜(舒服的一匹)
新用户可以入手试试,有一台属于自己的服务器,前期用来部署和学习都很方便