Paddle推理YOLOV5
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、模型转换
- 二、开始测试
-
- 1.数据处理
- 2.模型加载、推理、可视化的完整实现
- 3、摆放说明
- 三、 结果展示:
- 总结
前言
本篇文章主要用来记录用Paddle框架去推理YOLOV5,详情如下
一、模型转换
模型转换部分可参考我的另一篇博客,里面也有我在转换时遇到的错误记录,YOLOV5模型转换。另外,本人的运行环境主要为:
CUDA 11.4
torch 1.9
paddle-gpu 2.2.2
tensorrt 8.2.0.6
二、开始测试
1.数据处理
代码如下(示例):
#数据预处理
def preprocess(img,imgsz):
'''
:param: img:图片Mat矩阵
:param: imgsz: 期望得到的图片较长边尺寸,默认为640
'''
# 查看图片尺寸能被stride整除的最大尺寸
imgsz = check_img_size(imgsz, s=64)
# 等比例缩放
img=letterbox(img,imgsz,64,auto=False)[0]
img = img.transpose((2, 0, 1))[::-1] # HWC to CHW, BGR to RGB
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img) #将一个内存不连续存储的数组转换为内存连续存储的数组,使得运行速度更快。
img = img.astype(np.float32)
img /= 255.0 # 归一化
img=img[np.newaxis,:]
return img
其中,check_img_size()和letterbox()函数如下(这里偷了个懒,直接从YOLOV5那边copy了一份过来,其中耗时的地方可能是letterbox函数中插值resize和边界扩充哪里,如果你的实时性要去不高,可以跳过):
def check_img_size(img_size, s=32):
# Verify img_size is a multiple of stride s
new_size = make_divisible(img_size, int(s)) # ceil gs-multiple
if new_size != img_size:
print('WARNING: --img-size %g must be multiple of max stride %g, updating to %g' % (img_size, s, new_size))
return new_size
def make_divisible(x, divisor):
# Returns x evenly divisible by divisor
return math.ceil(x / divisor) * divisor
#resize and padding
def letterbox(img, new_shape=(640, 640), color=(114, 114, 114), auto=True, scaleFill=False, scaleup=True):
# Resize image to a 32-pixel-multiple rectangle https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/issues/232
shape = img.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# Scale ratio (new / old)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
if not scaleup: # only scale down, do not scale up (for better test mAP)
r = min(r, 1.0)
# Compute padding 计算填充像素
ratio = r, r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
if auto: # minimum rectangle
dw, dh = np.mod(dw, 64), np.mod(dh, 64) # wh padding
elif scaleFill: # stretch
dw, dh = 0.0, 0.0
new_unpad = (new_shape[1], new_shape[0])
ratio = new_shape[1] / shape[1], new_shape[0] / shape[0] # width, height ratios
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
img = cv2.resize(img, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border
return img, ratio, (dw, dh)
2.模型加载、推理、可视化的完整实现
这里的模型加载参考了PaddleOCR,其余大部分函数还是使用了原版的YOLOV5,如下:
#设备选取
def get_infer_gpuid():
if os.name == 'nt':
try:
return int(os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'].split(',')[0])
except KeyError:
return 0
if not paddle.fluid.core.is_compiled_with_rocm():
cmd = "env | grep CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"
else:
cmd = "env | grep HIP_VISIBLE_DEVICES"
env_cuda = os.popen(cmd).readlines()
if len(env_cuda) == 0:
return 0
else:
gpu_id = env_cuda[0].strip().split("=")[1]
return int(gpu_id[0])
#构建推理引擎
def Init_Paddle(model_dir,infer_type="fp16",use_tensorrt=True):
'''
:parma model_dir: 模型路径
:param infer_type: 推理以什么类型进行,如fp32、fp16、int8等
:param use_tensorrt: 是否使用tensorrt进行推理
'''
gpu_id = get_infer_gpuid()
if gpu_id is None:
print("GPU is not found in current device by nvidia-smi. Please check your device or ignore it if run on jeston.")
#模型文件
model_path=os.path.join(model_dir,"model.pdmodel")
#权重文件
weights_path=os.path.join(model_dir,"model.pdiparams")
config=Config(model_path,weights_path)
#数据类型确定
if infer_type=="fp32":
precision=PrecisionType.Float32
elif infer_type=="fp16":
precision=PrecisionType.Half
else:
precision=PrecisionType.Int8
# 设置使用gpu,参数一是初始化分配的gpu显存,以MB为单位;参数二是设备名称
config.enable_use_gpu(500, 0)
# 使用tensorrt
if use_tensorrt:
'''
workspace_size - 指定 TensorRT 使用的工作空间大小
max_batch_size - 设置最大的 batch 大小,运行时 batch 大小不得超过此限定值
min_subgraph_size - Paddle-TRT 是以子图的形式运行,为了避免性能损失,当子图内部节点个数
大于 min_subgraph_size 的时候,才会使用 Paddle-TRT 运行
precision - 指定使用 TRT 的精度,支持 FP32(kFloat32),FP16(kHalf),Int8(kInt8)
use_static - 若指定为 true,在初次运行程序的时候会将 TRT 的优化信息进行序列化到磁盘上,
下次运行时直接加载优化的序列化信息而不需要重新生成
use_calib_mode - 若要运行 Paddle-TRT INT8 离线量化校准,需要将此选项设置为 true
'''
config.enable_tensorrt_engine(
workspace_size=1 << 30,
precision_mode=precision,
max_batch_size=1,
use_static=True,
min_subgraph_size=15)
#enable_memory_optim推理优化
config.enable_memory_optim()
#预测时不出现日志
config.disable_glog_info()
config.switch_use_feed_fetch_ops(False)
config.switch_ir_optim(True) #是否启用IR优化
#创建预测器
predictor=create_predictor(config)
#输入
input_names=predictor.get_input_names()
for name in input_names:
input_tensor=predictor.get_input_handle(name)
#输出
output_names=predictor.get_output_names()
output_tensors=[]
for output_name in output_names:
output_tensor=predictor.get_output_handle(output_name)
output_tensors.append(output_tensor)
return predictor,input_tensor, output_tensors, config
def xywh2xyxy(x):
# Convert nx4 boxes from [x, y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2] where xy1=top-left, xy2=bottom-right
y = x.clone() if isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) else np.copy(x)
y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2 # top left x
y[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2 # top left y
y[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2 # bottom right x
y[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2 # bottom right y
return y
#nms计算
def nms(bbox, score, thresh):
"""
nms
:param dets: ndarray [x1,y1,x2,y2,score]
:param thresh: int
:return: list[index]
"""
dets = np.c_[bbox, score]
x1 = dets[:, 0]
y1 = dets[:, 1]
x2 = dets[:, 2]
y2 = dets[:, 3]
order = dets[:, 4].argsort()[::-1]
area = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order[1:]])
w = np.maximum(0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
over = (w * h) / (area[i] + area[order[1:]] - w * h)
index = np.where(over <= thresh)[0]
order = order[index + 1] # Not include the zero
return np.array(keep)
#IOU值计算
def box_iou(box1, box2):
# https://github.com/pytorch/vision/blob/master/torchvision/ops/boxes.py
"""
Return intersection-over-union (Jaccard index) of boxes.
Both sets of boxes are expected to be in (x1, y1, x2, y2) format.
Arguments:
box1 (Tensor[N, 4])
box2 (Tensor[M, 4])
Returns:
iou (Tensor[N, M]): the NxM matrix containing the pairwise
IoU values for every element in boxes1 and boxes2
"""
def box_area(box):
# box = 4xn
return (box[2] - box[0]) * (box[3] - box[1])
area1 = box_area(box1.T)
area2 = box_area(box2.T)
# inter(N,M) = (rb(N,M,2) - lt(N,M,2)).clamp(0).prod(2)
inter = (torch.min(box1[:, None, 2:], box2[:, 2:]) -
torch.max(box1[:, None, :2], box2[:, :2])).clamp(0).prod(2)
# iou = inter / (area1 + area2 - inter)
return inter / (area1[:, None] + area2 - inter)
#NMS部分
def non_max_suppression_paddle(prediction, conf_thres=0.25, iou_thres=0.45, classes=None, agnostic=False, multi_label=False,
labels=(), max_det=300):
"""Runs Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) on inference results
Returns:
list of detections, on (n,6) tensor per image [xyxy, conf, cls]
"""
nc = prediction.shape[2] - 5 # number of classes
xc = prediction[..., 4] > conf_thres # candidates
# Checks
assert 0 <= conf_thres <= 1, f'Invalid Confidence threshold {conf_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
assert 0 <= iou_thres <= 1, f'Invalid IoU {iou_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
# Settings
min_wh, max_wh = 2, 4096 # (pixels) minimum and maximum box width and height
max_nms = 30000 # maximum number of boxes into nms()
time_limit = 200.0 # seconds to quit after
redundant = True # require redundant detections
multi_label &= nc > 1 # multiple labels per box (adds 0.5ms/img)
merge = False # use merge-NMS
t = time.time()
output = [np.zeros((0, 6), dtype=np.float32)] * prediction.shape[0]
for xi, x in enumerate(prediction): # image index, image inference
# Apply constraints
# x[((x[..., 2:4] < min_wh) | (x[..., 2:4] > max_wh)).any(1), 4] = 0 # width-height
x = x[xc[xi]] # confidence
# Cat apriori labels if autolabelling
if labels and len(labels[xi]):
l = labels[xi]
v = np.zeros((len(l), nc + 5), dtype=np.float32)
v[:, :4] = l[:, 1:5] # box
v[:, 4] = 1.0 # conf
v[range(len(l)), l[:, 0].long() + 5] = 1.0 # cls
x = np.concatenate((x, v), 0)
# If none remain process next image
if not x.shape[0]:
continue
# Compute conf
x[:, 5:] *= x[:, 4:5] # conf = obj_conf * cls_conf
# Box (center x, center y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
box = xywh2xyxy(x[:, :4])
# Detections matrix nx6 (xyxy, conf, cls)
if multi_label:
i, j = np.array((x[:, 5:] > conf_thres).nonzero())
x = np.concatenate((box[i], x[i, j + 5, None], j[:, None].astype(np.float32)), 1)
else: # best class only
conf, j = x[:, 5:].max(1, keepdims=True), x[:, 5:].argmax(1)[:,None]
x = np.concatenate((box, conf, j.astype(np.float32)), 1)[conf.reshape(-1) > conf_thres]
# Filter by class
if classes is not None:
x = x[(x[:, 5:6] == np.array(classes)).any(1)]
# Check shape
n = x.shape[0] # number of boxes
if not n: # no boxes
continue
elif n > max_nms: # excess boxes
x = x[x[:, 4].argsort()[::-1][:max_nms]] # sort by confidence
# Batched NMS
c = x[:, 5:6] * (0 if agnostic else max_wh) # classes
boxes, scores = x[:, :4] + c, x[:, 4] # boxes (offset by class), scores
i = nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres) # NMS
if i.shape[0] > max_det: # limit detections
i = i[:max_det]
if merge and (1 < n < 3E3): # Merge NMS (boxes merged using weighted mean)
# update boxes as boxes(i,4) = weights(i,n) * boxes(n,4)
iou = box_iou(boxes[i], boxes) > iou_thres # iou matrix
weights = iou * scores[None] # box weights
x[i, :4] = np.matmul(weights, x[:, :4]).astype(np.float32) / weights.sum(1, keepdims=True) # merged boxes
if redundant:
i = i[iou.sum(1) > 1] # require redundancy
output[xi] = x[i]
if (time.time() - t) > time_limit:
print(f'WARNING: NMS time limit {time_limit}s exceeded')
break # time limit exceeded
return output
#推理
import os
import sys
root_path=os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__),"."))
sys.path.append(root_path)
from pathlib import Path
debug=False #控制是否保存推理结果
class Paddle_Infer():
def __init__(self):
model_dir = "" #模型路径
self.predictor, self.input_tensor, self.output_tensors, self.config = Init_Paddle(model_dir)
self.classes = [] # 类别信息
self.save_path = root_path + "/runs/inference_results" #推理结果保存路径
if debug:
os.makedirs(self.save_path,exist_ok=True)
def predict_img(self,img,imgpath,imgsz=640):
'''
:param img:图片Mat矩阵
:param imgsz: 期望得到的缩放后的图片尺寸
'''
# im0=img.copy() #原先的图片
img_pre=preprocess(img,imgsz) #resize后的图片
self.input_tensor.copy_from_cpu(img_pre)
self.predictor.run()
output=self.output_tensors[0].copy_to_cpu()
pred=non_max_suppression_paddle(output,0.25,0.5,None,False,max_det=1000)
# 释放内存池中的所有临时 Tensor
self.predictor.try_shrink_memory()
# 可视化
self.vis_show(pred, img, img_pre, imgpath)
def vis_show(self, pred, image, image_padding, img_path):
'''
:param: pred: 预测结果:
:param: image_old:原始图像
:param: image_padding: 缩放后的图片
:param: imgpath: 图片路径
'''
# names=[f'class{i}'for i in range(1000)]
names=self.classes
for i, det in enumerate(pred):
#绘制预测框
annotator = Annotator(image, line_width=3, example=str(names))
# 检测到目标时
if len(det):
det[:, :4] = scale_coords(image_padding.shape[2:], det[:, :4], image.shape).round()
# 写结果
for *xyxy, conf, cls in reversed(det):
c = int(cls)
label = f'{names[c]} {conf:.2f}'
annotator.box_label(xyxy, label, color=colors(c, True))
im0 = annotator.result()
#保存推理结果
if debug:
imgname=Path(imgpath).name #获取文件名
cv2.imwrite(self.save_path+os.sep+imgname,im0)
其中,可是话部分用到的函数如下,仅保留了opencv处理部分,删除了pillow可视化的部分:
class Colors:
# Ultralytics color palette https://ultralytics.com/
def __init__(self):
# hex = matplotlib.colors.TABLEAU_COLORS.values()
hex = ('FF3838', 'FF9D97', 'FF701F', 'FFB21D', 'CFD231', '48F90A', '92CC17', '3DDB86', '1A9334', '00D4BB',
'2C99A8', '00C2FF', '344593', '6473FF', '0018EC', '8438FF', '520085', 'CB38FF', 'FF95C8', 'FF37C7')
self.palette = [self.hex2rgb('#' + c) for c in hex]
self.n = len(self.palette)
def __call__(self, i, bgr=False):
c = self.palette[int(i) % self.n]
return (c[2], c[1], c[0]) if bgr else c
@staticmethod
def hex2rgb(h): # rgb order (PIL)
return tuple(int(h[1 + i:1 + i + 2], 16) for i in (0, 2, 4))
colors = Colors() # create instance for 'from utils.plots import colors'
#可视化
class Annotator:
# YOLOv5 Annotator for train/val mosaics and jpgs and detect/hub inference annotations
def __init__(self, im, line_width=None, font_size=None, font='Arial.ttf', pil=False, example='abc'):
assert im.data.contiguous, 'Image not contiguous. Apply np.ascontiguousarray(im) to Annotator() input images.'
self.im=im
self.lw = line_width or max(round(sum(im.shape) / 2 * 0.003), 2) # line width
def box_label(self, box, label='', color=(128, 128, 128), txt_color=(255, 255, 255)):
# Add one xyxy box to image with label
p1, p2 = (int(box[0]), int(box[1])), (int(box[2]), int(box[3]))
cv2.rectangle(self.im, p1, p2, color, thickness=self.lw, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
if label:
tf = max(self.lw - 1, 1) # font thickness
w, h = cv2.getTextSize(label, 0, fontScale=self.lw / 3, thickness=tf)[0] # text width, height
outside = p1[1] - h - 3 >= 0 # label fits outside box
p2 = p1[0] + w, p1[1] - h - 3 if outside else p1[1] + h + 3
cv2.rectangle(self.im, p1, p2, color, -1, cv2.LINE_AA) # filled
cv2.putText(self.im, label, (p1[0], p1[1] - 2 if outside else p1[1] + h + 2), 0, self.lw / 3, txt_color,
thickness=tf, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
def result(self):
# Return annotated image as array
return np.asarray(self.im)
3、摆放说明
这里,主要说明一下各个函数的摆放说明,仅供参考
utility.py里主要用来初始化推理引擎,所需依赖项如下:
import paddle
import os
from paddle.inference import Config,create_predictor,PrecisionType
#该文件中的函数为
def get_infer_gpuid()
def Init_Paddle()
general.py中主要存放各种前后处理函数,包含如下:
#所需依赖项
import math
import numpy as np
import cv2
import time
import torch
import os
#包含函数
def check_img_size
def make_divisible
def letterbox
def nms
def box_iou
def xywh2xyxy
def non_max_suppression_paddle
class Colors:
colors = Colors()
class Annotator:
def scale_coords(img1_shape, coords, img0_shape, ratio_pad=None):
# Rescale coords (xyxy) from img1_shape to img0_shape
if ratio_pad is None: # calculate from img0_shape
gain = min(img1_shape[0] / img0_shape[0], img1_shape[1] / img0_shape[1]) # gain = old / new
pad = (img1_shape[1] - img0_shape[1] * gain) / 2, (img1_shape[0] - img0_shape[0] * gain) / 2 # wh padding
else:
gain = ratio_pad[0][0]
pad = ratio_pad[1]
coords[:, [0, 2]] -= pad[0] # x padding
coords[:, [1, 3]] -= pad[1] # y padding
coords[:, :4] /= gain
clip_coords(coords, img0_shape)
return coords
def clip_coords(boxes, img_shape):
# Clip bounding xyxy bounding boxes to image shape (height, width)
if isinstance(boxes, torch.Tensor): # faster individually
boxes[:, 0].clamp_(0, img_shape[1]) # x1
boxes[:, 1].clamp_(0, img_shape[0]) # y1
boxes[:, 2].clamp_(0, img_shape[1]) # x2
boxes[:, 3].clamp_(0, img_shape[0]) # y2
else: # np.array (faster grouped)
boxes[:, [0, 2]] = boxes[:, [0, 2]].clip(0, img_shape[1]) # x1, x2
boxes[:, [1, 3]] = boxes[:, [1, 3]].clip(0, img_shape[0]) # y1, y2
predict.py里就是我们主要的推理代码,如下:
#所需依赖
import os
import sys
root_path=os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__),"."))
sys.path.append(root_path)
import cv2
import numpy as np
from utility import Init_Paddle
from general import check_img_size,letterbox,non_max_suppression_paddle,scale_coords,Annotator,colors
from pathlib import Path
import time
import glob
debug=False
#包含函数
def preprocess
class Paddle_Infer()
函数具体内容只需将上方代码移动到对应地方即可,漏掉的函数已在对应文件中做了补充,摆放位置仅供参考,函数别漏掉就可以。
三、 结果展示:
注意,初始化模型时,如果觉得耗时严重,可以在初始化模型时,也就是Init_Paddle()中设置tensorrt属性时加入use_static=True(默认已添加),这个是将模型序列化文件保存下来,仅第一次初始化时耗时,第二次便会快很多,生成的文件在你指定的模型文件路径下。还有代码发现有错误的也可直接打在评论区,欢迎指正。
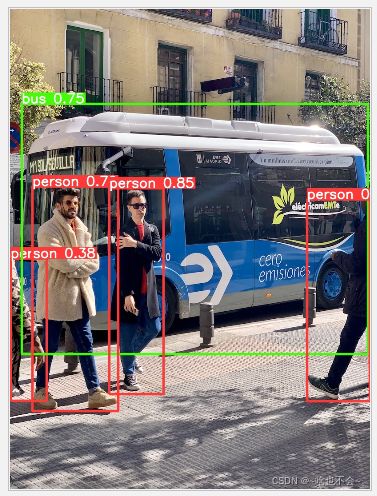
paddle不使用tensorrt推理结果如下(以官方模型为例):
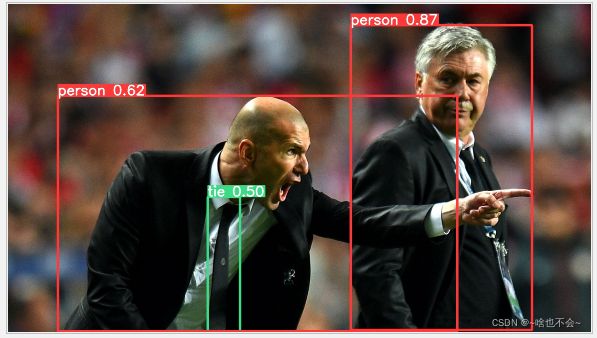
推理时间对比(是否使用tensorrt,格式为float32、图片尺寸为640的情况下)如下:
| use-tensorrt | 时间 |
|---|---|
| 是 | 5-7ms |
| 否 | 13-15ms |
总结
以上,就是本篇的全部内容,有什么问题,欢迎评论区交流,或者加入QQ群:995760755交流。