python 操作windows的Wlan
netsh介绍
Netsh(全称是network shell)简单来说 是命令行脚本工具,它允许从本地或远程显示或修改当前正在运行的计算机的网络配置。
关于net是的详细资料可以参考下面的连接:netsh命令_顺其自然~的博客-CSDN博客_netsh命令
由于今天我们只需要操作windows的WLAN,所以只需要了解netsh wlan的相关命令即可。
那么netsh wlan有哪些命令呢?
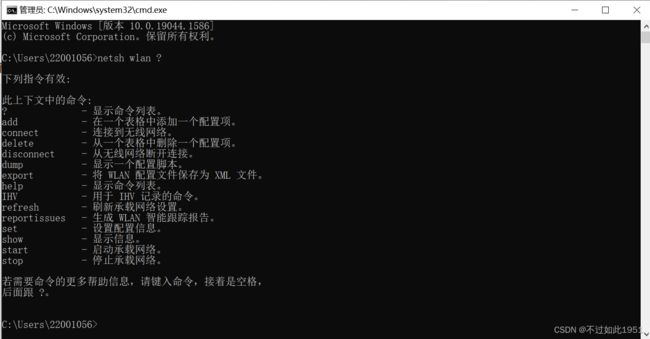
可以使用 netsh wlan ?来查看
每条命令是做什么的后面都带有解释。若想查看每条子命令的用法直接在后面加?即可;
比如想知道netsh wlan show 的用法,只需输入:netsh wlan show ?
连接之前连接过的WiFi
想用python实现此功能,首先需要知道具体的netsh命令,然后利用我之前文章里提到过的subprocess来执行命令,获取返回值即可。
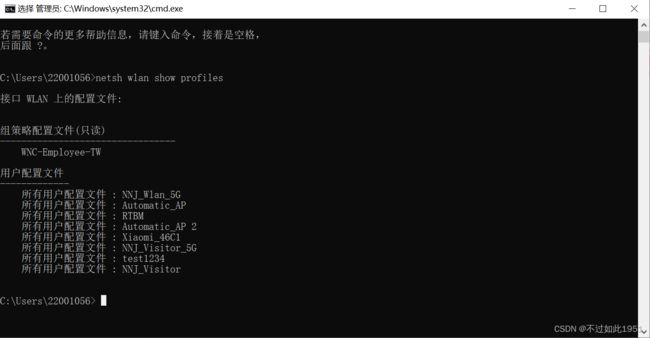
首先,通过命令:netsh wlan show profiles 列出所有该电脑连接过的wifi,以我本机为例
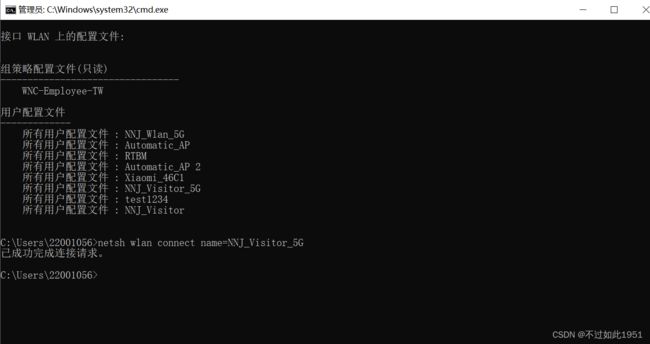
以上列出的名称是我电脑连接过的wifi列表;然后需要知道连接wifi所需命令: netsh wlan connect name=SSID名,SSID就是wifi名称,命令实现如下:
好了,知道具体命令后就可以用python的subprocess模块来实现自动连接功能了。
连接已连接过的wifi:
def get_connected_wlans(self):
cmdString = 'netsh wlan show profiles'
try:
process = subprocess.Popen(cmdString, shell=True, stdin=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
except Exception as err:
raise AssertionError('Execute command: {:s} error,{:s}'.format(cmdString, err))
resp = process.stdout.read().decode()
wlans = re.findall(r'所有用户配置文件\s*\S{1}\s*(?P\w*)', resp, re.S)
if wlans is None:
raise AssertionError('Not found connected wlan ssid in {:s}'.format(resp))
return wlans
def connect_to_wlan(self, ssid):
ssid = str(ssid).strip()
cmdString = 'netsh wlan connect name={:s}'.format(ssid)
try:
process = subprocess.Popen(cmdString, shell=True, stdin=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
except Exception as err:
raise AssertionError('Execute command: {:s} error,{:s}'.format(cmdString, err))
resp = process.stdout.read().decode()
if '已成功完成连接请求' in resp:
logger.info('Connect to {:s} success'.format(ssid)) 此外,netsh命令还可获取当前PC搜索到的所有可用的wifi,具体命令是:
netsh wlan show networks
获取当前所有可用wlan:
def get_all_accessible_wlans(self):
"""
Only for windows system
"""
self.disconnect_wlan_connection()
cmdString = 'netsh wlan show networks'
wlanItems = {}
try:
process = subprocess.Popen(cmdString, shell=True, stdin=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
except Exception as err:
raise AssertionError('Execute command: {:s} error,{:s}'.format(cmdString, err))
resp = process.stdout.read().decode('gbk')
items = re.findall(r'(?P[A-Z]+\s{1}\d{1,2})\s*\S{1}\s*(?P\w*)', resp, re.S)
#match = re.findall(r'SSID\s{1}\d{1,2}\s*\S{1}\s*(?P\w*)', resp, re.S)
if items is None:
raise AssertionError('Not found wlan ssid in {:s}'.format(resp))
for item in items:
wlanItems[item[0]] = item[1]
return wlanItems 除了以上,还可通过python脚本加netsh命令实现修改本机ip地址。命令格式为:
【netsh interface ip set address name="连接名称" static 新IP地址 子网掩码 网关】
这里我举个自己的例子,修改本机“WLAN”的ip地址为固定的地址。
修改本机WLAN的IP:
def modify_wlan_ip(self, ipAddress, mask='255.255.255.0'):
cmdString = 'netsh interface ip set address name="WLAN" source=static addr={:s} mask={:s}'.format(ipAddress, mask)
try:
process = subprocess.Popen(cmdString, shell=True, stdin=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
except Exception as err:
raise AssertionError('Execute command: {:s} error,{:s}'.format(cmdString, err))
resp = process.stdout.read().decode()
# ToDo Validation总结:
总的来说,所有netsh命令实现的功能都可以用python进行封装,但是你需要清除netsh命令是什么。但是netsh命令相当庞大,具体命令还需要自己去查询,然后用subprocess模块封装成函数。
我这里就是简单封装一些wlan相关的功能成关键字,然后在robotframework中进行调用,从而实现自动化测试的功能。
以上内容只用于抛砖引玉,更多更复杂的功能还需各位自己去调研! 感谢阅读!!