Nginx配置文件详解
Nginx配置文件详解
文章目录
-
- nginx的配置文件详解
-
- nginx.conf配置详解
- 用于调试、定位问题的配置参数
- 正常运行必备的配置参数
- 优化性能的配置参数
- 事件相关的配置:event{}段中的配置参数
- 网络连接相关的配置参数
- fastcgi的相关配置参数
- 常需要进行调整的参数
- nginx作为web服务器时使用的配置:http{}段的配置参数
-
- location区段
- 访问控制
- 基于用户认证
- 开启状态界面
- https配置
-
- openssl实现私有CA签发证书
- 免费SSL证书申请教程(推荐)
- 部署ssl证书实现https
前言:
想知道更详细更具体的参数配置请参考 Nginx官方文档
nginx的配置文件详解
主配置文件:/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
- 默认启动nginx时,使用的配置文件是:安装路径/conf/nginx.conf文件
- 可以在启动nginx时通过-c选项来指定要读取的配置文件
nginx常见的配置文件及其作用
| 配置文件 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| nginx.conf | nginx的基本配置文件 |
| mime.types | MIME类型关联的扩展文件 |
| fastcgi.conf | 与fastcgi相关的配置 |
| proxy.conf | 与proxy相关的配置 |
| sites.conf | 配置nginx提供的网站,包括虚拟主机 |
示例:
启动nginx时通过-c选项来指定要读取的配置文件
[root@localhost ~]# cp /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf .
[root@localhost ~]# ll nginx.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2656 Oct 12 16:19 nginx.conf
#如果这里报错或许是因为有些配置是相对路径,改成绝对路径即可
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -c /root/nginx.conf
#查看进程可以看到确实由指定的nginx配置文件启动了
[root@localhost ~]# ps aux | grep -v grep | grep nginx
root 49601 0.0 0.0 81716 1096 ? Ss 16:27 0:00 nginx: master process nginx -c /root/nginx.conf
nginx 49602 0.0 0.3 111740 6188 ? S 16:27 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx.conf配置详解
nginx.conf的内容分为以下几段:
- main配置段:全局配置段。其中main配置段中可能包含event配置段
- event {}:定义event模型工作特性
- http {}:定义http协议相关的配置
配置指令:要以分号结尾,语法格式如下:
derective value1 [value2 ...];
支持使用变量:
- 内置变量:模块会提供内建变量定义
- 自定义变量:
set var_name value
用于调试、定位问题的配置参数
daemon {on|off}; //是否以守护进程方式运行nginx,调试时应设置为off
master_process {on|off}; //是否以master/worker模型来运行nginx,调试时可以设置为off
error_log 位置 级别; //配置错误日志
error_log里的位置和级别能有以下可选项:
| 位置 | 级别 |
|---|---|
| file stderr syslog:server=address[,parameter=value] memory:size | debug:若要使用debug级别,需要在编译nginx时使用–with-debug选项 info notice warn error crit alert emerg |
示例:
例1:修改daemon的默认设置,默认是on(开启),我们off一下。关闭守护进程意为放到前台来执行。
想要恢复为后台运行nginx则只需删掉该字段即可,因默认daemon是开启的。
[root@localhost conf]# vim nginx.conf
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
daemon off; #加入此条,由于该参数是main字段的,所以需要在顶格写。
[root@localhost conf]# systemctl restart nginx.service
#这里的空白页是因为把nginx放到前台运行被占住了,无法进行操作
例2:默认是以master/worker模型来运行nginx,这里我们关掉试试。
#默认的nginx启动进程有这么几条
[root@localhost conf]# ps aux | grep -v grep | grep nginx
root 49824 0.0 0.0 81712 1104 ? Ss 16:59 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
nginx 49825 0.0 0.3 111736 6252 ? S 16:59 0:00 nginx: worker process
[root@localhost conf]# vim nginx.conf
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
master_process off; #加入此条
[root@localhost conf]# systemctl restart nginx.service
#跟上条进程对比可以看到没有master/worker进程了
[root@localhost conf]# ps aux | grep -v grep | grep nginx
root 49792 0.0 0.1 82084 2908 ? Ss 16:55 0:00 /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
例3:配置错误日志的存放位置。如果编译时未指定那么默认是在nginx目录下的logs目录里
[root@localhost conf]# vim nginx.conf
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
error_log /opt/error.log error; #设置错误日志存放在/opt/下的error.log文件,日志等级为error
#error_log logs/error.log; #可以看到配置文件默认就有错误日志的配置,取消注释就可用
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
[root@localhost conf]# systemctl reload nginx.service
[root@localhost conf]# ll /opt/error.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Oct 12 17:54 /opt/error.log
正常运行必备的配置参数
user USERNAME [GROUPNAME]; //指定运行worker进程的用户和组
pid /path/to/pid_file; //指定nginx守护进程的pid文件
worker_rlimit_nofile number; //设置所有worker进程最大可以打开的文件数,默认为1024
worker_rlimit_core size; //指明所有worker进程所能够使用的总体的最大核心文件大小,保持默认即可
示例:
例1:指定运行worker进程的用户为nobody
#可以看到worker进程默认的用户是root
[root@localhost conf]# ps aux | grep -v grep | grep nginx
root 49824 0.0 0.2 81844 4116 ? Ss 17:32 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
nginx 49932 0.0 0.3 111728 6340 ? S 17:54 0:00 nginx: worker process
[root@localhost conf]# vim nginx.conf
user nobody; #把原有的用户配置取消了注释
worker_processes 1;
#可以看到worker进程的用户是nobody了
[root@localhost conf]# systemctl reload nginx.service
[root@localhost conf]# ps aux | grep -v grep | grep nginx
root 49989 0.0 0.2 81848 4036 ? Ss 17:58 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
nobody 50007 0.0 0.3 111952 5996 ? S 17:59 0:00 nginx: worker process
例2:指定nginx守护进程的pid文件存放在/tmp目录下
[root@localhost conf]# vim nginx.conf
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
pid /tmp/nginx.pid;
[root@localhost conf]# systemctl reload nginx.service
[root@localhost conf]# ll /tmp/nginx.pid
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 6 Oct 12 18:08 /tmp/nginx.pid
例3:设置所有worker进程最大可以打开的文件数
[root@localhost conf]# vim nginx.conf
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
worker_rlimit_nofile 10240; #加入此条
优化性能的配置参数
worker_processes n; //启动n个worker进程,这里的n为了避免上下文切换,通常设置为cpu总核心数-1或等于总核心数
worker_cpu_affinity cpumask ...; //将进程绑定到某cpu中,避免频繁刷新缓存
//cpumask:使用8位二进制表示cpu核心,如:
0000 0001 //第一颗cpu核心
0000 0010 //第二颗cpu核心
0000 0100 //第三颗cpu核心
0000 1000 //第四颗cpu核心
0001 0000 //第五颗cpu核心
0010 0000 //第六颗cpu核心
0100 0000 //第七颗cpu核心
1000 0000 //第八颗cpu核心
timer_resolution interval; //计时器解析度。降低此值,可减少gettimeofday()系统调用的次数
worker_priority number; //定义worker进程的nice值(调度优先级),默认为0,负数表示更高的优先级。允许的范围通常为-20 ~ 20。
示例:
例1:设置启动几个worker进程,通常设置为等于总核心数或cpu总核心数-1
[root@localhost conf]# cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep name
model name : AMD Ryzen 7 4800H with Radeon Graphics
model name : AMD Ryzen 7 4800H with Radeon Graphics
[root@localhost conf]# vim nginx.conf
#user nobody;
worker_processes 2;
[root@localhost conf]# systemctl reload nginx.service
#可以看到有两个worker进程了
[root@localhost conf]# ps aux | grep -v grep | grep nginx
root 49989 0.0 0.2 81752 4188 ? Ss 17:58 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
nginx 50541 0.0 0.3 111836 6372 ? S 18:37 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 50542 0.0 0.3 111836 6372 ? S 18:37 0:00 nginx: worker process
例2:将进程绑定到某cpu中,根据worker进程有几个来绑定
[root@localhost conf]# vim nginx.conf
#user nobody;
worker_processes 2;
worker_cpu_affinity 00000001 00000010; #按照该格式依此类推
[root@localhost conf]# systemctl reload nginx.service
例3:提高工作(worker)进程的调度优先级
[root@localhost conf]# vim nginx.conf
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
worker_priority -10; #添加此条
[root@localhost conf]# systemctl reload nginx.service
#键入top命令,在top命令界面键入大写的L,输入nginx进行搜索,输错了按退格键无效,需要Ctrl+退格键
#可以看到有条nginx进程的nice值为-10,用户是nginx,那想必就是worker进程了
[root@localhost conf]# top
top - 19:18:25 up 8:53, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
Tasks: 164 total, 1 running, 163 sleeping, 0 stopped, 0 zombie
%Cpu(s): 0.0 us, 0.0 sy, 0.0 ni, 99.7 id, 0.0 wa, 0.2 hi, 0.2 si, 0.0 st
MiB Mem : 1790.0 total, 601.1 free, 261.2 used, 927.7 buff/cache
MiB Swap: 2080.0 total, 2080.0 free, 0.0 used. 1337.5 avail Mem
PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
49989 root 20 0 81752 4188 3020 S 0.0 0.2 0:00.00 nginx
50073 root 20 0 0 0 0 I 0.0 0.0 0:00.35 kworker/0:1-ata_sff
50505 root 20 0 0 0 0 I 0.0 0.0 0:00.08 kworker/u256:0-events_unbound
50595 root 20 0 0 0 0 I 0.0 0.0 0:01.28 kworker/1:1-events_power_efficient
50632 nginx 10 -10 111836 5996 4560 S 0.0 0.3 0:00.00 nginx #看这里!!
50633 root 20 0 0 0 0 I 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 kworker/1:0
50634 root 20 0 0 0 0 I 0.0 0.0 0:00.04 kworker/u256:2-events_unbound
50647 root 20 0 0 0 0 I 0.0 0.0 0:00.03 kworker/0:3-mm_percpu_wq
50673 root 20 0 0 0 0 I 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 kworker/u256:1-events_unbound
50675 root 20 0 0 0 0 I 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 kworker/0:0-ata_sff
50676 root 20 0 65436 4324 3676 R 0.0 0.2 0:00.01 top
事件相关的配置:event{}段中的配置参数
accept_mutex {off|on}; //master调度用户请求至各worker进程时使用的负载均衡锁;on表示能让多个worker轮流地、序列化地去响应新请求
lock_file file; //accept_mutex用到的互斥锁锁文件路径
use [epoll | rtsig | select | poll]; //指明使用的事件模型,建议让nginx自行选择
worker_connections #; //每个进程能够接受的最大连接数
示例:
例1:设置每个worker进程的最大连接数。
[root@localhost conf]# vim nginx.conf
events {
worker_connections 10240; #默认是1024,我这里修改为10240
}
[root@localhost conf]# systemctl reload nginx.service
网络连接相关的配置参数
keepalive_timeout number; //长连接的超时时长,默认为65s
keepalive_requests number; //在一个长连接上所能够允许请求的最大资源数
keepalive_disable [msie6|safari|none]; //为指定类型的UserAgent禁用长连接
tcp_nodelay on|off; //是否对长连接使用TCP_NODELAY选项,为了提升用户体验,通常设为on
client_header_timeout number; //读取http请求报文首部的超时时长
client_body_timeout number; //读取http请求报文body部分的超时时长
send_timeout number; //发送响应报文的超时时长
fastcgi的相关配置参数
LNMP:php要启用fpm模型
配置示例如下:
location ~ \.php$ {
root html;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; //定义反向代理
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
常需要进行调整的参数
- worker_processes
- worker_connections
- worker_cpu_affinity
- worker_priority
nginx作为web服务器时使用的配置:http{}段的配置参数
http{…}:配置http相关,由ngx_http_core_module模块引入。nginx的HTTP配置主要包括四个区块,结构如下:
http {//协议级别
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
keepalive_timeout 65;
gzip on;
upstream {//负载均衡配置
...
}
server {//服务器级别,每个server类似于httpd中的一个
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {//请求级别,类似于httpd中的,用于定义URL与本地文件系统的映射关系
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
}
http{}段配置指令:
server {}:定义一个虚拟主机,示例如下:
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.idfsoft.com;
root "/vhosts/web";
}
listen:指定监听的地址和端口
listen address[:port];
listen port;
server_name NAME [...]; 后面可跟多个主机,名称可使用正则表达式或通配符
当有多个server时,匹配顺序如下:
- 先做精确匹配检查
- 左侧通配符匹配检查,如
*.idfsoft.com - 右侧通配符匹配检查,如
mail.* - 正则表达式匹配检查,如
~ ^.*\.idfsoft\.com$ - default_server
root path; 设置资源路径映射,用于指明请求的URL所对应的资源所在的文件系统上的起始路径
alias path; 用于location配置段,定义路径别名
index file; 默认主页面
index index.php index.html;
error_page code [...] [=code] URI | @name` 根据http响应状态码来指明特用的错误页面,例如 `error_page 404 /404_customed.html
[=code]:以指定的响应码进行响应,而不是默认的原来的响应,默认表示以新资源的响应码为其响应码,例如 error_page 404 =200 /404_customed.html
log_format 定义日志格式
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log logs/access.log main;
//注意:此处可用变量为nginx各模块内建变量
location区段
通过指定模式来与客户端请求的URI相匹配
//功能:允许根据用户请求的URI来匹配定义的各location,匹配到时,此请求将被相应的location配置块中的配置所处理,例如做访问控制等功能
//语法:location [ 修饰符 ] pattern {......}
常用修饰符说明
| 修饰符 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| = | 精确匹配 |
| ~ | 正则表达式模式匹配,区分大小写 |
| ~* | 正则表达式模式匹配,不区分大小写 |
| ^~ | 前缀匹配,类似于无修饰符的行为,也是以指定模块开始,不同的是,如果模式匹配,那么就停止搜索其他模式了,不支持正则表达式 |
| @ | 定义命名location区段,这些区段客户端不能访问,只可以由内部产生的请求来访问,如try_files或error_page等 |
没有修饰符表示必须以指定模式开始,如:
server {
server_name www.idfsoft.com;
location /abc {
......
}
}
那么如下内容就可正确匹配:
- http://www.idfsoft.com/abc
- http://www.idfsoft.com/abc?p1=11&p2=22
- http://www.idfsoft.com/abc/
=:表示必须与指定的模式精确匹配,如:
server {
server_name www.idfsoft.com;
location = /abc {
......
}
}
那么如下内容就可正确匹配:
- http://www.idfsoft.com/abc
- http://www.idfsoft.com/abc?p1=11&p2=22
如下内容则无法匹配:
- http://www.idfsoft.com/abc/
- http://www.idfsoft.com/abc/abcde
~:表示指定的正则表达式要区分大小写,如:
server {
server_name www.idfsoft.com;
location ~ ^/abc$ {
......
}
}
那么如下内容就可正确匹配:
- http://www.idfsoft.com/abc
- http://www.idfsoft.com/abc?p1=11&p2=22
如下内容则无法匹配:
- http://www.idfsoft.com/abc/
- http://www.idfsoft.com/ABC
- http://www.idfsoft.com/abcde
~*:表示指定的正则表达式不区分大小写,如:
server {
server_name www.idfsoft.com;
location ~* ^/abc$ {
......
}
}
那么如下内容就可正确匹配:
- http://www.idfsoft.com/abc
- http://www.idfsoft.com/abc?p1=11&p2=22
- http://www.idfsoft.com/ABC
如下内容则无法匹配:
- http://www.idfsoft.com/abc/
- http://www.idfsoft.com/abcde
~:类似于无修饰符的行为,也是以指定模式开始,不同的是,如果模式匹配,则停止搜索其他模式
查找顺序和优先级:由高到底依次为
- 带有
=的精确匹配优先 - 正则表达式按照他们在配置文件中定义的顺序
- 带有
^~修饰符的,开头匹配 - 带有
~或~*修饰符的,如果正则表达式与URI匹配 - 没有修饰符的精确匹配
优先级次序如下:
( location = 路径 ) --> ( location ^~ 路径 ) --> ( location ~ 正则 ) --> ( location ~* 正则 ) --> ( location 路径 )
URI的匹配修饰符示例:
[root@localhost conf]# vim nginx.conf
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
location = / {
echo "A";
}
location / {
echo "B";
}
location /documents/ {
echo "C";
}
location ^~ /images/ {
echo "D";
}
location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {
echo "E";
}
[root@localhost conf]# systemctl restart nginx.service
#这里为什么匹配到的是A而不是B呢?是因为“=”是精准匹配,优先级最高。而B没有作修饰符,优先级最低
[root@localhost conf]# curl http://192.168.92.130/
A
#咦?这里你可能会奇怪,“=”不是精准匹配吗?为啥会识别到/后面的一大串呢,
#这里注意!“?”及后面的部分不会被识别为URI的一部分
[root@localhost conf]# curl http://192.168.92.130/?asdaer4542
A
#由于都没有匹配到该URI,而B没有作修饰符的匹配优先级最低,最后显示为B
[root@localhost conf]# curl http://192.168.92.130/qweasdzxc
B
#匹配到了该URI为/documents/
[root@localhost conf]# curl http://192.168.92.130/documents/abc
C
#“~^”是前缀匹配,这里匹配到了URI的首字段为/images/
[root@localhost conf]# curl http://192.168.92.130/images/test
D
#匹配到以.jpg作结尾的URI了
[root@localhost conf]# curl http://192.168.92.130/images.jpg
E
访问控制
官方文档的访问控制
常用于location段,也可以在http段和server段进行配置。
allow:设定允许哪台或哪些主机访问,多个参数间用空格隔开
deny:设定禁止哪台或哪些主机访问,多个参数间用空格隔开
官方文档的示例:
location / {
deny 192.168.1.1;
allow 192.168.1.0/24;
allow 10.1.1.0/16;
allow 2001:0db8::/32;
deny all;
}
例子解释:依次检查规则,直到找到第一个匹配。在本例中,只允许IPv4网络10.1.1.0/16和192.168.1.0/24(不包括192.168.1.1)和IPv6网络2001:0db8::/32进行访问。
案例1:拒绝本机访问
该虚拟机采用的是NAT网络模式所以要对VM8网卡的IP进行访问控制
location / {
echo "test"; #注意,我这是额外添加了echo模块的功能
deny 192.168.92.1;
}
案例2:除本机外,拒绝所有的访问
注意!deny all要写在后面,因为是依次检查规则的,如果第一条直接写deny all,下面的就不会被匹配到了。
location / {
echo "test";
allow 192.168.92.1;
deny all;
}
基于用户认证
官方文档的基本认证
配置示例:
auth_basic "欢迎信息";
auth_basic_user_file "/path/to/user_auth_file"
user_auth_file内容格式为:
username:password
这里的密码为加密后的密码串,建议用htpasswd来创建此文件:
htpasswd -c -m /path/to/.user_auth_file USERNAME
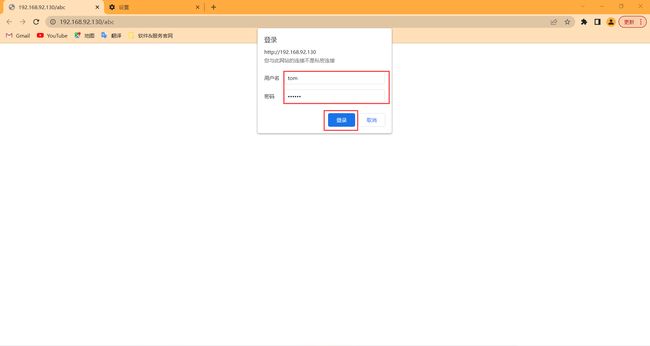
案例1:配置某个URI要输入用户名与密码方可访问
用户:tom 密码:123456
#须先下载htpasswd命令
[root@localhost conf]# dnf -y install httpd-tools
#-c创建passwdfile,-m使用MD5加密
[root@localhost conf]# htpasswd -c -m /usr/local/nginx/conf/.htpasswd tom
New password: #键入密码
Re-type new password: #确认密码
Adding password for user tom
[root@localhost conf]# cat .htpasswd
tom:$apr1$pXhY.o/u$9MZjOxfdtNz084iXRlxKJ. #该密码串是经过加密的
location / {
echo "test";
}
location = /abc { #关注该location段即可
echo "abc!";
auth_basic "欢迎访问~";
auth_basic_user_file ".htpasswd"; #因我把认证
}
#这样写两个location,就做到了资源隔离的效果了。
#在其中一个location段设置用户认证,是因为该资源不能什么人都可以访问,比如后面要介绍的状态界面
开启状态界面
官网文档的开启状态界面
开启status:
location /status {
stub_status {on | off};
allow 172.16.0.0/16;
deny all;
}
访问状态页面的方式:http://server_ip/status
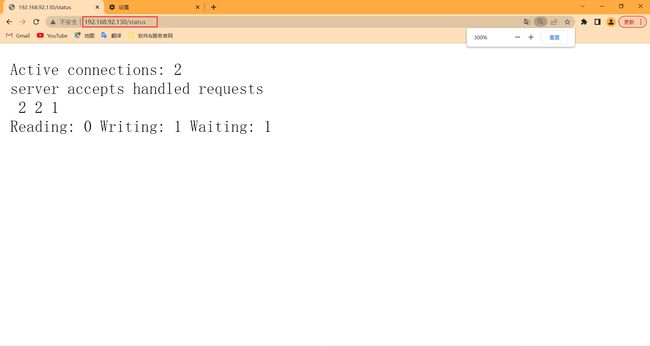
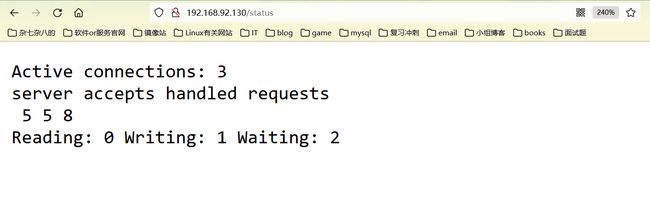
状态页面信息详解:
| 状态码 | 表示的意义 |
|---|---|
| Active connections | 当前所有处于打开状态的连接数 |
| accepts | 总共处理了多少个连接 |
| handled | 成功创建多少握手 |
| requests | 总共处理了多少个请求 |
| Reading | nginx读取到客户端的Header信息数,表示正处于接收请求状态的连接数 |
| Writing | nginx返回给客户端的Header信息数,表示请求已经接收完成, 且正处于处理请求或发送响应的过程中的连接数 |
| Waiting | 开启keep-alive的情况下,这个值等于active - (reading + writing), 意思就是Nginx已处理完正在等候下一次请求指令的驻留连接 |
演示开启状态界面:
案例1:开启状态界面。但这样做不安全,这样所有人都能看到nginx的状态,以防有心之人趁服务器负载高时进行DDOS攻击
location = /status {
stub_status;
}
案例2:开启状态界面,但基于用户认证进行访问。如何配置用户认证请往上翻
location = /status {
stub_status;
auth_basic "hello";
auth_basic_user_file ".htpasswd";
}
我这里换了个浏览器访问是因为刚刚那浏览器因为输入了密码被保存了登录信息,我清除缓存也没弹出用户认证窗口,换了个浏览器就有了。
https配置
生成私钥,生成证书签署请求并获得证书,然后在nginx.conf中配置
示例:
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name www.idfsoft.com;
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.key;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
ssl_session_timeout 5m;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
获取证书有方式有两种,其一是openssl实现私有CA签发证书,其二是免费SSL证书申请。在个人实验环境中二者选其一即可,但在企业的生产环境中必须要购买证书进行部署。
openssl实现私有CA签发证书
#创建私有CA存放位置
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir -p /etc/pki/CA
[root@localhost ~]# cd /etc/pki/CA
[root@localhost CA]# mkdir private
#服务端生成密钥
[root@localhost CA]# (umask 077;openssl genrsa -out private/cakey.pem 2048)
Generating RSA private key, 2048 bit long modulus (2 primes)
....+++++
.........................+++++
e is 65537 (0x010001)
#提取公钥
[root@localhost CA]# openssl rsa -in private/cakey.pem -pubout
writing RSA key
-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----
MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEA1R3BrFLzEFub1t8k2CPd
EZcUoXvmSJVGNf99LgISs+zzY7Jl0s97bcNLaB91h/riPNHq9Z/hyeqfTbSVNKeO
s4Z6RuM7m/Bpm1cSt53FOgrz41GBs/DT9V0CzJABCiWjJziQOIn93JElTNOttDKD
AOMwo88u+b1kG/GcSfkLpNn871X/5YKp1YRXMmE8TLfvpp6hXmvojai2MpxIGCcJ
DC/oDtKOKtsPGUAW6xB7ZpIcQsw+n3JMhiCgKsYeGZ1ZKHM9LFTB7s02Xe0pQwhZ
fzQ3N1nR9fpC6eiU3DkV1h4V+2mUD36Omgqz9H3+DrPn+xAfGSVBtxrmBFvxJMAV
+wIDAQAB
-----END PUBLIC KEY-----
#生成自签署证书,请记住这里填写的信息,后面生成的证书签署请求文件填写的信息要与这里完全一致
[root@localhost CA]# openssl req -new -x509 -key private/cakey.pem -out cacert.pem -days 365
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:CN
State or Province Name (full name) []:HB
Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:WH
Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:www.yf.com
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:www.yf.com
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:www.yf.com
Email Address []:[email protected]
[root@localhost CA]# ls
cacert.pem private
[root@localhost CA]# mkdir certs newcerts crl
[root@localhost CA]# touch index.txt && echo 01 > serial
[root@localhost CA]# ls
cacert.pem certs crl index.txt newcerts private serial
[root@localhost CA]# cd /usr/local/nginx/conf/
[root@localhost conf]# mkdir ssl
[root@localhost conf]# cd ssl/
#客户端生成密钥
[root@localhost ssl]# (umask 077;openssl genrsa -out nginx.key 2048)
Generating RSA private key, 2048 bit long modulus (2 primes)
.....+++++
..............................+++++
e is 65537 (0x010001)
#客户端生成证书签署请求文件,这里填写的信息要与前面的完全一致,不然无法签署成功
[root@localhost ssl]# openssl req -new -key nginx.key -days 365 -out nginx.csr
Ignoring -days; not generating a certificate
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:CN
State or Province Name (full name) []:HB
Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:WH
Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:www.yf.com
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:www.yf.com
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:www.yf.com
Email Address []:[email protected]
Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []:
An optional company name []:
[root@localhost ssl]# ls
nginx.csr nginx.key
#CA签署客户端的证书
[root@localhost ssl]# openssl ca -in nginx.csr -out nginx.crt -days 365
Using configuration from /etc/pki/tls/openssl.cnf
Check that the request matches the signature
Signature ok
Certificate Details:
Serial Number: 1 (0x1)
Validity
Not Before: Oct 13 12:38:41 2022 GMT
Not After : Oct 13 12:38:41 2023 GMT
Subject:
countryName = CN
stateOrProvinceName = HB
organizationName = www.yf.com
organizationalUnitName = www.yf.com
commonName = www.yf.com
emailAddress = 1@2.com
X509v3 extensions:
X509v3 Basic Constraints:
CA:FALSE
Netscape Comment:
OpenSSL Generated Certificate
X509v3 Subject Key Identifier:
04:7E:A7:7C:55:34:E8:B8:52:D0:C5:CE:FA:C4:14:E2:A5:96:08:A2
X509v3 Authority Key Identifier:
keyid:76:81:2D:69:5B:17:F6:52:4C:C4:91:7C:BC:FD:90:21:01:C0:49:F7
Certificate is to be certified until Oct 13 12:38:41 2023 GMT (365 days)
Sign the certificate? [y/n]:y
1 out of 1 certificate requests certified, commit? [y/n]y
Write out database with 1 new entries
Data Base Updated
[root@localhost ssl]# ls
nginx.crt nginx.csr nginx.key
#csr是证书签署请求文件,已完成了它的使命,后续不再用到
[root@localhost ssl]# rm -f nginx.csr
[root@localhost ssl]# ls
nginx.crt nginx.key
#后续如何部署ssl证书请往后看,点击文章目录跳转到【部署ssl证书实现https】
免费SSL证书申请教程(推荐)
阿里云免费SSL证书介绍:
免费证书只能保护一个域名(带www和不带www可以通用),阿里云个人账号和企业账号均可申请,多个域名可以申请多个免费证书,免费为每个通过实名验证的阿里云账号提供20张DigiCert DV单域名证书。申请教程如下:
一、证书选购
- 打开阿里云SSL证书申请页面,点击“选购证书”
- 证书选择
选择证书类型:免费版(个人)DV
选择品牌:DigiCert
域名类型:单域名(1个域名)
选择域名个数:只能选择1
购买数量:可以购买多个
购买时长:最多购买一年
总配置费用为0元,点击“立即购买”,结算即可。
二、证书申请
购买完的SSL证书是未签发状态,还要提交证书申请,阿里云系统会将请求发送给CA机构审核。
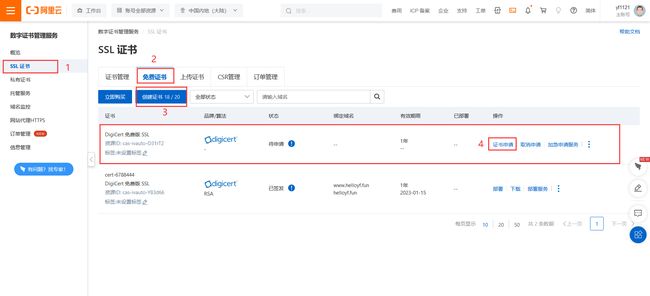
- 登录到阿里云SSL控制台
- 在刚购买未签发的免费版SSL,选择“证书申请”
如下图:
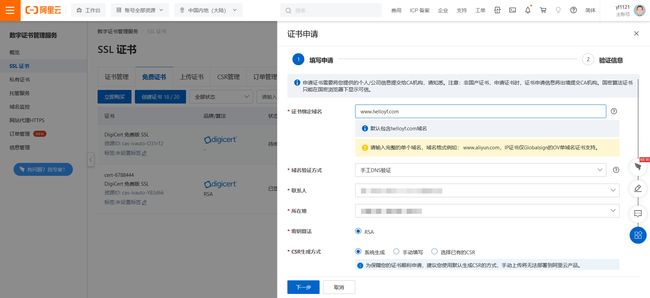
- 填写SSL证书申请表单
证书绑定域名:免费证书只能填写一个域名,带www和不带www域名可以通用
申请人姓名:按照实际填写
申请人手机号:按照实际填写
申请人邮箱:按照实际填写
所在地:按照实际填写
域名验证方式:参考(阿里云SSL证书申请域名验证选择及操作流程)
CSR生成方式:系统生成
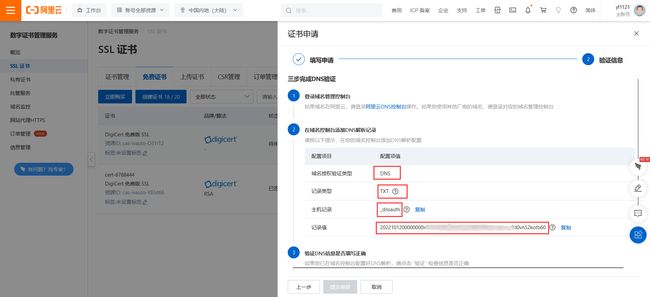
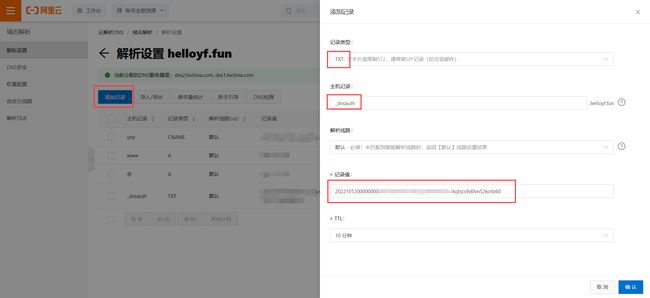
- 完成DNS验证
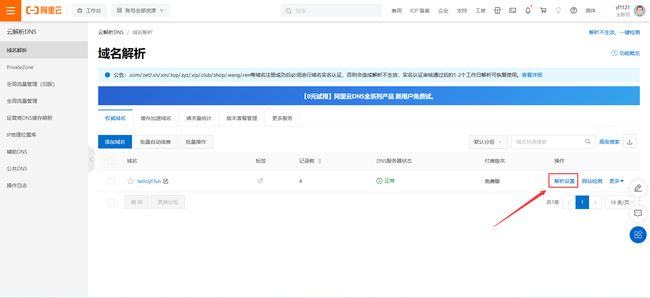
如果你的域名在阿里云,直接点图片里的链接跳转。如不是则自行打开自己的域名控制台
把证书申请的DNS验证信息复制过来
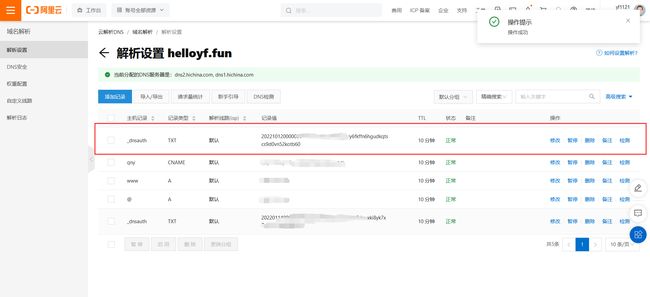
添加后看到此项的状态是【正常】的即可
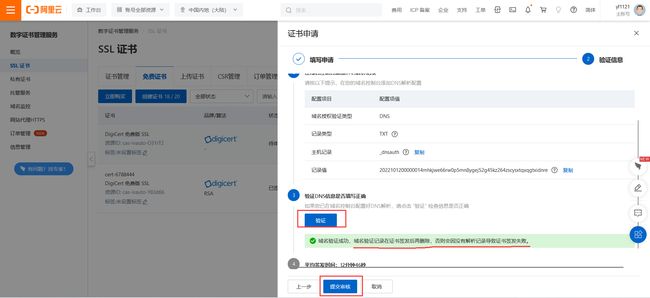
完成上述操作后,回到证书申请界面,点击【验证】,验证成功后点击【提交申请】
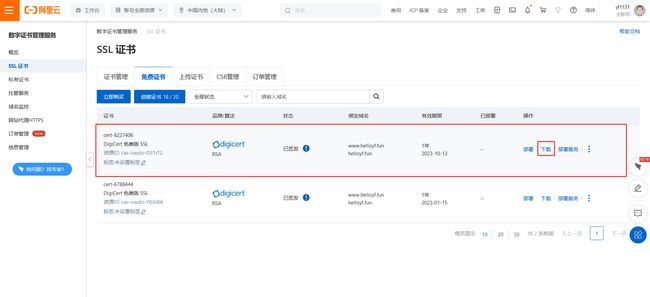
- 下载证书
看到证书的状态是【已签发】,则证明该证书可以实际使用了,点击【下载】
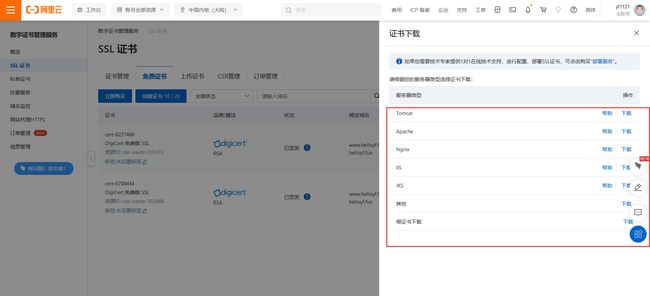
证书下载界面可以看到有这么多类型,这里我选择nginx,因为我要部署到nginx服务器上,根据服务类型选择相对应的
下载到本地后上传至nginx服务器
部署ssl证书实现https
[root@localhost conf]# pwd
/usr/local/nginx/conf
[root@localhost conf]# mkdir ssl
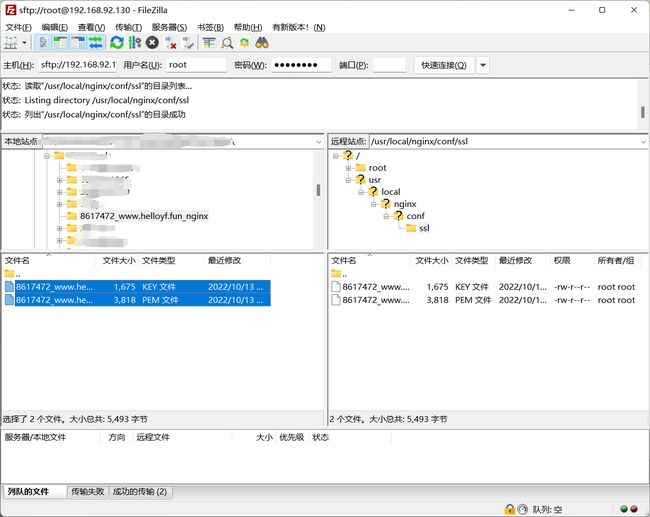
将本地的证书文件上传至nginx服务器
[root@localhost conf]# cd ssl/
[root@localhost ssl]# ls
8617472_www.helloyf.fun.key 8617472_www.helloyf.fun.pem
#我这里改名是为了方便记忆。pem证书可以更名为crt证书
[root@localhost ssl]# mv 8617472_www.helloyf.fun.key nginx.key
[root@localhost ssl]# mv 8617472_www.helloyf.fun.pem nginx.crt
[root@localhost ssl]# ls
nginx.crt nginx.key
#进行配置https,直接在原有配置中取消这大一段的注释
[root@localhost conf]# vim nginx.conf
#HTTPS server
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name www.helloyf.fun; #将此修改为自己的域名
ssl_certificate ssl/nginx.crt; #【pem|crt】证书存放的位置
ssl_certificate_key ssl/nginx.key; #key证书存放的位置
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
ssl_session_timeout 5m;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
[root@localhost conf]# systemctl restart nginx.service
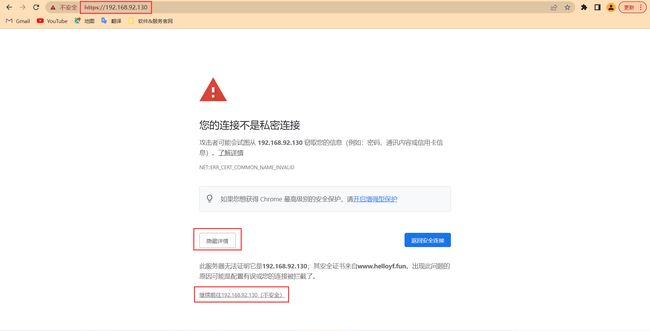
去浏览器访问
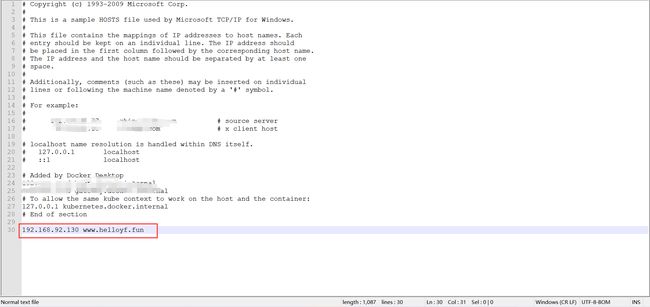
此时也可以用域名进行访问,不过我的域名已经用公网IP部署了网站。所以先要在本机的hosts文件写本地域名映射,这样就不会访问我公网的站点了。这里涉及到DNS解析的工作流程,感兴趣可以去查查。
Windows系统中该文件的默认路径:C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts
在该文件的最后一行添加IP和域名,保存即可。我这个域名要用于访问博客,所以做完实验后会恢复,恢复的话直接把这一行映射删掉。
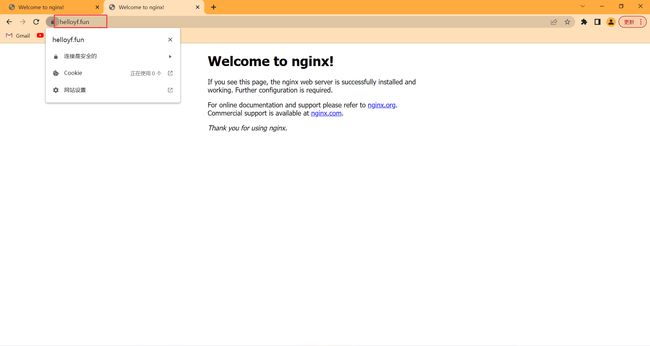
这次用域名访问。可以看到访问成功了,并且显示连接是安全的!