C语言小游戏——三子棋
目录
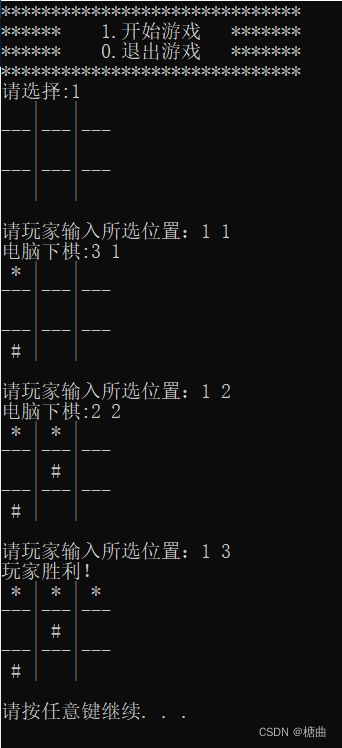
游戏展示:
基础代码
文件
game.h
game.c
初始化
打印
玩家输入
电脑输入
判断胜负
text.c
优化代码
展示
game.c
电脑输入
电脑判断输入
总结
绝大多数情况下你并不孤单,你遇到的问题早就有人遇到,你踩过的坑里尽是前人的脚印。
游戏展示:
基础代码
文件
- game.h头文件
- game.c函数实现文件
- text.c主函数调用文件
game.h
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#define Row 3 //行
#define Line 3 //列
void SzqInit(char ch[Row][Line]);//初始化
void Szqprint(char ch[Row][Line]);//打印
void Playergame(char ch[Row][Line]);//玩家输入 - *
void Computergame(char ch[Row][Line]);//电脑输入 - #
int Judgegame(char ch[Row][Line]);//判断游戏胜负 game.c
初始化
//初始化
void SzqInit(char ch[Row][Line])
{
for (int i = 0; i < Row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < Line; j++)
{
ch[i][j] = ' ';
}
}
}使用两个for循环,将二维数组初始化,方便之后的输入数据和查看结果做区别
打印
//打印
void Szqprint(char ch[Row][Line])
{
for (int i = 0; i < Row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < Line; j++)
{
printf(" %c ", ch[i][j]);
if (j != Line-1)
printf("|");
}
printf("\n");
if (i != Row - 1)
{
for (int j = 0; j < Line; j++)
{
printf("---");
if (j != Line - 1)
printf("|");
}
}
printf("\n");
}
}打印三子棋的棋盘和其上棋子
玩家输入
//玩家输入 - *
void Playergame(char ch[Row][Line])
{
while (1)
{
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
printf("请玩家输入所选位置:");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
//判断输入范围是否正确
if (x>3 || y>3 || x<1 || y<1)
{
printf("输入错误,请重新输入!\n");
continue;
}
//判断输入位置是否为空,0—空,1—非空
if (ch[x-1][y-1] == ' ')
{
ch[x - 1][y - 1] = '*';
break;
}
}
}首先判断所输入数字是否符合要求
其次判断所输入位置是否为空,若为空则输入玩家表示元素—“*”
电脑输入
//电脑输入 - #
void Computergame(char ch[Row][Line])
{
printf("电脑下棋:");
while (1)
{
int x = rand() % Row;
int y = rand() % Line;
if (ch[x][y] == ' ')
{
ch[x][y] = '#';
printf("%d %d\n", x + 1, y + 1);
break;
}
}
}使用rand函数获取随机数,判断随机生成位置是否为空,若为空输入电脑表示符,并在输出显示上输出位置坐标,方便观察
判断胜负
//判断游戏胜负
int Judgegame(char ch[Row][Line])
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
if (ch[i][1] == ch[i][2] && ch[i][2] == ch[i][0])
{
if (ch[i][1] == '*')
{
printf("玩家胜利!\n");
return 1;
}
if(ch[i][1] == '#')
{
printf("电脑胜利!\n");
return 1;
}
}
if (ch[0][i] == ch[1][i] && ch[1][i] == ch[2][i])
{
if (ch[1][i] == '*')
{
printf("玩家胜利!\n");
return 1;
}
if (ch[1][i] == '#')
{
printf("电脑胜利!\n");
return 1;
}
}
}
if (ch[0][0] == ch[1][1] && ch[1][1] == ch[2][2])
{
if (ch[1][1] == '*')
{
printf("玩家胜利!\n");
return 1;
}
if (ch[1][1] == '#')
{
printf("电脑胜利!\n");
return 1;
}
}
if (ch[0][2] == ch[1][1] && ch[1][1] == ch[2][0])
{
if (ch[1][1] == '*')
{
printf("玩家胜利!\n");
return 1;
}
if (ch[1][1] == '#')
{
printf("电脑胜利!\n");
return 1;
}
}
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
if (ch[i][j] == ' ')
{
count++;
}
}
}
if (count == 0)
{
printf("游戏平局\n");
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}若由三个非空的相同字符可以连在一起,输出对应的胜利对象。并返回1,使text.c中的循环退出,进入下一场游戏
text.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "game.h"
void menu()
{
printf("******************************\n");
printf("****** 1.开始游戏 *******\n");
printf("****** 0.退出游戏 *******\n");
printf("******************************\n");
}
void game()
{
char ch[Row][Line] = { 0 };
SzqInit(ch);//初始化
Szqprint(ch);//打印
while (1)
{
Playergame(ch);//玩家输入 - *
//判断游戏胜负
if (Judgegame(ch))
{
Szqprint(ch);//打印
break;
}
Computergame(ch);//电脑输入 - #
Szqprint(ch);//打印
if (Judgegame(ch))
break;
}
}
int main()
{
int input = 0;
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
do
{
menu();//菜单
printf("请选择:");
scanf("%d", &input);
switch (input)
{
case 1://游戏开始
game();
break;
case 0://游戏退出
printf("游戏退出!\n");
break;
default:
printf("输入错误,请重新输入\n");
break;
}
system("pause");
system("cls");
} while (input);
return 0;
}在此文件中调用相对应的函数完成三子棋游戏
优化代码
上述三子棋无法在玩家有利或者电脑有利的时候做出正确的反映,电脑选择位置太过随机,可以优化选择电脑输出位置
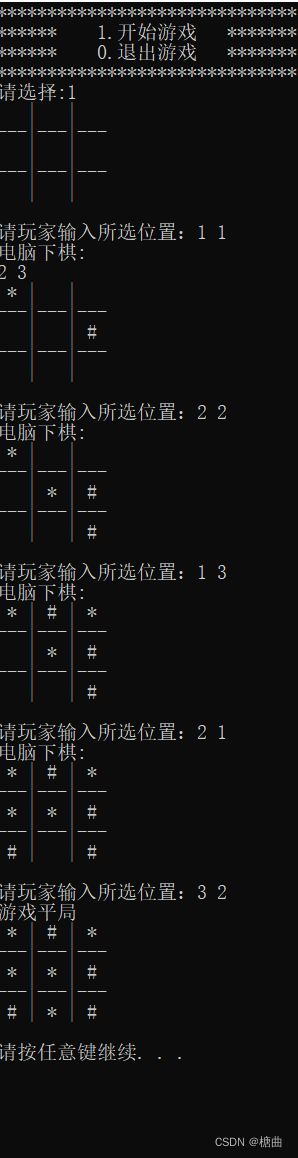
展示
以下为优化代码:
game.c
电脑输入
//电脑输入 - #
void Computergame(char ch[Row][Line])
{
int a = 0;
printf("电脑下棋:\n");
while (1)
{
int x = rand() % Row;
int y = rand() % Line;
if (ch[x][y] == ' ' && a == 2)
{
ch[x][y] = '#';
printf("%d %d\n", x + 1, y + 1);
break;
}
//如果已经选择判断,则重复循环随机查找坐标
if (a == 2)
{
continue;
}
//判断输入
//2—玩家和电脑都没有两个连续的
//1—玩家或电脑有两个连续的,并且以输入坐标
a = Choosegame(ch);
//输入成功继续,否则再次输入
if (a == 1)
break;
else
continue;
}
}电脑判断输入
//判断输入
int Choosegame(char ch[Row][Line])
{
for (int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for (int j=0;j<3;j++)
{
//行 相邻两个位置
if (j != 2)
{
if (ch[i][j] == ch[i][j + 1] && ch[i][j] != ' ')
{
if (j == 0)
{
if (ch[i][j + 2] == ' ')
{
ch[i][j + 2] = '#';
return 1;
}
}
if (j == 1)
{
if (ch[i][j - 1] == ' ')
{
ch[i][j - 1] = '#';
return 1;
}
}
}
}
//行 1和3相同
if (j == 0)
{
if (ch[i][j] == ch[i][j+2] && ch[i][j]!=' ')
{
if (ch[i][j + 1] == ' ')
{
ch[i][j + 1] = '#';
return 1;
}
}
}
//列 相邻两个位置
if (i != 2)
{
if (ch[i][j] == ch[i + 1][j] && ch[i][j] != ' ')
{
if (i == 0)
{
if (ch[i + 2][j] == ' ')
{
ch[i + 2][j] = '#';
return 1;
}
}
if (i == 1)
{
if (ch[i -1 ][j] == ' ')
{
ch[i - 1][j] = '#';
return 1;
}
}
}
}
//列 1 3
if (i == 0)
{
if (ch[i][j] == ch[i+2][j] && ch[i][j] != ' ')
{
if (ch[i + 1][j] == ' ')
{
ch[i + 1][j] = '#';
return 1;
}
}
}
// \对角
if (i!=2 && i==j)
{
if (ch[i][j] == ch[i + 1][i + 1] && ch[i][j] != ' ')
{
if (i==0)
{
if (ch[i + 2][j + 2] == ' ')
{
ch[i + 2][j + 2] = '#';
return 1;
}
}
if (i == 1)
{
if (ch[i - 1][j - 1] == ' ')
{
ch[i - 1][j - 1] = '#';
return 1;
}
}
}
if (ch[0][0] == ch[2][2] && ch[0][0] != ' ')
{
if (ch[1][1] == ' ')
{
ch[1][1] = '#';
return 1;
}
}
}
// /对角线
if (i != 2 && i + j == 2)
{
if (ch[0][2] == ch[1][1] && ch[0][2] != ' ')
{
if (ch[2][0] == ' ')
{
ch[2][0] = '#';
return 1;
}
}
if (ch[1][1] == ch[2][0] && ch[1][1] != ' ')
{
if (ch[0][2] == ' ')
{
ch[0][2] = '#';
return 1;
}
}
if (ch[0][2] == ch[2][0] && ch[0][2] != ' ')
{
if (ch[1][1] == ' ')
{
ch[1][1] = '#';
return 1;
}
}
}
}
}
return 2;
}通过判断各位置是否有相同的符号做出动作,使游戏更加灵活
总结
- 使用循环完成的c语言小游戏
- 可以尝试扩大棋盘
- 该代码无法完全做到智能输出,在电脑和玩家都有优势时,电脑根据代码顺序判断,无法做到正确的选择,可以在循环到一个位置时两次使用这个位置,一次查看电脑是否有优势,一次查看玩家是否有优势,之后再++进入下一次循环