springboot- redis常见数据存取
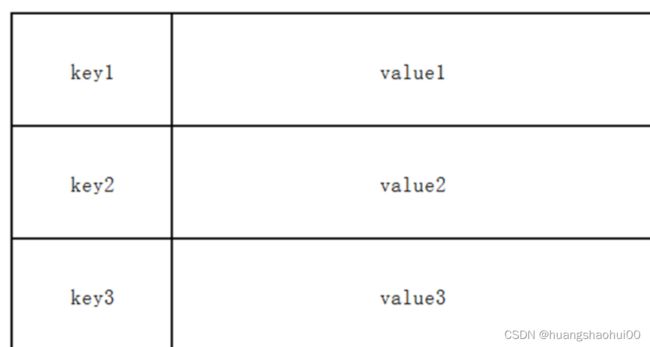
1 字符串类型 string
基本操作
- set:存数据
SET key value
set name zhangsan
- get:取数据
GET key
get name
- del:删除数据
DEL key [key ...]
del name
- mset:一次性存储多个key
MSET key value [key value ...]
mset a zhangsan b lisi c wangwu
- mget:一次性取多个key
MGET key [key ...]
mget a b c
- strlen:获取字符个数
STRLEN key
strlen a
- append:追加字符串(如果没有则新增)
APPEND key value
append a 88
string扩展操作
- 自增
incr key # 自增1
set num 10
incr num
incrby key increment # 自增increment
incrby key 20
incrbyfloat key increment # 自增小数
set num2 0.5
incrbyfloat key 0.5 # 只能对小数自增小数
- 自减
decr key
decr num
decrby key incremnet
decr num 10
string类型的注意事项
- 数据操作不成功的反馈与数据正常操作之间的差异
- 1): 表示运行结果是否成功
- (integer) 0 -> false 失败
- (integer) 1-> true 成功
- 2):表示运行结果值
- (integer) 3 -> 3 3个
- (integer) 1 -> 1 1个
- 1): 表示运行结果是否成功
- 数据未获取到
- (nil)等同于null
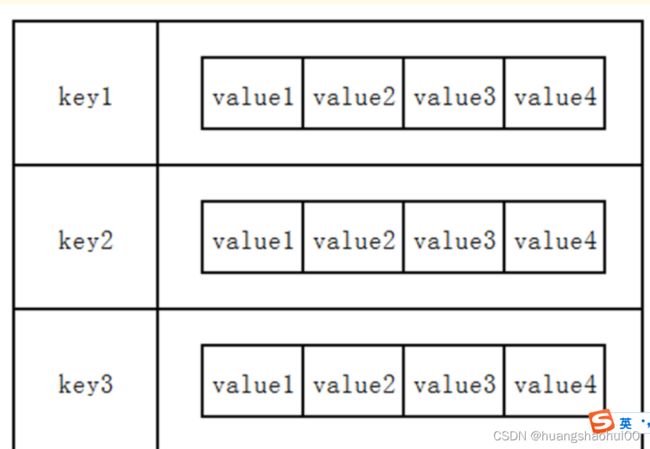
2 列表类型 list
在Redis中,List类型是按照插入顺序排序的字符串链表。和数据结构中的普通链表一样,我们可以在其头部(left)和尾部(right)添加新的元素。在插入时,如果该键并不存在,Redis将为该键创建一个新的链表。与此相反,如果链表中所有的元素均被移除,那么该键也将会被从数据库中删除。Redis中的list类型采用的是双向链表。
redis存储结构如下:
基本操作
- 添加/修改数据
LPUSH key value [value ...] # 添加到队列左侧
RPUSH key value [value ...] # 添加到队列右侧
lpush fruits apple pear
rpush fruits banana tomato
- 获取数据
LRANGE key start stop # 从左边开始读取数据,从start索引查询到stop索引
lrange fruits 0 3 # 从0开始查询到3索引
lrange fruits 0 -2 # 从0开始查询到-2索引
lrange fruits 0 -1 # 从0开始查询到-1索引(倒数第二),通常用此命令来查询全部数据
LINDEX key index # 根据指定的索引查询,从0开始
lindex fruits 3
- 获取并移除数据
LPOP key # 从队列左边移除一个元素并返回
lpop fruits
RPOP key # 从队列右边移除一个元素并返回
rpop fruits
list扩展操作
- 规定时间内获取并移除数据
BLPOP key [key ...] timeout # 在timeout时间内取出key中的值
BRPOP key [key ...] timeout
blpop fruits 5 # 5秒内取出fruits中的值并删除,如果没取到则一直处于等待状态
- 规定时间内移除list左边的一个元素到另一个list中,并将此元素返回
BRPOPLPUSH source destination timeout
brpoplpush fruits temp 5
- 移除指定数据
LREM key count value # 从list左边开始移除元素
# count:移除多少个 value:移除什么元素
rpush data a b c d e a b c k o;
lrem data 2 a # 移除两个a
3 集合类型 set
在Redis中,我们可以将Set类型看作为没有排序的字符集合,和List类型一样,我们也可以在该类型的数据值上执行添加、删除或判断某一元素是否存在等操作。需要说明的是,这些操作的时间是常量时间。Set可包含的最大元素数是4294967295。
和List类型不同的是,Set集合中不允许出现重复的元素。和List类型相比,Set类 型在功能上还存在着一个非常重要的特性,即在服务器端完成多个Sets之间的聚合计算操作,如unions、intersections和differences。由于这些操作均在服务端完成, 因此效率极高,而且也节省了大量的网络IO开销
基本操作
- 添加数据
SADD key member [member ...]
sadd nums 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
- 读取全部数据
SMEMBERS key
smembers nums
- 删除数据
SREM key member [member ...]
srem nums 1 3 5 7
- 获取集合中元素的个数
SCARD key
scard nums
- 判断集合中是否包含指定的数据
SISMEMBER key member
sismember nums 1
扩展操作
- 在指定的key中随机获取几个个值
SRANDMEMBER key [count]
srandmember nums 3
- 在指定的key中随机获取几个值,并将这几个值移除
SPOP key [count]
spop nums 3
- 获取两个集合的交、并、差集
sinter key [key ...] # 交集
sunion key [key ...] # 并集
sdiff key [key ...] # 差集
4 有序集合类型sortedset
Sorted-Sets和Sets类型极为相似,它们都是字符串的集合,都不允许重复的成员出现,在一个Set中。它们之间的主要差别是Sorted-Sets中的每一个成员都会有一个分数(score)与之关联,Redis正是通过分数来为集合中的成员进行从小到大的排序。然而需要额外指出的是,尽管Sorted-Sets中的成员必须是唯一的,但是分数(score) 却是可以重复的。
在Sorted-Set中添加、删除或更新一个成员都是非常快速的操作,其时间复杂度为集合中成员数量的对数。由于Sorted-Sets中的成员在集合中的位置是有序的,因此,即便是访问位于集合中部的成员也仍然是非常高效的。事实上,Redis所具有的这一特征在很多其它类型的数据库中是很难实现的,换句话说,在该点上要想达到和Redis 同样的高效,在其它数据库中进行建模是非常困难的。
基本操作
- 添加数据
zadd key score1 member1 [score2 member2]
- 实例:
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd students 90 zs
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd students 80 ls 85 ww 60 zl 70 tq
(integer) 4
- 读取数据
zrange key start stop [WITHSCORES]
zrevrange key start stop [WITHSCORES]
- withscores:是否显示分值
- zrevrange:将查询结果反转
示例:
127.0.0.1:6379> zrange students 0 -1
1) "zl"
2) "tq"
3) "ls"
4) "ww"
5) "zs"
127.0.0.1:6379> zrevrange students 0 -1 withscores
1) "zs"
2) "90"
3) "ww"
4) "85"
5) "ls"
6) "80"
7) "tq"
8) "70"
9) "zl"
10) "60"
- 删除数据
zrem key member [member ...]
- 实例:
127.0.0.1:6379> zrem students zs zl
(integer) 2
127.0.0.1:6379> zrevrange students 0 -1 withscores
1) "ww"
2) "85"
3) "ls"
4) "80"
5) "tq"
6) "70"
- 根据分值筛选
zrangebyscore key min max [WITHSCORES] [LIMIT offset count]
zrevrangebyscore key max min [WITHSCORES] [LIMIT offset count]
- min:最小分值(包含)
- max:最大分值(包含)
- limit:限定查询结果(分页查询)
- offset:起始索引(从0开始)
- count:查询几条数据
- zrevrangebyscore:根据分值反转查询
示例:
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd students 90 zs 80 ls 95 ww 60 zl 75 tq
(integer) 5
127.0.0.1:6379> zrange students 0 -1 withscores
1) "zl"
2) "60"
3) "tq"
4) "75"
5) "ls"
6) "80"
7) "zs"
8) "90"
9) "ww"
10) "95"
127.0.0.1:6379> zrangebyscore students 60 95 withscores
1) "zl"
2) "60"
3) "tq"
4) "75"
5) "ls"
6) "80"
7) "zs"
8) "90"
9) "ww"
10) "95"
- 查询集合总数量
zcard key
zcard students
- 根据分值范围查询集合总数量
zcount key min max
zcount student 60 80
- 取多个集合中的交集、并集
zinterstore destination numkeys key [key ...]
zunionstore destination numkeys key [key ...]
示例:
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd num1 1 a 4 b 7 c
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd num2 2 a 5 b 8 c
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd num3 3 a 6 b 9 c
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> zinterstore temp1 3 num1 num2 num3
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> zrange temp1 0 -1 withscores
1) "a"
2) "6"
3) "b"
4) "15"
5) "c"
6) "24"
zinterstore首先取并集,然后把分数累加。
总结:不允许重复元素,且元素有顺序。每个元素都会关联一个double类型的分数。redis正是通过分数来为集合中的成员进行从小到大的排序。
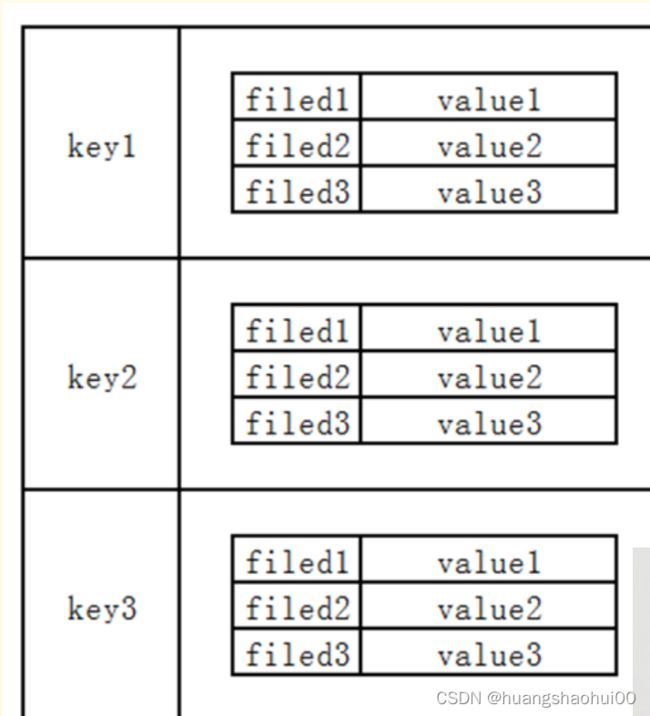
5 哈希类型 hash
hash类型的存储结构如下:
hash类型的数据结构,底层采用hash表存储。
基本操作
- hset:添加/修改数据
HSET key field value
hset user username zs
hset user password admin
- hget:取数据
HGET key field
hget user username
- hdel:删除数据
HDEL key field [field ...]
hdel user password
- hmset:一次性添加/修改多个字段
HMSET key field value [field value ...]
hmset user username zs password admin age 20
- hmget
HMGET key field [field ...]
hmget user username password age
- 获取指定key的field的数量
HLEN key
hlen user
- hexists:判断指定的key中是否包含有指定的field(返回1[有]或0[没有])
HEXISTS key field
hexists user username
hexists user aa
- hgetall:获取指定key中所有的field以及value值
HGETALL key
hgetall user
扩展操作
- hkeys:获取key中所有的field
HKEYS key
hkeys key
- hvals:获取key中所有的value
HVALS key
hvals key
- 给指定key中的指定field增加指定范围的值
HINCRBY key field increment
HINCRBYFLOAT key field increment
hincrby user age 2
hincrbyfloat user age 0.5
- hsetnx:如果指定key中有对应的field则返回0(false),如果没有则存对应的值进去
HSETNX key field value
hsetnx user flag 1
6 通用命令
key基本操作
- 删除key
del key
- 判断key是否存在
exists key
- 获取key的类型
type key
控制key的时效性
setex key seconds value # 秒
setex name 5 zhangsan
psetex key milliseconds value # 毫秒
psetex name 5000 zhangsan
- 为指定key设置有效期
expire key seconds
pexpire key milliseconds
expireat key timestamp
pexpireat key milliseconds-timestamp
- 获取key的有效时间
ttl key # 返回key的有效时间,单位秒
pttl key # 返回key的有效时间,单位毫秒
如果key没有设置有效期(永久存在),返回-1,如果key不存在返回-2,如果key存在返回key的有效时间
- 切换key从时效性转换为永久性
persist key
key的查询操作
- 查询key
keys pattern
查询匹配规则:
*:匹配任意数量的任意符号?:匹配任意一个符号[]匹配一个指定符号
keys * 查询所有
keys java* 查询所有以java开头
keys *java 查询所有以java结尾
keys ??java 查询所有前面两个字符任意,后面以java结尾
keys user:? 查询所有以user:开头,最后一个字符任意
keys j[av]a:1 查询所有以j开头,以a:1结尾,中间包含一个字母,a或v
key的其他操作
- key改名
rename key newkey
renamenx key newkey
rename:如果改名的时候newkey已经存在了,则会把key中的值覆盖newkey中的值。
renamenx:如果newkey已经存在,则不允许修改名称
- 对所有key排序:只能对集合进行排序list、sort、sorted-set
SORT key [BY pattern] [LIMIT offset count] [ASC|DESC] [ALPHA] [STORE destination]
- 关于key的其他操作在帮助文档中的@generic组中可以查询到
help @generic
数据库通用操作
在一个redis中会有16个数据库,分别为db0、db1、db2…
- 切换数据库
select num
select 0 # 切换到0数据库
select 1 # 切换到1数据库
- 数据清除
dbsize # 查看当前数据库共有多少个key
flushdb # 清除当前数据库的所有数据
flushall # 清除所有数据库的所有数据
SpringBoot中使用Redis
基本逻辑
- 先读缓存,缓存有则直接返回。
- 缓存没有,则读数据库。
- 读取后,缓存数据,且设置数据的超时时间。
1 增加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-redisartifactId>
<version>1.3.3.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
2 redis配置文件
application.properties增加配置
#
#redis 单机配置
spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1
spring.redis.port=6379
spring.redis.password=
#
spring.redis.jedis.pool.min-idle=100
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle=300
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active=500
新增RedisConfig
package com.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurerSupport;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import java.time.Duration;
/**
* @auth admin
* @date
* @Description redis的操作组件自定义注入配置
*/
@Configuration
//@EnableCaching:开启缓存(注解生效的)
@EnableCaching
public class RedisConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
//注入connectionFactory
@Autowired
private RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory;
@Bean
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate() {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
//设置序列化策略
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
return redisTemplate;
}
@Bean
public StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate() {
StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate = new StringRedisTemplate();
stringRedisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
return stringRedisTemplate;
}
//缓存cache管理器
@Override
public CacheManager cacheManager() {
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofSeconds(120)).disableCachingNullValues();
return RedisCacheManager.builder(connectionFactory).cacheDefaults(config)
.transactionAware().build();
}
}
3 测试
controller
// 通过id查询用户
@GetMapping("getById")
@ResponseBody
public User getById(Integer id) {
return userService.getById(id);
}
//通过id修改用户
@GetMapping("update")
@ResponseBody
public void update(User user) {
userService.update(user);
}
UserService
/**
* @auth admin
* @date
* @Description
*/
@Service
public class UserService {
@Resource
private UserDao userDao;
//从spring容器中获取RedisTemplate实例
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
//通过id查询
public User getById(Integer id) {
User user = null;
ValueOperations valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
String key = "SpringBootRedis:String:" + id;
if (id != null) {
//判断key是否存在,如果存在则从redis中取出数据,如果不存在直接从数据库中查
if (redisTemplate.hasKey(key)) {
Object obj = valueOperations.get(key);
if (obj != null) {
user = (User) obj;
}
} else {
//从数据库中查询,然后把结果再放入redis中
user = userDao.getById(id);
if (user != null) {
valueOperations.set(key, user);
//设置过期时间
redisTemplate.expire(key,60*30,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
}
return user;
}
//修改
public void update(User user) {
int result = userDao.update(user);
if (result > 0) {
String key = "SpringBootRedis:String:" + user.getId();
ValueOperations valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
//修改实体数据库的同时需要修改redis中的数据
//方式1:直接删除key
//redisTemplate.delete(key);
//方式2:更新redis中的数据
valueOperations.set(key, user);
}
}
}
测试流程:
第一次调用getById(),打一个断点进行调试,发现直接查询的是数据库
第二次调用getById(),发现直接查询的是redis,不会再从数据库中查询,这样可以减轻数据库的压力
当对同一条数据修改时,需要同步更新redis中的数据。
缓存常见问题
缓存最常见的3个问题:
-
缓存穿透
-
缓存雪崩
-
缓存击穿
缓存穿透是指查询一个不存在的数据,由于缓存无法命中,将去查询数据库,但是数据库也无此记录,并且出于容错考虑,我们没有将这次查询的null写入缓存,这将导致这个不存在的数据每次请求都要到存储层去查询,失去了缓存的意义。在流量大时,可能DB就挂掉了,要是有人利用不存在的key频繁攻击我们的应用,这就是漏洞。
解决:空结果也进行缓存,但它的过期时间会很短,最长不超过五分钟。
缓存雪崩是指在我们设置缓存时采用了相同的过期时间,导致缓存在某一时刻同时失效,请求全部转发到DB,DB瞬时压力过重雪崩。
解决:原有的失效时间基础上增加一个随机值,比如1-5分钟随机,这样每一个缓存的过期时间的重复率就会降低,就很难引发集体失效的事件。
缓存击穿是指对于一些设置了过期时间的key,如果这些key可能会在某些时间点被超高并发地访问,是一种非常“热点”的数据。这个时候,需要考虑一个问题:如果这个key在大量请求同时进来之前正好失效,那么所有对这个key的数据查询都落到db,我们称为缓存击穿。
与缓存雪崩的区别:
- 击穿是一个热点key失效
- 雪崩是很多key集体失效
6 springboot -redis 五种数据存储
bean注入
/*容器中 存在 对应的bean,注入即可使用*/
@Autowired
// @Qualifier("stringRedisTemplate")
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
//StringRedisTemplate 和 redisTemplate 的区别
继承关系 ,数据不通用
StringRedisTemplate默认采用的是String的序列化策略,保存的key和value都是采用此策略序列化保存的。 显示原文
RedisTemplate默认采用的是JDK的序列化策略,保存的key和value都是采用此策略序列化保存的。
RedisTemplate默认使用的序列类在在操作数据的时候,比如说存入数据会将数据先序列化成字节数组然后在存入Redis数据库,这个时候打开Redis查看的时候,你会看到你的数据不是以可读的形式展现的,而是以字节数组显示,显示乱码
用 redisTemplate 存取都加上下面两条代码
/*可以 改变 序列化策略*/
/* 设置 key 的序列化策略 为 字符串*/
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(RedisSerializer.string());
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(RedisSerializer.json());
/*springmvc 容器 中会自动创建bean ,创建Obj对象*/
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
1 、String类型
1 、spring存数据
/*opsForValue 键值对操作器*/
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name","张三");
/*只能存 string数据,将java对象转换为 json字符串 储存*/
Category category = new Category();
category.setName("二次元");
category.setId(1);
/*writeValueAsString 將 java对象 序列化为 json字符串*/
String json= objectMapper.writeValueAsString(category);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("user",json);
2、取数据
String name = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name");
/*获取 json数据 进行 发序列化*/
String userJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("user");
Category category = objectMapper.readValue(userJson, Category.class);
System.out.println(category.toString());
spring类型的存取为set 和get
2 List集合
1、List 存数据
/*集合对象*/
List<Category> categories = new ArrayList<>();
categories.add(new Category(1,"赛车"));
categories.add(new Category(2,"恐怖"));
categories.add(new Category(3,"爱情"));
String categoriesJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(categories);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("categories",categoriesJson);
/*存*/
/*lsit*/
stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().rightPush("stus","张三");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().rightPush("stus","李四");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().rightPush("stus","王五");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().rightPush("stus","赵六");
/*list*/
List<String> stus = stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().range("stus", 0, -1);
stus.forEach(x -> System.out.println(x));
2 、取数据
/*list 集合 得用 TypeReference*/
String categoriesJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("categories");
List<Category> categories
= objectMapper.readValue(categoriesJson, new TypeReference<List<Category>>(){});
categories.forEach(x-> System.out.println(x.toString()));
3 Map
1 map存数据
Map<String,Category> categoryMap = new HashMap<>();
categoryMap.put("1",new Category(1,"赛车"));
categoryMap.put("2",new Category(2,"恐怖"));
categoryMap.put("3",new Category(3,"爱情"));
String categoryMapJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(categoryMap);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("categoryMapJson",categoryMapJson);
2 、取数据
String categoryMapJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("categoryMapJson");
Map<String,Category> categoryMap
= objectMapper.readValue(categoryMapJson, new TypeReference<Map<String,Category>>() {
});
System.out.println(categoryMap);
System.out.println(categoryMap.get("2"));
4 set
/*set*/ 存
stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().add("category","动作");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().add("category","战争");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().add("category","悬疑");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().add("category","警匪");
/*set*/ 取
Set category = stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().members("category");
category.forEach(x -> System.out.println(x.toString()));
5 hash
/*hash*/
stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().put("user","name","帅哥");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().put("user","age","18");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().put("user","sex","男");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().put("user","hobby","rap");
/*hash*/
String name = (String) stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().get("user", "name");
System.out.println("name:"+name);
/*获取所有的键*/
Set6 zset
/*zset*/
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().add("score","zhangsan",80);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().add("score","lisi",60);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().add("score","wangwu",90);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().add("score","zhaoliu",70);
/*zset*/
Set score = stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().range("score", 0, -1);
score.forEach(x -> System.out.println(x.toString()));
Set> score1 =
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().rangeWithScores("score", 0, -1);
score1.forEach(x->{
System.out.println(x.getValue());
System.out.println(x.getScore());
});
/*从大到小获取*/
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().reverseRangeByScoreWithScores("score", 0, -1);
7 设置数据存储时间
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name","李四");
stringRedisTemplate.expire("name",5,TimeUnit.MINUTES);
/*键绑定器*/
BoundValueOperations operations = stringRedisTemplate.boundValueOps("namme");
operations.set("王五");
Boolean expire = operations.expire(1, TimeUnit.HOURS);
Long name3 = stringRedisTemplate.getExpire("name");//获取过期时间
Boolean name2 = stringRedisTemplate.persist("name");//取消过期
Boolean name1 = stringRedisTemplate.delete("name");
Boolean name = stringRedisTemplate.hasKey("name");//判断redis中是否存在改键
8 完整代码
package com.powernode.controller;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.type.TypeReference;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectReader;
import com.powernode.model.Category;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.BoundValueOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ZSetOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@RestController
public class RedisController {
/*容器中 存在 对应的bean,注入即可使用*/
@Autowired
// @Qualifier("stringRedisTemplate")
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
/*springmvc 容器 中会自动创建bean*/
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
/*存*/
@RequestMapping("/strSet")
public String setStrRedisTemplate() throws JsonProcessingException {
/*opsForValue 键值对操作器*/
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name","张三");
/*只能存 string数据,将java对象转换为 json字符串 储存*/
Category category = new Category();
category.setName("二次元");
category.setId(1);
/*writeValueAsString 將 java对象 序列化为 json字符串*/
String json= objectMapper.writeValueAsString(category);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("user",json);
/*集合对象*/
List<Category> categories = new ArrayList<>();
categories.add(new Category(1,"赛车"));
categories.add(new Category(2,"恐怖"));
categories.add(new Category(3,"爱情"));
String categoriesJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(categories);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("categories",categoriesJson);
Map<String,Category> categoryMap = new HashMap<>();
categoryMap.put("1",new Category(1,"赛车"));
categoryMap.put("2",new Category(2,"恐怖"));
categoryMap.put("3",new Category(3,"爱情"));
String categoryMapJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(categoryMap);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("categoryMapJson",categoryMapJson);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name","李四");
stringRedisTemplate.expire("name",5,TimeUnit.MINUTES);
/*键绑定器*/
BoundValueOperations<String, String> operations = stringRedisTemplate.boundValueOps("namme");
operations.set("王五");
Boolean expire = operations.expire(1, TimeUnit.HOURS);
Long name3 = stringRedisTemplate.getExpire("name");//获取过期时间
Boolean name2 = stringRedisTemplate.persist("name");//取消过期
Boolean name1 = stringRedisTemplate.delete("name");
Boolean name = stringRedisTemplate.hasKey("name");//判断redis中是否存在改键
return "success";
}
/*取*/
@RequestMapping("/strGet")
public String getStrRedisTemplate() throws JsonProcessingException {
String name = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name");
System.out.println(name);
/*获取 json数据 进行 发序列化*/
String userJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("user");
Category category = objectMapper.readValue(userJson, Category.class);
System.out.println(category.toString());
/*list 集合 得用 TypeReference*/
String categoriesJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("categories");
List<Category> categories
= objectMapper.readValue(categoriesJson, new TypeReference<List<Category>>(){});
categories.forEach(x-> System.out.println(x.toString()));
String categoryMapJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("categoryMapJson");
Map<String,Category> categoryMap
= objectMapper.readValue(categoryMapJson, new TypeReference<Map<String,Category>>() {
});
System.out.println(categoryMap);
System.out.println(categoryMap.get("2"));
return "success";
}
/*存*/
@RequestMapping("/set")
public String setRedisTemplate(){
/*可以 改变 序列化策略*/
/* 设置 key 的序列化策略 为 字符串*/
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(RedisSerializer.string());
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(RedisSerializer.json());
/*redisTemplate 默认 对 key 和value 进行二进制序列化*/
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("hobby","唱歌");
Category category = new Category(1,"武打");
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("1",category);
List<Category> categories = new ArrayList<>();
categories.add(new Category(1,"赛车"));
categories.add(new Category(2,"恐怖"));
categories.add(new Category(3,"爱情"));
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("categories",categories);
return "success";
}
/*取*/
@RequestMapping("/get")
public String getRedisTemplate(){
/* 存的时候 是什么策略 取的 也得是对应的策略*/
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(RedisSerializer.string());
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(RedisSerializer.json());
/* 默认 将 结果 进行二进制反序列化*/
String hobby = (String) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("hobby");
System.out.println(hobby);
Category category = (Category) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("1");
System.out.println(category);
List<Category> categories = (List<Category>) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("categories");
categories.forEach(x-> System.out.println(x.toString()));
return "success";
}
@RequestMapping("/other")
public String otherType(){
/*存*/
/*lsit*/
stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().rightPush("stus","张三");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().rightPush("stus","李四");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().rightPush("stus","王五");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().rightPush("stus","赵六");
/*set*/
stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().add("category","动作");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().add("category","战争");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().add("category","悬疑");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().add("category","警匪");
/*hash*/
stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().put("user","name","帅哥");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().put("user","age","18");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().put("user","sex","男");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().put("user","hobby","rap");
/*zset*/
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().add("score","zhangsan",80);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().add("score","lisi",60);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().add("score","wangwu",90);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().add("score","zhaoliu",70);
/*取*/
/*list*/
List<String> stus = stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().range("stus", 0, -1);
stus.forEach(x -> System.out.println(x));
/*set*/
Set<String> category = stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().members("category");
category.forEach(x -> System.out.println(x.toString()));
/*hash*/
String name = (String) stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().get("user", "name");
System.out.println("name:"+name);
/*获取所有的键*/
Set<Object> userKeys = stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().keys("user");
userKeys.forEach(x -> System.out.println(x.toString()));
/*获取所有的值*/
List<Object> userValues = stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().values("user");
userValues.forEach(x -> System.out.println(x.toString()));
/*获取所有 键值对*/
Map<Object, Object> userMap = stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().entries("user");
/*zset*/
Set<String> score = stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().range("score", 0, -1);
score.forEach(x -> System.out.println(x.toString()));
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> score1 =
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().rangeWithScores("score", 0, -1);
score1.forEach(x->{
System.out.println(x.getValue());
System.out.println(x.getScore());
});
/*从大到小获取*/
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().reverseRangeByScoreWithScores("score", 0, -1);
return "success";
}
}
实体类
package com.powernode.model;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Category implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Category{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
public Category(Integer id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public Category() {
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
/*hash*/
String name = (String) stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().get("user", "name");
System.out.println("name:"+name);
/*获取所有的键*/
Set<Object> userKeys = stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().keys("user");
userKeys.forEach(x -> System.out.println(x.toString()));
/*获取所有的值*/
List<Object> userValues = stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().values("user");
userValues.forEach(x -> System.out.println(x.toString()));
/*获取所有 键值对*/
Map<Object, Object> userMap = stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().entries("user");
/*zset*/
Set<String> score = stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().range("score", 0, -1);
score.forEach(x -> System.out.println(x.toString()));
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> score1 =
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().rangeWithScores("score", 0, -1);
score1.forEach(x->{
System.out.println(x.getValue());
System.out.println(x.getScore());
});
/*从大到小获取*/
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().reverseRangeByScoreWithScores("score", 0, -1);
return "success";
}
}
实体类
package com.powernode.model;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Category implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Category{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
public Category(Integer id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public Category() {
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}