【Spring】一文带你吃透基于注解的DI技术
![]()
个人主页: 几分醉意的CSDN博客_传送门
本文目录
- 基于注解的DI
-
- ✨概念
- ✨@Component注解创建对象
- ✨声明组件扫描器
- ✨创建对象的四个注解
- ✨扫描多个包的三种方式
- ✨@Value简单类型属性赋值
- ✨@Value使用外部属性配置文件
- ✨@Autowired引用类型属性赋值
-
- byType自动注入
- byName自动注入
- required属性
- ✨@Resource引用类型属性赋值
- 投票传送门(欢迎伙伴们投票)
基于注解的DI
✨概念
基于注解的DI:使用spring提供的注解,完成java对象创建,属性赋值。
注解使用的核心步骤:
1.在源代码加入注解,例如@Component。
2.在spring的配置文件,加入组件扫描器的标签。
✨@Component注解创建对象
@Component: 表示创建对象,对象放到容器中。 作用是
-
属性:value ,表示对象名称,也就是bean的id属性值 -
位置:在类的上面,表示创建此类的对象。
@Component(value = "myStudent") 等同于
< bean id="myStudent" class="com.ba01.Student" />
//使用value 指定对象的名称
//@Component(value = "myStudent")
//省略value
@Component("myStudent")
//没有提供自定义对象名称, 使用框架的默认对象名称:类名首字母小写
//@Component
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
System.out.println("Student无参数构造方法");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
✨声明组件扫描器
声明组件扫描器:使用注解必须加入这个语句。
<context:component-scan base-package="注解所在的包名"/>
component-scan:翻译过来是组件扫描器,组件是java对象。
属性: base-package 注解在你的项目中的包名。
框架会扫描这个包和子包中的所有类,找类中的所有注解。
遇到注解后,按照注解表示的功能,去创建对象, 给属性赋值。
认识了组件扫描器,然后我们来到Spring配置文件来使用它
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.b01"/>
beans>
注意:最上面的都是一些需要的约束文件,当你把组件扫描器写上去后,也会自动的添加对应的约束文件。
那么接下来我们创建一个测试类,进行测试。
public class MyTest {
@Test
public void test01(){
String config="applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
//后面的myStudent是上面@Component注解创建对象时设置的对象名
Student student = (Student) ctx.getBean("myStudent");
System.out.println("student=="+student);
}
}
✨创建对象的四个注解
经过刚刚的学习,我们已经了解了@Component注解创建对象的使用方法,那么还有其它的相关注解吗?当然有,下面我们将介绍的是和@Component功能相同的创建对象的注解。
1. @Repository : 放在dao接口的实现类上面,表示创建dao对象,持久层对象,能访问数据库。
2).@Service : 放在业务层接口的实现类上面, 表示创建业务层对象, 业务层对象有事务的功能。
3.@Controller:放在控制器类的上面,表示创建控制器对象。 属于表示层对象。控制器对象能接受请求,把请求的处理结果显示给用户。
以上四个注解都能创建对象,但是@Repository @Service @Controller有角色说明, 表示对象是分层的。
✨扫描多个包的三种方式
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.b01"/>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.b01"/>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.b02"/>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.b01;com.b02"/>
<context:component-scan base-package="com"/>
beans>
✨@Value简单类型属性赋值
@Value: 简单类型属性赋值
属性:value 简单类型属性值
位置:1.在属性定义的上面 ,无需set方法,推荐使用。2.在set方法的上面。
在属性定义的上面定义
package com.bjpowernode.ba02;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("myStudent")
public class Student {
@Value(value = "李四")
private String name ;
//括号里面的value也可以省略
@Value("20")
private int age;
public Student() {
System.out.println("Student无参数构造方法");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
第二种方式:在set方法的上面
package com.bjpowernode.ba02;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("myStudent")
public class Student {
private String name ;
private int age;
public Student() {
System.out.println("Student无参数构造方法");
}
@Value("22")
public void setAge(int age) {
System.out.println("setAge===="+age);
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
✨@Value使用外部属性配置文件
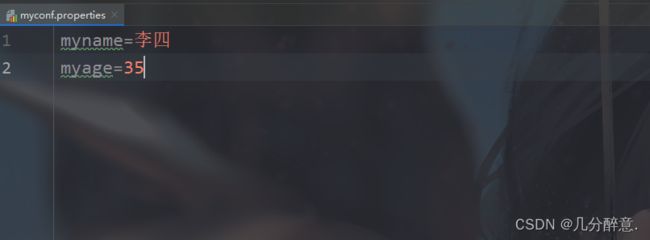
这里我创建了一个名为myconf.properties的配置文件
然后在配置文件输入相应的内容。
然后我们打开spring配置文件,在spring文件中读取使用它
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--声明组件扫描器:使用注解必须加入这个语句
component-scan:翻译过来是组件扫描器,组件是java对象。
属性: base-package 注解在你的项目中的包名。
框架会扫描这个包和子包中的所有类,找类中的所有注解。
遇到注解后,按照注解表示的功能,去创建对象, 给属性赋值。
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.b01"/>
<!--读取外部的属性配置文件
property-placeholder:读取properties这样的文件
-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:/myconf.properties" />
</beans>
注意:location=“classpath:/类路径”
下一步我们开始还有外部文配置件。
语法 :@Value(${"key"})
@Component("myStudent")
public class Student {
//使用外部属性文件中的数据,语法 @Value(${"key"})
@Value("${myname}")
private String name ;
private int age;
public Student() {
System.out.println("Student无参数构造方法");
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
//使用外部属性文件中的数据
@Value("${myage}")
public void setAge(int age) {
System.out.println("setAge===="+age);
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
✨@Autowired引用类型属性赋值
* @Autowired: spring框架提供的,给引用类型赋值的,使用自动注入原理。
* 支持byName,byType。默认是byType.
byType自动注入
-
位置:1)在属性定义的上面,无需set方法,推荐使用 -
2)在set方法的上面
创建一个School类
@Component("mySchool")
public class School {
@Value("安徽大学")
private String name;
@Value("安徽的合肥市")
private String address;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "School{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
在Student类中使用School
@Component("myStudent")
public class Student {
//默认使用byType
@Autowired
private School school;
public Student() {
System.out.println("Student无参数构造方法");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", school=" + school +
'}';
}
}
Spring配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.bjpowernode.ba07"/>
<!--读取外部的属性配置文件
property-placeholder:读取properties这样的文件
-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:/myconf.properties" />
</beans>
测试
public class MyTest3 {
@Test
public void test01(){
String config="applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
Student student = (Student) ctx.getBean("myStudent");
System.out.println("student=="+student);
}
}
byName自动注入
byName自动注入
1.@Autowired:给引用类型赋值。
2.@Qualifer(value=“bean的id”):从容器中找到指定名称的对象,把这个对象赋值给引用类型。
@Component("myStudent")
public class Student {
//byName
@Autowired
@Qualifier("mySchool")
private School school;
public Student() {
System.out.println("Student无参数构造方法");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", school=" + school +
'}';
}
}
测试
public class MyTest3 {
@Test
public void test01(){
String config="applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
Student student = (Student) ctx.getBean("myStudent");
System.out.println("student=="+student);
}
}
required属性
* 属性:required :boolean类型的属性, 默认true
* true:spring在启动的时候,创建容器对象时候,会检查引用类型是否赋值成功。
* 如果赋值失败, 终止程序执行,并报错。
* false:引用类型赋值失败,程序正常执行,不报错。引用类型的值是null
✨@Resource引用类型属性赋值
* 引用类型
* @Resource: 来自jdk中,给引用类型赋值的,支持byName,byType.默认是byName
* spring支持这个注解的使用。
* 位置:1)在属性定义的上面,无需set方法, 推荐使用
* 2)在set方法的上面
*
* 说明,使用jdk1.8带有@Resource注解, 高于jdk1.8没有这个@Resource,
* 需要加入一个依赖。
*
* javax.annotation
* javax.annotation-api
* 1.3.2
*

