python计算机视觉--局部图像描述子:Harris角点检测算法、SIFT算法(尺度不变特征变换)
一:Harris角点检测算法
1.1 什么是角点
特征:
①轮廓之间的交点;
②局部窗口沿任意方向移动,均产生明显变化的点;
③图像局部曲率突变的点;
④对于同一场景,即使视角发生变化,通常具备稳定性质的特征;
⑤该点附近区域的像素点无论在梯度方向上还是其梯度幅值上有着较大变化。
1.2 好的检测算法具备的基本特征
• 检测出图像中“真实的”角点
• 准确的定位性能
• 很高的稳定性
• 具有对噪声的鲁棒性
• 具有较高的计算效率
1.3 角点检测算法的基本原理
模拟人眼对角点的检测:
人眼对角点的识别通常是在一个局部的小区域或小窗口完成的。使用一个固定窗口在图像上进行任意方向上的滑动,比较滑动前与滑动后两种情况,如果滑动前后窗口内区域的灰度发生了较大的变化,那么就认为在窗口内遇到了角点;如果滑动前后窗口内区域的灰度没有发生变化那么窗口内就不存在角点。
1.4 Harris算法数学表达
窗口灰度变化函数E(u,v)
其中窗口函数(权重矩阵)的变化可以是平坦的也可以是高斯的(权重矩阵W通常为高斯滤波器):
对函数泰勒展开以便易于求解
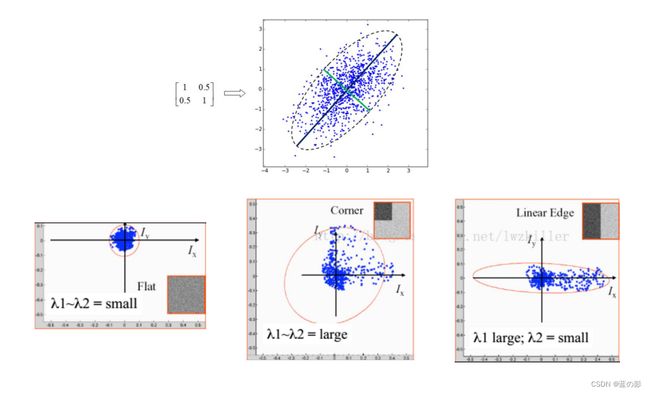
忽略余项之后的表达式为一个二项式函数,然而二项式函数的本质上就是一个椭圆函数,椭圆的扁率和尺寸是由M(x,y)的特征值λ1、λ2决定的,椭圆的方向是由M(x,y)的特征矢量决定的,如下图所示,椭圆方程为:
椭圆函数特征值与图像中的角点、直线(边缘)和平面之间的关系如下图所示。共可分为三种情况:
(1) 图像中的直线:一个特征值大,另一个特征值小,λ1>λ2或λ2>λ1。自相关函数值在某一方向上大,在其他方向上小。
(2)图像中的平面:两个特征值都小,且近似相等;自相关函数数值在各个方向上都小。
(3)图像中的角点:两个特征值都大,且近似相等,自相关函数在所有方向都增大。
通过M的两个特征值λ1和λ2的大小对图像点进行分类:
定义角点检测算法 R = det M - k (trace M)²
det M = λ1λ2 trace M = λ1 + λ2 (k – empirical constant, k = 0.04~0.06)
然后利用角点检测算法进行分类
角点计算流程:
对角点响应函数R进行阈值处理:
R>threshold 提取R的局部极大值
为了消除参数k的影响也可以采用商来计算响应:R = det M/(trace M)²
代码实践
#coding=utf-8
import cv
import cv2
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread('D:/Python/vison2/2.jpg')
cv2.namedWindow('dst', cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray = np.float32(gray)
# 输入图像必须是float32,最后一个参数在0.04到0.05
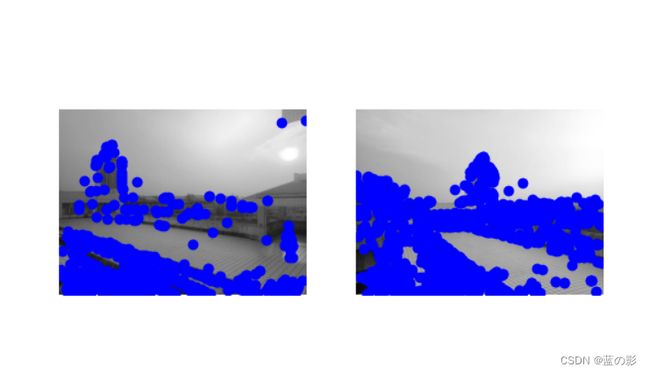
dst = cv2.cornerHarris(gray, 2, 3, 0.04)
dst = cv2.dilate(dst, None)
# Threshold for an optimal value, it may vary depending on the image.
img[dst > 0.01 * dst.max()] = [0, 0, 255]
cv2.imshow('dst', img)
if cv2.waitKey(0) == 27:
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
2.SIFT特征变换
SIFT,即尺度不变特征变换(Scale-invariant feature transform,SIFT),是用于图像处理领域的一种描述方式。这种描述具有尺度不变性,可在图像中检测出关键点,是一种局部特征描述子。
SIFT算法实现特征匹配主要有三个流程,1、提取关键点;2、对关键点附加 详细的信息(局部特征),即描述符;3、通过特征点(附带上特征向量的关键点)的两两比较找出相互匹配的若干对特征点,建立景物间的对应关系 。
这些点是一些十分突出的点,不会因光照、尺度、旋转等因素的改变而消 失,比如角点、边缘点、暗区域的亮点以及亮区域的暗点。假定两幅图像中 有相同的景物,那么使用某种算法分别提取各自的特征点,这些点之间会有 相互对应的匹配关系
什么是尺度空间(scale space )?
尺度空间理论最早于1962年提出,其主要思想是通过对原 始图像进行尺度变换,获得图像多尺度下的空间表示。从而实 现边缘、角点检测和不同分辨率上的特征提取,以满足特征点 的尺度不变性。
尺度空间中各尺度图像的模 糊程度逐渐变大,能够模拟人在 距离目标由近到远时目标在视网 膜上的形成过程
#coding=utf-8
from PIL import Image
import os
from pylab import *
""" 处理一幅图像,然后将结果保存在文件中 """
def process_image(imagename, resultname, params="--edge-thresh 10 --peak-thresh 5"):
if imagename[-3:] != 'pgm':
# create a pgm file
im = Image.open(imagename).convert('L')
im.save('tmp.pgm')
imagename = 'tmp.pgm'
cmmd = str("D:/Python/vison2/sift.exe " + imagename + " --output=" + resultname +
" " + params)
os.system(cmmd)
print('processed', imagename, 'to', resultname)
""" 读取特征属性值,然后将其以矩阵的形式返回 """
def read_features_from_file(filename):
f = loadtxt(filename)
return f[:, :4], f[:, 4:] # feature locations, descriptors
""" 将特征位置和描述子保存到文件中 """
def write_features_to_file(filename, locs, desc):
savetxt(filename, hstack((locs, desc)))
""" 显示带有特征的图像
输入:im(数组图像),locs(每个特征的行、列、尺度和朝向)"""
def plot_features(im, locs, circle=False):
def draw_circle(c, r):
t = arange(0, 1.01, .01) * 2 * pi
x = r * cos(t) + c[0]
y = r * sin(t) + c[1]
plot(x, y, 'b', linewidth=2)
imshow(im)
if circle:
for p in locs:
draw_circle(p[:2], p[2])
else:
plot(locs[:, 0], locs[:, 1], 'ob')
axis('off')
imname = 'D:/Python/vison2/2.jpg'
im1 = array(Image.open(imname).convert('L'))
process_image(imname, 'jmu2.sift')
l1, d1 = read_features_from_file('jmu2.sift')
figure()
gray()
plot_features(im1, l1, circle=True)
show()
""" 对于第一幅图像中的每个描述子,选取其在第二幅图像中的匹配
输入:desc1(第一幅图像中的描述子),desc2(第二幅图像中的描述子)"""
def match(desc1, desc2):
desc1 = array([d / linalg.norm(d) for d in desc1])
desc2 = array([d / linalg.norm(d) for d in desc2])
dist_ratio = 0.6
desc1_size = desc1.shape
matchscores = zeros((desc1_size[0]), 'int')
desc2t = desc2.T # 预先计算矩阵转置
for i in range(desc1_size[0]):
dotprods = dot(desc1[i, :], desc2t) # 向量点乘
dotprods = 0.9999 * dotprods
# 反余弦和反排序,返回第二幅图像中特征的索引
indx = argsort(arccos(dotprods))
# 检查最近邻的角度是否小于 dist_ratio 乘以第二近邻的角度
if arccos(dotprods)[indx[0]] < dist_ratio * arccos(dotprods)[indx[1]]:
matchscores[i] = int(indx[0])
return matchscores
def appendimages(im1, im2):
rows1 = im1.shape[0]
rows2 = im2.shape[0]
if rows1 < rows2:
im1 = concatenate((im1, zeros((rows2 - rows1, im1.shape[1]))), axis=0)
elif rows1 > rows2:
im2 = concatenate((im2, zeros((rows1 - rows2, im2.shape[1]))), axis=0)
return concatenate((im1, im2), axis=1)
def plot_matches(im1, im2, locs1, locs2, matchscores, show_below=True):
im3 = appendimages(im1, im2)
if show_below:
im3 = vstack((im3, im3))
# show image
imshow(im3)
# draw lines for matches
cols1 = im1.shape[1]
for i, m in enumerate(matchscores):
if m > 0:
plot([locs1[i][1], locs2[m][1] + cols1], [locs1[i][0], locs2[m][0]], 'c')
axis('off')
""" 双向对称版本的 match()"""
def match_twosided(desc1, desc2):
matches_12 = match(desc1, desc2)
matches_21 = match(desc2, desc1)
ndx_12 = matches_12.nonzero()[0]
# remove matches that are not symmetric
for n in ndx_12:
if matches_21[int(matches_12[n])] != n:
matches_12[n] = 0
return matches_12
imname1 = 'D:\CV\images\chp2-3.jpg'
im1 = array(Image.open(imname1).convert('L'))
process_image(imname1,'chp2-3.sift')
l1,d1 = read_features_from_file('chp2-3.sift')
# figure()
# gray()
# subplot(121)
# plot_features(im1,l1,circle=False)
imname2 = 'D:\CV\images\chp2-5.jpg'
im2 = array(Image.open(imname2).convert('L'))
process_image(imname2,'chp2-5.sift')
l2,d2 = read_features_from_file('chp2-5.sift')
# subplot(122)
# plot_features(im2,l2,circle=False)
# show()
matches=match_twosided(d1,d2)
figure(dpi=180)
gray()
subplot(121)
plot_matches(im1,im2,l1,l2,matches,show_below=True)
show()# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# from pylab import *
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from Localdescriptors import sift
from tools import imtools
import pydot
# 将其设置为存储图像的路径
download_path = "D:\python\RRJ\pycharmproject\jmu_image\in2_jmu"
# 保存缩略图的路径(pydot需要完整的系统路径)
path = "D:\\python\\RRJ\\pycharmproject\\jmu_image\\out_jmu\\"
# 下载的文件名列表
imlist = imtools.get_imlist(download_path)
nbr_images = len(imlist)
# 提取特征
featlist = [imname[:-3] + 'sift' for imname in imlist]
for i, imname in enumerate(imlist):
sift.process_image(imname, featlist[i])
matchscores = np.zeros((nbr_images, nbr_images))
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i, nbr_images): # 仅仅计算上三角
print('comparing ', imlist[i], imlist[j])
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[i])
l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[j])
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2)
nbr_matches = sum(matches > 0)
print('number of matches = ', nbr_matches)
matchscores[i, j] = nbr_matches
print("The match scores is: \n", matchscores)
# 复制值
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images): # 无需复制对角线
matchscores[j, i] = matchscores[i, j]
# 可视化
threshold = 2 # 创建关联所需的最小匹配数目
g = pydot.Dot(graph_type='graph') # 不使用默认的有向图
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images):
if matchscores[i, j] > threshold:
# 图像对中的第一幅图像
im = Image.open(imlist[i])
im.thumbnail((100, 100))
filename = path + str(i) + '.png'
im.save(filename) # 需要大小合适的临时文件
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(i), fontcolor='transparent', shape='rectangle', image=filename))
# 图像对中的第一幅图像
im = Image.open(imlist[j])
im.thumbnail((100, 100))
filename = path + str(j) + '.png'
im.save(filename) # 需要大小合适的临时文件
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(j), fontcolor='transparent', shape='rectangle', image=filename))
g.add_edge(pydot.Edge(str(i), str(j)))
g.write_png('jmu1.png')
print('结束')