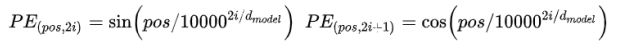【MindSpore易点通】网络构建经验总结下篇
MindSpore实现梯度不回传以及梯度回传后不更新权重
背景信息
训练中经常会用到某层的梯度不回传(比如互学习)或者梯度回传但是不更新权重(Fine-tuning)
经验总结
- 梯度不回传使用stop_gradient接口实现,代码示例如下:
import mindspore.nn as nnfrom mindspore.ops
import operations as Pfrom mindspore.ops
import functional as Ffrom mindspore.nn.loss.loss
import _Lossfrom mindspore
import Tensor, Parameterfrom mindspore.common
import dtype as mstypefrom mindspore.ops.functional
import stop_gradient
class Contrastive(_Loss):
def __init__(self, args):
super(Contrastive, self).__init__()
self.args = args
self.stride_slice = P.StridedSlice()
self.pow = P.Pow()
self.sum = P.CumSum()
self.dist_weight = Tensor(4, dtype=mstype.float32)
emb_list = list(range(args.per_batch_size))
emb1_list = emb_list[0::2]
emb2_list = emb_list[1::2]
self.emb1_param = Tensor(emb1_list, dtype=mstype.int32)
self.emb2_param = Tensor(emb2_list, dtype=mstype.int32)
self.add = P.TensorAdd()
self.div = P.RealDiv()
self.cast = P.Cast()
self.gatherv2 = P.GatherV2()
def construct(self, nembeddings):
nembeddings_shape = F.shape(nembeddings)
emb1 = self.gatherv2(nembeddings, self.emb1_param, 0)
emb2 = self.gatherv2(nembeddings, self.emb2_param, 0)
emb2_detach = stop_gradient(emb2) //阻止emb2的梯度回传
emb3 = emb1 - emb2_detach
pow_emb3 = emb3 * emb3
dist = self.sum(pow_emb3, 1)
return self.div(dist*self.dist_weight, self.cast(F.scalar_to_array(nembeddings_shape[0]), mstype.float32))- 梯度回传后不更新权重,使用requires_grad=False来实现,代码示例如下(假设要把名字为conv1的层权重冻结):
for param in net.trainable_params():
if 'conv1' in param.name:
param.requires_grad = False
else:
param.requires_grad = TrueMindSpore中使用Loss Scale(Feed模式下)关于sens参数的配置
背景信息
D芯片的卷积只有FP16精度,所以用D芯片训练一定是在跑混合精度。为避免梯度下溢,需要使用Loss Scale。
经验总结
Feed模式流程下,接口中Optimizer和TrainOneStepCell的sens需要手动设置成同一数值
opt = nn.Momentum(params=train_net.trainable_params(),
learning_rate=lr_iter,
momentum=0.9,
weight_decay=0.0001,
loss_scale=1000.0)
train_net = TrainOneStepCell(train_net, opt, sens=1000.0)MindSpore中使用SequentialCell的输入必须为nn.Cell组成的List
背景信息
PyTorch在网络定义中经常使用torch.nn.Sequential来构造算子的列表,在MindSpore中要使用mindspore.nn.SequentialCell来实现这个功能。
经验总结
mindspore.nn.SequentialCell的输入和PyTorch的Sequential有所不同,输入必须为Cell组成的List,否则会有不符合预期的错误。 使用示例如下:
class MyNet(nn.Cell):
def __init__(self):
super(MyNet, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(16, 64, 3, pad_mode='pad', padding=0, dilation=2)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.seq = nn.SequentialCell([self.conv, self.bn, self.relu]) #这里必须把nn.Cell的对象包装为List作为SequentialCell的输入
def construct(self, x):
x = self.seq(x)
return xTransformer中Positional Encoding的MindSpore简单实现
背景信息
《Attention Is All You Need》中的位置编码方法,Transformer中较为常用。公式如下:
经验总结
为了适用于动态shape的输入,又由于mindspore.nn.Cell.construct中不便于进行numpy操作,采用先生成一个足够长的positional encodding向量再根据输入长度进行截取的方法。
import mindspore.ops.operations as Pimport mindspore.nn as nnfrom mindspore.common
import dtype as mstypefrom mindspore import Tensorimport numpy as npimport math
class PositionalEncoding(nn.Cell):
"""Positional encoding as in Sec 3.5 https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.03762.pdf
:param int dim: dimension of input
:param int maxlen: upper limit of sequence length
:param float dropout_rate: dropout rate
"""
def __init__(self, dim, maxlen=10000, dropout_rate=0.1):
"""Construct an PositionalEncoding object."""
super(PositionalEncoding, self).__init__()
xscale = math.sqrt(dim)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(1 - dropout_rate)
self.mul = P.Mul()
self.add = P.TensorAdd()
self.shape = P.Shape()
self.pe = self.postion_encoding_table(maxlen, dim)
self.te = Tensor([xscale, ], mstype.float32)
def construct(self, x):
"""
Add positional encoding
:param mindspore.Tensor x: batches of inputs (B, len, dim)
:return: Encoded x (B, len, dim)
"""
(_, l, _) = self.shape(x)
pos = self.pe[:, :l, :]
x = self.mul(x, self.te)
x = self.add(x, pos)
x = self.dropout(x)
return x
def postion_encoding_table(self, max_length, dims):
pe = np.zeros((max_length, dims))
position = np.arange(0, max_length).reshape((max_length, 1))
div_term = np.exp(np.arange(0, dims, 2) * (-(math.log(10000.0) / dims)))
div_term = div_term.reshape((1, div_term.shape[0]))
pe[:, 0::2] = np.sin(np.matmul(position, div_term))
pe[:, 1::2] = np.cos(np.matmul(position, div_term))
pe = pe.reshape((1, max_length, dims))
pe = Tensor(pe, mstype.float32)
return pe