线程同步问题--共享资源--读者写者问题--Linux && C
记录型信号量解决读者-写者问题
算法:
//伪代码 计算机操作系统(第四版)西安电子科技大学出版社
semaphore rmutex = 1,wmutex;//互斥信号量,解决读者和写者之间的互斥信号量wmutex
//读者数量readerCount全局变量(共享资源)设置信号量rmutex
int readerCount = 0;//表示当前读者数量
//编写读者进程的操作
void Reader(){
do{
wait(rmutex);//为readerCount设置的信号量
if(readerCount == 0)wait(wmutex);//解决读者写者互斥
readerCount++;
signal(rmutex);
//...
//perform read operation;
//操作一般要长时间,sleep(毫秒数)
//...
wait(rmutex);
readercount--;
if(readerCount == 0)signal(wmutex);
signal(rmutex);
}while(TRUe);
}
//编写写者进程
void Writer(){
do{
wait(wmutex);//读者写者互斥冲突信号量
//...
//perform write operation
//操作一般要长时间,sleep(毫秒数)模拟
//...
signal(wmutex);
}while(TRUE);
}
void main(){
cobegin()
Reader();
Writer();
coend
}
线程同步实现上述算法
对于线程,定义--创建初始化-线程运行函数--线程退出
对于信号量,定义--创建初始化--信号量wait和signal--信号量销毁
信号量为什么要销毁:防止资源泄密---信号量是用来解决进程互斥资源共享冲突的,那么,信号量的值可以表示当前某些进程之间共享资源的使用情况,若不销毁,随后无意中改变了信号量的值,可能会导致进程间死锁现象。
对于一个进程,可以在该进程中创建多个线程,多个线程之间共享资源,资源申请就存在互斥关系,需要有锁的概念,信号量可以实现锁。
对于写者线程pthread_t writerTidp;定义了了该线程writerTidp,pthread_create(&writerTidp,NULL,writerThread,NULL) 创建了该线程,并指明线程函数入口是writerThread,该函数入口声明如下static void *writerThread(void *arg);该函数具体定义如下
static void *writerThread(void *arg){
for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++)
{
sem_wait(&wmutex);
//writer operation
n = n+1;
for(int k = 0;k < 26;k++)
contentArticle[nowLen-1][k] = 'a'+k;//模拟写的操作
sleep(2);//模拟写了一段时间--可以采用随机数生成这里写的时间
nowLen++;
printf("\n\nWriter thread :writing opration the global variable n equals to %d \n",n);
sleep(5);//模拟写了一段时间
sem_post(&wmutex);
sleep(3);
}
}
看该函数writerThread前,看一下解决读者写者之间互斥冲突的semaphore信号量wmutex :
定义sem_t wmutex;--全局变量,初始化sem_init(&wmutex,0,1),若返回-1表示线程创建失败,否则表示线程创建成功,其中的1表示wmutex的初始值,线程销毁sem_destroy(&wmutex);
该函数writerThread,先进行与读者互斥的信号量wmutex的wait操作,再进行写的操作,由于实际写操作要花一定时间,这里简单写几个字符串进去实际用时很短,采用sleep延时,若不采用延时,可能会出现一写者多读者最后发现对于读者每次只有一个人在读(运行太快,没有发生共享资源访问冲突的情况)。对于读者线程,类似。
线程同步,即算法中的
cobegin
Reader();
Writer();
coend换成代码是
void * retval;
pthread_join(ReaderTidp,&retval);
pthread_join(WriterTidp,&retval);一读者一写者且读写操作极简单的实现代码
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
sem_t rmutex,wmutex;
static void *readerThread(void *arg);
static void *writerThread(void *arg);
int readcount = 0;
int n = 0;
int main(){
pthread_t readerTidp,writerTidp;
void *retval;
if(sem_init(&rmutex,0,1)==-1||sem_init(&wmutex,0,1)==-1){
printf("sem_init error\n");
return -1;
}//init semaphore
if(pthread_create(&readerTidp,NULL,readerThread,NULL) !=0||pthread_create(&writerTidp,NULL,writerThread,NULL) !=0){
printf("pthread_create error\n");
return -2;
}//init pthread
pthread_join(readerTidp,&retval);
pthread_join(writerTidp,&retval);
sem_destroy(&rmutex);
sem_destroy(&wmutex);
return 0;
}
static void *readerThread(void *arg){
for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++)
{
sem_wait(&rmutex);
if(readcount == 0)sem_wait(&wmutex);
readcount = readcount+1;
sem_post(&rmutex);
//read operatiom
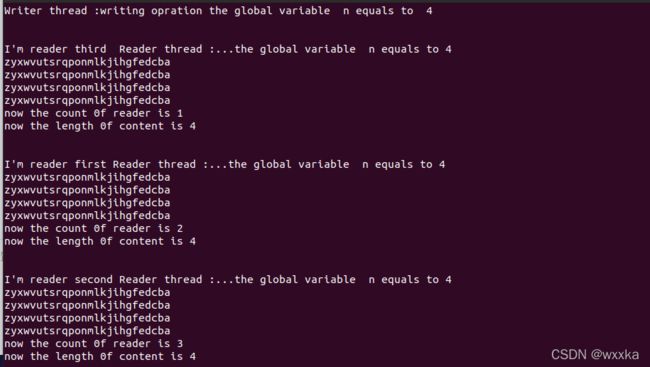
printf("\n\nI'm reader first Reader thread :...the global variable n equals to %d\n",n);
printf("now the count 0f reader is %d\n",readcount);
sem_wait(&rmutex);
readcount = readcount-1;
if(readcount == 0)sem_post(&wmutex);
sem_post(&rmutex);
}
}
static void *writerThread(void *arg){
for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++)
{
sem_wait(&wmutex);
//writer operation
n = n+1;
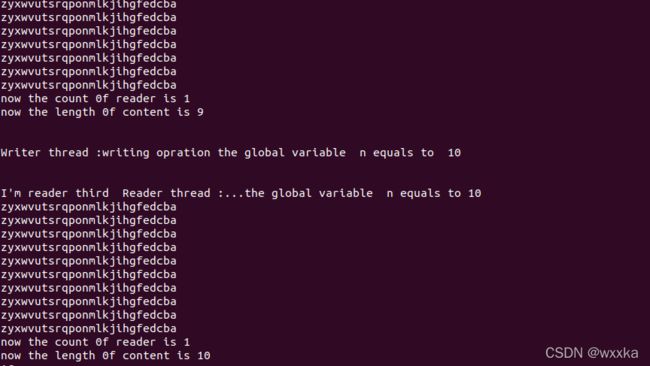
printf("\n\nWriter thread :writing opration the global variable n equals to %d \n",n);
sem_post(&wmutex);
}
}
改成如下的一写者多读者的程序
代码如下
//test2.c reader-writer problem --threadiSolving
// Create by Wenxin Li on 2022/04/12
//copyright © 2022 wxl_person. All rights reserved
//v1.0.0.1
//ubuntu 20.04 Linux
//gcc test2.c -o test2 -lpthread
//./test2
#include
//#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
sem_t rmutex,wmutex;
static void *readerThread(void *arg);
static void *reader3Thread(void *arg);
static void *reader2Thread(void *arg);
static void *writerThread(void *arg);
int readcount = 0;
int n = 0;
int nowLen = 1;
char contentArticle[10][100];
int main(){
pthread_t readerTidp,writerTidp,reader3Tidp,reader2Tidp;
void *retval;
if(sem_init(&rmutex,0,1)==-1||sem_init(&wmutex,0,1)==-1){
printf("sem_init error\n");
return -1;
}//init semaphore
if(pthread_create(&readerTidp,NULL,readerThread,NULL) !=0||pthread_create(&writerTidp,NULL,writerThread,NULL) !=0||pthread_create(&reader3Tidp,NULL,reader3Thread,NULL) !=0||pthread_create(&reader2Tidp,NULL,reader2Thread,NULL) !=0){
printf("pthread_create error\n");
return -2;
}//init pthread
pthread_join(readerTidp,&retval);
pthread_join(reader3Tidp,&retval);
pthread_join(reader2Tidp,&retval);
pthread_join(writerTidp,&retval);
sem_destroy(&rmutex);
sem_destroy(&wmutex);
return 0;
}
static void *readerThread(void *arg){
for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++)
{
sem_wait(&rmutex);
if(readcount == 0)sem_wait(&wmutex);
readcount = readcount+1;
sem_post(&rmutex);
//read operatiom
printf("\n\nI'm reader first Reader thread :...the global variable n equals to %d\n",n);
for(int j = 0;j < nowLen-1;j++)
{
for(int k = 0;k < 26;k++)
printf("%c",contentArticle[j][k]);
printf("\n");
}
printf("now the count 0f reader is %d\n",readcount);
printf("now the length 0f content is %d\n",nowLen-1);
sleep(5);
sem_wait(&rmutex);
readcount = readcount-1;
if(readcount == 0)sem_post(&wmutex);
sem_post(&rmutex);
sleep(1);
}
}
static void *reader3Thread(void *arg){
for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++)
{
sem_wait(&rmutex);
if(readcount == 0)sem_wait(&wmutex);
readcount = readcount+1;
sem_post(&rmutex);
//read operatiom
printf("\n\nI'm reader third Reader thread :...the global variable n equals to %d\n",n);
for(int j = 0;j < nowLen-1;j++)
{
for(int k = 0;k < 26;k++)
printf("%c",contentArticle[j][k]);
printf("\n");
}
printf("now the count 0f reader is %d\n",readcount);
printf("now the length 0f content is %d\n",nowLen-1);
sleep(5);
sem_wait(&rmutex);
readcount = readcount-1;
if(readcount == 0)sem_post(&wmutex);
sem_post(&rmutex);
sleep(8);
}
}
static void *reader2Thread(void *arg){
for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++)
{
sem_wait(&rmutex);
if(readcount == 0)sem_wait(&wmutex);
readcount = readcount+1;
sem_post(&rmutex);
//read operatiom
printf("\n\nI'm reader second Reader thread :...the global variable n equals to %d\n",n);
for(int j = 0;j < nowLen-1;j++)
{
for(int k = 0;k < 26;k++)
printf("%c",contentArticle[j][k]);
printf("\n");
}
printf("now the count 0f reader is %d\n",readcount);
printf("now the length 0f content is %d\n",nowLen-1);
sem_wait(&rmutex);
readcount = readcount-1;
if(readcount == 0)sem_post(&wmutex);
sem_post(&rmutex);
sleep(4);
}
}
static void *writerThread(void *arg){
for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++)
{
sem_wait(&wmutex);
//writer operation
n = n+1;
for(int k = 0;k < 26;k++)
contentArticle[nowLen-1][k] = 'z'-k;
nowLen++;
printf("\n\nWriter thread :writing opration the global variable n equals to %d \n",n);
sleep(2);
sem_post(&wmutex);
sleep(3);
}
}
运行截图