Java - 密码学
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、概述
-
- 1 名词概念
- 2 密钥证书管理体系
- 3 常见的加密手段
- 4 DES加解密Demo
- 5 区别toString与newString
- 6 编码算法
-
- URL编码
- Base64编码
- 7 哈希算法
- 二、Java加密安全体系
-
- 1 内置组件包
-
- security
- crypto
- spec
- cert
- ssl
- 2 Bouncy Castle
- 3 Commons Codec
- 三、数据加密算法
-
- 1 消息摘要算法
- 2 对称加密算法
- 3 非对称加密算法
- 4 数字签名算法
- 总结
前言
Java 密码学
| 文章目录 |
|---|
| 《Java加密与解密的艺术(第2版)》 |
现在不管是从哪家博客以及一些书籍内容上看,都很少能看到把Java密码学讲明白能让人学的明白的,包括这本书,不是科班出身的我感觉还有很长的一条路要走。
一、概述
从密码的体制上看,大致分为
- 明文
- 密文
- 密钥
- 加解密算法
在学习密码学之前,了解一下柯克霍夫原则
“即使密码系统的任何细节已为人悉知,只要密匙(key,又称密钥或秘钥)未泄漏,它也应是安全的”
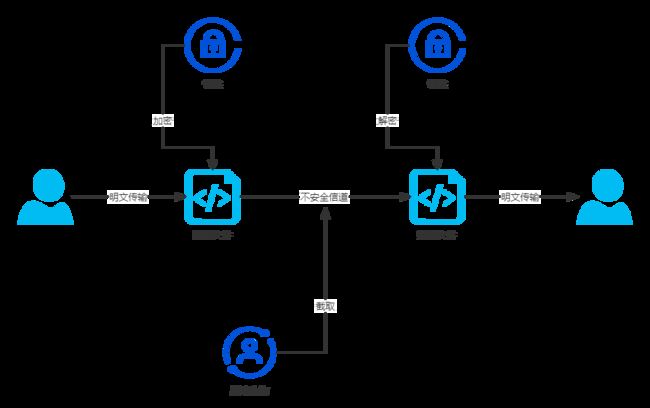
1 名词概念
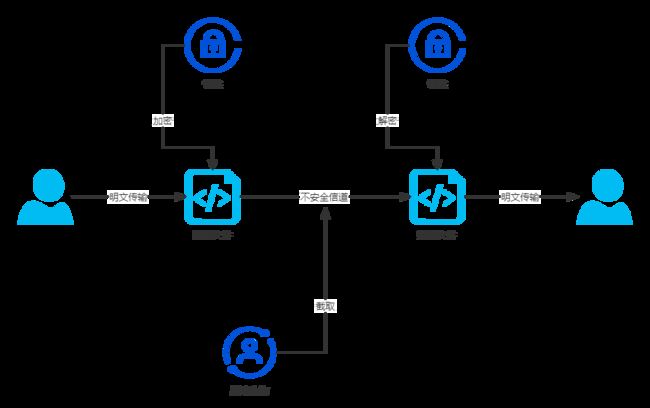
从加解密的流程上看
-
公钥
密码持有者给其他人的一把钥匙,用于数据加密,
公钥加密过的数据只能私钥来解 -
私钥
密码持有者独有的一把钥匙,用来解开公钥加密的数据
-
摘要
对需要传输的数据,做一个HASH计算,一般采用SHA1,SHA2来获得
-
签名
数据发送,对需要传输的数据的摘要进行加密,得到的结果就是签名
-
签名验证
数据接收,把拿到的数据,用公钥先对签名解密,然后把解密后的摘要再次用哈希算法校对是否被篡改
从密钥的分类上看
-
对称加密
两头用同一把钥匙,优点是加解密速度快,缺点是钥匙不好管理
-
非对称加密
两头用不一样的钥匙。优点是钥匙保密性更强,缺点是加解密速度慢
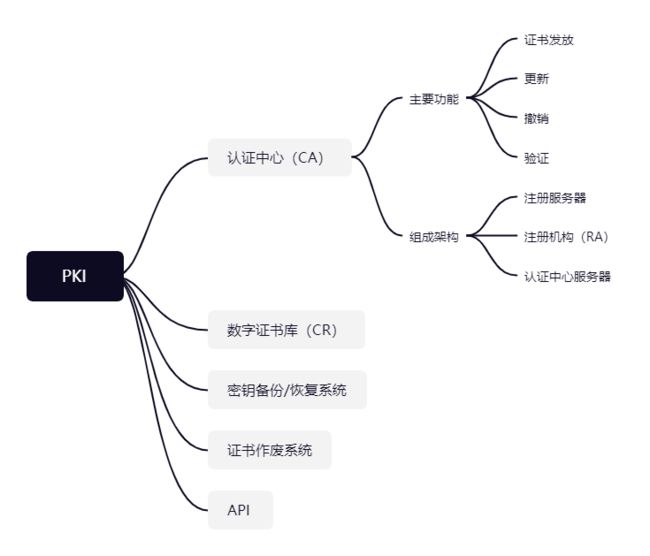
2 密钥证书管理体系
Public Key Infrastructure,PKI
3 常见的加密手段
对称加密
双方拥有的加解密的锁是同一把,所以加解密速度快,特点如下:
-
加密速度快, 可以加密大文件
-
密文可逆, 一旦密钥文件泄漏, 就会导致数据暴露
-
加密后编码表找不到对应字符, 出现乱码
-
一般结合Base64使用
常见的对称加密算法有:DES(数据加密标准)、AES(高级加密标准/Rijndael加密法)等。
非对称加密
也叫公私钥密码,公钥和私钥均可以用来作加解密的处理,不同之处在于,一份密文的处理需要公私钥同时参与,公钥的加密需要私钥的解密;反之,私钥的加密也需要公钥的解密。
4 DES加解密Demo
Java代码
import javax.crypto.BadPaddingException;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.IllegalBlockSizeException;
import javax.crypto.NoSuchPaddingException;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.security.InvalidKeyException;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.util.Base64;
/**
* @author 李家民
*/
public class PasswordTest {
/**
* 加密
*
* @return
*/
public static String ciphertext()
throws NoSuchPaddingException,
NoSuchAlgorithmException,
InvalidKeyException,
IllegalBlockSizeException,
BadPaddingException {
// 原文
String dataStr = "好好学习爬上岸";
// 钥匙 必须是8位
String key = "77498864";
// Cipher:密码,获取加密对象
// transformation:参数表示使用什么类型加密
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES");
// 指定秘钥规则
// 第一个参数表示:密钥,key的字节数组
// 第二个参数表示:算法
SecretKeySpec sks = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(), "DES");
// 对加密进行初始化
// 第一个参数:表示模式,有加密模式和解密模式
// 第二个参数:表示秘钥规则
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, sks);
// 进行加密(这是数据流加密)
byte[] bytes = cipher.doFinal(dataStr.getBytes());
// 打印密文
// 因为ascii码有负数 解析不出来 所以乱码
String mData = new String(bytes);
System.out.println("打印密文(乱码):" + mData);
Base64.Encoder encoder = Base64.getEncoder();
String resCipData = encoder.encodeToString(bytes);
System.out.println("打印密文(正常):" + resCipData);
return resCipData;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchPaddingException, IllegalBlockSizeException, NoSuchAlgorithmException, BadPaddingException, InvalidKeyException {
// 加密方法 拿密文
String ciphertext = ciphertext();
// 获取Cipher对象 填写加密的类型
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES");
// 拿密码锁并指定密钥规则
SecretKeySpec sks = new SecretKeySpec("77498864".getBytes(), "DES");
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, sks);
// 解密
// 上面使用的base64编码 下面直接用密文
byte[] bytesDe = Base64.getDecoder().decode(ciphertext);
byte[] bytesRes = cipher.doFinal(bytesDe);
// 因为是明文,所以直接返回
System.out.println("解密后:" + new String(bytesRes));
}
}
执行结果
打印密文(乱码):�tCH�k��3����u�B.�~��
打印密文(正常):3wd0Q0jea6TPM6WZnrd13FEIQi69ft/I
解密后:好好学习爬上岸
Base64补等号问题
提问:base64编码为什么要用等号来做最后空白的填补而不是其它?
回答:因为这是人为规定的,为的是形成统一标准,在网络传输上不会出现错误。比如说,如果A用了?填充将char转变为base64,而B在转换回来时用的是=将base64转回char,这样子因为标准不统一就会出现错误。
5 区别toString与newString
toString()是调用这个object对象的类的toString方法,而new String(str)是根据parameter是一个字节数组,使用java虚拟机默认的编码格式,将这个字节数组decode为对应的字符toString()对象打印的时候使用,new String()一般使用字符转码的时候,byte[]数组的时候
6 编码算法
什么是编码?就是把一个汉字或者英文翻译成另外的一种形式来表达它的意思。
举例一个ASCII编码表
| Bin(二进制) | Oct(八进制) | Dec(十进制) | Hex(十六进制) | 缩写/字符 | 解释 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0000 0000 | 00 | 0 | 0x00 | NUL(null) | 空字符 |
| 0000 0001 | 01 | 1 | 0x01 | SOH(start of headline) | 标题开始 |
| 0000 0010 | 02 | 2 | 0x02 | STX (start of text) | 正文开始 |
| 0000 0011 | 03 | 3 | 0x03 | ETX (end of text) | 正文结束 |
| 0000 0100 | 04 | 4 | 0x04 | EOT (end of transmission) | 传输结束 |
| 0000 0101 | 05 | 5 | 0x05 | ENQ (enquiry) | 请求 |
| 0000 0110 | 06 | 6 | 0x06 | ACK (acknowledge) | 收到通知 |
| 0000 0111 | 07 | 7 | 0x07 | BEL (bell) | 响铃 |
| 0000 1000 | 010 | 8 | 0x08 | BS (backspace) | 退格 |
| 0000 1001 | 011 | 9 | 0x09 | HT (horizontal tab) | 水平制表符 |
| 0000 1010 | 012 | 10 | 0x0A | LF (NL line feed, new line) | 换行键 |
| 0000 1011 | 013 | 11 | 0x0B | VT (vertical tab) | 垂直制表符 |
| 0000 1100 | 014 | 12 | 0x0C | FF (NP form feed, new page) | 换页键 |
| 0000 1101 | 015 | 13 | 0x0D | CR (carriage return) | 回车键 |
| 0000 1110 | 016 | 14 | 0x0E | SO (shift out) | 不用切换 |
| 0000 1111 | 017 | 15 | 0x0F | SI (shift in) | 启用切换 |
| 0001 0000 | 020 | 16 | 0x10 | DLE (data link escape) | 数据链路转义 |
| 0001 0001 | 021 | 17 | 0x11 | DC1 (device control 1) | 设备控制1 |
| 0001 0010 | 022 | 18 | 0x12 | DC2 (device control 2) | 设备控制2 |
| 0001 0011 | 023 | 19 | 0x13 | DC3 (device control 3) | 设备控制3 |
| 0001 0100 | 024 | 20 | 0x14 | DC4 (device control 4) | 设备控制4 |
| 0001 0101 | 025 | 21 | 0x15 | NAK (negative acknowledge) | 拒绝接收 |
| 0001 0110 | 026 | 22 | 0x16 | SYN (synchronous idle) | 同步空闲 |
| 0001 0111 | 027 | 23 | 0x17 | ETB (end of trans. block) | 结束传输块 |
| 0001 1000 | 030 | 24 | 0x18 | CAN (cancel) | 取消 |
| 0001 1001 | 031 | 25 | 0x19 | EM (end of medium) | 媒介结束 |
| 0001 1010 | 032 | 26 | 0x1A | SUB (substitute) | 代替 |
| 0001 1011 | 033 | 27 | 0x1B | ESC (escape) | 换码(溢出) |
| 0001 1100 | 034 | 28 | 0x1C | FS (file separator) | 文件分隔符 |
| 0001 1101 | 035 | 29 | 0x1D | GS (group separator) | 分组符 |
| 0001 1110 | 036 | 30 | 0x1E | RS (record separator) | 记录分隔符 |
| 0001 1111 | 037 | 31 | 0x1F | US (unit separator) | 单元分隔符 |
| 0010 0000 | 040 | 32 | 0x20 | (space) | 空格 |
| 0010 0001 | 041 | 33 | 0x21 | ! | 叹号 |
| 0010 0010 | 042 | 34 | 0x22 | " | 双引号 |
| 0010 0011 | 043 | 35 | 0x23 | # | 井号 |
| 0010 0100 | 044 | 36 | 0x24 | $ | 美元符 |
| 0010 0101 | 045 | 37 | 0x25 | % | 百分号 |
| 0010 0110 | 046 | 38 | 0x26 | & | 和号 |
| 0010 0111 | 047 | 39 | 0x27 | ’ | 闭单引号 |
| 0010 1000 | 050 | 40 | 0x28 | ( | 开括号 |
| 0010 1001 | 051 | 41 | 0x29 | ) | 闭括号 |
| 0010 1010 | 052 | 42 | 0x2A | * | 星号 |
| 0010 1011 | 053 | 43 | 0x2B | + | 加号 |
| 0010 1100 | 054 | 44 | 0x2C | , | 逗号 |
| 0010 1101 | 055 | 45 | 0x2D | - | 减号/破折号 |
| 0010 1110 | 056 | 46 | 0x2E | . | 句号 |
| 0010 1111 | 057 | 47 | 0x2F | / | 斜杠 |
| 0011 0000 | 060 | 48 | 0x30 | 0 | 字符0 |
| 0011 0001 | 061 | 49 | 0x31 | 1 | 字符1 |
| 0011 0010 | 062 | 50 | 0x32 | 2 | 字符2 |
| 0011 0011 | 063 | 51 | 0x33 | 3 | 字符3 |
| 0011 0100 | 064 | 52 | 0x34 | 4 | 字符4 |
| 0011 0101 | 065 | 53 | 0x35 | 5 | 字符5 |
| 0011 0110 | 066 | 54 | 0x36 | 6 | 字符6 |
| 0011 0111 | 067 | 55 | 0x37 | 7 | 字符7 |
| 0011 1000 | 070 | 56 | 0x38 | 8 | 字符8 |
| 0011 1001 | 071 | 57 | 0x39 | 9 | 字符9 |
| 0011 1010 | 072 | 58 | 0x3A | : | 冒号 |
| 0011 1011 | 073 | 59 | 0x3B | ; | 分号 |
| 0011 1100 | 074 | 60 | 0x3C | < | 小于 |
| 0011 1101 | 075 | 61 | 0x3D | = | 等号 |
| 0011 1110 | 076 | 62 | 0x3E | > | 大于 |
| 0011 1111 | 077 | 63 | 0x3F | ? | 问号 |
| 0100 0000 | 0100 | 64 | 0x40 | @ | 电子邮件符号 |
| 0100 0001 | 0101 | 65 | 0x41 | A | 大写字母A |
| 0100 0010 | 0102 | 66 | 0x42 | B | 大写字母B |
| 0100 0011 | 0103 | 67 | 0x43 | C | 大写字母C |
| 0100 0100 | 0104 | 68 | 0x44 | D | 大写字母D |
| 0100 0101 | 0105 | 69 | 0x45 | E | 大写字母E |
| 0100 0110 | 0106 | 70 | 0x46 | F | 大写字母F |
| 0100 0111 | 0107 | 71 | 0x47 | G | 大写字母G |
| 0100 1000 | 0110 | 72 | 0x48 | H | 大写字母H |
| 0100 1001 | 0111 | 73 | 0x49 | I | 大写字母I |
| 01001010 | 0112 | 74 | 0x4A | J | 大写字母J |
| 0100 1011 | 0113 | 75 | 0x4B | K | 大写字母K |
| 0100 1100 | 0114 | 76 | 0x4C | L | 大写字母L |
| 0100 1101 | 0115 | 77 | 0x4D | M | 大写字母M |
| 0100 1110 | 0116 | 78 | 0x4E | N | 大写字母N |
| 0100 1111 | 0117 | 79 | 0x4F | O | 大写字母O |
| 0101 0000 | 0120 | 80 | 0x50 | P | 大写字母P |
| 0101 0001 | 0121 | 81 | 0x51 | Q | 大写字母Q |
| 0101 0010 | 0122 | 82 | 0x52 | R | 大写字母R |
| 0101 0011 | 0123 | 83 | 0x53 | S | 大写字母S |
| 0101 0100 | 0124 | 84 | 0x54 | T | 大写字母T |
| 0101 0101 | 0125 | 85 | 0x55 | U | 大写字母U |
| 0101 0110 | 0126 | 86 | 0x56 | V | 大写字母V |
| 0101 0111 | 0127 | 87 | 0x57 | W | 大写字母W |
| 0101 1000 | 0130 | 88 | 0x58 | X | 大写字母X |
| 0101 1001 | 0131 | 89 | 0x59 | Y | 大写字母Y |
| 0101 1010 | 0132 | 90 | 0x5A | Z | 大写字母Z |
| 0101 1011 | 0133 | 91 | 0x5B | [ | 开方括号 |
| 0101 1100 | 0134 | 92 | 0x5C | \ | 反斜杠 |
| 0101 1101 | 0135 | 93 | 0x5D | ] | 闭方括号 |
| 0101 1110 | 0136 | 94 | 0x5E | ^ | 脱字符 |
| 0101 1111 | 0137 | 95 | 0x5F | _ | 下划线 |
| 0110 0000 | 0140 | 96 | 0x60 | ` | 开单引号 |
| 0110 0001 | 0141 | 97 | 0x61 | a | 小写字母a |
| 0110 0010 | 0142 | 98 | 0x62 | b | 小写字母b |
| 0110 0011 | 0143 | 99 | 0x63 | c | 小写字母c |
| 0110 0100 | 0144 | 100 | 0x64 | d | 小写字母d |
| 0110 0101 | 0145 | 101 | 0x65 | e | 小写字母e |
| 0110 0110 | 0146 | 102 | 0x66 | f | 小写字母f |
| 0110 0111 | 0147 | 103 | 0x67 | g | 小写字母g |
| 0110 1000 | 0150 | 104 | 0x68 | h | 小写字母h |
| 0110 1001 | 0151 | 105 | 0x69 | i | 小写字母i |
| 0110 1010 | 0152 | 106 | 0x6A | j | 小写字母j |
| 0110 1011 | 0153 | 107 | 0x6B | k | 小写字母k |
| 0110 1100 | 0154 | 108 | 0x6C | l | 小写字母l |
| 0110 1101 | 0155 | 109 | 0x6D | m | 小写字母m |
| 0110 1110 | 0156 | 110 | 0x6E | n | 小写字母n |
| 0110 1111 | 0157 | 111 | 0x6F | o | 小写字母o |
| 0111 0000 | 0160 | 112 | 0x70 | p | 小写字母p |
| 0111 0001 | 0161 | 113 | 0x71 | q | 小写字母q |
| 0111 0010 | 0162 | 114 | 0x72 | r | 小写字母r |
| 0111 0011 | 0163 | 115 | 0x73 | s | 小写字母s |
| 0111 0100 | 0164 | 116 | 0x74 | t | 小写字母t |
| 0111 0101 | 0165 | 117 | 0x75 | u | 小写字母u |
| 0111 0110 | 0166 | 118 | 0x76 | v | 小写字母v |
| 0111 0111 | 0167 | 119 | 0x77 | w | 小写字母w |
| 0111 1000 | 0170 | 120 | 0x78 | x | 小写字母x |
| 0111 1001 | 0171 | 121 | 0x79 | y | 小写字母y |
| 0111 1010 | 0172 | 122 | 0x7A | z | 小写字母z |
| 0111 1011 | 0173 | 123 | 0x7B | { | 开花括号 |
| 0111 1100 | 0174 | 124 | 0x7C | | | 垂线 |
| 0111 1101 | 0175 | 125 | 0x7D | } | 闭花括号 |
| 0111 1110 | 0176 | 126 | 0x7E | ~ | 波浪号 |
| 0111 1111 | 0177 | 127 | 0x7F | DEL (delete) | 删除 |
URL编码
然后来聊聊URL编码,我们经常在浏览网页的时候可以看到这么一串东西
之所以使用URL编码,是因为出于对兼容性的考虑,很多服务器只识别ASCII字符,一般来说如果需要转换URL编码,对于一些无法识别到的其他字符,会先需要转换成UTF-8编码。
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.net.URLDecoder;
import java.net.URLEncoder;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
/**
* URL编码练习
* @author 李家民
*/
public class UrlCodeDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
// URL编码
String encode = URLEncoder.encode("我测试一下URL编码", String.valueOf(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
System.out.println(encode);
// URL解码
String decode = URLDecoder.decode(encode, String.valueOf(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
System.out.println(decode);
}
}
Base64编码
URL编码是对字符进行编码,是一种用64个字符来表示任意二进制数据的方法,表示成%xx的形式;而Base64编码是对二进制数据进行编码,表示成文本格式,但是编码后数据量会膨胀三分之一。
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Base64;
/**
* Base64编码练习
* @author 李家民
*/
public class Base64DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ...解码
byte[] decodeBy = Base64.getDecoder().decode("5Lit");
String toStringBase = Arrays.toString(decodeBy);
System.out.println(toStringBase);
// ...编码
byte[] input = new byte[]{(byte) 0xe4, (byte) 0xb8, (byte) 0xad};
String b64encoded = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(input);
System.out.println(b64encoded);
}
}
转换表
| 索引 | 对应字符 | 索引 | 对应字符 | 索引 | 对应字符 | 索引 | 对应字符 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | A | 17 | R | 34 | i | 51 | z |
| 1 | B | 18 | S | 35 | j | 52 | 0 |
| 2 | C | 19 | T | 36 | k | 53 | 1 |
| 3 | D | 20 | U | 37 | l | 54 | 2 |
| 4 | E | 21 | V | 38 | m | 55 | 3 |
| 5 | F | 22 | W | 39 | n | 56 | 4 |
| 6 | G | 23 | X | 40 | o | 57 | 5 |
| 7 | H | 24 | Y | 41 | p | 58 | 6 |
| 8 | I | 25 | Z | 42 | q | 59 | 7 |
| 9 | J | 26 | a | 43 | r | 60 | 8 |
| 10 | K | 27 | b | 44 | s | 61 | 9 |
| 11 | L | 28 | c | 45 | t | 62 | + |
| 12 | M | 29 | d | 46 | u | 63 | / |
| 13 | N | 30 | e | 47 | v | ||
| 14 | O | 31 | f | 48 | w | ||
| 15 | P | 32 | g | 49 | x | ||
| 16 | Q | 33 | h | 50 | y |
后面还需要重新补一下计算机基础知识
7 哈希算法
哈希算法又称摘要算法,通过哈希算法计算出来的数据,是一个固定长度的输出摘要,目的是为了验证原始数据是否被篡改。
/**
* 哈希算法 练习程序
* @author 李家民
*/
public class HashDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int hashCode = "我是数据".hashCode();
// result = 773872316
System.out.println(hashCode);
}
}
但是,不同的数据计算出的哈希值也有相同的情况,我们称这种情况为哈希碰撞。
/**
* 哈希算法 练习程序
* @author 李家民
*/
public class HashDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 哈希碰撞
System.out.println("AaAaAa".hashCode());
System.out.println("BBAaBB".hashCode());
}
}
虽然我们允许碰撞,但是,一个安全的哈希算法需要满足两个条件
- 碰撞的概率低
- 不能被反推(很难被暴力穷举)
常见的哈希算法有这些:
| 算法 | 输出长度(位) | 输出长度(字节) |
|---|---|---|
| MD5 | 128 bits | 16 bytes |
| SHA-1 | 160 bits | 20 bytes |
| RipeMD-160 | 160 bits | 20 bytes |
| SHA-256 | 256 bits | 32 bytes |
| SHA-512 | 512 bits | 64 bytes |
你学废了吗
二、Java加密安全体系
Java的加密安全领域分为了四个部分
-
JCA,加密体系结构提供加密框架,如证书、数字签名、消息摘要和密钥对产生器
-
JCE,加密扩展提供各种加密算法、消息摘要算法和密钥管理等功能
-
JSSE,安全套接字扩展 -
JAAS,鉴别安全服务
然后这些加密的算法或者加密方式等是有一些好人给我们进行了提供
1 内置组件包
Java中的内置包类
- java.security
- javax.crypto
- java.security.spec
- javax.crypto.spec
- java.security.cert
- javax.net.ssl
security
隶属于*package java.security;*包下
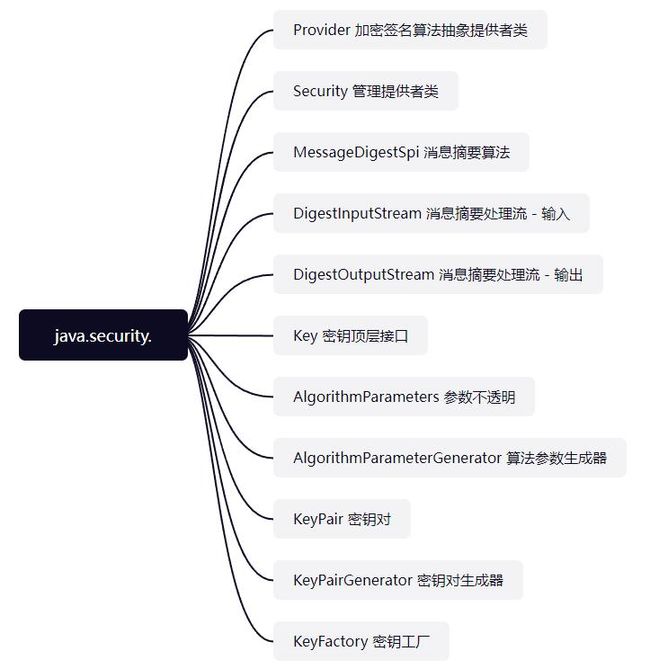
以后根据实际的案例再挨个看,现在先随便举个例子
import sun.security.rsa.SunRsaSign;
/**
* 密码学练习
* @author 李家民
*/
public class PasswdApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// extends Provider
SunRsaSign sunRsaSign = new SunRsaSign();
System.out.println("算法提供者名称:" + sunRsaSign.getName());
System.out.println("算法提供者版本号:" + sunRsaSign.getVersion());
System.out.println("算法提供者信息串:" + sunRsaSign.getInfo());
}
}
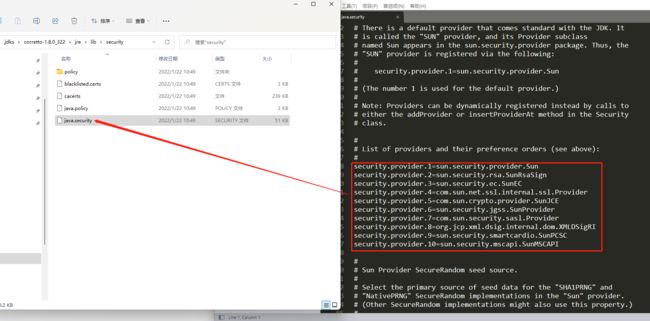
下面这个提供者名单是JDK 1.8 中内置的

C:\Users\13544.jdks\corretto-1.8.0_322\jre\lib\security\java.security
回来补充—
crypto
加解密操作的接口和类的提供,加解密的实现。
回来补充—
spec
回来补充—
cert
回来补充—
ssl
回来补充—
2 Bouncy Castle
脱离JDK之外的额外的轻量级密码Jar包,就是一个第三方的库。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.bouncycastlegroupId>
<artifactId>bcprov-jdk15onartifactId>
<version>1.70version>
dependency>
本次采用RipeMD160算法来做这个Demo
/**
* BouncyCastleProvider 密码学练习
* @author 李家民
*/
public class PasswdApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException, NoSuchAlgorithmException {
// java.security.中提供了一种标准 可以将第三方提供者接入注册
Security.addProvider(new BouncyCastleProvider());
// 指定要使用的消息摘要算法
MessageDigest md = MessageDigest.getInstance("RipeMD160");
// 使用指定的字节数组(数据)更新摘要
md.update("测试一下这个加密算法好用不".getBytes("UTF-8"));
byte[] result = md.digest();
String toString = new BigInteger(1, result).toString(16);
System.out.println(toString);
}
}
关于里面的其他算法后续再继续补充学习
3 Commons Codec
Apache提供的一个编码进制等转换的工具包
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-codecgroupId>
<artifactId>commons-codecartifactId>
<version>1.15version>
dependency>
大概有这么几个类包
细节以后用上了再说
三、数据加密算法
主要是说各个流派的加密算法以及用处在哪
1 消息摘要算法
作用:验证数据的完整性。
消息摘要算法主要分为三个大类
- MD:Message Digest 消息摘要算法
- SHA-1:Secure Hash Algorithm 安全散列算法
- HmacMD5:Message Authentication Code 消息认证码算法
- 另外还有RipeMD系列
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
/**
* 消息摘要算法练习
* @author 李家民
*/
public class DigestApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException {
// MD5加密
MessageDigest messageDigest = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
byte[] bytes = messageDigest.digest("hello".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
// 解决乱码输出 - 需将得到的字节码再次进行编码,一般是16进制编码
StringBuilder ret = new StringBuilder(bytes.length << 1);
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
ret.append(Character.forDigit((bytes[i] >> 4) & 0xf, 16));
ret.append(Character.forDigit(bytes[i] & 0xf, 16));
}
System.out.println(ret.toString());
}
}
实现的方式有很多种上述只是其中一种,另外还有
- Sun
- Bouncy Castle
- Commons Codec
第一种比较偏向底层,但是支持的算法还是蛮多的,第三种就是对之前的底层算法去封装更易使用。
此时不得不提上一嘴 CRC - 循环冗余校验算法,消息摘要算法与CRC算法同属散列函数,而且是消息摘要的前身,可以根据数据产生简短固定位数的一种散列函数,主要用来检测或校验数据传输/保存后出现的错误。
2 对称加密算法
对称加密,就是共用一把锁加密,书中有举例这些
- DES - 数据加密标准
- DESede - 上述升级
- AES - 高级标准
- IDEA - 国际标准
- PBE - 基于口令
下面打码Des加密的Demo看看
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.util.Base64;
/**
* @author 李家民
*/
public class DesDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String data = "我是原始数据";
String key = "98761234";
String encryptData = encrypt(data, key);
decrypt(encryptData, key);
}
/**
* 加密
* @param data 原数据
* @param key 密钥
* @return
*/
public static String encrypt(String data, String key) {
try {
// 1 获取加密对象
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES");
// 2 指定密钥
SecretKeySpec sks = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(), "DES");
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, sks);
// 3 执行加密动作
byte[] bytes = cipher.doFinal(data.getBytes());
// 打印密文
// 需要经过处理 因为因为ascii码有负数 解析不出来 会导致乱码
Base64.Encoder encoder = Base64.getEncoder();
String resCipData = encoder.encodeToString(bytes);
System.out.println("打印密文:" + resCipData);
return resCipData;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* 解密
* @param data 密文
* @param key 密钥
* @return
*/
public static String decrypt(String data, String key) {
try {
// 获取Cipher对象 填写加密的类型
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES");
// 拿密码锁并指定密钥规则
SecretKeySpec sks = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(), "DES");
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, sks);
// 解密
// 上面使用的base64编码 下面直接用密文
byte[] bytesDe = Base64.getDecoder().decode(data);
byte[] bytesRes = cipher.doFinal(bytesDe);
// 因为是明文,所以直接返回
String s = new String(bytesRes);
System.out.println("解密后:" + s);
return s;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
}
加密手段很多,就先这样
3 非对称加密算法
公私钥加密,安全性相较于前面两种是最高的,但是解密效率也低。
密钥处一分为二,分为公钥和私钥,公钥通过非安全通道发放,私钥则由发放者保留。公钥与私钥相对应,成对出现。公钥加密的数据,只可使用私钥对其解密。反之,私钥加密的数据,只可使用公钥对其解密。
下面上一个RSA加密的工具类,都标注好注释了,标准的公私钥加密形式。
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.security.KeyFactory;
import java.security.KeyPair;
import java.security.KeyPairGenerator;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.security.interfaces.RSAPrivateKey;
import java.security.interfaces.RSAPublicKey;
import java.security.spec.PKCS8EncodedKeySpec;
import java.security.spec.RSAPrivateKeySpec;
import java.security.spec.RSAPublicKeySpec;
import java.security.spec.X509EncodedKeySpec;
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* RSA 加解密工具
* @author xxx
*/
public class RSAUtils {
/**
* 生成公私钥
* @return map:public,private
* @throws NoSuchAlgorithmException
*/
public static HashMap<String, Object> getKeys() throws NoSuchAlgorithmException {
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGen = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA");
keyPairGen.initialize(1024);
KeyPair keyPair = keyPairGen.generateKeyPair();
RSAPublicKey publicKey = (RSAPublicKey) keyPair.getPublic();
RSAPrivateKey privateKey = (RSAPrivateKey) keyPair.getPrivate();
map.put("public", publicKey);
map.put("private", privateKey);
return map;
}
/**
* 使用模和指数生成RSA公钥
* 注意:【此代码用了默认补位方式,为RSA/None/PKCS1Padding,不同JDK默认的补位方式可能不同,如Android默认是RSA
* /None/NoPadding】
* @param modulus 模
* @param exponent 指数
* @return
*/
public static RSAPublicKey getPublicKey(String modulus, String exponent) {
try {
BigInteger b1 = new BigInteger(modulus);
BigInteger b2 = new BigInteger(exponent);
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA");
RSAPublicKeySpec keySpec = new RSAPublicKeySpec(b1, b2);
return (RSAPublicKey) keyFactory.generatePublic(keySpec);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* 使用X.509 标准编码构建公钥
* @param pubKeyBytes
* @return
*/
public static RSAPublicKey restorePublicKey(byte[] pubKeyBytes) {
try {
X509EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(pubKeyBytes);
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA");
RSAPublicKey publicKey = (RSAPublicKey) keyFactory.generatePublic(keySpec);
return publicKey;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* 使用X.509 标准编码构建私钥
* @param priKeyBytes
* @return
*/
public static RSAPrivateKey restorePrivateKey(byte[] priKeyBytes) {
try {
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(priKeyBytes);
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA");
RSAPrivateKey privateKey = (RSAPrivateKey) keyFactory.generatePrivate(keySpec);
return privateKey;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* 使用模和指数生成RSA私钥
* 注意:【此代码用了默认补位方式,为RSA/None/PKCS1Padding,不同JDK默认的补位方式可能不同,如Android默认是RSA
* /None/NoPadding】
* @param modulus 模
* @param exponent 指数
* @return
*/
public static RSAPrivateKey getPrivateKey(String modulus, String exponent) {
try {
BigInteger b1 = new BigInteger(modulus);
BigInteger b2 = new BigInteger(exponent);
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA");
RSAPrivateKeySpec keySpec = new RSAPrivateKeySpec(b1, b2);
return (RSAPrivateKey) keyFactory.generatePrivate(keySpec);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* 对数据 使用公钥 进行加密
* @param data
* @param publicKey
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static String encryptByPublicKey(String data, RSAPublicKey publicKey)
throws Exception {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey);
// 模长
int key_len = publicKey.getModulus().bitLength() / 8;
// 加密数据长度 <= 模长-11
String[] datas = splitString(data, key_len - 11);
String mi = "";
//如果明文长度大于模长-11则要分组加密
for (String s : datas) {
mi += bcd2Str(cipher.doFinal(s.getBytes()));
}
return mi;
}
/**
* 对数据 使用私钥 进行解密
* @param data
* @param privateKey
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static String decryptByPrivateKey(String data, RSAPrivateKey privateKey)
throws Exception {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey);
//模长
int key_len = privateKey.getModulus().bitLength() / 8;
byte[] bytes = data.getBytes();
byte[] bcd = ASCII_To_BCD(bytes, bytes.length);
System.err.println("BCDLength:" + bcd.length);
//如果密文长度大于模长则要分组解密
String ming = "";
byte[][] arrays = splitArray(bcd, key_len);
for (byte[] arr : arrays) {
ming += new String(cipher.doFinal(arr));
}
return ming;
}
/**
* ASCII码转BCD码
*/
public static byte[] ASCII_To_BCD(byte[] ascii, int asc_len) {
byte[] bcd = new byte[asc_len / 2];
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < (asc_len + 1) / 2; i++) {
bcd[i] = asc_to_bcd(ascii[j++]);
bcd[i] = (byte) (((j >= asc_len) ? 0x00 : asc_to_bcd(ascii[j++])) + (bcd[i] << 4));
}
return bcd;
}
public static byte asc_to_bcd(byte asc) {
byte bcd;
if ((asc >= '0') && (asc <= '9')) {
bcd = (byte) (asc - '0');
} else if ((asc >= 'A') && (asc <= 'F')) {
bcd = (byte) (asc - 'A' + 10);
} else if ((asc >= 'a') && (asc <= 'f')) {
bcd = (byte) (asc - 'a' + 10);
} else {
bcd = (byte) (asc - 48);
}
return bcd;
}
/**
* BCD转字符串
*/
public static String bcd2Str(byte[] bytes) {
char temp[] = new char[bytes.length * 2], val;
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
val = (char) (((bytes[i] & 0xf0) >> 4) & 0x0f);
temp[i * 2] = (char) (val > 9 ? val + 'A' - 10 : val + '0');
val = (char) (bytes[i] & 0x0f);
temp[i * 2 + 1] = (char) (val > 9 ? val + 'A' - 10 : val + '0');
}
return new String(temp);
}
/**
* 拆分字符串
*/
public static String[] splitString(String string, int len) {
int x = string.length() / len;
int y = string.length() % len;
int z = 0;
if (y != 0) {
z = 1;
}
String[] strings = new String[x + z];
String str = "";
for (int i = 0; i < x + z; i++) {
if (i == x + z - 1 && y != 0) {
str = string.substring(i * len, i * len + y);
} else {
str = string.substring(i * len, i * len + len);
}
strings[i] = str;
}
return strings;
}
/**
* 拆分数组
*/
public static byte[][] splitArray(byte[] data, int len) {
int x = data.length / len;
int y = data.length % len;
int z = 0;
if (y != 0) {
z = 1;
}
byte[][] arrays = new byte[x + z][];
byte[] arr;
for (int i = 0; i < x + z; i++) {
arr = new byte[len];
if (i == x + z - 1 && y != 0) {
System.arraycopy(data, i * len, arr, 0, y);
} else {
System.arraycopy(data, i * len, arr, 0, len);
}
arrays[i] = arr;
}
return arrays;
}
}
这类算法对安全性较高的场景会用上,像电商交易平台或者融资贷款平台。
4 数字签名算法
| 文章目录 |
|---|
| 数字签名算法_百度百科 (baidu.com) |
一种带有密钥的消息摘要算法,是公钥基础设施(Public Key Infrastructure,PKI)以及许多网络安全机制(SSL/TLS、VPN等)的基础,走的是签名+验证的路线,私钥签名,公钥验证。
主要有这么几种
- RSA
- DSA
- ECDSA
不细学,以后再说。
总结
提示:这里对文章进行总结:
例如:以上就是今天要讲的内容。