20150423 字符驱动程序的另一种写法(附源程序)
20150423 字符驱动程序的另一种写法(附源程序)
2015-04-23 李海沿
以前刚开始学习编写驱动程序时,为了简单易懂,我们写注册字符驱动程序时,都是使用register_chrdev来实现。但是register_chrdev有一个缺点就是,使用它注册之后,一个主设备号的256个次设备号对应的同一个file_operation结构体,从而使操作系统最多就只能支持255个驱动程序,严重的束缚了操作系统。
今天我们要实现的是另一种驱动程序编写方式,register_chrdev_region,使用它可以规定次设备号的某个区域是对应某一个file_operation结构体,而剩下的次设备号还可以做其他用途,很好的解决了前面register_chrdev所带来的缺点
那我们开始吧!
一、实现步骤
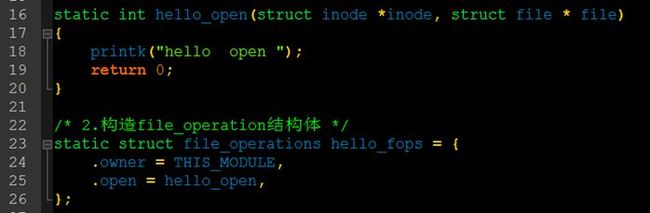
1.定义主设备号为全局变量
2.编写file_operation结构体
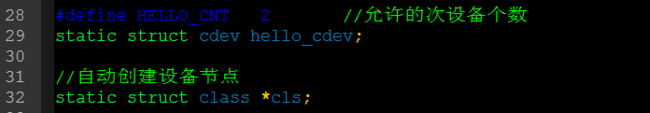
3.定义cdev结构体,并且定义本驱动程序允许的次设备数目,定义一个class结构体用于自动创建设备节点
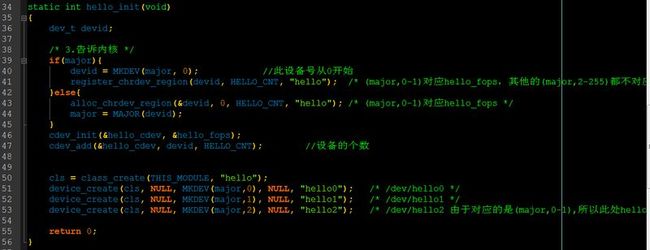
4.在入口函数中注册字符设备
如图所示:
36行:定义一个dev_t的结构体,用于保存mkdev得到的设备号的信息
39行:下来,若是已经制定了major主设备号,并且major不为0的话,则使用register_chrdev_region函数申请,参数分别为(dev_t,要申请的此设备号的个数,名字)。
所以,由于我们前面devid = MKDEV(major,0)并且次设备号的个数为2,所以若是申请成功的话,我们的hell_fops所定义的次设备号仅仅是(major,0)与(major,1)两个。
42行:当major未制定,或者major为0时,就会进入并且使用alloc_chrdev_region自动申请主设备号。
46行:初始化cdev结构体,并且添加cdev结构体,前面我们申请的次设备号个数为2,所以此处应该填2
50行:这一行,大家应该很熟悉了,主要是创建一个类,然后再类下面自动创建设备节点,省去了手工敲mknod命令。
5.在出口函数中依次卸载或者删除
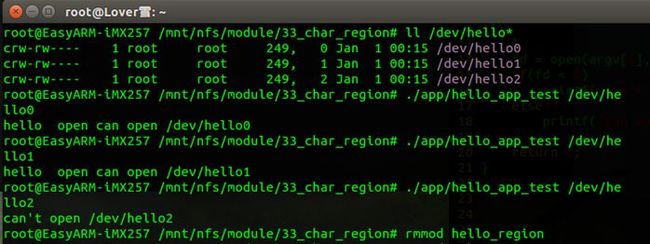
6.在imx257开发板上编译测试:
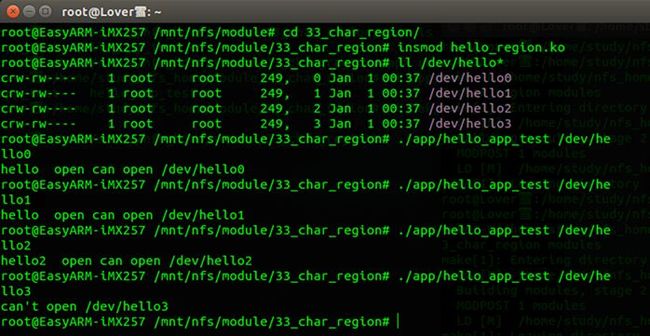
加载驱动程序
如图所示,当我们打开/dev/hello0与/dev/hello1时是成功打开的,而打开/dev/hello2时,却发现打不开了,因为前面我们申请的字符驱动的次设备号的区域为(major,0)与(major,1),而(major,2)却是并没有申请的,它没有对应的file_operations结构体,无法打开.
附上驱动程序1:
1 /* 字符设备的另一种写法 */ 2 #include <linux/kernel.h> 3 #include <linux/init.h> 4 #include <linux/module.h> 5 #include <linux/slab.h> 6 #include <linux/jiffies.h> 7 #include <linux/mutex.h> 8 #include <linux/i2c.h> 9 #include <linux/fs.h> 10 #include <asm/uaccess.h> 11 #include <linux/cdev.h> 12 13 /* 1.确定主设备号 */ 14 static int major; 15 16 static int hello_open(struct inode *inode, struct file * file) 17 { 18 printk("hello open "); 19 return 0; 20 } 21 22 /* 2.构造file_operation结构体 */ 23 static struct file_operations hello_fops = { 24 .owner = THIS_MODULE, 25 .open = hello_open, 26 }; 27 28 #define HELLO_CNT 2 //允许的次设备个数 29 static struct cdev hello_cdev; 30 31 //自动创建设备节点 32 static struct class *cls; 33 34 static int hello_init(void) 35 { 36 dev_t devid; 37 /* 3.告诉内核 */ 38 #if 0 39 register_chrdev(0,"hello",&hello_fops); 40 /* (major,0),(major,1)...(major,255) 都对应file_operation结构体 ,一个结构体占有了256个次设备号*/ 41 #else 42 if(major){ 43 devid = MKDEV(major, 0); //此设备号从0开始 44 register_chrdev_region(devid, HELLO_CNT, "hello"); /* (major,0-1)对应hello_fops,其他的(major,2-255)都不对应hello_fops */ 45 }else{ 46 alloc_chrdev_region(&devid, 0, HELLO_CNT, "hello"); /* (major,0-1)对应hello_fops */ 47 major = MAJOR(devid); 48 } 49 cdev_init(&hello_cdev, &hello_fops); 50 cdev_add(&hello_cdev, devid, HELLO_CNT); //设备的个数 51 52 #endif 53 54 cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "hello"); 55 device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major,0), NULL, "hello0"); /* /dev/hello0 */ 56 device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major,1), NULL, "hello1"); /* /dev/hello1 */ 57 device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major,2), NULL, "hello2"); /* /dev/hello2 由于对应的是(major,0-1),所以此处hello2是无法使用的 */ 58 59 return 0; 60 } 61 62 static void hello_exit(void) 63 { 64 device_destroy(cls,MKDEV(major,0)); 65 device_destroy(cls,MKDEV(major,1)); 66 device_destroy(cls,MKDEV(major,2)); 67 class_destroy(cls); 68 69 cdev_del(&hello_cdev); 70 unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major,0), HELLO_CNT); 71 } 72 module_init(hello_init); 73 module_exit(hello_exit); 74 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); 75 76 77 /* 78 ①register_chrdev_region / alloc_chrdev_region 从(主,次)到(主,次+n)都对应某个file_operation结构体 79 ②cdev_add 80 81 和以前 255(主) x 255(次)不一样的是 82 现在已经拓展到20位了, 2^12(主) x 2^20(次), 基本上已经足够支持很多驱动程序了 83 84 */
附上测试程序2:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 #include <sys/types.h> 5 #include <sys/stat.h> 6 #include <fcntl.h> 7 8 int main(int argc,char **argv) 9 { 10 int fd; 11 if(argc != 2){ 12 printf("%s <dev> {/dev/hello0 | /dev/hello1 | /dev/hello2} \n",argv[0]); 13 } 14 fd = open(argv[1],O_RDWR); 15 if(fd < 0) 16 printf("can't open %s\n",argv[1]); 17 else 18 printf("can open %s\n",argv[1]); 19 20 return 0; 21 }
二、一个主设备号是否能对应不同的file_operation结构体呢?
前面,我们已经确定了,我们申请字符设备时可以指定次设备号的区域,但是,我们可以如何使用/dev/hello2这个次设备号,同一个主设备号下,能不能有两个file_operations结构体呢?
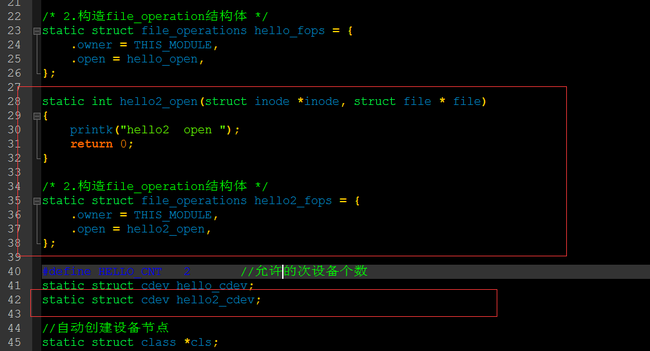
接下来,在前面的驱动程序的基础上,我们来增加第二个file_operation结构体。
步骤和前面第一个是一样的。
在入口函数中注册第二个file_operation结构体
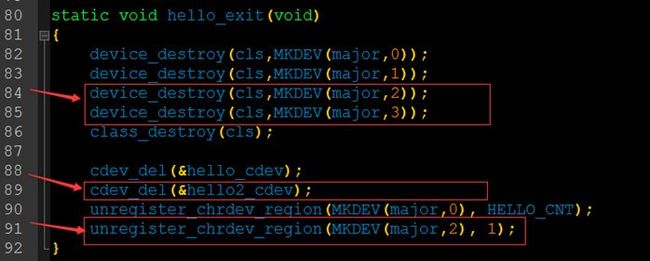
在出口函数中
在IMX257开发板上,编译加载驱动程序。
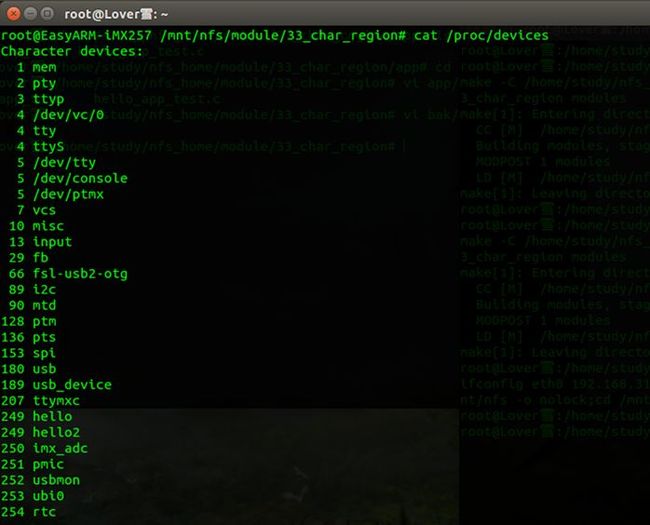
接下来,我们运行,cat /proc/devices
注意主设备为249所对应有两个名字,从而更加明确了,同一个主设备号可以对应多个file_operation结构体.
附上驱动程序2:
1 /* 字符设备的另一种写法 */ 2 #include <linux/kernel.h> 3 #include <linux/init.h> 4 #include <linux/module.h> 5 #include <linux/slab.h> 6 #include <linux/jiffies.h> 7 #include <linux/mutex.h> 8 #include <linux/i2c.h> 9 #include <linux/fs.h> 10 #include <asm/uaccess.h> 11 #include <linux/cdev.h> 12 13 /* 1.确定主设备号 */ 14 static int major; 15 16 static int hello_open(struct inode *inode, struct file * file) 17 { 18 printk("hello open "); 19 return 0; 20 } 21 22 /* 2.构造file_operation结构体 */ 23 static struct file_operations hello_fops = { 24 .owner = THIS_MODULE, 25 .open = hello_open, 26 }; 27 28 static int hello2_open(struct inode *inode, struct file * file) 29 { 30 printk("hello2 open "); 31 return 0; 32 } 33 34 /* 2.构造file_operation结构体 */ 35 static struct file_operations hello2_fops = { 36 .owner = THIS_MODULE, 37 .open = hello2_open, 38 }; 39 40 #define HELLO_CNT 2 //允许的次设备个数 41 static struct cdev hello_cdev; 42 static struct cdev hello2_cdev; 43 44 //自动创建设备节点 45 static struct class *cls; 46 47 static int hello_init(void) 48 { 49 dev_t devid; 50 /* 3.告诉内核 */ 51 #if 0 52 register_chrdev(0,"hello",&hello_fops); 53 /* (major,0),(major,1)...(major,255) 都对应file_operation结构体 ,一个结构体占有了256个次设备号*/ 54 #else 55 if(major){ 56 devid = MKDEV(major, 0); //此设备号从0开始 57 register_chrdev_region(devid, HELLO_CNT, "hello"); /* (major,0-1)对应hello_fops,其他的(major,2-255)都不对应hello_fops */ 58 }else{ 59 alloc_chrdev_region(&devid, 0, HELLO_CNT, "hello"); /* (major,0-1)对应hello_fops */ 60 major = MAJOR(devid); 61 } 62 cdev_init(&hello_cdev, &hello_fops); 63 cdev_add(&hello_cdev, devid, HELLO_CNT); //设备的个数 64 65 devid = MKDEV(major, 2); //此设备号从3开始 66 register_chrdev_region(devid, 1, "hello2"); /* (major,2)对应hello2_fops,其他的(major,2-255)都不对应hello_fops */ 67 cdev_init(&hello2_cdev, &hello2_fops); 68 cdev_add(&hello2_cdev, devid, 1); //设备的个数 69 #endif 70 71 cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "hello"); 72 device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major,0), NULL, "hello0"); /* /dev/hello0 */ 73 device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major,1), NULL, "hello1"); /* /dev/hello1 */ 74 device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major,2), NULL, "hello2"); /* /dev/hello2 由于对应的是(major,0-1),所以此处hello2是无法使用的 */ 75 76 device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major,3), NULL, "hello3"); /* /dev/hello2 由于对应的是(major,0-1),所以此处hello2是无法使用的 */ 77 return 0; 78 } 79 80 static void hello_exit(void) 81 { 82 device_destroy(cls,MKDEV(major,0)); 83 device_destroy(cls,MKDEV(major,1)); 84 device_destroy(cls,MKDEV(major,2)); 85 device_destroy(cls,MKDEV(major,3)); 86 class_destroy(cls); 87 88 cdev_del(&hello_cdev); 89 cdev_del(&hello2_cdev); 90 unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major,0), HELLO_CNT); 91 unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major,2), 1); 92 } 93 module_init(hello_init); 94 module_exit(hello_exit); 95 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); 96 97 98 /* 99 ①register_chrdev_region / alloc_chrdev_region 从(主,次)到(主,次+n)都对应某个file_operation结构体 100 ②cdev_add 101 102 和以前 255(主) x 255(次)不一样的是 103 现在已经拓展到20位了, 2^12(主) x 2^20(次), 基本上已经足够支持很多驱动程序了 104 105 */
附上测试程序2:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 #include <sys/types.h> 5 #include <sys/stat.h> 6 #include <fcntl.h> 7 8 int main(int argc,char **argv) 9 { 10 int fd; 11 if(argc != 2){ 12 printf("%s <dev> {/dev/hello0 | /dev/hello1 | /dev/hello2} \n",argv[0]); 13 } 14 fd = open(argv[1],O_RDWR); 15 if(fd < 0) 16 printf("can't open %s\n",argv[1]); 17 else 18 printf("can open %s\n",argv[1]); 19 20 return 0; 21 }