保姆级教程:Python数据库编程(SQLite3+MySQL)
Python数据库编程
- 操作SQLite3数据库
- 使用SQLite3创建表
- 使用SQLite3插入数据
- 使用SQLite3查询数据
- 下载安装MySQL
-
- 下载MySQL
- 安装MySQL
- 配置MySQL
- 操作MySQL数据库
-
- 搭建PyMySQL环境
- 创建数据库表
- 数据库插入操作
- 数据库查询操作
- 数据库更新操作
- 数据库删除操作
操作SQLite3数据库
从Python3.x版本开始,在标准库中已经内置了SQLlite3模块,它可以支持SQLite3数据库的访问和相关的数据库操作。在需要操作SQLite3数据库数据时,只须在程序中导入SQLite3模块即可。Python语言操作SQLite3数据库的基本流程如下所示。
- 导入相关库或模块(SQLite3)。
- 使用connect()连接数据库并获取数据库连接对象。它提供了以下方法:
cursor() 方法来创建一个游标对象
commit() 方法来处理事务提交
rollback() 方法来处理事务回滚
close() 方法来关闭一个数据库连接 - 使用con.cursor()获取游标对象。
- 使用游标对象的方法(execute()、executemany()、fetchall()等)来操作数据库,实现插入、修改和删除操作,并查询获取显示相关的记录。在Python程序中,连接函数sqlite3.connect()有如下两个常用参数。
database:表示要访问的数据库名。
timeout:表示访问数据的超时设定。 - 使用close()关闭游标对象和数据库连接。数据库操作完成之后,必须及时调用其close()方法关闭数据库连接,这样做的目的是减轻数据库服务器的压力。
使用SQLite3创建表
使用sqlite3模块的connect方法来创建/打开数据库,需要指定数据库路径,不存在则创建一个新的数据库。
con=sqlite3.connect(‘e:/sqllitedb/first.db’)
下面实例代码演示使用SQLite3创建数据库的过程。
【示例】使用SQLite3创建表
#导入sqllite3模块
import sqlite3
#1.硬盘上创建连接
con = sqlite3.connect('e:/sqlitedb/first.db')
#获取cursor对象
cur = con.cursor()
#执行sql创建表
sql = 'create table t_person(pno INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT ,pname varchar(30) NOT NULL ,age INTEGER)'
try:
cur.execute(sql)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
print('创建表失败')
finally:
# 关闭游标
cur.close()
# 关闭连接
con.close()
使用SQLite3插入数据
调用游标对象的execute执行插入的sql,使用executemany()执行多条sql语句,使用executmany()比循环使用excute()执行多条sql语句效率高。
【示例】使用SQLite3插入一条数据
#导入sqllite3模块
import sqlite3
#1.硬盘上创建连接
con = sqlite3.connect('e:/sqlitedb/first.db')
#获取cursor对象
cur = con.cursor()
#执行sql创建表
sql = 'insert into t_person(pname,age) values(?,?)'
try:
cur.execute(sql,('张三',23))
#提交事务
con.commit()
print('插入成功')
except Exception as e:
print(e)
print('插入失败')
con.rollback()
finally:
# 关闭游标
cur.close()
# 关闭连接
con.close()
【示例】使用SQLite3插入多条数据
#导入sqllite3模块
import sqlite3
#1.硬盘上创建连接
con = sqlite3.connect('e:/sqlitedb/first.db')
#获取cursor对象
cur = con.cursor()
try:
#执行sql创建表
sql = 'insert into t_person(pname,age) values(?,?)'
cur.executemany(sql, [('张三', 23), ('李四', 25), ('小红', 24), ('小李', 12)])
#提交事务
con.commit()
print('插入成功')
except Exception as e:
print('插入失败')
con.rollback()
finally:
# 关闭游标
cur.close()
# 关闭连接
con.close()
使用SQLite3查询数据
查询数据,游标对象提供了fetchall()和fetchone()方法 。fetchall()方法获取所有数据,返回一个列表。fetchone()方法获取其中一个结果,返回一个元组。
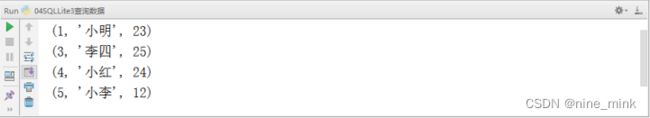
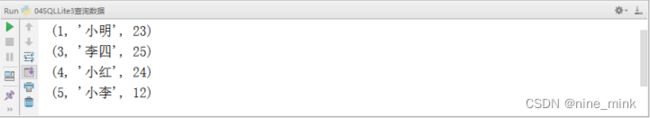
【示例】fetchall()查询所有数据
#导入sqllite3模块
import sqlite3
#1.硬盘上创建连接
con = sqlite3.connect('e:/sqlitedb/first.db')
#获取cursor对象
cur = con.cursor()
#执行sql创建表
sql = 'select * from t_person'
try:
cur.execute(sql)
# 获取所有数据
person_all = cur.fetchall()
# print(person_all)
# 遍历
for p in person_all:
print(p)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
print('查询失败')
finally:
# 关闭游标
cur.close()
# 关闭连接
con.close()
执行结果如下图:
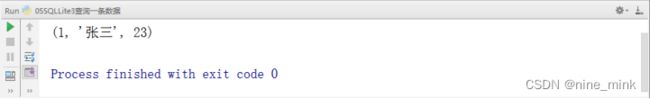
【示例】fetchone()查询一条数据
#导入sqllite3模块
import sqlite3
# 1.硬盘上创建连接
con = sqlite3.connect('e:/sqlitedb/first.db')
# 获取cursor对象
cur = con.cursor()
# 执行sql创建表
sql = 'select * from t_person'
try:
cur.execute(sql)
# 获取一条数据
person = cur.fetchone()
print(person)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
print('查询失败')
finally:
# 关闭游标
cur.close()
# 关闭连接
con.close()
执行结果如下图:
【示例】修改数据
#导入sqllite3模块
import sqlite3
#1.硬盘上创建连接
con=sqlite3.connect('e:/sqlitedb/first.db')
#获取cursor对象
cur=con.cursor()
try:
#执行sql创建表
update_sql = 'update t_person set pname=? where pno=?'
cur.execute(update_sql, ('小明', 1))
#提交事务
con.commit()
print('修改成功')
except Exception as e:
print(e)
print('修改失败')
con.rollback()
finally:
# 关闭游标
cur.close()
# 关闭连接
con.close()
执行结果如下图:
【示例】删除数据
#导入sqllite3模块
import sqlite3
#1.硬盘上创建连接
con=sqlite3.connect('e:/sqlitedb/first.db')
#获取cursor对象
cur=con.cursor()
#执行sql创建表
delete_sql = 'delete from t_person where pno=?'
try:
cur.execute(delete_sql, (2,))
#提交事务
con.commit()
print('删除成功')
except Exception as e:
print(e)
print('删除失败')
con.rollback()
finally:
# 关闭游标
cur.close()
# 关闭连接
con.close()
执行结果如下图:
在上述实例代码中,首先定义查询所有数据、插入数据、修改数据、删除数据的方法。然后,定义主方法中依次建立连接,获取连接的cursor,通过cursor的execute()等方法来执行SQL语句,调用插入记录、更加记录、删除记录的方法。
下载安装MySQL
下载MySQL
如果大家安装MySQL只是为了个人的学习和软件开发,那么安装免费的社区版即可。首先我们要进入MySQL的官网:https://www.mysql.com/,如下图所示。
然后点击DOWNLOADS导航栏,就会默认进入到MySQL的Enterprise(企业版)产品下载页面,所以还需要我们点击Community(社区版),切换到社区版的下载页面,最后点击MySQL Community Server下边的DOWNLOAD按钮即可进入MySQL数据库的下载页面。操作如下图所示。
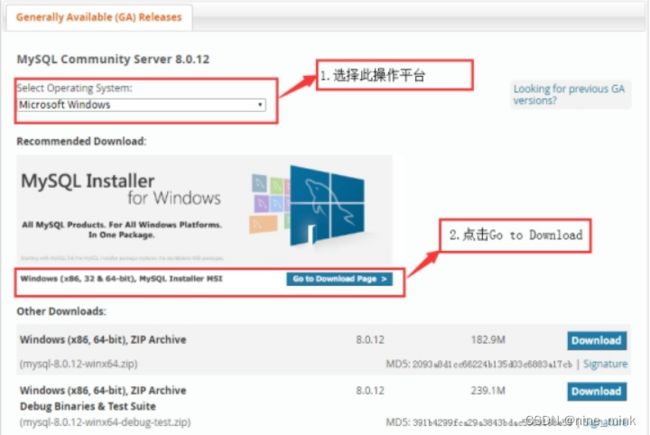
进入MySQL的数据库下载界面后,首先在“Select Operating System”下拉菜单中选择“Microsoft Windows”平台,然后进入MySQL Installer MSI下载页面,如下图所示。
在MSI下载页面,按照下图所示,选择正确的文件下载,此时MySQL官网会建议你注册或者登陆账号然后下载,当然我们也可以选择“No thanks, just start my download.”直接下载。
安装MySQL
根据下载路径找到下载好的MySQL安装程序(mysql-installer-community-8.0.12.0.msi),具体步骤如下所示。
- 双击安装程序mysql-installer-community-8.0.12.0.msi,此时会弹出MySQL许可协议界面,如下图所示。单击选中复选框“I accept the license terms”后,点击“Next”按钮,进入安装类型选择界面。
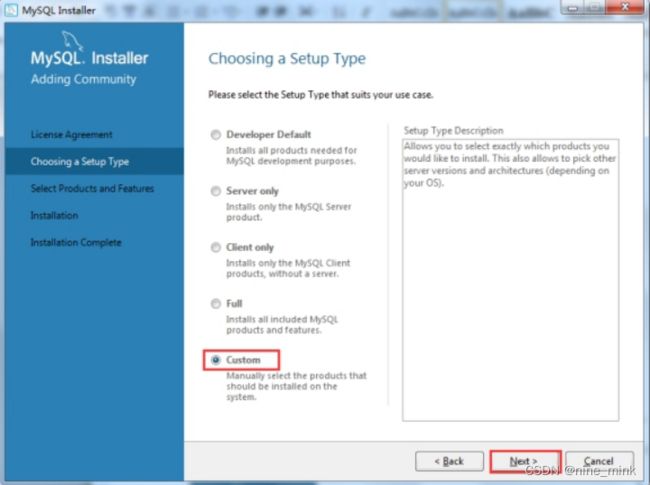
- 选择自定义安装类型“Custom”(此类型可以根据用户自己的需求选择安装需要的产品),然后单击“Next”按钮,如图下图所示。
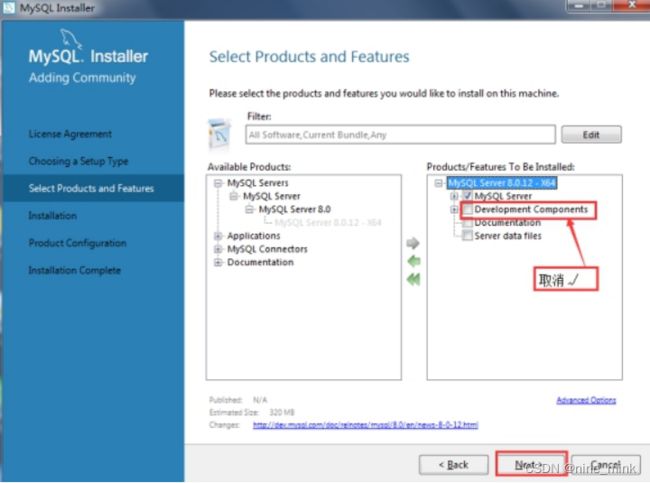
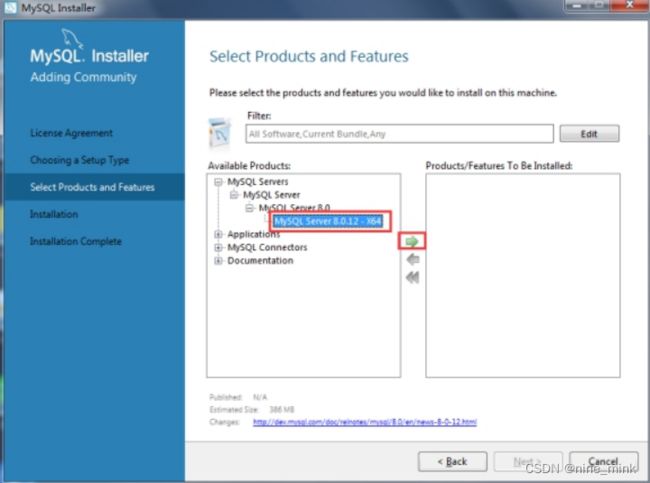
- 在选择安装版本界面,展开第一个节点“MySQL Servers”,找到并点击“MySQL Server 8.0.12-X64”,之后向右的箭头会变成绿色,,如图下图所示。点击该绿色的箭头,将选中的产品添加到右边的待安装列表框中,然后在展开安装列表中的MySQL Server 8.0.12-X64节点,取消“Development Components”选项前边的“√”,然后点击“Next”按钮进入安装列表界面,如图下图所示。
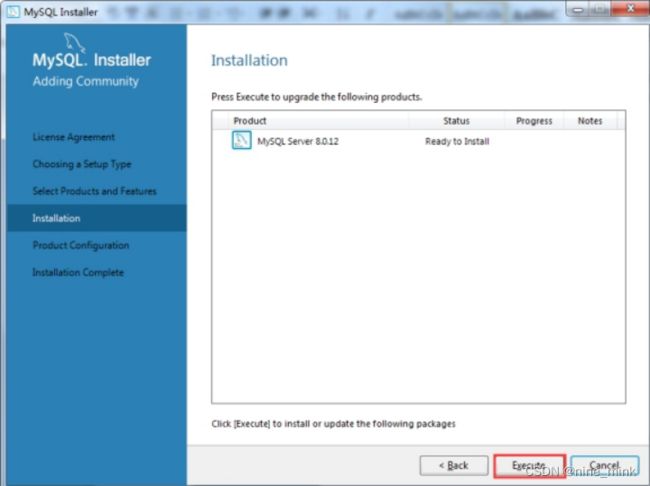
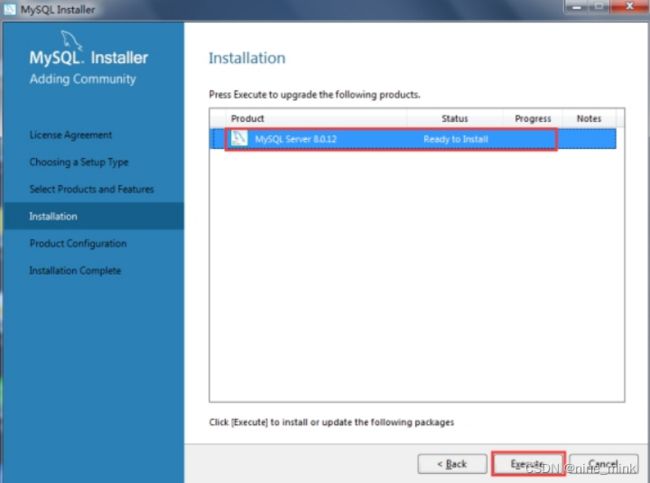
- 点击安装列表界面的“Execute”按钮后,要安装的产品右边会显示一个进度百分比,安装完成之后会前边会出现绿色个的“√”,如图下图所示。之后继续点击“Next”按钮即可。
完成上述4个步骤后,我们的MySQL终于安装成功了,剩下的就是对其进行配置,我们将在下一小节中讲述。
配置MySQL
安装完成后,还需要设置MySQL的各项参数才能正常使用。我们仍然使用图形化界面对其进行配置,具体步骤如下所示。
- 直接点击下图中的“Next”按钮,直接进入参数配置页面中的“Type and NetWorking”界面。
-
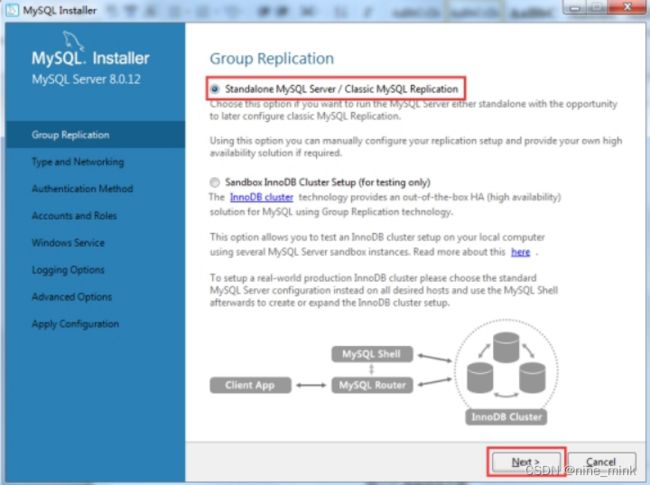
进入“Type and Networking”界面后,会看到两个选项“Standalone MySQL Server / Classic MySQL Replication”和“InnoDB Cluster Sandbox Test Setup(for testing only)”。
如果要运行独立的MySQL服务器可以选择前者,以便稍后配置经典的MySQL复制,使用该选项,用户可以手动配置复制设置,并在需要时提供自己的高可用性解决方案。
而后者是InnoDB集群沙箱测试设置,仅用于测试。
我们要选择的是“Standalone MySQL Server / Classic MySQL Replication”选项,然后点击“Next”按钮即可,如下图所示。
-
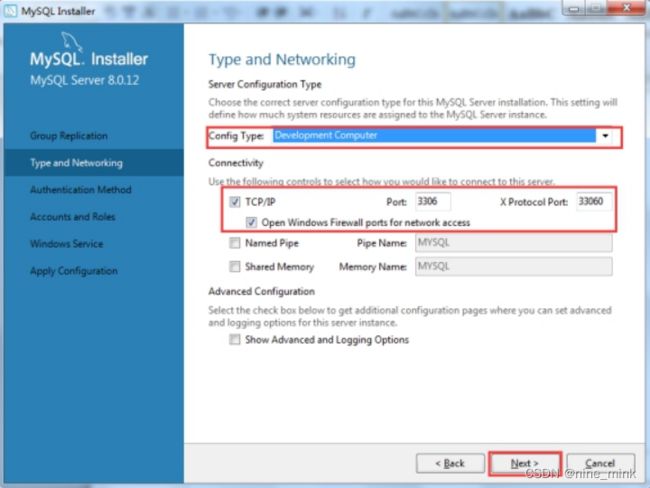
服务器配置类型“Config Type”选择“Development machine”,不同的选择将决定系统为MySQL服务器实例分配资源的大小,“Development machine”占用的内存是最少的;连接方式保持默认的TCP/IP,端口号也保持默认的3306即可;点击“Next”按钮。
- 接下来就是设置MySQL数据库Root账户密码,需要输入两遍。这个密码必须记住,后边会用到。此处我们将密码设置成“bjsxt”,之后点击“Next”按钮,如下图所示。
在配置Windows服务时,需要以下几部操作:勾选“Configure MySQL Server as a Windows Service”选项,将MySQL服务器配置为Windows服务;取消“Start the MySQL Server at System Startup”选项前边的“√”(该选项是设置是否开机自启动MySQL服务,在此我们选择开机不启动,大家也可以根据自己的需要来选择);勾选“Standard System Account”选项,该选项是标准系统账户,推荐使用该账户;点击“Next”按钮,如下图所示。
- 下面就是准备执行上述一系列配置的时候了,直接点击“Execute”按钮。等到所有的配置完成之后,会出现如下图所示的界面,点击“Finish”按钮,就会跳到配置成功界面,之后点击界面的“Next”按钮,再弹出的界面中点击“Finish”按钮即可完成配置。
操作MySQL数据库
PyMySQL 是在 Python3.x 版本中用于连接 MySQL 服务器的一个库,Python2中则使用mysqldb。
搭建PyMySQL环境
在使用 PyMySQL 之前,我们需要确保 PyMySQL 已安装。如果还未安装,我们可以使用以下命令安装最新版的 PyMySQL
pip install PyMySQL
如果使用命令无法安装,需要下载PyMySQL-0.9.3-py2.py3-none-any.whl文件,进行安装。
- 进入python官网https://www.python.org 点击菜单PyPI ,如下图:
- 输入pymsql,进行搜索。如下图所示:
- 点击PyMySQL0.9.3,直接点击左侧Download files进行下载,如下图所示。
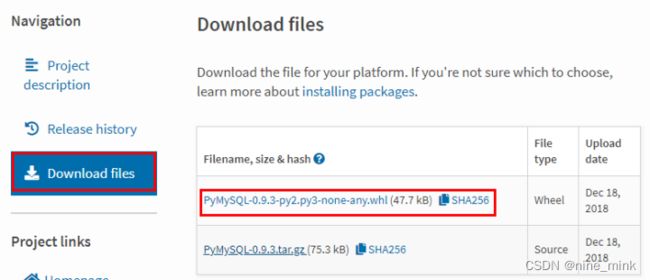
4. windows+R打开doc窗口,进入PyMySQL-0.9.3-py2.py3-none-any.whl文件所在目录,执行如命令进行安装。
pip install PyMySQL-0.9.3-py2.py3-none-any.whl
创建数据库表
在Python程序中,可以使用execute()在数据库中创建一个新表。下面的实例代码演示了在PyMySQL数据库中创建新表student的过程。
【示例】创建表student
import pymysql
try:
#创建与数据库的连接
db=pymysql.connect('localhost','root','root','testdb')
#创建游标对象cursor
cursor=db.cursor()
#使用execute()方法执行sql,如果表存在则删除
cursor.execute('drop table if EXISTS student')
#创建表的sql
sql='''
create table student(
sno int(8) primary key auto_increment,
sname varchar(30) not null,
sex varchar(5) ,
age int(2),
score float(3,1)
)
'''
cursor.execute(sql)
except:
print('创建表失败')
finally:
#关闭数据库连接
db.close()
数据库插入操作
在Python程序中,可以使用SQL语句向数据库中插入新的数据信息。
【示例】向student表中插入数据信息
import pymysql
#创建与数据库的连接
db=pymysql.connect('localhost','root','root','testdb')
#创建游标对象cursor
cursor=db.cursor()
#插入sql语句
sql='''
insert into student(sname,sex,age,score) values(%s,%s,%s,%s)
'''
try:
#执行sql语句
cursor.execute(sql,('李四','woman',25,99.6))
#提交事务
db.commit()
print('插入成功')
except Exception as e:
print(e)
#如果出现异常,回滚
db.rollback()
print('插入失败')
finally:
#关闭数据库连接
db.close()
【示例】向student表同时插入多条数据
import pymysql
#创建与数据库的连接
db=pymysql.connect('localhost','root','root','testdb')
#创建游标对象cursor
cursor=db.cursor()
#插入sql语句
sql='''
insert into student(sname,sex,age,score) values(%s,%s,%s,%s)
'''
args=[('王五','woman',22,98.6),('赵六','man',21,99.1)]
try:
#执行sql语句
cursor.executemany(sql,args)
#提交事务
db.commit()
print('插入成功')
except Exception as e:
print(e)
#如果出现异常,回滚
db.rollback()
print('插入失败')
finally:
#关闭数据库连接
db.close()
数据库查询操作
Python查询Mysql使用 fetchone() 方法获取单条数据, 使用fetchall() 方法获取多条数据。
- fetchone(): 该方法获取下一个查询结果集。结果集是一个对象
- fetchall(): 接收全部的返回结果行.
- rowcount: 这是一个只读属性,并返回执行execute()方法后影响的行数。
【示例】查询学生 年龄大于等于23的所有学生信息
import pymysql
#创建与数据库的连接
db=pymysql.connect('localhost','root','root','testdb')
#创建游标对象cursor
cursor=db.cursor()
#查询年龄大于等于23的所有学生信息
sql='select * from student where age>=23'
try:
#执行sql
cursor.execute(sql)
#获取查询结果
results=cursor.fetchall()
for row in results:
sno=row[0]
sname=row[1]
sex=row[2]
age=row[3]
score=row[4]
#输出
print('sno:',sno,'sname:',sname,'sex:',sex,'age:',age,'score:',score)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
print('查询失败')
finally:
db.close()
数据库更新操作
在Python程序中,可以使用update语句更新数据库中数据信息。
【示例】更新数据库中的数据
import pymysql
#创建与数据库的连接
db=pymysql.connect('localhost','root','root','testdb')
#创建游标对象cursor
cursor=db.cursor()
#将sno=5的学生成绩修改为99.5
sql='update student set score=%s where sno=%s'
try:
#执行sql
cursor.execute(sql,(99.5,5))
#提交数据
db.commit()
print('修改成功')
except:
print('修改失败')
db.rollback()
finally:
db.close()
数据库删除操作
在Python程序中,可以使用delete语句删除数据库中的数据信息
【示例】删除年龄小于22的学生
import pymysql
#创建与数据库的连接
db=pymysql.connect('localhost','root','root','testdb')
#创建游标对象cursor
cursor=db.cursor()
#删除sql
sql='delete from student where age < 22'
try:
#执行sql语句
cursor.execute(sql)
#提交事务
db.commit()
print('删除数据成功')
except:
db.rollback()
print('删除数据失败')
finally:
#关闭连接
db.close()