基于AidLux的街道人数统计
基于AidLux的街道人数统计
文章目录
- 为什么使用aidlux([aidlux官网](https://aidlux.com/))
- 一、在连接上Aidlux的情况下开发
- 二、使用教程
- 三、使用步骤
-
- 1.写utils
- 2.人体扫描判断越界
- 效果
- 致谢
为什么使用aidlux(aidlux官网)
- 基于ARM架构的跨生态(Android/鸿蒙+Linux)一站式AIoT应用开发和部署平台
创新性的Android/鸿蒙+Linux融合架构与AI工具链,构建下一代AIoT解决方案,服务开发者探索新未来。
使用方便,功能强大 vscode联调等。
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
一、在连接上Aidlux的情况下开发
使用vscode在ssh连接上 将文件导入home下
二、使用教程
1.打开手机下载 Aidlux
2.
2.打开后找到
3.在浏览器输入 端口 进入界面输入默认密码aidlux

4.出现问题配置参数
(1) 小米手机和平板设置教程:
(2)OPPO 手机与平板设置教程:
(3)vivo 手机与平板设置教程:
(4)华为鸿蒙/HarmonyOS 2.0 设置教程:
(5)华为鸿蒙/HarmonyOS 3.0 设置教程:
5.运行代码需要python和opencv
6.安装Remote SSH
(1) 点击Vscode左侧的“Extensions”,输入“Remote”,针对跳出的Remote SSH,点击安装。
(2) 点击"Remote Explorer" ,进行远程连接的页面,点击左下角的 “Open a Remote Window”,再选择 “Open SSH Configuration file” 针对跳出的弹窗,再选择第一个config .

7.界面选择链接按钮 选linux 密码aidlux 当左下角跳出SSH Aidlux时,表示已经连接成功。

8.本次需要的文件 请在aidlux公众号 输入lesson5获取
9.下载后上传到aidlux平台home下即可链接 ssh休要修改的地请观看代码
三、使用步骤
1.写utils
代码如下(示例):
import time
import cv2
import numpy as np
coco_class = ['person']
def xywh2xyxy(x):
'''
Box (center x, center y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
'''
y = np.copy(x)
y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2 # top left x
y[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2 # top left y
y[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2 # bottom right x
y[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2 # bottom right y
return y
def xyxy2xywh(box):
'''
Box (left_top x, left_top y, right_bottom x, right_bottom y) to (left_top x, left_top y, width, height)
'''
box[:, 2:] = box[:, 2:] - box[:, :2]
return box
def NMS(dets, thresh):
'''
单类NMS算法
dets.shape = (N, 5), (left_top x, left_top y, right_bottom x, right_bottom y, Scores)
'''
x1 = dets[:,0]
y1 = dets[:,1]
x2 = dets[:,2]
y2 = dets[:,3]
areas = (y2-y1+1) * (x2-x1+1)
scores = dets[:,4]
keep = []
index = scores.argsort()[::-1]
while index.size >0:
i = index[0] # every time the first is the biggst, and add it directly
keep.append(i)
x11 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[index[1:]]) # calculate the points of overlap
y11 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[index[1:]])
x22 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[index[1:]])
y22 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[index[1:]])
w = np.maximum(0, x22-x11+1) # the weights of overlap
h = np.maximum(0, y22-y11+1) # the height of overlap
overlaps = w*h
ious = overlaps / (areas[i]+areas[index[1:]] - overlaps)
idx = np.where(ious<=thresh)[0]
index = index[idx+1] # because index start from 1
return dets[keep]
def letterbox(img, new_shape=(640, 640), color=(114, 114, 114), auto=True, scaleFill=False, scaleup=True, stride=32):
# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraints
shape = img.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# Scale ratio (new / old)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
if not scaleup: # only scale down, do not scale up (for better test mAP)
r = min(r, 1.0)
# Compute padding
ratio = r, r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
if auto: # minimum rectangle
dw, dh = np.mod(dw, stride), np.mod(dh, stride) # wh padding
elif scaleFill: # stretch
dw, dh = 0.0, 0.0
new_unpad = (new_shape[1], new_shape[0])
ratio = new_shape[1] / shape[1], new_shape[0] / shape[0] # width, height ratios
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
img = cv2.resize(img, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border
return img, ratio, (dw, dh)
def preprocess_img(img, target_shape:tuple=None, div_num=255, means:list=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], stds:list=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]):
'''
图像预处理:
target_shape: 目标shape
div_num: 归一化除数
means: len(means)==图像通道数,通道均值, None不进行zscore
stds: len(stds)==图像通道数,通道方差, None不进行zscore
'''
img_processed = np.copy(img)
# resize
if target_shape:
# img_processed = cv2.resize(img_processed, target_shape)
img_processed = letterbox(img_processed, target_shape, stride=None, auto=False)[0]
img_processed = img_processed.astype(np.float32)
img_processed = img_processed/div_num
# z-score
if means is not None and stds is not None:
means = np.array(means).reshape(1, 1, -1)
stds = np.array(stds).reshape(1, 1, -1)
img_processed = (img_processed-means)/stds
# unsqueeze
img_processed = img_processed[None, :]
return img_processed.astype(np.float32)
def convert_shape(shapes:tuple or list, int8=False):
'''
转化为aidlite需要的格式
'''
if isinstance(shapes, tuple):
shapes = [shapes]
out = []
for shape in shapes:
nums = 1 if int8 else 4
for n in shape:
nums *= n
out.append(nums)
return out
def scale_coords(img1_shape, coords, img0_shape, ratio_pad=None):
# Rescale coords (xyxy) from img1_shape to img0_shape
if ratio_pad is None: # calculate from img0_shape
gain = min(img1_shape[0] / img0_shape[0], img1_shape[1] / img0_shape[1]) # gain = old / new
pad = (img1_shape[1] - img0_shape[1] * gain) / 2, (img1_shape[0] - img0_shape[0] * gain) / 2 # wh padding
else:
gain = ratio_pad[0][0]
pad = ratio_pad[1]
coords[:, [0, 2]] -= pad[0] # x padding
coords[:, [1, 3]] -= pad[1] # y padding
coords[:, :4] /= gain
clip_coords(coords, img0_shape)
return coords
def clip_coords(boxes, img_shape):
# Clip bounding xyxy bounding boxes to image shape (height, width)
boxes[:, 0].clip(0, img_shape[1], out=boxes[:, 0]) # x1
boxes[:, 1].clip(0, img_shape[0], out=boxes[:, 1]) # y1
boxes[:, 2].clip(0, img_shape[1], out=boxes[:, 2]) # x2
boxes[:, 3].clip(0, img_shape[0], out=boxes[:, 3]) # y2
def detect_postprocess(prediction, img0shape, img1shape, conf_thres=0.25, iou_thres=0.45):
'''
检测输出后处理
prediction: aidlite模型预测输出
img0shape: 原始图片shape
img1shape: 输入图片shape
conf_thres: 置信度阈值
iou_thres: IOU阈值
return: list[np.ndarray(N, 5)], 对应类别的坐标框信息, xywh、conf
'''
h, w, _ = img1shape
cls_num = prediction.shape[-1] - 5
valid_condidates = prediction[prediction[..., 4] > conf_thres]
valid_condidates[:, 0] *= w
valid_condidates[:, 1] *= h
valid_condidates[:, 2] *= w
valid_condidates[:, 3] *= h
valid_condidates[:, :4] = xywh2xyxy(valid_condidates[:, :4])
valid_condidates = valid_condidates[(valid_condidates[:, 0] > 0) & (valid_condidates[:, 1] > 0) & (valid_condidates[:, 2] > 0) & (valid_condidates[:, 3] > 0)]
box_cls = valid_condidates[:, 5:].argmax(1)
cls_box = []
for i in range(cls_num):
temp_boxes = valid_condidates[box_cls == i]
if(len(temp_boxes) == 0):
cls_box.append([])
continue
temp_boxes = NMS(temp_boxes, iou_thres)
temp_boxes[:, :4] = scale_coords([h, w], temp_boxes[:, :4] , img0shape).round()
temp_boxes[:, :4] = xyxy2xywh(temp_boxes[:, :4])
cls_box.append(temp_boxes[:, :5])
return cls_box
def draw_detect_res(img, all_boxes):
'''
检测结果绘制
'''
img = img.astype(np.uint8)
color_step = int(255/len(all_boxes))
for bi in range(len(all_boxes)):
if len(all_boxes[bi]) == 0:
continue
for box in all_boxes[bi]:
x, y, w, h = [int(t) for t in box[:4]]
score = str(box[4:5][0])
cv2.putText(img, str(round(float(score),2)), (x, y-5), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (255, 255, 255), 2)
cv2.rectangle(img, (x,y), (x+w, y+h),(0, bi*color_step, 255-bi*color_step),thickness = 2)
return img
def process_points(img,points,color_light_green):
points = np.array([points], dtype=np.int32)
###绘制mask
zeros = np.zeros((img.shape), dtype=np.uint8)
mask = cv2.fillPoly(zeros, points, color=color_light_green) ####填充颜色
##绘制轮廓
cv2.drawContours(img, points, -1, (144, 238, 144), 5) ###绘制轮廓
##叠加mask和普通图片
mask_img = 0.01 * mask + img
return mask_img
def is_in_poly(p, poly):
"""
:param p: [x, y]
:param poly: [[], [], [], [], ...]
:return:
"""
px, py = p
is_in = False
for i, corner in enumerate(poly):
next_i = i + 1 if i + 1 < len(poly) else 0
x1, y1 = corner
x2, y2 = poly[next_i]
if (x1 == px and y1 == py) or (x2 == px and y2 == py): # if point is on vertex
is_in = True
break
if min(y1, y2) < py <= max(y1, y2): # find horizontal edges of polygon
x = x1 + (py - y1) * (x2 - x1) / (y2 - y1)
if x == px: # if point is on edge
is_in = True
break
elif x > px: # if point is on left-side of line
is_in = not is_in
if is_in == True:
person_status = 1
else:
person_status = -1
return person_status
def is_passing_line(point, polyline):
# 在直线下方,status =-1
# 在直线上方,status =1
status = 1
# 点映射在直线的高度
poly_y = ((polyline[1][1] - polyline[0][1]) * (point[0] - polyline[0][0])) / (polyline[1][0] - polyline[0][0]) + \
polyline[0][1]
if point[1] > poly_y:
status = -1
return status
2.人体扫描判断越界
代码如下(示例):
# aidlux相关
from cvs import *
import aidlite_gpu
from utils import detect_postprocess,is_passing_line, preprocess_img, draw_detect_res,process_points,is_in_poly #isInsidePolygon
import cv2
# bytetrack
from track.tracker.byte_tracker import BYTETracker
from track.utils.visualize import plot_tracking
import requests
import time
# 加载模型
model_path = '/home/lesson4_codes/aidlux/yolov5n_best-fp16.tflite'
in_shape = [1 * 640 * 640 * 3 * 4]
out_shape = [1 * 25200 * 6 * 4]
# 载入模型
aidlite = aidlite_gpu.aidlite()
# 载入yolov5检测模型
aidlite.ANNModel(model_path, in_shape, out_shape, 4, 0)
tracker = BYTETracker(frame_rate=30)
track_id_status = {}
cap = cvs.VideoCapture("/home/lesson4_codes/aidlux/video.mp4")
frame_id = 0
count_person = 0
while True:
frame = cap.read()
if frame is None:
print("camera in over!")
id = 'trDa9G0'
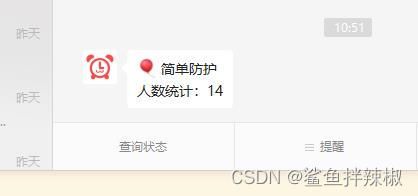
# 填写喵提醒中,发送的消息,这里放上前面提到的图片外链
text = "人数统计:" + str(count_person)
ts = str(time.time()) # 时间戳
type = 'json' # 返回内容格式
request_url = "http://miaotixing.com/trigger?"
headers = {'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/87.0.4280.67 Safari/537.36 Edg/87.0.664.47'}
result = requests.post(request_url + "id=" + id + "&text=" + text + "&ts=" + ts + "&type=" + type,headers=headers)
break
frame_id += 1
if frame_id % 3 != 0:
continue
# 预处理
img = preprocess_img(frame, target_shape=(640, 640), div_num=255, means=None, stds=None)
# 数据转换:因为setTensor_Fp32()需要的是float32类型的数据,所以送入的input的数据需为float32,大多数的开发者都会忘记将图像的数据类型转换为float32
aidlite.setInput_Float32(img, 640, 640)
# 模型推理API
aidlite.invoke()
# 读取返回的结果
pred = aidlite.getOutput_Float32(0)
# 数据维度转换
pred = pred.reshape(1, 25200, 6)[0]
# 模型推理后处理
pred = detect_postprocess(pred, frame.shape, [640, 640, 3], conf_thres=0.4, iou_thres=0.45)
# 绘制推理结果
res_img = draw_detect_res(frame, pred)
# 目标追踪相关功能
det = []
# Process predictions
for box in pred[0]: # per image
box[2] += box[0]
box[3] += box[1]
det.append(box)
if len(det):
# Rescale boxes from img_size to im0 size
online_targets = tracker.update(det, [frame.shape[0], frame.shape[1]])
online_tlwhs = []
online_ids = []
online_scores = []
# 取出每个目标的追踪信息
for t in online_targets:
tlwh = t.tlwh
tid = t.track_id
online_tlwhs.append(tlwh)
online_ids.append(tid)
online_scores.append(t.score)
res_img = plot_tracking(res_img,online_tlwhs,online_ids,0,0)
#1,绘制统计人流线
lines = [[186,249],[1235,366]]
cv2.line(res_img,(186,249),(1235,366),(255,255,0),3)
#计算 人体下中心位置
pt = [tlwh[0]+1/2*tlwh[2],tlwh[1]+tlwh[3]]
track_info = is_passing_line(pt,lines)
if tid not in track_id_status.keys():
track_id_status.update({tid:[track_info]})
else:
if track_info != track_id_status[tid][-1]:
track_id_status[tid].append(track_info)
# 当某个track_id的状态,上一帧是-1,但是这一帧是1时,说明越界了
if track_id_status[tid][-1] == 1 and len(track_id_status[tid]) >1:
# 判断上一个状态是否是-1,是否的话说明越界,为了防止继续判别,随机的赋了一个3的值
if track_id_status[tid][-2] == -1:
track_id_status[tid].append(3)
count_person +=1
cv2.putText(res_img,"-1 to 1 person_count:" +str(count_person),(50,50),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,1,(255,0,255),2)
cvs.imshow(res_img)
效果
视频
致谢
1.首先要感谢江大白老师和群友的帮助和细心讲解, 让我收获颇多。我也是刚接触这一领域已经adilux平台挺好用的。希望大家学习的时候,认真仔细不出错。