深度学习:AlexNet实现服装分类(Pytorch)
深度学习:AlexNet实现服装分类(Pytorch)
- 前置知识
- 表征学习
- 模型介绍
-
- 模型架构
- 模型特点
- 代码实战
-
- 服装分类数据集
- 定义模型
- 测试数据
- 训练模型
- 结果展示
前置知识
Lenet-5服装分类
卷积神经网络详细指南
SGD+动量法
反向传播公式推导
表征学习
- 在2012年前,图像特征都是机械地计算出来的。事实上,设计一套新的特征函数、改进结果,并撰写论文是盛极一时的潮流。SIFT [Lowe, 2004]、SURF [Bay et al., 2006]、HOG(定向梯度直方图) [Dalal & Triggs, 2005]、bags of visual words和类似的特征提取方法占据了主导地位。
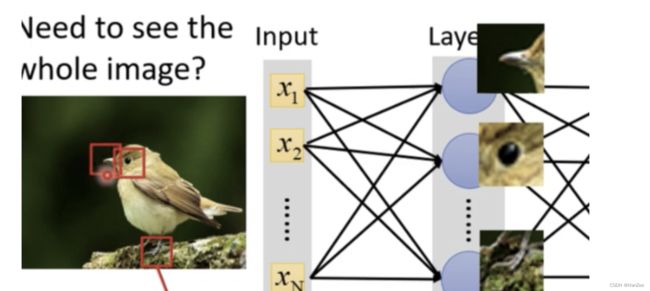
- 在2012年之后,另一组研究人员认为表征可以被学习,通过前面的卷积层提取了图片的底层信息,如检测边缘、颜色和纹理。在2012年,人们把alexnet 第一个卷积层提取的信息可视化:
由这些底层的信息,通过后面的全连接层训练,得到了高层的语义信息 ,如:鼻子、眼睛、嘴巴,更易于数据划分。
模型介绍
模型架构
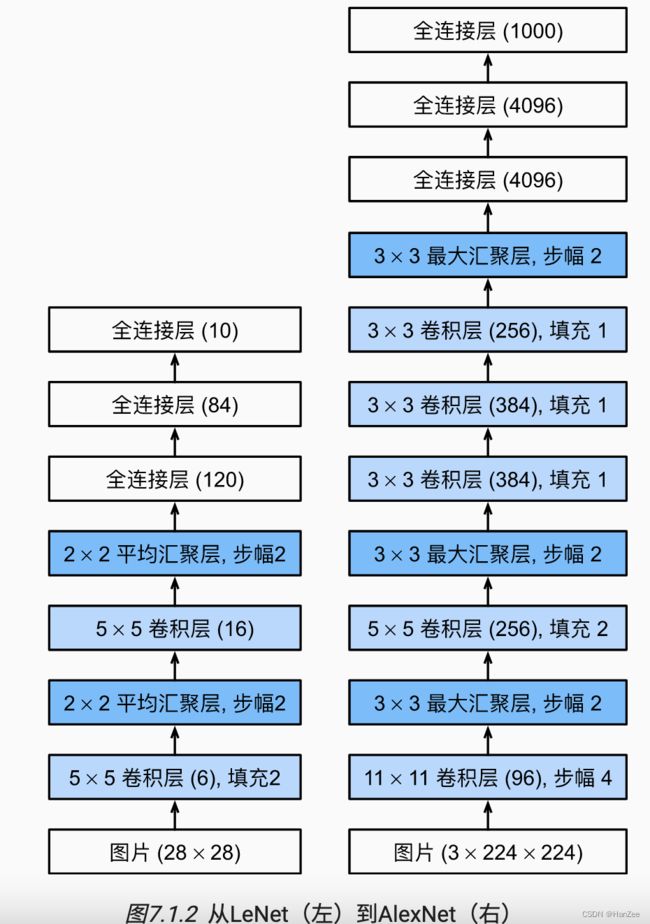
2012年,AlexNet横空出世。它首次证明了学习到的特征可以超越手工设计的特征。它一举打破了计算机视觉研究的现状。
AlexNet使用了8层卷积神经网络,并以很大的优势赢得了2012年ImageNet图像识别挑战赛。AlexNet和LeNet的架构非常相似,如 图7.1.2所示。
注意,这里我们提供了一个稍微精简版本的AlexNet,去除了当年需要两个小型GPU同时运算的设计特点。
模型特点
相比较与LeNet:
- 卷积核从33-> 先1111,然后55,接着是33。
- 激活函数从Sigmoid-> ReLu 让训练更稳定,ReLU计算更快。
- 新加入DropOut层与数据增强方法,Lenet只有权重衰减方法。
- 采用多种参数初始化。
- 均匀池化层->最大池化层,只保留激活最明显的feature。
代码实战
服装分类数据集
我们可以通过框架中的内置函数将Fashion-MNIST数据集下载并读取到内存中。
# 通过ToTensor实例将图像数据从PIL类型变换成32位浮点数格式,
# 并除以255使得所有像素的数值均在0到1之间
def load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=None): #@save
"""下载Fashion-MNIST数据集,然后将其加载到内存中"""
trans = [transforms.ToTensor()]
if resize:
trans.insert(0, transforms.Resize(resize))
trans = transforms.Compose(trans)#通过compose组合多个操作
mnist_train = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(
root="../data", train=True, transform=trans, download=True)
mnist_test = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(
root="../data", train=False, transform=trans, download=True)
return (data.DataLoader(mnist_train, batch_size, shuffle=True,
num_workers=4),
data.DataLoader(mnist_test, batch_size, shuffle=False,
num_workers=4))
#num workers 为线程数
定义模型
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
net = nn.Sequential(
# 这里,我们使用一个11*11的更大窗口来捕捉对象。
# 同时,步幅为4,以减少输出的高度和宽度。
# 另外,输出通道的数目远大于LeNet
nn.Conv2d(1, 96, kernel_size=11, stride=4, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
# 减小卷积窗口,使用填充为2来使得输入与输出的高和宽一致,且增大输出通道数
nn.Conv2d(96, 256, kernel_size=5, padding=2), nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
# 使用三个连续的卷积层和较小的卷积窗口。
# 除了最后的卷积层,输出通道的数量进一步增加。
# 在前两个卷积层之后,汇聚层不用于减少输入的高度和宽度
nn.Conv2d(256, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(384, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
nn.Flatten(),
# 这里,全连接层的输出数量是LeNet中的好几倍。使用dropout层来减轻过拟合
nn.Linear(6400, 4096), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
# 最后是输出层。由于这里使用Fashion-MNIST,所以用类别数为10,而非论文中的1000
nn.Linear(4096, 10))
测试数据
def evaluate_accuracy_gpu(net, data_iter, device=None): #@save
"""使用GPU计算模型在数据集上的精度"""
if isinstance(net, nn.Module):
net.eval() # 设置为评估模式
if not device:
device = next(iter(net.parameters())).device
# 正确预测的数量,总预测的数量
metric = d2l.Accumulator(2)#累加器
with torch.no_grad():#禁止计算梯度
for X, y in data_iter:
if isinstance(X, list):
# BERT微调所需的(之后将介绍)
X = [x.to(device) for x in X]
else:
X = X.to(device)
y = y.to(device)
metric.add(d2l.accuracy(net(X), y), y.numel())
return metric[0] / metric[1]
训练模型
#@save
def train_ch6(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, lr, device):
"""用GPU训练模型(在第六章定义)"""
def init_weights(m):
if type(m) == nn.Linear or type(m) == nn.Conv2d:
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight)
net.apply(init_weights)
print('training on', device)
net.to(device)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=lr)
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', xlim=[1, num_epochs],
legend=['train loss', 'train acc', 'test acc'])
timer, num_batches = d2l.Timer(), len(train_iter)
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
# 训练损失之和,训练准确率之和,样本数
metric = d2l.Accumulator(3)
net.train()
for i, (X, y) in enumerate(train_iter):
timer.start()
optimizer.zero_grad()
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
y_hat = net(X)
l = loss(y_hat, y)
l.backward()
optimizer.step()#更新参数
with torch.no_grad():
metric.add(l * X.shape[0], d2l.accuracy(y_hat, y), X.shape[0])
timer.stop()
train_l = metric[0] / metric[2]
train_acc = metric[1] / metric[2]
if (i + 1) % (num_batches // 5) == 0 or i == num_batches - 1:
animator.add(epoch + (i + 1) / num_batches,
(train_l, train_acc, None))
test_acc = evaluate_accuracy_gpu(net, test_iter)
animator.add(epoch + 1, (None, None, test_acc))
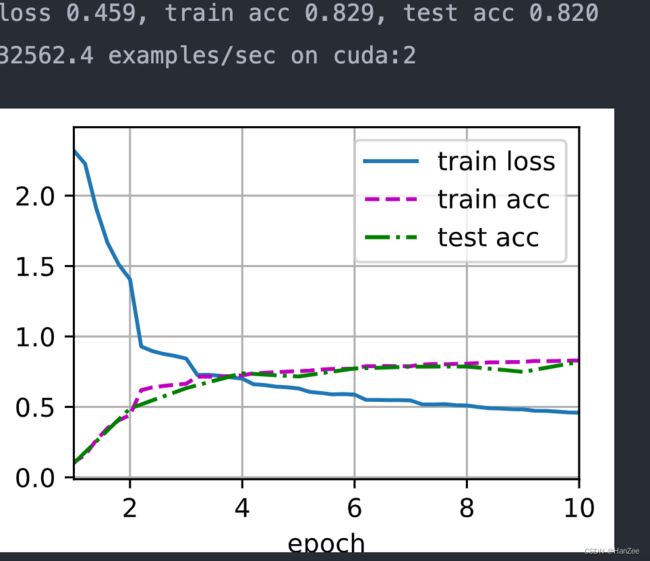
print(f'loss {train_l:.3f}, train acc {train_acc:.3f}, '
f'test acc {test_acc:.3f}')
print(f'{metric[2] * num_epochs / timer.sum():.1f} examples/sec '
f'on {str(device)}')
train_iter, test_iter = load_data_fashion_mnist(256, resize=224)
train_ch6(net, train_iter, test_iter, 10, 0.01, d2l.try_gpu())