springboot项目使用seata实现分布式事务
springboot项目使用seata实现分布式事务
目录
- 所有文章
- 正文
- 环境说明
- 步骤说明
- 搭建springboot项目
- 引入seata依赖
- 配置
- 添加并修改file.conf和registry.conf
- 添加数据源配置
- 添加undo_log表
- 测试
- 数据源添加业务表和业务数据
- 编写业务代码
- 全局回滚测试
- 总结
正文
回到顶部
所有文章
https://www.cnblogs.com/lay2017/p/12078232.html
回到顶部
正文
在上一篇文章中,我们简单地了解了一下什么是seata。它是来自阿里巴巴的内部项目不断地发展出来的。2019年以fescar命名开源于apache开源协议,同年改名为seata。
本文将入手seata,官方的文档和demo主要以dubbo和springcloud体系的接入为主。本文选取springboot作为项目构建框架,快速构建示例。
回到顶部
环境说明
seata的发展还是比较快的,而版本的更新带来的使用变化可能会导致文档的过时。本文在阅读官方提供的quickStart基础上完成。为了过程顺利最好保持环境版本一致,否则你可能得自己debug问题所在。
- jdk1.8
- mysql8.0.18
- springboot 2.2.5.RELEASE
- spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies 2.2.0.RELEASE
- seata-server v1.1.0
当然,版本并不一定需要完全一样。比如你可以使用mysql5+,但是就得强制指定对应的mysql-connector-java.jar的版本。
回到顶部
步骤说明
要完成这个示例项目,需要不少的步骤。这里提前罗列一下,比较心里有数
- 搭建springboot项目
- 引入seata依赖
- 配置
- 添加并修改file.conf和registry.conf配置
- 添加数据源配置
- 数据源添加undo_log表
- 测试
- 数据源添加业务表和数据
- 编写业务代码
- 全局回滚测试
回到顶部
搭建springboot项目
搭建springboot项目比较简单,本文采用idea构建了两个项目
1)user-service
application.properties配置为:
server.port=8080 server.servlet.context-path=/user-service spring.application.name=user-service
2) good-service
server.port=8081 server.servlet.context-path=/good-service spring.application.name=good-service
继承自
基础依赖为
回到顶部
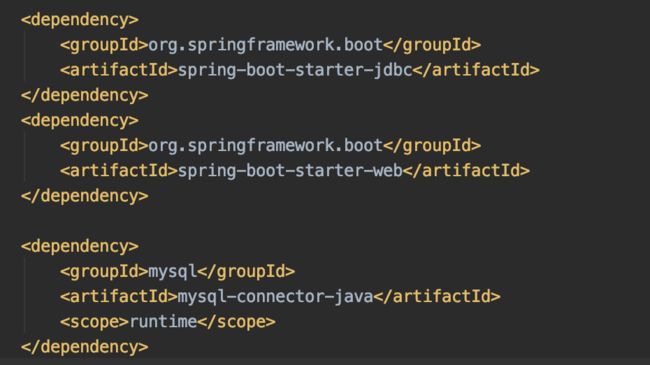
引入seata依赖
首先Import一下dependencies,注意:groupId和官方文档写的不一样,版本是2.2.0.RELEASE
![]()
com.alibaba.cloud spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies 2.2.0.RELEASE pom import
![]()
接着引入seata的依赖
com.alibaba.cloud spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-seata
回到顶部
配置
添加并修改file.conf和registry.conf
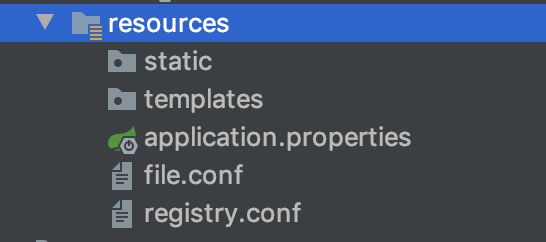
我们需要在resources目录下,创建file.conf和registry.conf这两个文件。
registry.conf文件不需要修改,直接拷贝即可
registry {
# file 、nacos 、eureka、redis、zk、consul、etcd3、sofa
type = "file"
nacos {
serverAddr = "localhost"
namespace = "public"
cluster = "default"
}
eureka {
serviceUrl = "http://localhost:8761/eureka"
application = "default"
weight = "1"
}
redis {
serverAddr = "localhost:6379"
db = "0"
}
zk {
cluster = "default"
serverAddr = "127.0.0.1:2181"
session.timeout = 6000
connect.timeout = 2000
}
consul {
cluster = "default"
serverAddr = "127.0.0.1:8500"
}
etcd3 {
cluster = "default"
serverAddr = "http://localhost:2379"
}
sofa {
serverAddr = "127.0.0.1:9603"
application = "default"
region = "DEFAULT_ZONE"
datacenter = "DefaultDataCenter"
cluster = "default"
group = "SEATA_GROUP"
addressWaitTime = "3000"
}
file {
name = "file.conf"
}
}
config {
# file、nacos 、apollo、zk、consul、etcd3
type = "file"
nacos {
serverAddr = "localhost"
namespace = "public"
cluster = "default"
}
consul {
serverAddr = "127.0.0.1:8500"
}
apollo {
app.id = "seata-server"
apollo.meta = "http://192.168.1.204:8801"
}
zk {
serverAddr = "127.0.0.1:2181"
session.timeout = 6000
connect.timeout = 2000
}
etcd3 {
serverAddr = "http://localhost:2379"
}
file {
name = "file.conf"
}
}
file.conf内容如下,但是要service节点下的一个配置。我们示例项目是user-service和good-service,分别在对应的项目中要做修改。
![]()
transport {
# tcp udt unix-domain-socket
type = "TCP"
#NIO NATIVE
server = "NIO"
#enable heartbeat
heartbeat = true
#thread factory for netty
thread-factory {
boss-thread-prefix = "NettyBoss"
worker-thread-prefix = "NettyServerNIOWorker"
server-executor-thread-prefix = "NettyServerBizHandler"
share-boss-worker = false
client-selector-thread-prefix = "NettyClientSelector"
client-selector-thread-size = 1
client-worker-thread-prefix = "NettyClientWorkerThread"
# netty boss thread size,will not be used for UDT
boss-thread-size = 1
#auto default pin or 8
worker-thread-size = 8
}
shutdown {
# when destroy server, wait seconds
wait = 3
}
serialization = "seata"
compressor = "none"
}
service {
#vgroup->rgroup
vgroup_mapping.取spring.application.name的值-seata-service-group = "default"
#only support single node
default.grouplist = "127.0.0.1:8091"
#degrade current not support
enableDegrade = false
#disable
disable = false
#unit ms,s,m,h,d represents milliseconds, seconds, minutes, hours, days, default permanent
max.commit.retry.timeout = "-1"
max.rollback.retry.timeout = "-1"
}
client {
async.commit.buffer.limit = 10000
lock {
retry.internal = 10
retry.times = 30
}
report.retry.count = 5
}
## transaction log store
store {
## store mode: file、db
mode = "file"
## file store
file {
dir = "sessionStore"
# branch session size , if exceeded first try compress lockkey, still exceeded throws exceptions
max-branch-session-size = 16384
# globe session size , if exceeded throws exceptions
max-global-session-size = 512
# file buffer size , if exceeded allocate new buffer
file-write-buffer-cache-size = 16384
# when recover batch read size
session.reload.read_size = 100
# async, sync
flush-disk-mode = async
}
## database store
db {
## the implement of javax.sql.DataSource, such as DruidDataSource(druid)/BasicDataSource(dbcp) etc.
datasource = "dbcp"
## mysql/oracle/h2/oceanbase etc.
db-type = "mysql"
url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/seata"
user = "mysql"
password = "mysql"
min-conn = 1
max-conn = 3
global.table = "global_table"
branch.table = "branch_table"
lock-table = "lock_table"
query-limit = 100
}
}
lock {
## the lock store mode: local、remote
mode = "remote"
local {
## store locks in user's database
}
remote {
## store locks in the seata's server
}
}
recovery {
committing-retry-delay = 30
asyn-committing-retry-delay = 30
rollbacking-retry-delay = 30
timeout-retry-delay = 30
}
transaction {
undo.data.validation = true
undo.log.serialization = "jackson"
}
## metrics settings
metrics {
enabled = false
registry-type = "compact"
# multi exporters use comma divided
exporter-list = "prometheus"
exporter-prometheus-port = 9898
}
![]()
添加数据源配置
分布式事务的实现,数据源代理是很重要的方式。在2.2.0.RELEASE中,数据源代理自动实现了,不需要我们去配置一个代理类。但是我们还是需要配置一下数据源的。
首先在application.properties中添加配置
user-service的配置
spring.datasource.driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_user?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&allowMultiQueries=true&useSSL=false spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=
good-service的配置
spring.datasource.driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_good?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&allowMultiQueries=true&useSSL=false spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=
注意:你可能选择了与本文不同的MySQL版本,那么driverClassName或许并不是com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver而是早期的com.mysql.jdbc.Driver 。否则会报驱动类找不到的问题
然后我们添加一个配置类,这里以druid数据源为例。
@Configuration
public class DataSourceProxyConf {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
public DataSource dataSource() {
return new DruidDataSource();
}
}
这样,数据源就配置好了。后面的测试中,我们将会使用JdbcTemplate进行数据源操作,以及resttemplate作为服务调用。所以这里也顺便配置两个Bean吧
@Configuration
public class DataSourceProxyConf {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
public DataSource dataSource() {
return new DruidDataSource();
}
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) {
return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
}
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
这里要注意,jdbcTemplate注入的dataSource不是纯粹的DruidDataSource,而是DataSourceProxy。前面我们说过,seata在2.2.0版本进行了自动代理,不需要像2.1.0那种配置代理对象了。
添加undo_log表
配置的最后一个项目,就是在两个数据源中添加undo_log表。我们将两个db分别命名为db_user和db_good吧。
undo_log表用于保存回滚数据,直接将以下sql在db里面执行一下即可。
CREATE TABLE `undo_log`
(
`id` BIGINT(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`branch_id` BIGINT(20) NOT NULL,
`xid` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
`context` VARCHAR(128) NOT NULL,
`rollback_info` LONGBLOB NOT NULL,
`log_status` INT(11) NOT NULL,
`log_created` DATETIME NOT NULL,
`log_modified` DATETIME NOT NULL,
`ext` VARCHAR(100) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `ux_undo_log` (`xid`, `branch_id`)
) ENGINE = InnoDB
AUTO_INCREMENT = 1
DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8
到这里,配置的部分就结束了,后续进入测试的部分
回到顶部
测试
数据源添加业务表和业务数据
在db_user和db_good分别添加表t_user和t_good
CREATE TABLE `t_good` ( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `amount` int(255) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_bin;
CREATE TABLE `t_user` ( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `account` decimal(10,2) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_bin;
并添加数据如下
t_user
t_good
编写业务代码
数据准备好了,我们简单编写一下controller
GoodController对t_good表的amount字段-1操作,再1/0发生算术异常
@RestController
@RequestMapping("good")
public class GoodController {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@GetMapping("amount/reduce")
public String reduceAmount() {
jdbcTemplate.update("update t_good set amount = amount - 1 where id = 1");
int i = 1/0;
return "success";
}
}
UserController先对t_user表的account字段-1操作,然后调用GoodController。
这里我们注意到@GlobalTransactional这个注解,表示开启分布式事务。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@GetMapping("account/reduce")
@GlobalTransactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public String reduceAccount() {
jdbcTemplate.update("update t_user set account = account - 1 where id = 1");
restTemplate.getForEntity("http://localhost:8081/good-service/good/amount/reduce", String.class);
return "success";
}
}
全局回滚测试
1、我们先启动seata-server,直接执行.seata-server.sh(mac或linux) 或者 seata-server.bat(windows)。seata-server下载地址为:https://github.com/seata/seata/releases/download/v1.1.0/seata-server-1.1.0.zip
2、接着启动user-service和good-service
3、当调用接口:http://localhost:8080/user-service/user/account/reduce的时候会爆出500内部错误。这时候检查一下数据源或者seata-server的console你会发现数据没有变化,console出现了两个branchId对应的doRollback输出。再看看undo_log表,自增ID从1变成了2.
回到顶部
总结
本文到此结束了,简单搭建并测试了一下commit和rollback。虽然阿里已经尽量把使用变得很简单了,但是明显的是搭建一个示例项目还是经历了不少步骤。可见分布式项目带来的成本降低,但是复杂度上升的困难是很难逾越的。
后续的文章中将从源码角度了解seata的实现,虽然很麻烦,但是...莫名地其乐无穷吧~